Pholcus ceylonicus O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1869
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4550.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2F7D1EC4-D4ED-4FAE-B227-CF7B79EAE833 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4581621 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CA3B104C-FF98-FF94-FF3D-FC4BFA2FE077 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pholcus ceylonicus O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1869 |
| status |
|
Pholcus ceylonicus O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1869 View in CoL
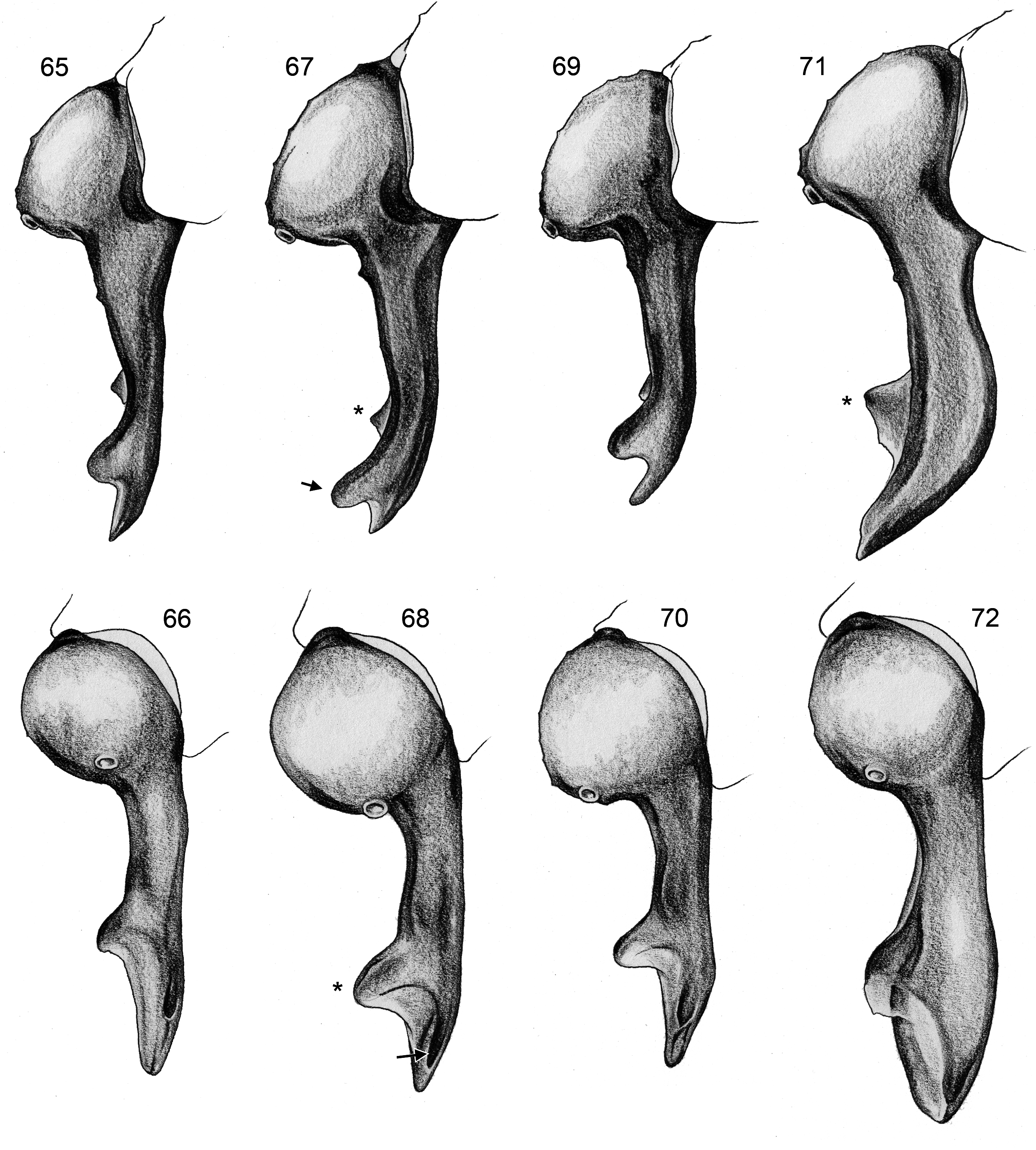
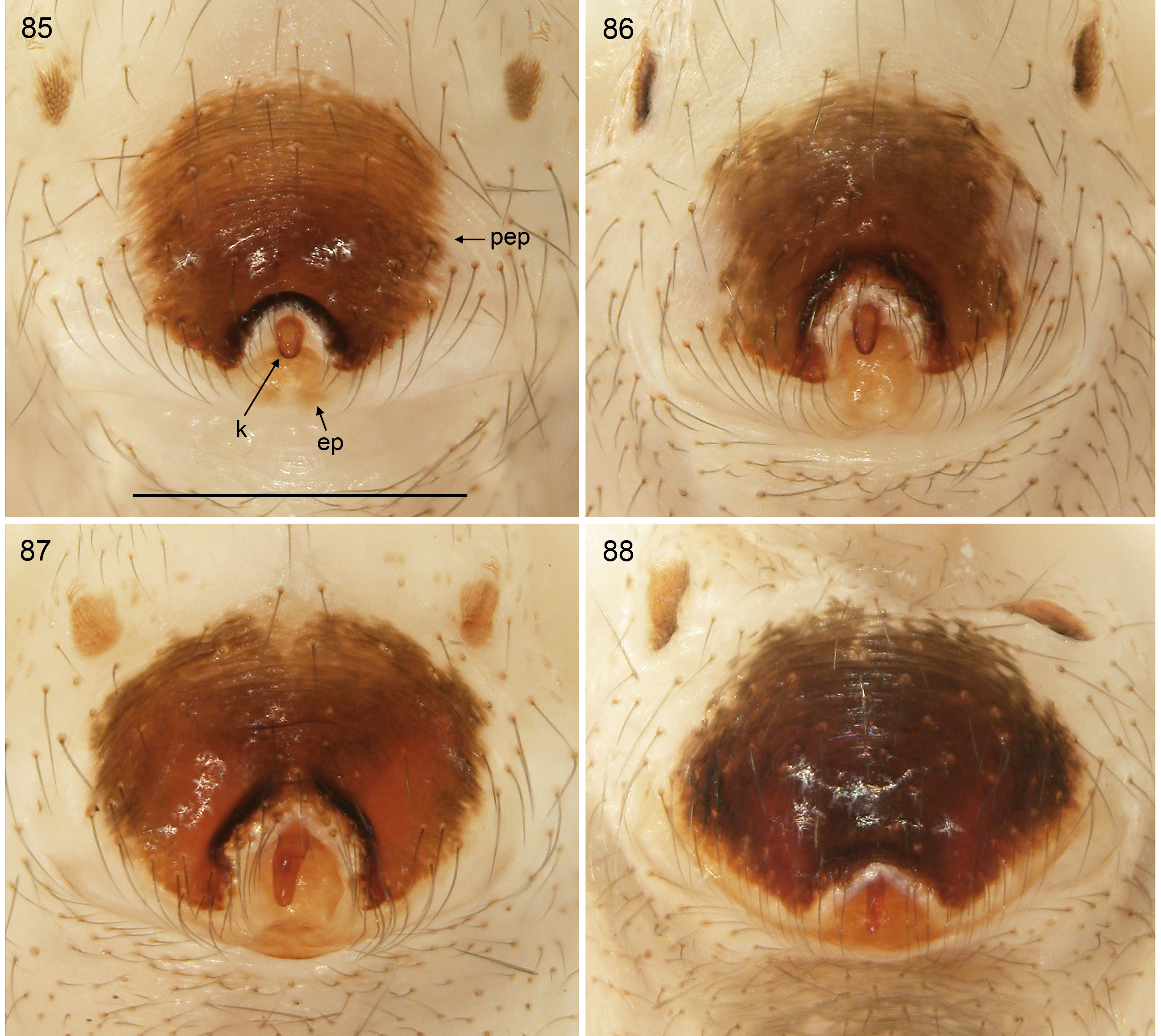
Figs 47, 49–50 View FIGURES 47–52 , 53–55 View FIGURES 53–58 , 65–66 View FIGURES 65–72 , 73–75 View FIGURES 73–78 , 85 View FIGURES 85–88 , 89 View FIGURES 89–92
Pholcus ceylonicus O. Pickard-Cambridge 1869: 378 View in CoL , pl. 11, figs 13, 21–27 ( ♂ ♀, Sri Lanka).
Pholcus ceylonicus View in CoL — Brignoli 1972: 909, figs 1–2, 4–7. Brignoli 1975: 36, fig. 2f (copied from Brignoli 1972). Huber & Benjamin 2005: 3306 View Cited Treatment , figs 1–4. Eberle et al. 2018 (molecular data). Huber et al. 2018: fig. 12.
Sihala ceylonica — Huber 2011: 31, fig. 145. Transferred back to Pholcus in Huber et al. 2018: 83 View in CoL .
Diagnosis. Males are easily distinguished from other species in ceylonicus group by shape of genital bulb ( Figs 73–75 View FIGURES 73–78 ): distinctive main bulbal process (‘appendix’), i.e. large sclerotized process with conical projection and unique membrane on retrolateral side. Females similar to P. metta sp. n. and P. puranappui sp. n. but with consistently smaller posterior excavation of pre-epigynal plate (compare Figs 85–87 View FIGURES 85–88 ).
Description (amendments; see Huber & Benjamin 2005). Dark mark on carapace variably large and either undivided or medially posteriorly divided. Dark mark on sternum usually star-shaped, sometimes rather triangular with long posterior point. Males from Minneriya with slightly smaller retrolateral conical projection on main bulbal process. Males from Gowindahela with slightly wider main bulbal process in dorsal view. Tibia 1 in 32 newly examined males: 9.5–14.8 (mean 11.9); in 24 females: 8.7–12.0 (mean 10.4). Diameter of posterior excavation of pre-epigynal plate usually 90–140 µm, in females from Gowindahela 140–150 µm.
New records. SRI LANKA: 1♂ 1♀, NMSL , 7♂ 2♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20036) and 1♀ 3 juvs in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL96 About ZFMK ), Western Province, Mitirigala Forest ( 6.997°N, 80.175°E), 70 m a.s.l., 6.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 2♂, ZFMK ( Ar 20037) and 1♂ in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL102 About ZFMK ), Sabaragamuwa Province, outside of Belilena Cave near Kitulgala ( 7.003°N, 80.436°E), 370 m a.s.l., 7.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 1♂ 3♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20038) , Sabaragamuwa Province, near Kitulgala ( 6.985°N, 80.430°E), 170 m a.s.l., 7.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 3♂ 7♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20039) and 2♀ in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL106 About ZFMK ), Central Province, Kandy, Dunumadallawa Forest ( 7.282°N, 80.643°E), 600– 680 m a.s.l., 8.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 10♂ 2♀ 6 juvs, ZFMK ( Ar 20040) and 1♂ 2♀ in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL113 About ZFMK ), North Western Province, Kurunegala, at base of Ethagala (Athugala) Mountain ( 7.490°N, 80.369°E), 170 m a.s.l., 9.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 2♂ 2♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20041) and 2♀ in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL119 About ZFMK ), Central Province, Kandalama Forest ( 7.859°N, 80.711°E), 220 m a.s.l., 10.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 2♂ 3♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20042) , North Central Province, Minneriya Forest ( 8.047°N, 80.832°E), 150 m a.s.l., 10.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 3♂ 4♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20043) and 1♀ in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL132 About ZFMK ), Uva Province, near Gowindahela ( 7.041°N, 81.538°E), 130–180 m a.s.l., 12.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 1♂ 2♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20044) and 1♀ 1 juv. in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL141 About ZFMK ), Uva Province, outside of cave near Ella ( 6.863°N, 81.050°E), 1030 m a.s.l., 13.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 1♂, ZFMK ( Ar 20045) , Western Province, Poruwadanda ( 6.742°N, 80.132°E), 130 m a.s.l., 18.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 2♂ 2♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20046) and 1♀ 1 juv. in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL162 About ZFMK ), Sabaragamuwa Province, Mapalena Ella ( 6.774°N, 80.460°E), 270 m a.s.l., forest below waterfall, 19.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps . 1♀, ZFMK ( Ar 20047) and 1 juv. in pure ethanol, ZFMK ( SL166 About ZFMK ), Western Province, Labugama Forest ( 6.846°N, 80.175°E), 150 m a.s.l., 20.iii.2017 ( B.A. Huber) GoogleMaps .
Natural history. This species is common and often abundant among large rocks in humid forests, sometimes also between tree buttresses. Webs are often densely connected to each other, resulting in high numbers of specimens in relatively small spaces. In a horizontal rock cleft (~ 10 m long, ~ 30 cm high,> 1 m deep) at Ethagala Mountain ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 47–52 ), ~100 large specimens (i.e. excluding small juveniles) were counted per meter. The large domed sheet webs were often shared with numerous cecidomyiid flies. When disturbed, the spiders started swinging in high amplitude and retreated back to the rocks and to sheltered spaces.
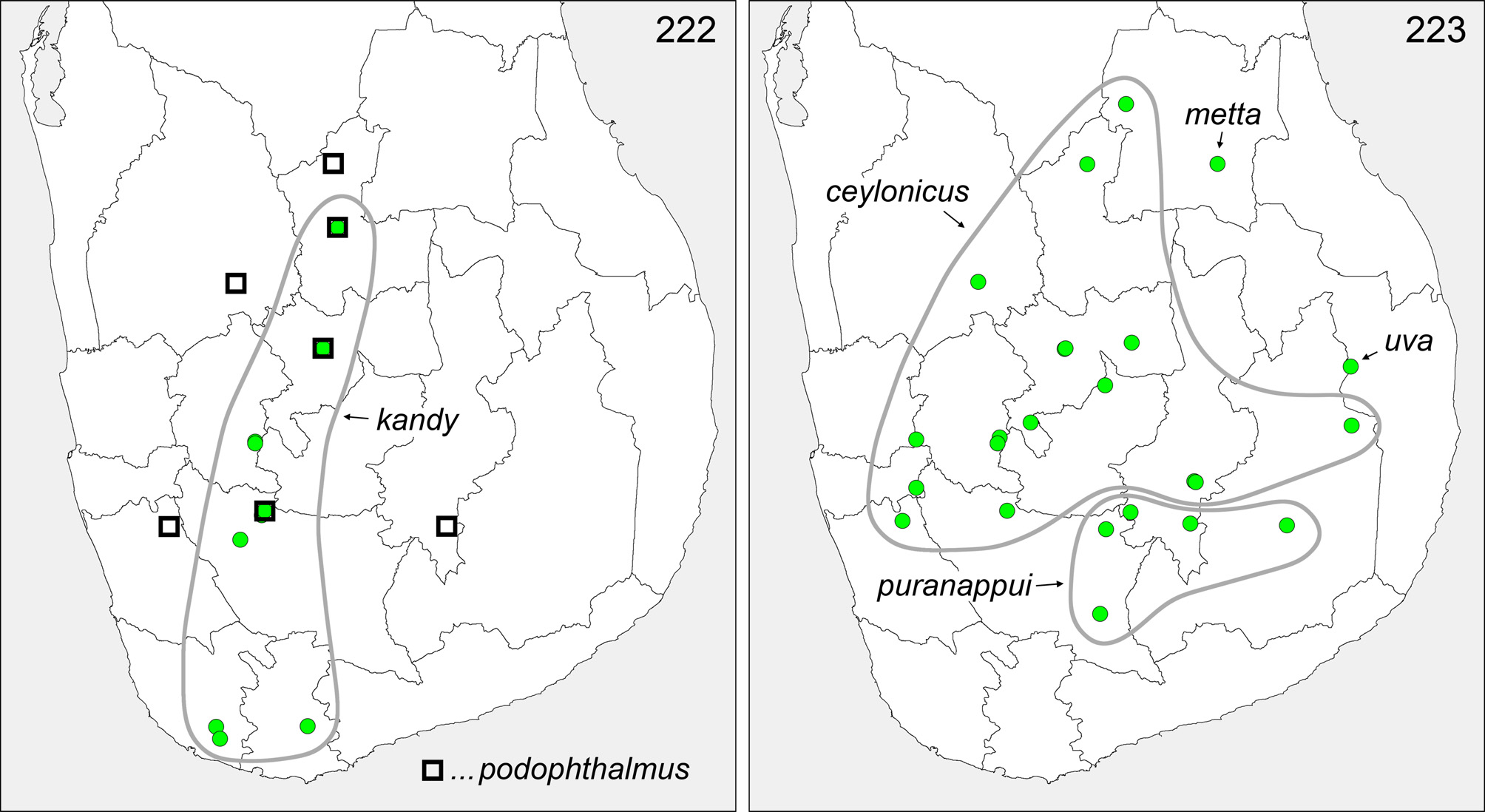
Distribution. Widely distributed in central Sri Lanka ( Fig. 223 View FIGURES 222–223 ). The female specimens from Belihul Oya and Diyaluma Falls reported in Huber (2011) were reexamined and found to belong to Pholcus puranappui (see below).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Pholcus ceylonicus O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1869
| Huber, Bernhard A. 2019 |
Sihala ceylonica
| Huber, B. A. & Eberle, J. & Dimitrov, D. 2018: 83 |
| Huber, B. A. 2011: 31 |
Pholcus ceylonicus
| Huber, B. A. & Benjamin, S. 2005: 3306 |
| Brignoli, P. M. 1975: 36 |
| Brignoli, P. M. 1972: 909 |
Pholcus ceylonicus
| Pickard-Cambridge, O. 1869: 378 |