Physoderes impexa (Distant 1903)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.201129 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6183393 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D9598780-FF9C-FFF8-48BF-89F0FD5CBFD2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Physoderes impexa (Distant 1903) |
| status |
|
Physoderes impexa (Distant 1903) View in CoL
( Figs. 13–24 View FIGURE 13 View FIGURES 14 – 24 )
Epirodera impexa Distant 1903: 56 ; Distant 1904: 247.
Physoderes fuscus Breddin 1903: 126 ; synonymized by Distant 1904: 247. Physoderes impexa Izzard 1936: 583 View in CoL ; Maldonado-Capriles 1990: 380.
Redescription. Color. Body brown to blackish brown; eyes black; ocelli silvery white with margins reddish; antennae (except fourth segments), anterior margin of each corium, outer margin of membrane, apical part of vein of outer cell on membrane, posterior half of each connexival segment, basal and subapical annulations on femora, tibiae, and apex of scutellum dull yellow; fourth segments of antennae yellow; coria, membranes, anterior half of each connexival segment, and apical part of each femur dark brown.
Structure. Head, pronotum, lateral margins of scutellum, coria, outer margins of connexiva, abdomen beneath, and legs clothed with club-shaped erect setae; antennae with slender club-shaped setae, and with dense short setae on fourth segment.
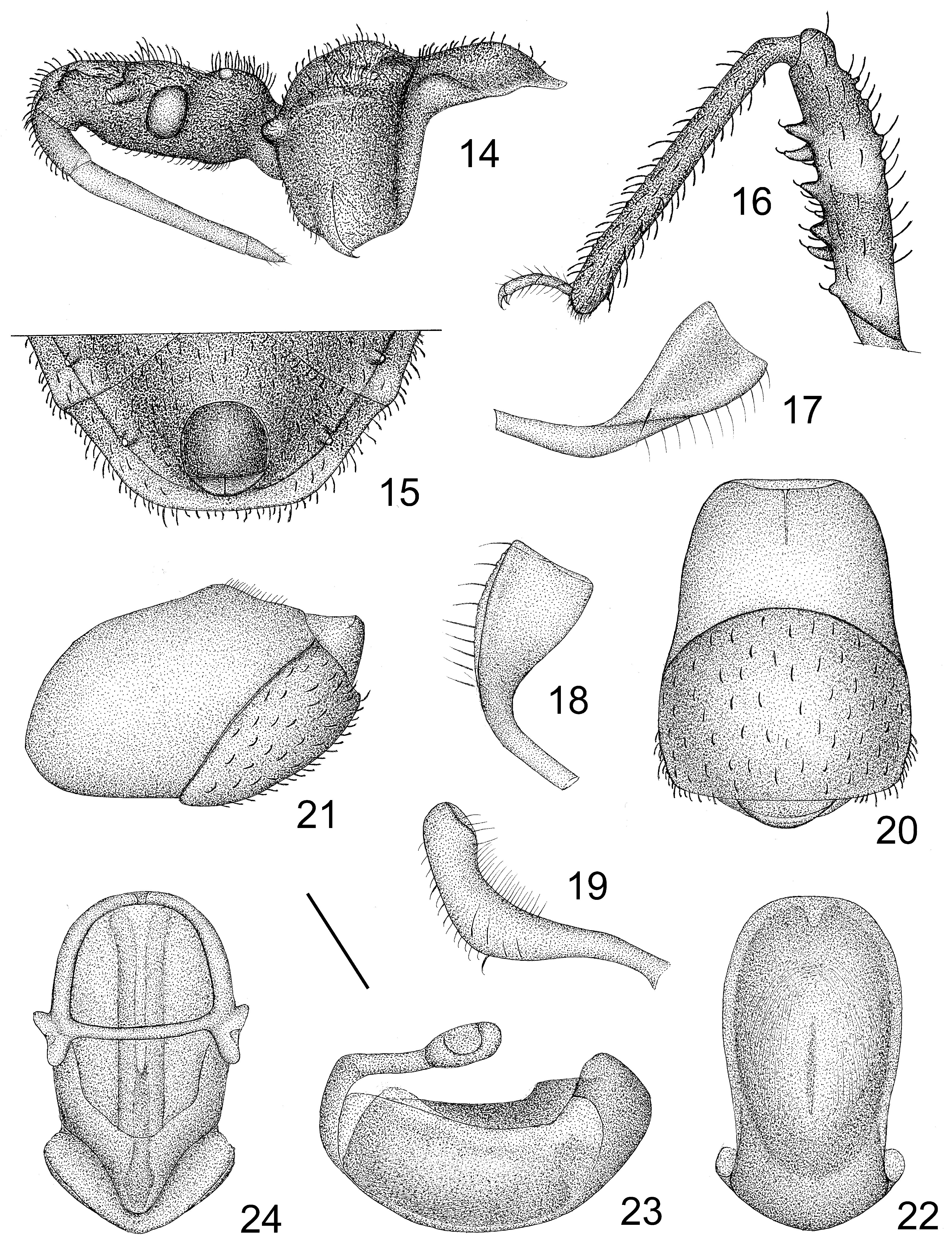
Head ( Figs. 13 View FIGURE 13 , 14 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) cylindrical; clypeus developed; anteocular portion slender and protruding between first antennal segments; transverse constriction behind eyes shallow; postocular portion globose. Eyes ( Figs. 13 View FIGURE 13 , 14 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) medium-sized, more adjacent to ventral surface of head than to dorsal surface in lateral view. Ocelli ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ) large. Antennae ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ) with first segment slightly curved, surpassing apex of head; second to fourth segments clubshaped, almost straight; third segment shortest and thinnest. First visible labial segment ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) thick, about 1/3 of second one, not reaching to level of antennifer; second segment slender and nearly straight, reaching to prosternum, with basal portion slightly thick; third segment short.
Collar ( Figs. 13 View FIGURE 13 , 14 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) undeveloped and processes prominent bilaterally. Pronotum ( Figs. 13 View FIGURE 13 , 14 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) rough and uneven; anterior lobe slightly longer and narrower than posterior, with a deep hollow centrally, and with sculptures covered with erect setae; posterior lobe anteriorly with two ridges; humeral angles rounded and swollen; posterior angles semicircular, prominent backward; posterior margin before scutellum nearly straight. Scutellum ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ) ridged along lateral margins, concave mediobasally, ligulate in apical portion. Hemelytra ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ) not reaching to tip of abdomen. Fore and mid femora ( Figs. 13 View FIGURE 13 , 16 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) each with two rows of spines ventrally; fore tibia ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ) each with a distinct tibial spur subapically.
Pygophore ( Figs. 15, 20, 21 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) nearly straight along posterior margin; pygophore process hemi-annular, middle thick ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ). Paramere ( Figs. 17–19 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) flattened, elongate-triangular, curved at median portion, swollen in apical half, nearly straight along anterior margin, with outer side concave centrally. Phallus as shown in Figs. 22–24 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ; basal plate slender and long, swollen at apex; basal plate bridge ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 14 – 24 ) thin and nearly straight; pedicel short and broad; phallosoma oblong, anchor-shaped and swollen apically; dorsal phallothecal sclerite with two sclerotized irregularly symmetrical sclerites subapically; ventral phallothecal sclerite strongly sclerotized; struts fused each other, nearly reaching to apical part of phallosoma; endosoma simple.
Measurements. [3 (n=1)]. Body length 10.8; maximum width of abdomen 4.1; head length 2.3; length of anteocular portion 1.2; length of postocular portion 0.7; synthlipsis 0.7; interocellar space 0.25; lengths of antennal segments I-IV=0.8, 1.0, 0.7, 0.7; lengths of visible labial segments I-III=0.6, 1.85, 0.4; length of anterior pronotal lobe 1.2; length of posterior pronotal lobe 1.5; maximum width of thorax 3.3; length of scutellum 1.2; length of hemelytron 6.4.
Material examined. 13, China, Yunnan, Province, Jingping, 16.XII.2003, 1960 m, alt, Liang Hongbing leg (Zoological Institute, CAS).
Distribution. China (Yunnan); India; Myanmar.
| CAS |
California Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Physoderinae |
|
Genus |
Physoderes impexa (Distant 1903)
| Cao, Liangming, Tomokuni, Masaaki & Cai, Wanzhi 2011 |
Physoderes fuscus
| Maldonado-Capriles 1990: 380 |
| Izzard 1936: 583 |
| Breddin 1903: 126 |