Limosilactobacillus reuteri, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1099/ijsem.0.004644 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6310191 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CD6F3526-FFC9-252A-477E-FA0FFBEE25A4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Limosilactobacillus reuteri |
| status |
subsp. nov. |
DESCRIPTION OF LIMOSILACTOBACILLUS REUTERI SUBSP. SUIS SUBSP. NOV.
Limosilactobacillus reuteri subsp. suis (su′ is. L. gen. n. suis, of swine, reflecting the host origin of most strains of this subspecies being the swine intestinal tract).
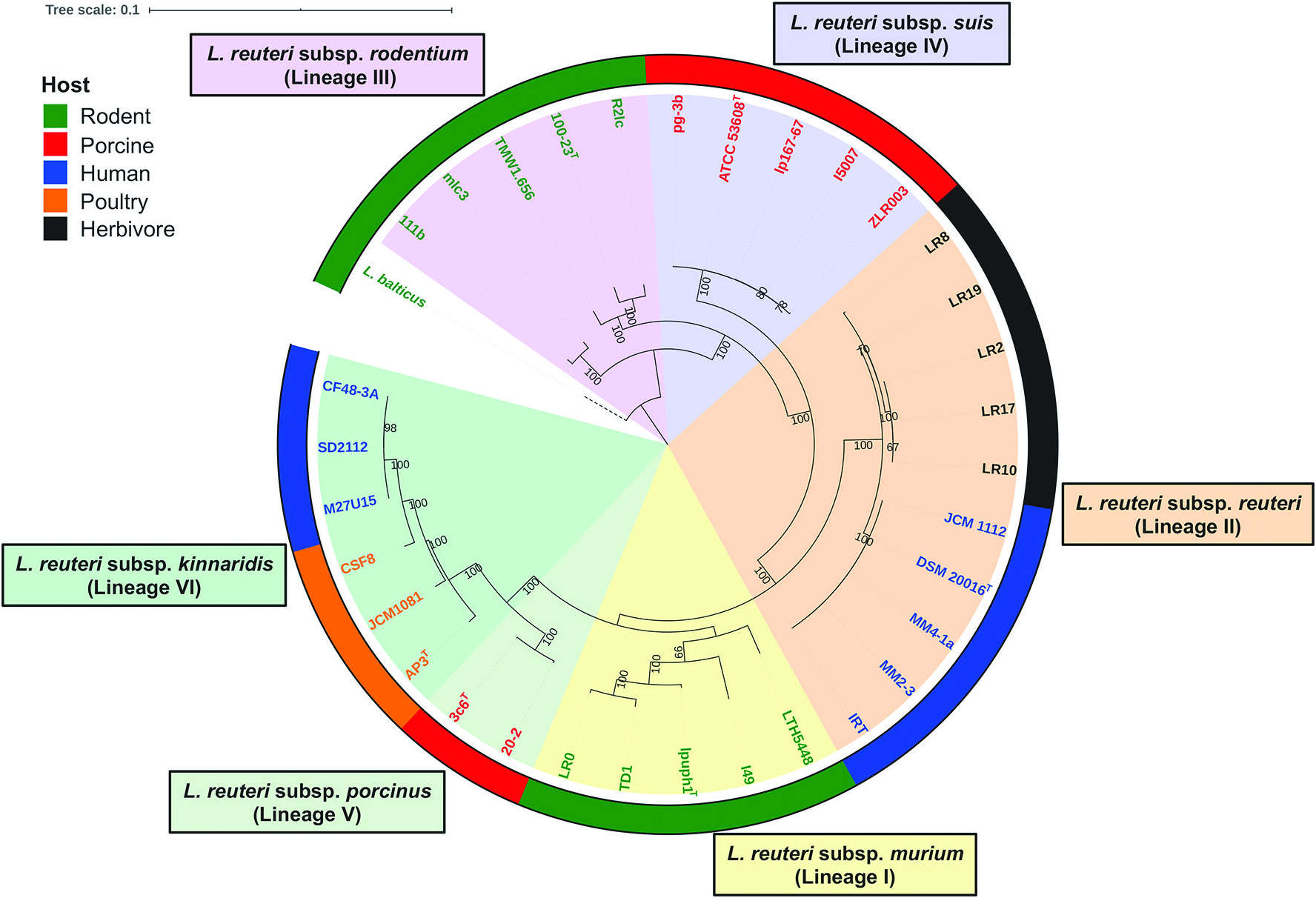
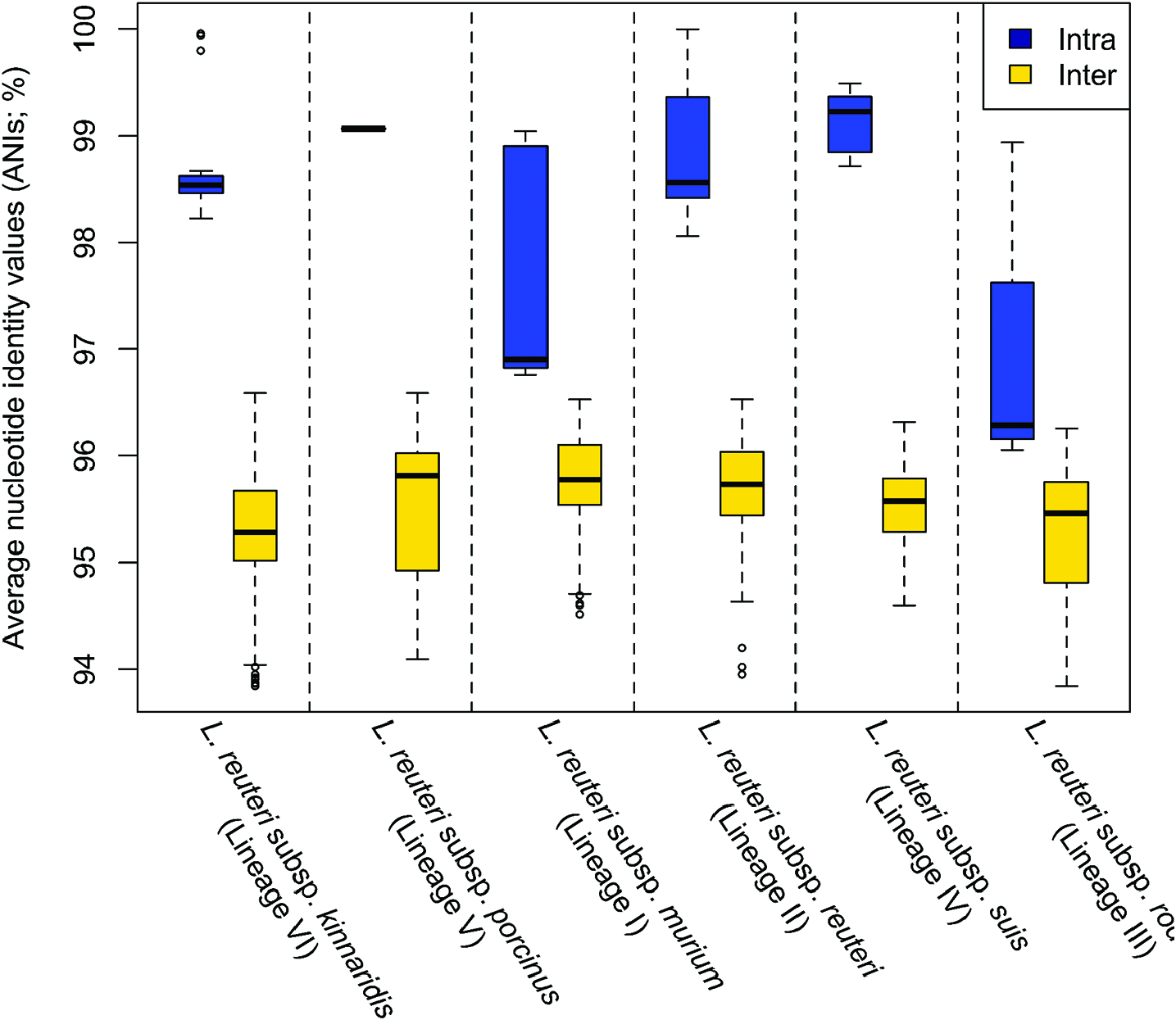
L. reuteri strains clustered in lineage IV ( Fig. 3 View Fig ) belong to L. reuteri subsp. porcinus and were isolated from pig [ 5, 7]. Strains belonging to this subspecies have ANI values of 98.7–99.5% with each other and ANI values of 94.6–96.3% with other L. reuteri strains belonging to different subspecies ( Fig. 4 View Fig ). Acid is produced from L-arabinose, D-ribose, D-xylose, D-galactose, D-glucose, maltose, lactose, melibiose, sucrose and raffinose; acid is not produced from D-fructose, D-mannose, methyl α- D-glucopyranoside, aesculin, potassium gluconate, glycerol, erythritol, D-arabinose, L-xylose, D-adonitol, methyl β -D-xylopyranoside, L-sorbose, L-rhamnose, dulcitol, inositol, D-mannitol, D-sorbitol, methyl α- Dmannopyranoside, N -acetylglucosamine, amygdalin, arbutin, salicin, cellobiose, trehalose, inulin, melezitose, starch, glycogen, xylitol, gentiobiose, turanose, D-lyxose, D-tagatose, D-fucose, L-fucose, D-arabitol, L-arabitol, potassium 2-ketogluconate or potassium 5-ketogluconate. Phylogenetic analyses based on the core genes identified in this study ( Fig. 3 View Fig ) and previous studies [ 5, 43, 46, 47], AFLP and MLSA (using concatenated sequences of ddl, pkt, leuS, gyrB, dltA, rpoA and recA genes) [ 7] indicate that strains clustered in this lineage are pig-specific. A mucus-binding protein (Mub) that could bind mucus and/or IgA [ 8, 41, 42] exists within this subspecies and it specifically supports the colonization of this subspecies to the porcine gastrointestinal tract. Strains within this subspecies have been applied as probiotics to improve porcine intestinal health, enhance production, prevent diarrhoea, release stress and immune modulation [ 48].
The type strain, ATCC 53608 T (=LMG 31752 T =1063 T [original designation]), was isolated from porcine gastrointestinal tract [ 7, 49, 50], with a DNA G+C content of 39.0mol%.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Limosilactobacillus reuteri
| Li, Fuyong, Cheng, Christopher C., Zheng, Jinshui, Liu, Junhong, Quevedo, Rodrigo Margain, Li, Junjie, Roos, Stefan, Gänzle, Michael G. & Walter, Jens 2021 |
L. reuteri
| SUBSP. SUIS 2021 |
L. reuteri subsp. porcinus
| Li & Cheng & Zheng & Liu & Quevedo & Li & Roos & Gänzle & Walter 2021 |
L. reuteri
| SUBSP. SUIS 2021 |