Holcoglossum × kunmingense D.K. Zhao, Z. Zhang & R.B. Wang
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.573.1.9 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7334690 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/DC7787BB-5A43-FFDB-FF7B-F89EFC0F82EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Holcoglossum × kunmingense D.K. Zhao, Z. Zhang & R.B. Wang |
| status |
|
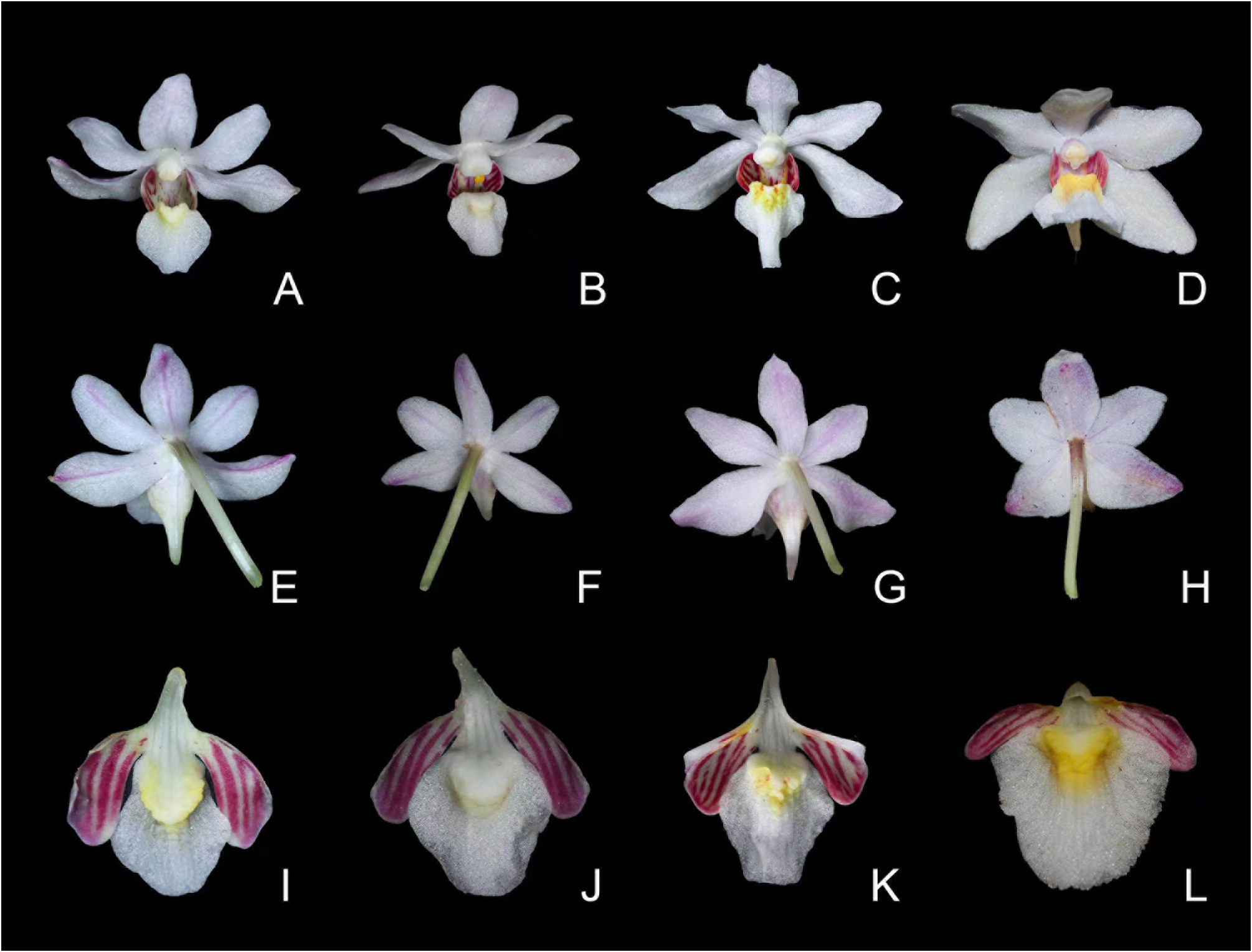
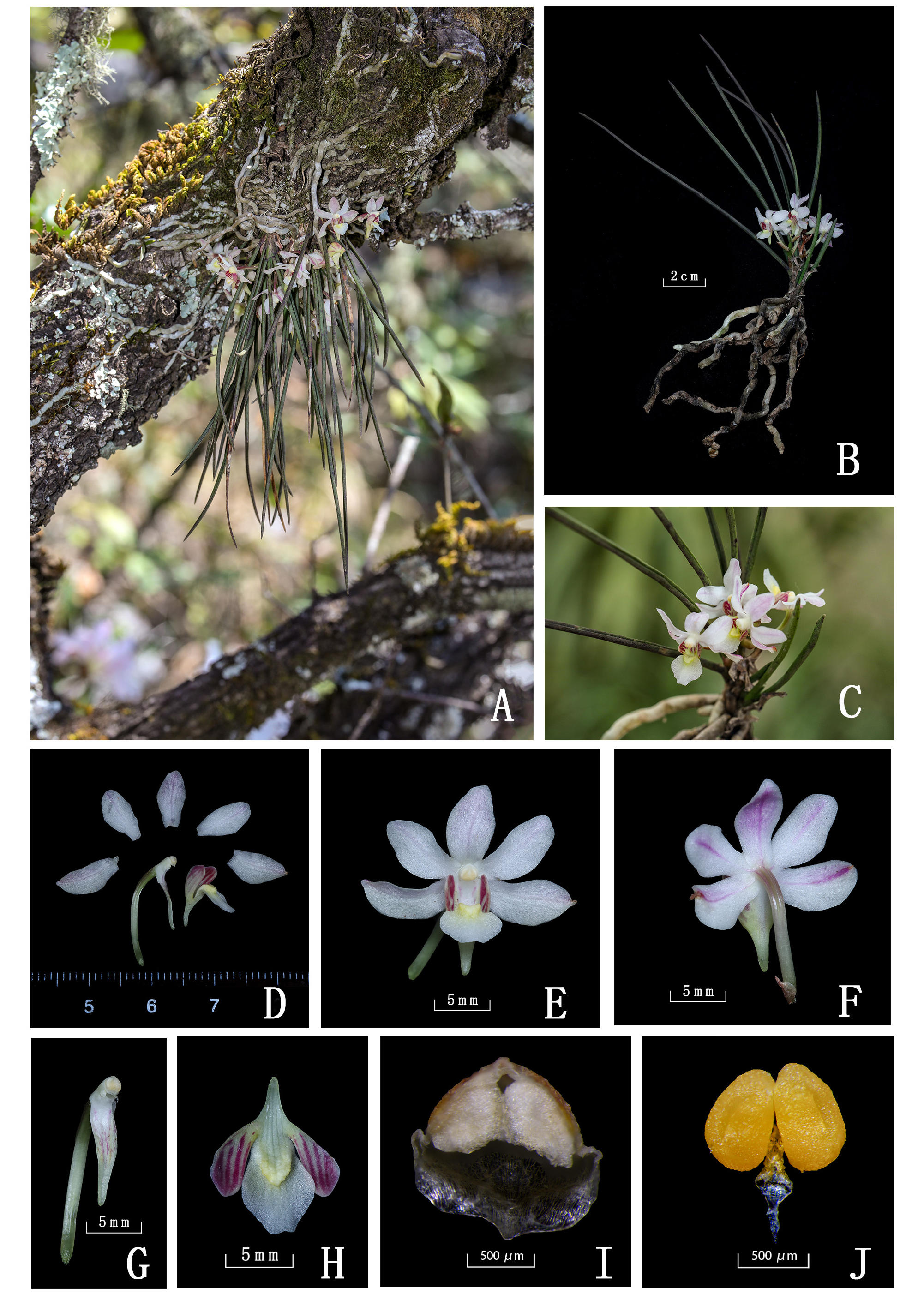
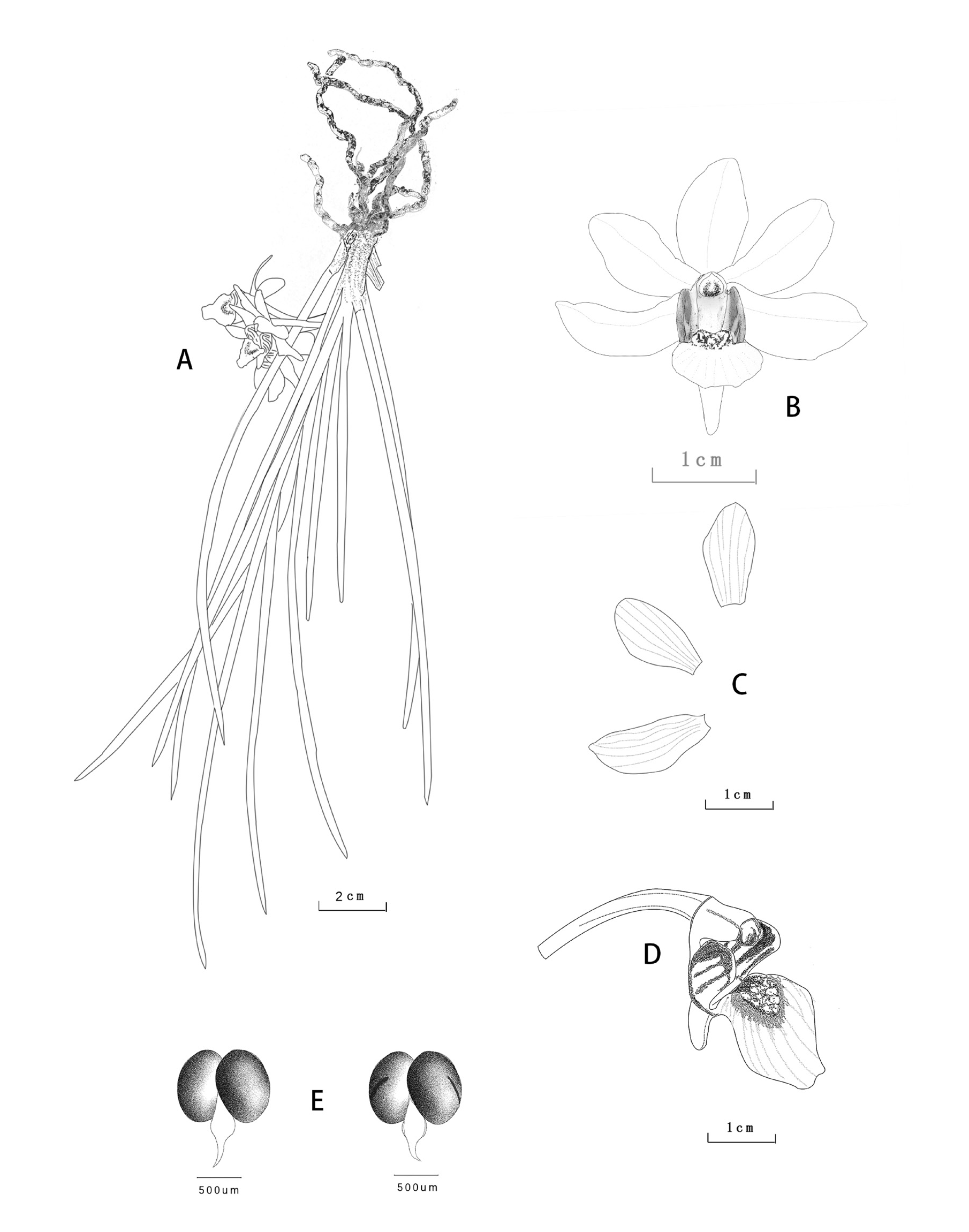
Holcoglossum × kunmingense D.K. Zhao, Z. Zhang & R.B. Wang , hybr. nat. nov. ( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 ).
Type:— CHINA. Yunnan: Northern Kunming , elev. 2435.91 m, 25 April 2021, Z. Zhang, R.B. Wang & D.K. Zhao (holotype YUKU! [barcode YUKU02074676], isotypes YUKU! [barcode YUKU02074677]) .
Diagnosis: — Holcoglossum × kunmingense is most similar to Holcoglossum sinicum , but it is distinguished from the latter by sides swollen and forming 2 ridges ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ), all sepals and petals curved backward ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 2E, and 2F View FIGURE 2 ) with obviously thick pink midrib ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ) on the reverse side.
Description
Plants pendulous, perennial, epiphytic. Aerial roots many, subterete, long, curved. Stems short. Leaves 8–10, fleshy, blade nearly subterete, 8–18 cm × ca. 1 mm, apex acute, basal sheaths enlarged. Inflorescences short, racemose, 1–3- flowered; pedicel and ovary 6-ribbed, ca. 1.4 cm; floral bracts broadly ovate, ca. 5 mm, apex acute. Flowers opening widely, slightly reflexed; sepals and petals white, tinged with pale pink, reverse side midrib obviously pink; dorsal sepals elliptic, ca. 9 mm × 5 mm, apex obtuse, attenuate at base; lateral sepals oblong, oblique, ca. 11 mm × 5 mm, apex obtuse; petals elliptic, ca. 10 mm × 5 mm, apex obtuse; lip spurred white, 3-lobed; lateral lobes erect, ovatetriangular, interior surface with red stripes, apex obtuse; mid-lobe broadly ovate-rhombic, ca. 8 mm × 5 mm, apex obtuse-rounded, retuse, margins slightly undulate; basal callus, broadly ovate-triangular, yellow, strongly thickened, center channeled, sides swollen and forming 2 ridges; spur horn-shaped, bent forward, ca. 4 mm, narrowed toward tip, apex obtuse; column ca. 4 mm, foot ca. 2 mm; anther cap white, slightly narrowed toward apex.
Distribution and habitat: — H. × kunmingense is found in northern Kunming, Yunnan province, southeastern China. It grows on the tree in mixed coniferous broad-leaved forest at elevation of 2440 m.
Phenology: —Flowering in April; fruiting from April to the following January.
Etymology: —The epithet is derived from Kunming, the southeastern Chinese city, where this novel species is discovered. It is also to commemorate the success of United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 15th Conference of the Parties (UNFCCC-COP15) in Kunming, October, 2021.
Chinese name: —kun ming cao she lan (DZẹDzfflä).
Conservation status: —During our field surveys, about 100 matured individuals of Holcoglossum × kunmingense have only been found in one separate location in northern Kunming, Yunnan. The stable population is important to speciation ( Alencar, 2021), providing the further evidence for the support of this new orchid. Its geographic range and frequency were needed further investigation to authoritatively determine whether it is endangered. Therefore, we classified the conservation status of this novel specie as Data Deficient (DD) according to IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (IUCN Standards and Petitions Subcommittee, 2021). We have not given the precise locality of H. × kunmingense as we are concerned this natural species may be the target of illegal collection.
Notes:— Holcoglossum × kunmingense morphologically resembles to H. sinicum , H. nujiangense , and H.weixiense by pendent growing pattern, fleshy subterete leaves, racemose inflorescences, similar color, and structure of flowers. Nevertheless, H. × kunmingense can be clearly distinguished from H. sinicum by pedicel and ovary ca. 1.4 cm (vs. ca. 2cm), sepal and petal with conspicuously thick pink (vs. pink) midrib on the reverse side, callus strongly thickened (vs. slightly thickened), sides swollen (vs. without sides swollen), and forming 2 ridges (vs. no ridges), floral bract ca. 5mm (vs. ca. 2 mm); from H. nujiangense by leaf blade 8–18 cm × ca. 1 mm (vs. 20–30 cm × ca. 1.5 mm), pedicel and ovary ca. 1.4 cm (vs. ca. 2cm), all sepal and petal curved backward (vs. dorsal sepal erect) with thick pink (vs. pale pink) midrib on the reverse side, floral bract ca. 5mm (vs. ca. 7 mm); from H. weixiense by leaf blade 8–18 cm × ca. 1 mm (vs. 20–30 cm × 1.5–2.5 cm), pedicel and ovary 1.4 cm (vs. ca. 2cm), all sepal and petal curved backward (vs. dorsal sepal erect) with thick pink (vs. pale pink) midrib on the reverse side, floral bract ca. 5mm (vs. ca. 7mm), inflorescences 2–4-flowered (vs. 1–3-flowered), lateral sepal ca. 11 × 5 mm (vs. ca. 15 × 9 mm), mid-lobe ca. 9 × 5 mm (vs. ca. 12 × 10 mm).
Furthermore, a comparison between H. × kunmingense, H. sinicum , H. nujiangense , H. weixiense , and putative parents ( H. tsii and H. flavescens ) is represented in Table 2 View TABLE 2 and Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |