Enneapterygius gracilis Fricke, 1994
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5374.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D8FF43DE-4A2F-4E72-A621-B0A11EEACE72 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10248459 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D166C557-FFE0-FFB8-FF7E-D42AFAF85152 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2023-11-17 17:34:37, last updated 2024-11-27 11:31:38) |
|
scientific name |
Enneapterygius gracilis Fricke, 1994 |
| status |
|
Enneapterygius gracilis Fricke, 1994 View in CoL
[English name: Northern Yellow-black Triplefin]
Figures 4 View FIGURE 4 , 7 View FIGURE 7 ; Tables 2 View TABLE 2 , 6 View TABLE 6 , 7 View TABLE 7
Enneapterygius gracilis Fricke, 1994: 209 View in CoL , fig. 34 (original description; type locality: Danger Point, Cobourg Peninsula, Northern Territory, Australia); Larson and Williams, 1997: 367 (Nightcliff, East Point, and Lee Point Reef, Northern Territory); Fricke, 1997: 567 (Western Australia, Northern Territory, and Queensland); Hutchins, 2001: 41 (Western Australia); Hoese, 2006: 1520 (Gulf of Carpentaria, Northern Territory); Larson et al., 2013: 177 (Northern Territory: Burford Island; Trepang Bay, Cobourg Peninsula; North Oxley Island; East Vernon island; Veronica Island, Gove Peninsula; Yirrkala Reef).
Holotype. NTM S. 10431-027 , male, 19.7 mm SL, Danger Point , Cobourg Peninsula, Northern Territory, Australia, 11°08′S, 132°20′E, 0–1.5 m, 1 May 1982, B. Russell et al. GoogleMaps
Paratypes. 8 specimens (15.8–20.7 mm SL). NTM S. 10431-034 , female, 16.5 mm SL, same data as holotype; GoogleMaps AMS I. 17060-043 , 3 males and 3 females, 18.3–20.7 mm SL, Exmouth Gulf, Western Australia, 22°15′S, 114°15′E, 19 Jan. 1972, W. Ponder; GoogleMaps AMS IB. 7075 , female, 15.8 mm SL, Bountiful Island, Gulf of Carpentaria , Queensland, 16°41′S, 139°50′E, Dec. 1963, J. Yaldwyn GoogleMaps .
Non-type specimen. AMS I. 25500-005 , male, 19.5 mm SL, 5 km north of Learmouth, Exmouth Gulf , Western Australia, 22°20′S, 114°10′E, 10 Sept. 1985, D. Hoese & D. Rennis GoogleMaps .
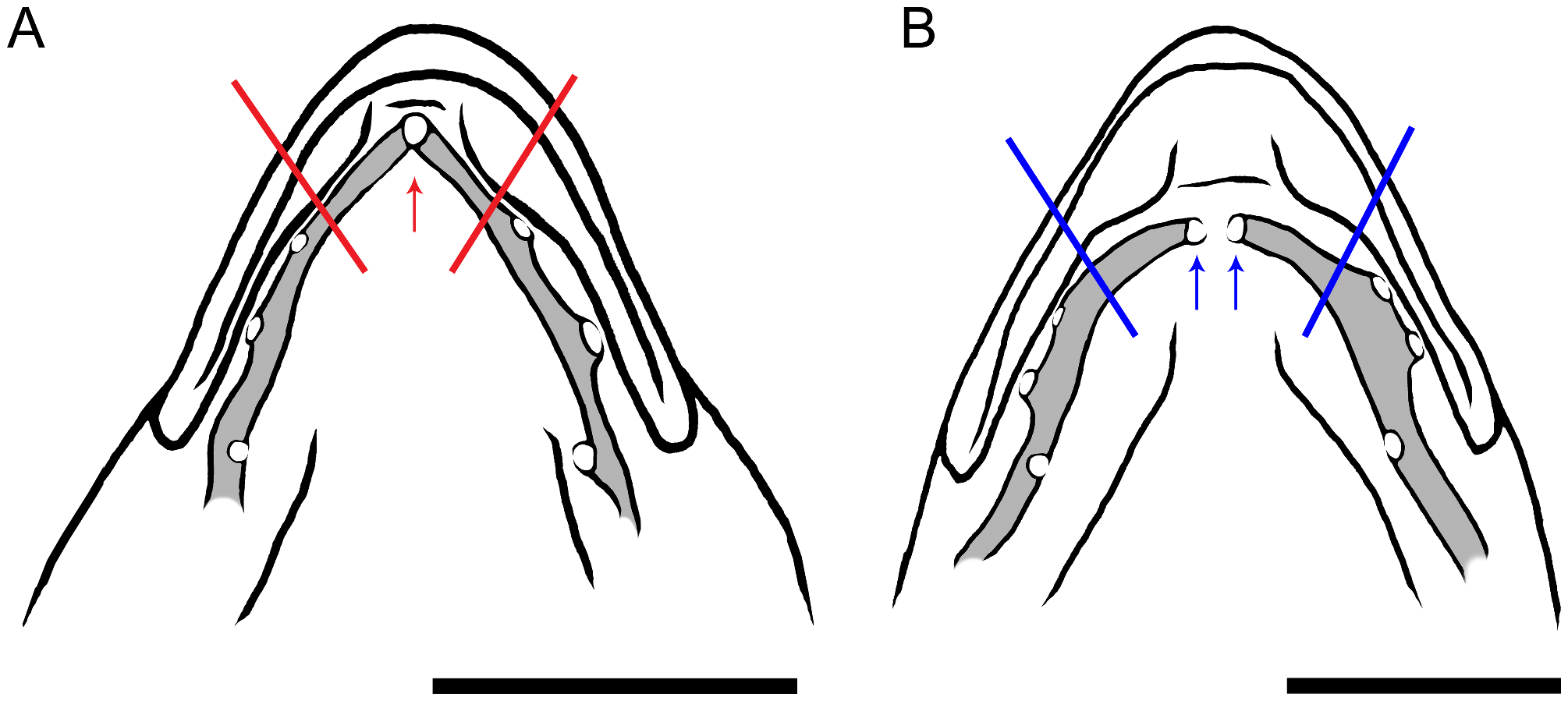
Diagnosis. A species of Enneapterygius ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ) with the following combination of characters: 11 or 12 (modally 12) second dorsal-fin spines; 9–11 (9) third dorsal-fin rays; I, 16–18 (7) anal-fin rays; ii–iv (iii) + 4–6 (5) + vi–vii (vii) = 14–16 (15) pectoral-fin rays (iii + 5 + vii = 15 in holotype and 4 paratypes, iv + 4 + vii = 15 in 2 paratypes, iv + 5 + vii = 16 and ii + 6 + vi = 14 in single paratype specimen and non-type specimen); 12 or 13 (13) pored lateral-line scales; 19–22 (21) notched lateral-line scales; 31–34 (32) scales rows in longitudinal series; 2 or 2½ (2) scales above 1st pored lateral-line scale; 3 or 3½ (3) scales below 1st notched lateral-line scale; 8 circumpeduncular scales; mandibular pores 3–4 + 1–2 + 3–4 (usually 3 + 2 + 3) ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ) (3 + 2 + 3 in holotype, 6 paratypes, and a non-type specimen, 3 + 1 + 3 and 4 + 2 + 4 in single paratype only); head relatively long, its length 29.2–32.5% (mean 30.6%) of SL; upper jaw length 9.2–11.7% (11.0%) of SL; 1st spine of first dorsal fin slightly longer than that of 2nd dorsal fin, its length 10.8–17.9% (13.9%) of SL; anterior nostril tentacle unbranched; orbital tentacle circular, the edge slightly pointed, its length slightly less than or subequal to pupil diameter; body generally yellowish or brownish with 6 or 7 bands, darker around lateral line; brownish blotches on each pectoral-fin ray, forming 3 or 4 narrow bands; anal fin with 7–9 brownish oblique bands; caudal fin translucent with 5 vertical bars; body yellowish, lower half of head and pectoral-fin base black in nuptial males.
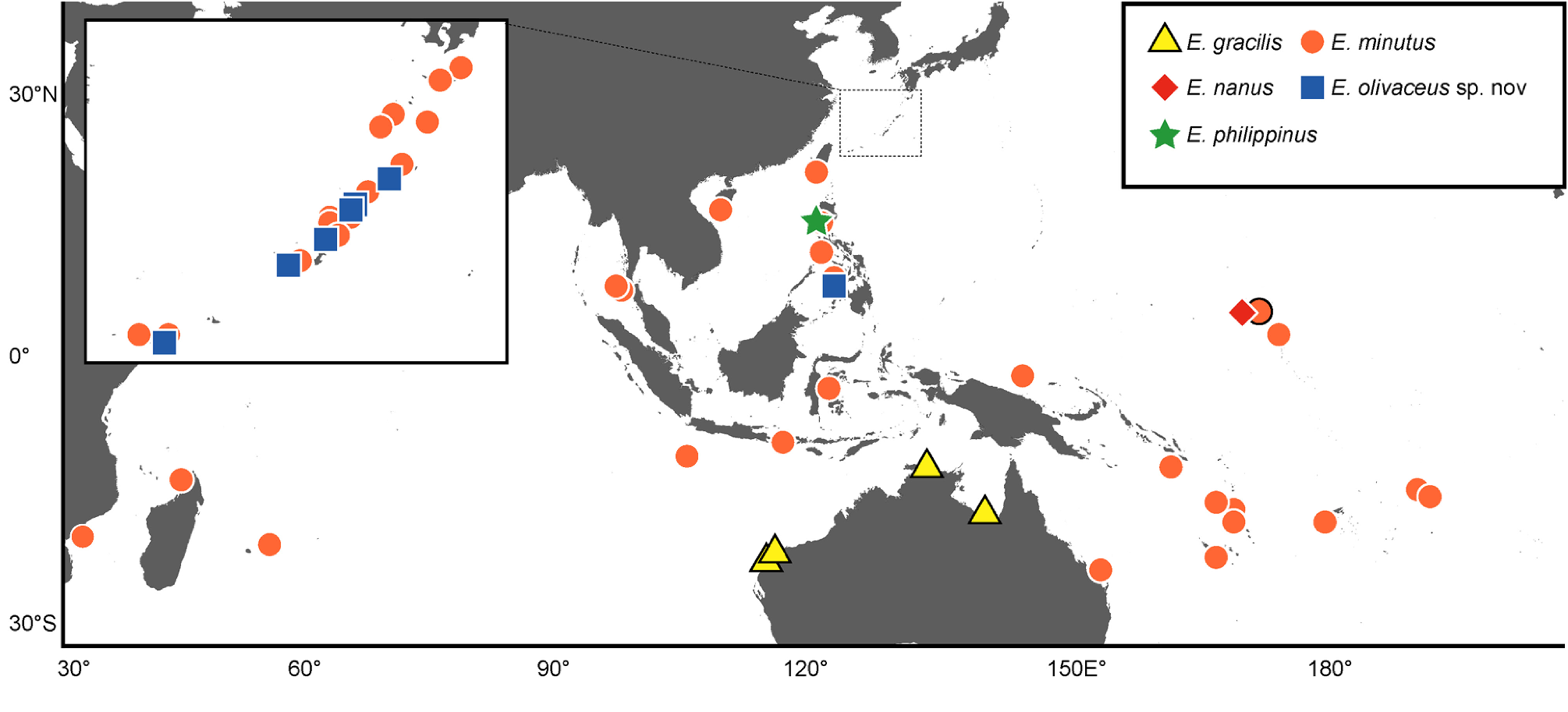
Distribution. Enneapterygius gracilis is distributed only in northern Australia, where it ranges from Western Australia (Exmouth Gulf) to the Northern Territory (East Point, Nightcliff, Lee Point, East Vernon Island, Burford Island, Trepang Bay, North Oxley Island, Veronica Island, Yirrkala Reef) and Queensland (Bountiful Island) ( Fricke, 1994; Larson & Williams, 1997; Fricke, 1997; Hutchins, 2001; Hoese, 2006; Larson et al., 2013) ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
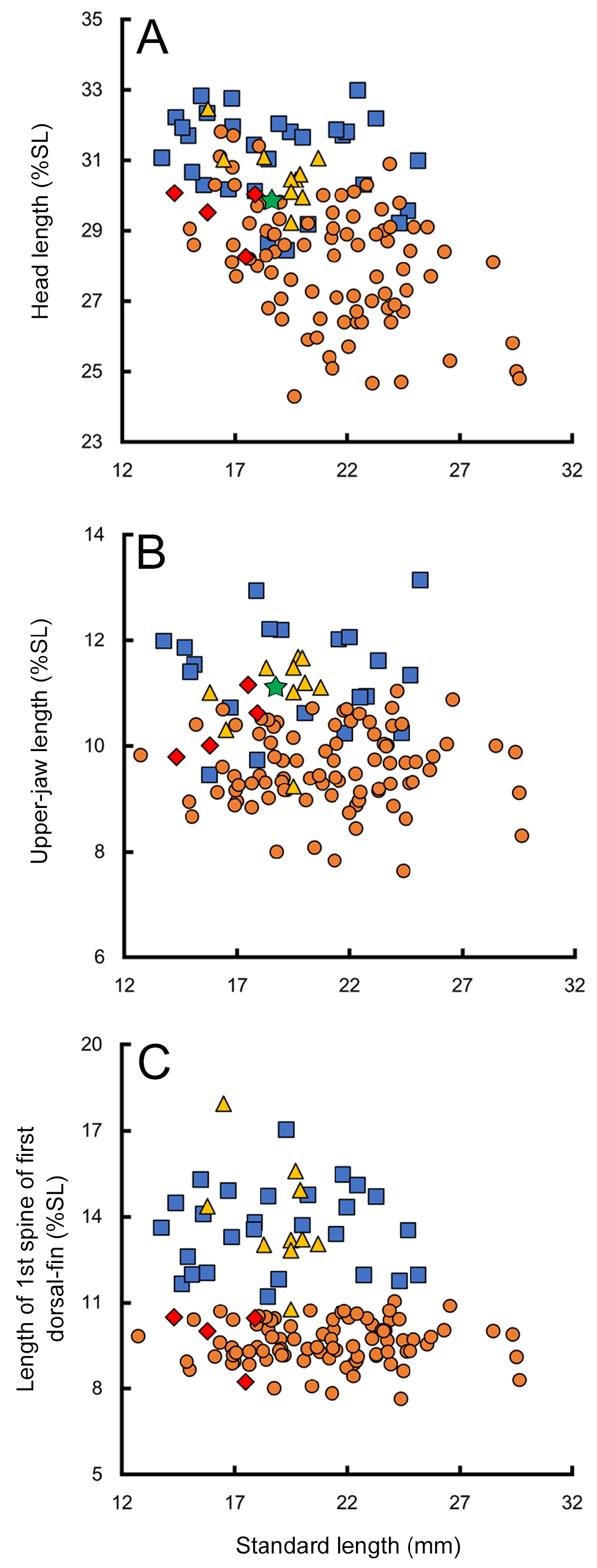
Remarks. Although Fricke (1994) described the symphyseal mandibular pore of E. gracilis as single (mandibular pore formula 3 + 1 + 3), examination of specimens, including the holotype, in this study revealed that E. gracilis has double symphyseal mandibular pores, the mandibular pore formula being revised as 3 + 2 + 3, accordingly. Enneapterygius gracilis is similar to E. olivaceus n. sp. in having a long head [29.2–32.5% (mean 30.6%) of SL], 1st spine of the first dorsal fin [10.8–17.9% (13.9%) of SL], and orbital tentacles (slightly less than or subequal to pupil diameter) ( Figs 5 View FIGURE 5 , 6 View FIGURE 6 ). However, the former differs from the latter in notched lateral-line scale and scales below the 1st notched scale numbers, and mandibular pore formula ( Figs 5 View FIGURE 5 , 6 View FIGURE 6 ) (see E. olivaceus n. sp. Remarks.)
Fricke, R. (1994) Tripterygiid Fishes of Australia, New Zealand and the Southwest Pacific Ocean (Teleostei). Koeltz Scientific Books, Konigstein, 585 pp.
Fricke, R. (1997) Tripterygiid Fishes of the Western and Central Pacific (Teleostei). Koeltz Scientific Books, Konigstein, 607 pp.
Hoese, D. F. (2006) Tripterygiidae. In: House, D. F., Bray, D. J., Paxton, J. R. & Allen, G. R. (Eds.), Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 35. Fishes. Parts 1 - 3. ABRS & CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood, pp. 1517 - 1528.
Hutchins, J. B. (2001) Checklist of the fishes of Western Australia. Records of the Western Australian Museum Supplement, 63, 9 - 50. https: // doi. org / 10.18195 / issn. 0313 - 122 x. 63.2001.009 - 050
Larson, H. K. & Williams, R. S. (1997) Darwin Harbour fishes: a survey and annotated checklist. In: Hanley, J. R., Caswell, G., Megirian, D. & Larson, H. K. (Eds.), Proceedings of the Sixth International Marine Biological Workshop. The Marine Flora and Fauna of Darwin Harbour, Northern Territory, Australia. Museums and Art Galleries, Northern Territory and Australian Scientific Association, Darwin, pp. 339 - 380.
Larson, H. K., Williams, R. S. & Hammer, M. P. (2013) An annotated checklist of the fishes of the Northern Territory, Australia. Zootaxa, 3696 (1), 1 - 293. https: // doi. org / 10.11646 / zootaxa. 3696.1.1
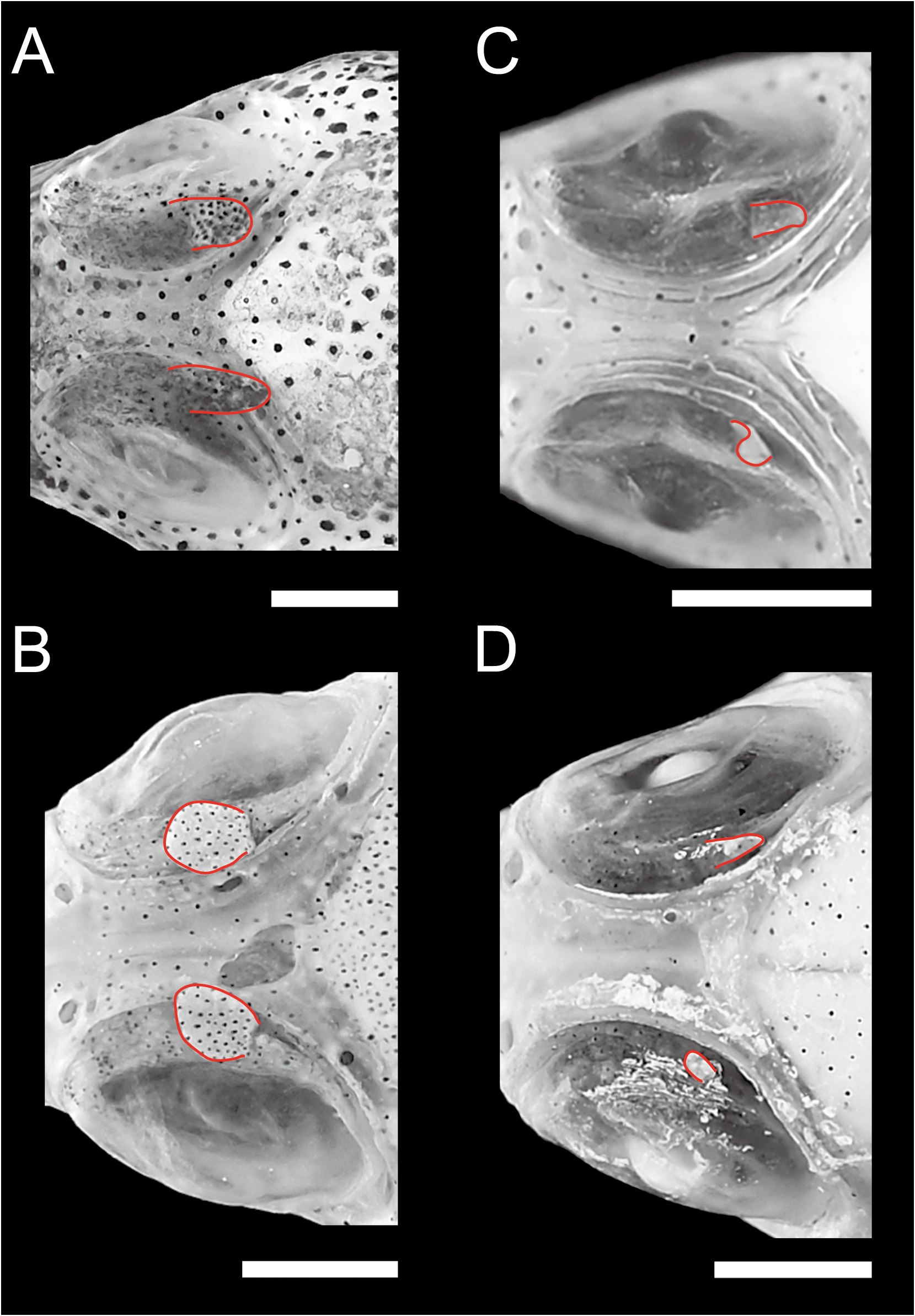
FIGURE 5. Orbital tentacle shape of A Enneapterygius olivaceus n. sp., KAUM–I. 101347, holotype, male, 19.3 mm SL, Yoron-jima Island, Japan; B E. gracilis, AMS I. 25500-005, male, 19.5 mm SL, Western Australia; C E. nanus, NSMT-P 54443, male, 14.3 mm SL, Eroj Island, Marshall Islands; D E. minutus, lectotype, BMNH 1961.10.20.1, female, 20.4 mm SL, Apia, Western Samoa. Bars represent 1 mm
FIGURE 6. Lengths of A head, B upper jaw, and c 1st spine length of first dorsal-fin (% standard length) relative to standard length in five species of Enneapterygius. Yellow triangles, orange circles, red diamonds, blue squares, and a green star indicate E. gracilis, E. minutus, E. nanus, E. olivaceus n. sp., and E. philippinus, respectively
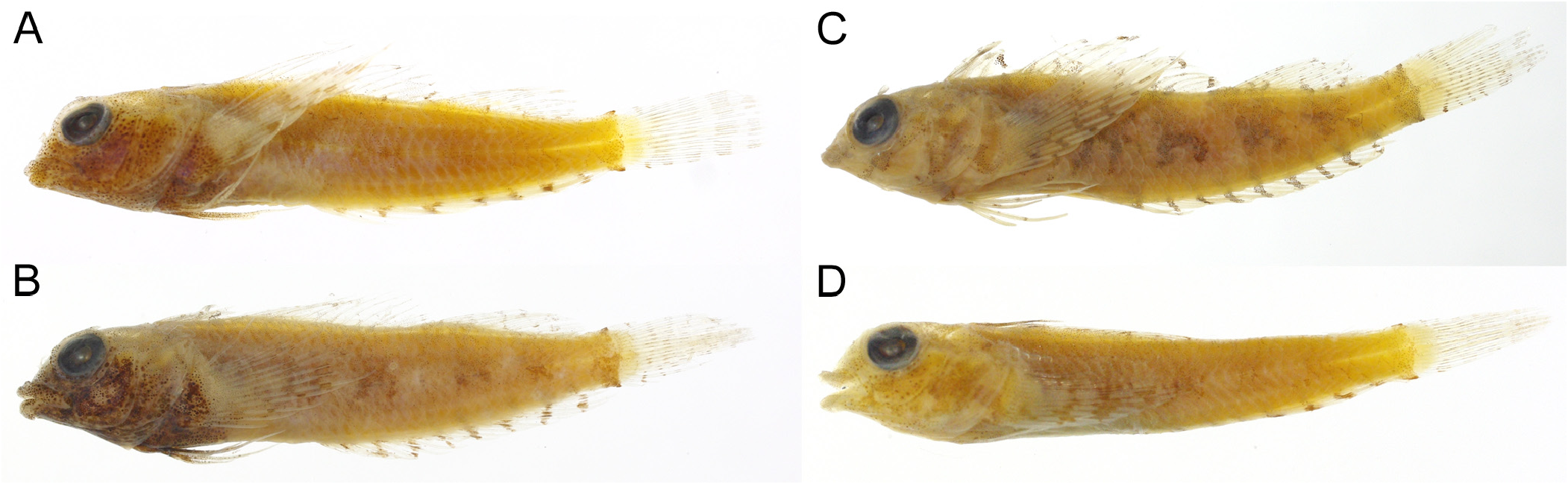
FIGURE 7. Photographs of preserved specimens of Enneapterygius gracilis. A NTM S. 10431-027, holotype, male, 19.7 mm SL, Northern Territory, Australia; B AMS I. 17060-043 (1), paratype, male, 19.9 mm SL, Western Australia; C AMS I. 17060- 043 (3), paratype, female, 19.5 mm SL; D NTM S. 10431-034, paratype, female, 16.5 mm SL, Northern Territory
FIGURE 8. Illustrations of mandibular pore system of Enneapterygius gracilis and Enneapterygius minutus. A double symphyseal mandibular-pores (3 + 2 + 3) (Enneapterygius gracilis, AMS I. 25500-005, male, 19.5 mm SL), B single symphyseal mandibular-pore (mandibular pore formula: 3 + 1 + 3) (Enneapterygius minutus, BMNH 1961.10.20.1, female, 20.4 mm SL) Bars represent 1 mm
TABLE 2. Counts and morphometric measurements (as % of SL) of specimens of Enneapterygius gracilis
| Holotype | Paratypes | Non-type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTM S. 10431-027 | n = 3 | n = 5 | AMS I. 25500-005 | |
| Australia | Australia | Australia | Australia | |
| Male | Males | Females | Male | |
| Standard length (SL; mm) | 19.7 | 18.3–19.9 | 15.8–20.7 | 19.5 |
| Counts | ||||
| Dorsal-fin rays | III, XII, 10 | III, XI, 9–11 | III, XI–XII, 9–10 | III, XII, 9 |
| Anal-fin rays | I, 17 | I, 16–18 | I, 16–17 | I, 17 |
| Pectoral-fin rays | iii + 5 + vii = 15 | iii + 5 + vii = 15 | ii–iv + 4–6 + vi–vii = 14–15 | iv + 5 + vii = 16 |
| Scale rows in longitudinal series | 32 | 33–34 | 32–34 | 31 |
| Pored lateral-line scales | 12 | 13 | 13 | 12 |
| Notched lateral-line scales | 21 | 21–22 | 21–22 | 19–20 |
| Scales above of 1st PLL | 2 | 2 | 2–2½ | 2 |
| Scales below 2nd dorsal fin | 3 | 2½–3½ | 2½–3½ | 2½ |
| Scales below of 1st NLL | 3 | 3–3½ | 3–3½ | 3 |
| Circumpeduncular scales | 8 | 8 | — | 8 |
| Mandibular pore formula | 3 + 2 + 3 | 3 + 2 + 3 | 3–4 + 1–2 + 3–4 (usually 3 + 2 + 3) | 3 + 2 + 3 |
| Measurements (% SL) | ||||
| Body depth | 21.0 | 20.8–22.2 (21.6) | 19.8–21.1 (20.3) | 20.5 |
| Body width | 18.6 | 17.3–19.8 (18.7) | 17.3–20.0 (18.1) | 21.0 |
| Head length | 30.5 | 30.5–31.1 (30.7) | 30.0–32.5 (30.9) | 29.2 |
| Snout length | 9.4 | 7.9–8.9 (8.3) | 7.7–8.6 (8.2) | 10.3 |
| Orbit diameter | 10.9 | 10.7–10.9 (10.8) | 10.2–11.0 (10.5) | 10.3 |
| Interorbital width | 2.7 | 2.4–2.8 (2.7) | 2.1–2.9 (2.5) | 3.1 |
| Upper-jaw length | 11.7 | 11.5–11.7 (11.5) | 10.3–11.2 (10.9) | 9.2 |
| Postorbital length | 13.5 | 13.5–14.3 (13.9) | 13.7–14.2 (13.8) | 13.3 |
| Pre-1st-dorsal-fin length | 26.6 | 24.6–25.9 (25.4) | 23.6–26.5 (25.2) | 26.2 |
| Pre-2nd-dorsal-fin length | 38.0 | 37.6–39.6 (38.7) | 36.9–38.1 (37.7) | 37.4 |
| Pre-3rd-dorsal-fin length | 71.6 | 72.5–74.1 (73.4) | 68.8–72.1 (70.9) | 70.3 |
| Pre-anal-fin length | 48.8 | 50.7–52.6 (51.9) | 50.1–53.9 (52.6) | 52.3 |
| Anal-fin base length | 43.5 | 40.8–43.3 (42.4) | 39.1–43.5 (41.1) | 37.9 |
| Pre-pectoral-fin length | 31.5 | 32.2–33.0 (32.6) | 31.9–33.5 (32.9) | 31.3 |
| Pre-pelvic-fin length | 23.7 | 24.5–24.9 (24.7) | 22.1–24.8 (23.6) | 23.6 |
| Caudal peduncle length | 9.2 | 8.1–9.9 (9.2) | 8.5–10.4 (9.6) | 14.9 |
| Caudal peduncle depth | 8.6 | 9.2–10.7 (10.1) | 8.2–10.3 (9.2) | 9.2 |
| 1st spine length of 1st dorsal fin | 15.6 | 13.0–14.9 (13.7) | 12.8–17.9 (14.3) | 10.8 |
| 2nd spine length of 1st dorsal fin | 12.5 | 10.2–11.6 (10.7) | 10.1–14.7 (11.8) | 10.3 |
| 3rd spine length of 1st dorsal fin | 9.8 | 8.4–9.3 (8.9) | 8.9–10.8 (9.9) | 7.2 |
| 1st dorsal-fin base length | 6.6 | 6.4–7.3 (6.8) | 5.9–6.8 (6.5) | 5.1 |
| 1st spine length of 2nd dorsal fin | 15.1 | 13.3–13.8 (13.6) | 13.2–13.9 (13.6) | 12.8 |
| 2nd spine length of 2nd dorsal fin | 16.2 | 13.6–14.6 (14.1) | 13.8–15.5 (14.9) | 14.9 |
| 3rd spine length of 2nd dorsal fin | 16.9 | 13.9 | 14.1–15.8 (15.2) | 14.9 |
| 2nd dorsal-fin base length | 34.5 | 29.1–32.8 (30.7) | 26.8–30.4 (28.9) | 29.2 |
| 1st ray length of 3rd dorsal fin | damaged | 18.9 | 16.2–18.5 (17.6) | 15.9 |
| 2nd ray length of 3rd dorsal fin | 16.0 | 16.3–18.4 (17.3) | 17.2–17.7 (17.4) | 15.9 |
| 3rd dorsal fin base length | 20.1 | 17.2–21.1 (19.2) | damaged | 16.4 |
| Pectoral-fin length | 33.1 | 33.6–37.3 (35.3) | 33.9–37.3 (36.0) | 29.7 |
| 1st ray length of pelvic fin | 17.2 | 16.2–19.9 (18.5) | 17.2–20.3 (18.5) | damaged |
| 2nd ray length of pelvic fin | 25.0 | 25.7–27.7 (26.8) | 25.6–28.0 (26.6) | damaged |
Means in parentheses
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Enneapterygius gracilis Fricke, 1994
| Dewa, Yuna, Tashiro, Satokuni & Motomura, Hiroyuki 2023 |
Enneapterygius gracilis
| Larson, H. K. & Williams, R. S. & Hammer, M. P. 2013: 177 |
| Hoese, D. F. 2006: 1520 |
| Hutchins, J. B. 2001: 41 |
| Larson, H. K. & Williams, R. S. 1997: 367 |
| Fricke, R. 1997: 567 |
| Fricke, R. 1994: 209 |
1 (by plazi, 2023-11-17 17:34:37)
2 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-11-17 17:43:55)
3 (by juliana, 2023-11-23 18:59:43)
4 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-11-23 19:04:45)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-11-23 19:15:07)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-11-23 20:40:29)
7 (by juliana, 2023-11-27 16:26:41)
8 (by ExternalLinkService, 2023-11-27 16:31:44)