Euops (Riedeliops) pseudoindicus, Riedel, Alexander, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.188214 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6221711 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C84EAB6E-FFA9-FF85-64F2-02AB0FEEF906 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Euops (Riedeliops) pseudoindicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Euops (Riedeliops) pseudoindicus sp. n.
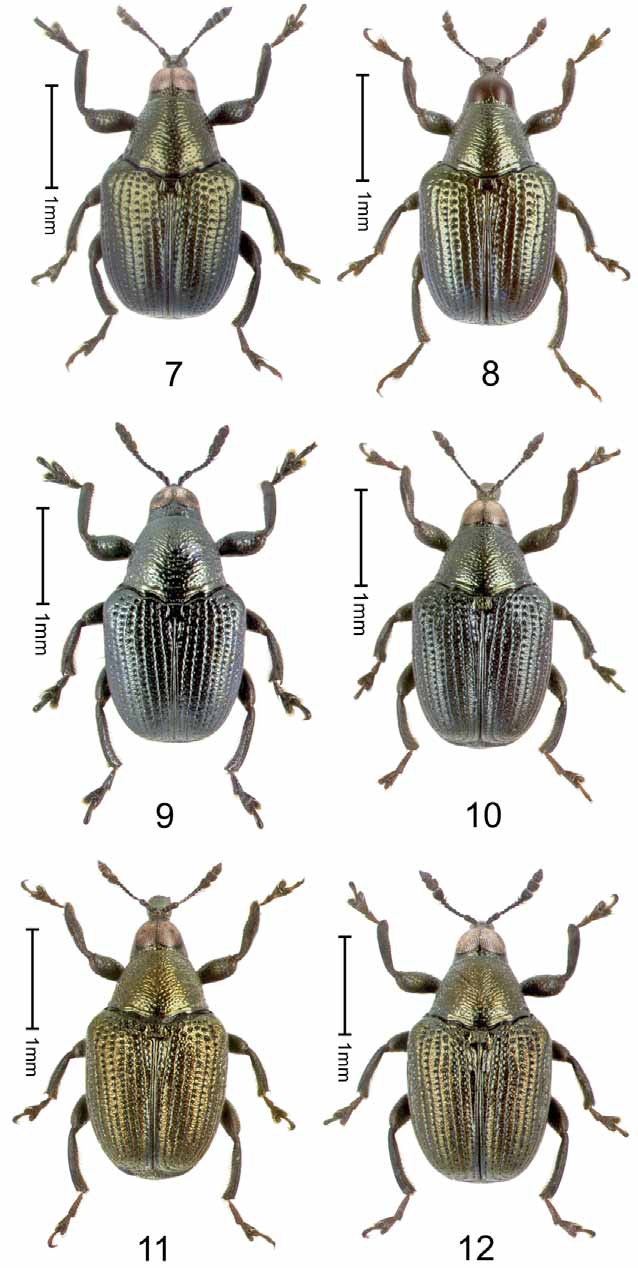
( Figs. 11–12 View FIGURES 7 – 12 , 23–24 View FIGURES 19 – 24 , 76 View FIGURES 71 – 78 , 88 View FIGURES 87 – 92 , 95–96 View FIGURES 93 – 99 , 102 View FIGURES 100 – 103 , 114–115 View FIGURES 110 – 115 , 121 View FIGURES 116 – 122 , 128 View FIGURES 123 – 129 , 135 View FIGURES 130 – 135 , 153–157 View FIGURES 153 – 157 , 164 View FIGURES 161 – 167 , 172 View FIGURES 168 – 173 , 181 View FIGURES 174 – 182 , 188 View FIGURE 188 )
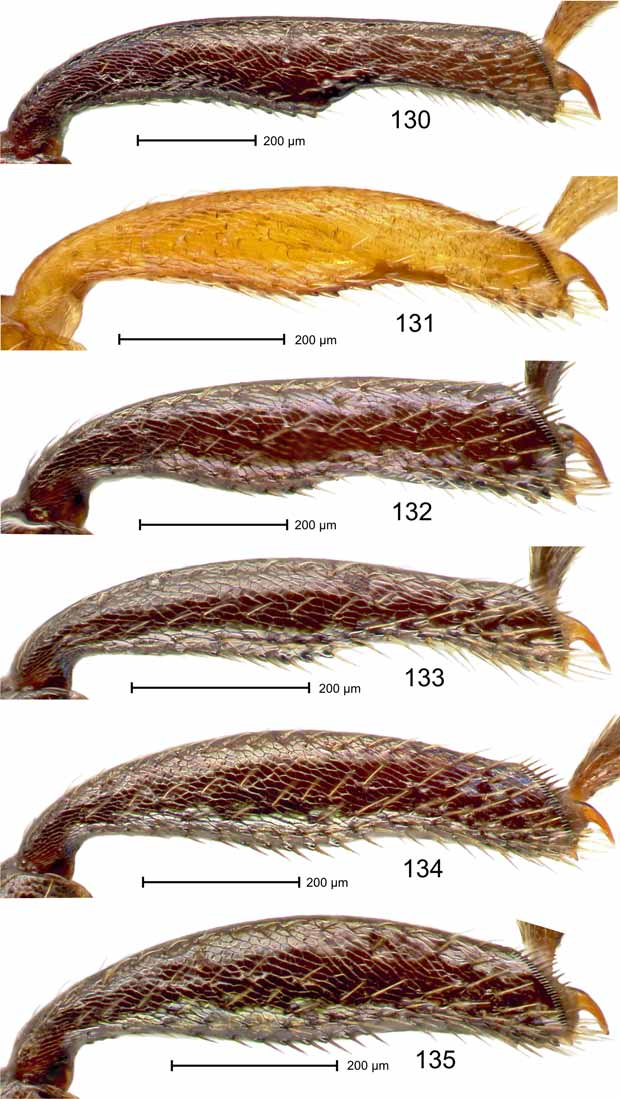
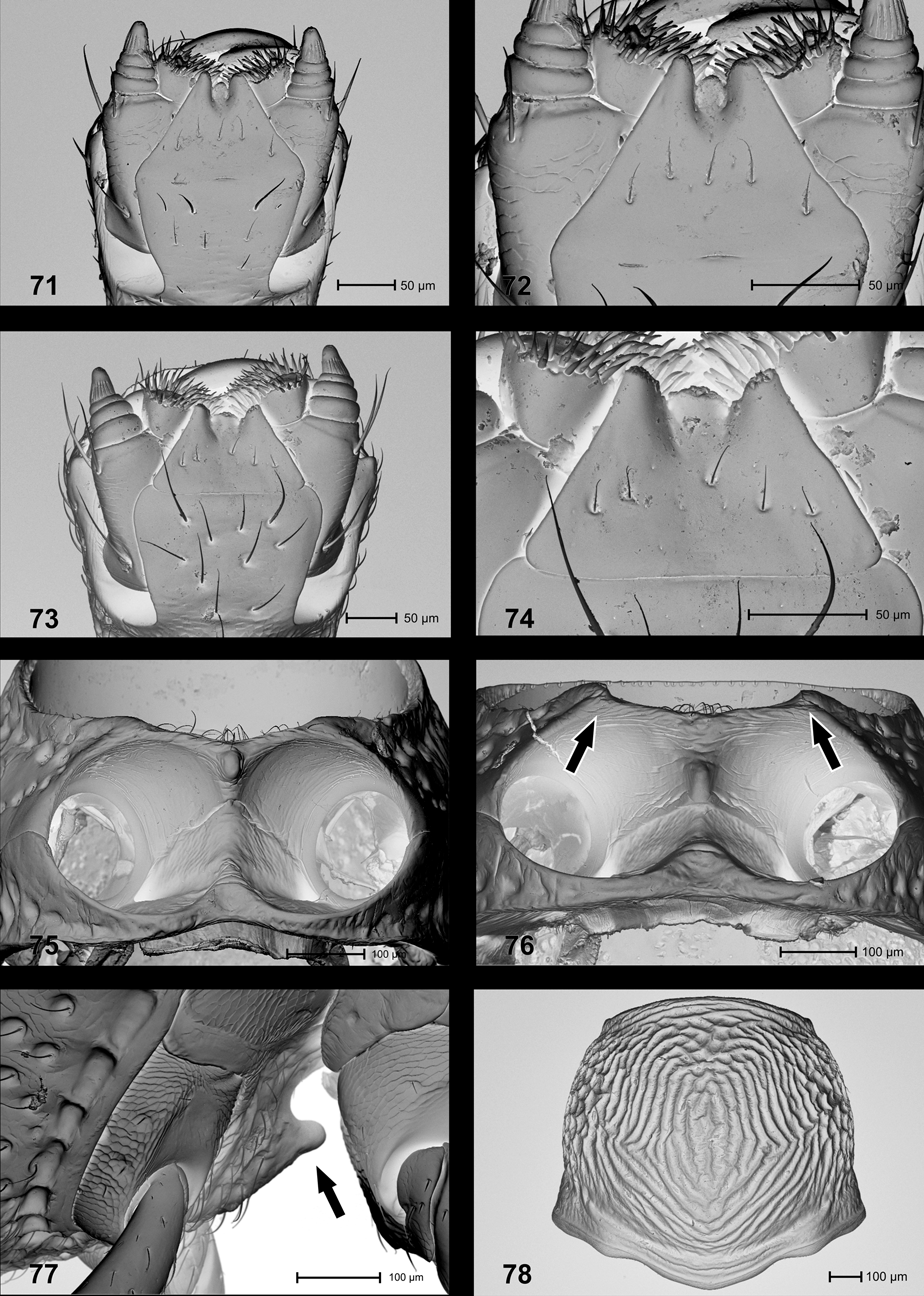
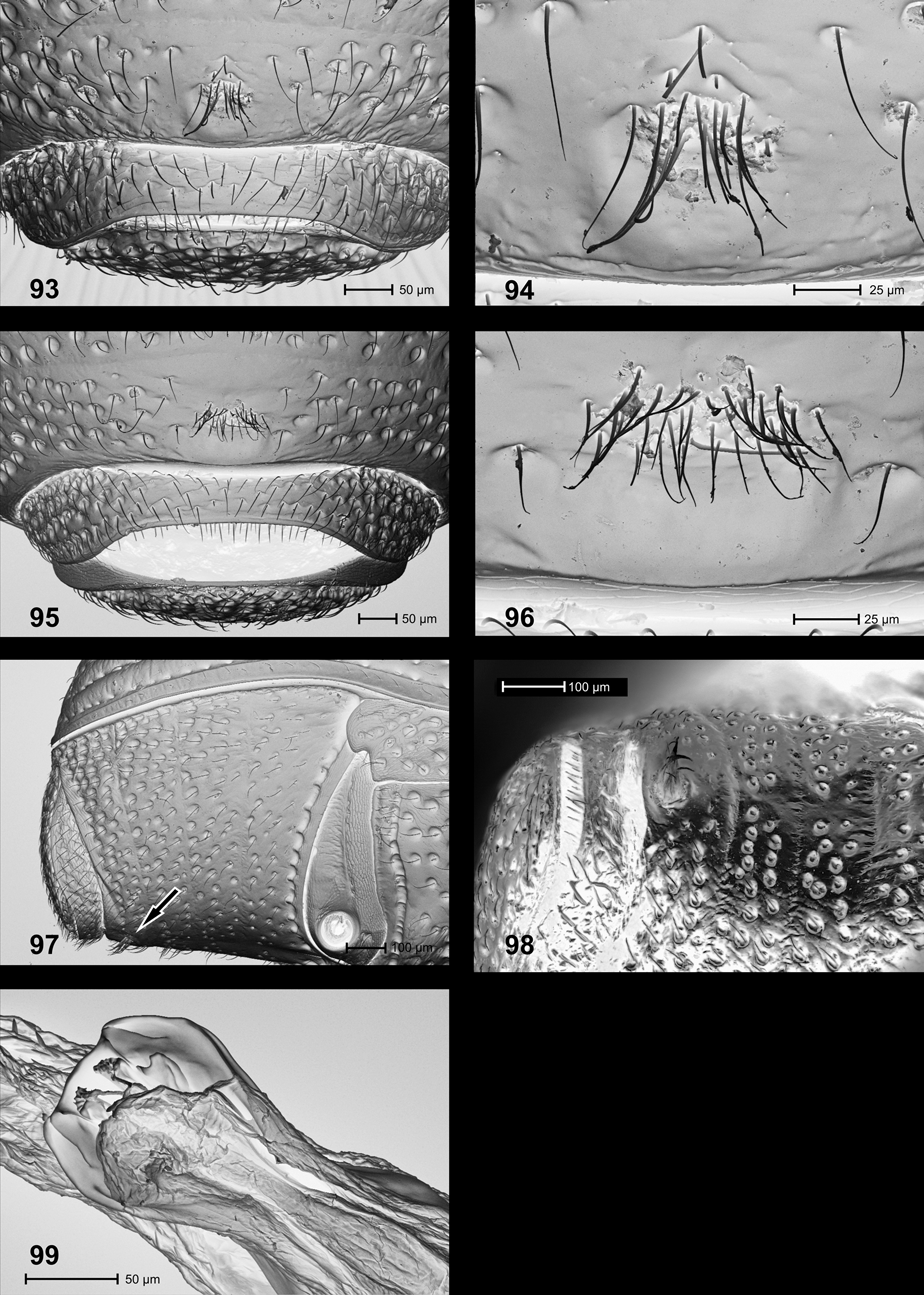
Diagnosis. Pronotum relatively short, 0.75–0.81 X as long as wide; anterior margin of prothorax in front of procoxa angulately projecting; mesosternum with apically rounded, cone-shaped protrusion directed anteriad ( Fig. 77 View FIGURES 71 – 78 ); protibia in female ( Fig. 135 View FIGURES 130 – 135 ) with dorsal contour evenly convex; mesotibia in male ( Fig. 128 View FIGURES 123 – 129 ) with subapical dorsal extension short, dentiform; ventrite 4 in male in middle with inconspicuous transverse row of suberect setae ( Figs. 95–96 View FIGURES 93 – 99 ); aedeagus with apical scoop of pedon ( Fig. 156 View FIGURES 153 – 157 ) pointed.
Description. Holotype, male. Body length: 2.30 mm. Coloration of dorsal surface coppery, sides and venter bronze, tarsi ferruginous.
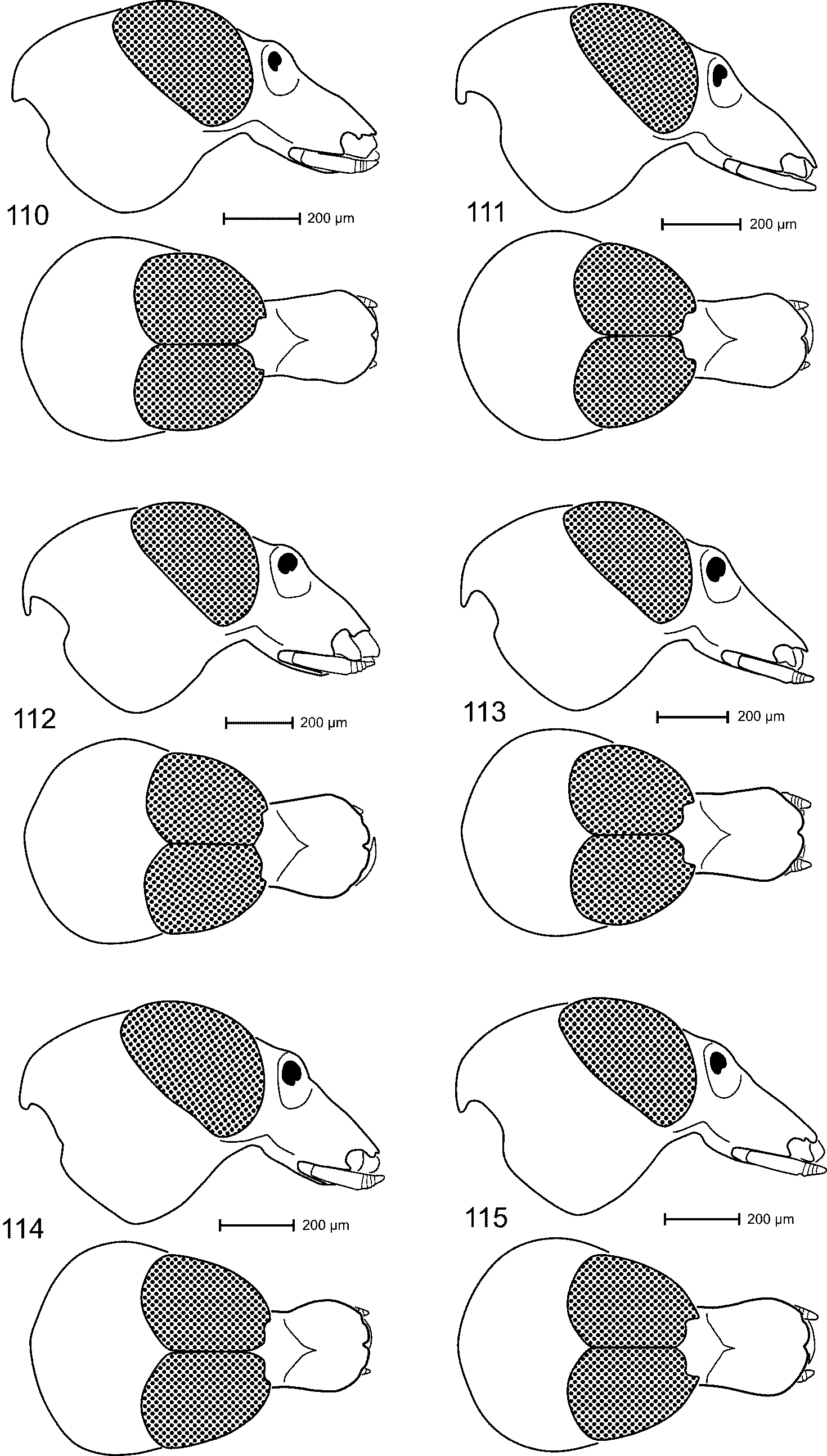
Head ( Fig. 114 View FIGURES 110 – 115 ) short. Gena 0.66 x as long as width of head behind eyes. Vertex microreticulate, markedly rugose-punctate. Eyes dorsally contiguous in middle for 0.7 x their length. Ventral surface markedly transversely rugose, anteriorly near eye with few interspersed punctures.
Rostrum 1.64 x longer than mouthparts; sides subparallel to antennal insertion, anteriorly diverging until subapically rounded; at widest point 1.21 x wider than at base; dorsum above antennal insertions with weakly rounded prominence, anteriorly flat to apex. Clypeus medially with simple notch. Basal lateral groove distinct, ventrally curved, its convex side anteriorly; terminating at level of ventral eye margin. Venter basally without submental median carina. Submentum posteriorly microreticulate, anteriorly shining, with two long, stiff, suberect setae. Prementum at base 1.7 x wider than long, ca. 3.4 x wider than at apex; sides straight, converging apicad.
Antenna as in Fig. 121 View FIGURES 116 – 122 .
Proventriculus ( Fig. 102 View FIGURES 100 – 103 ) with eight primary folds bearing spiniform processes.
Thorax. Prothorax 0.76 x as long as wide; subbasal constriction laterally absent, dorsally shallow; sides converging in straight line to apex, without preapical constriction; anterior margin laterally in front of procoxa with collar-like extension abruptly truncated ventrally, angular in profile; disc markedly punctate-rugose, in basal half with transverse wrinkles concave, in apical half rather V-shaped; sides punctate; prepectus in lateral aspect as long as postpectus; mesosternum with apically rounded, cone-shaped protrusion directed anteriad. Height of pterothorax 0.85 x length of elytron.
Elytron 2.15 x longer than wide; intervals weakly shining, somewhat dull, with distinct coriarious sculpture of irregularly transverse wrinkles ( Fig. 88 View FIGURES 87 – 92 ).
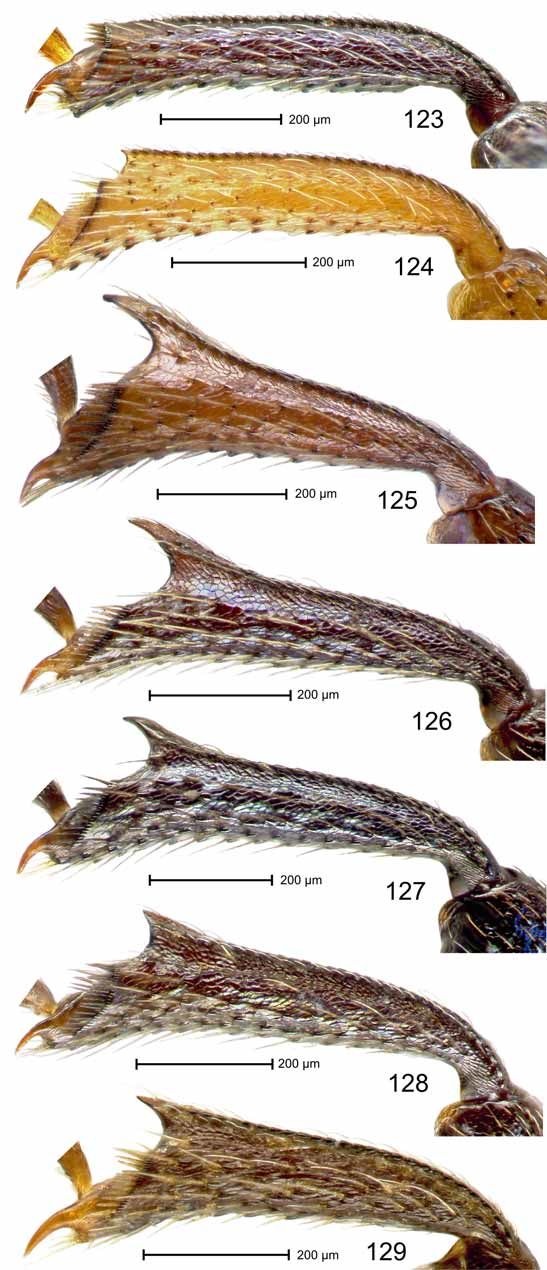
Legs. Procoxa 0.89 x as long as wide; approaching anterior margin of prothorax; in anterior aspect coxae with inner contour diverging in convex line; anterior surface microreticulate, sparsely shallowly punctate. Protibia with dorsal contour evenly convex; uncus subventral. Mesotibia ( Fig. 128 View FIGURES 123 – 129 ) with subapical dorsal extension acute, subtriangularly dentiform.
Abdomen. Venter flat, surface medially sparsely punctate, sparsely setose with recumbent setae; ventrite 4 in middle with inconspicuous transverse row of suberect setae pointing backwards ( Figs. 95–96 View FIGURES 93 – 99 ). Pygidium 1.08 x wider than long.
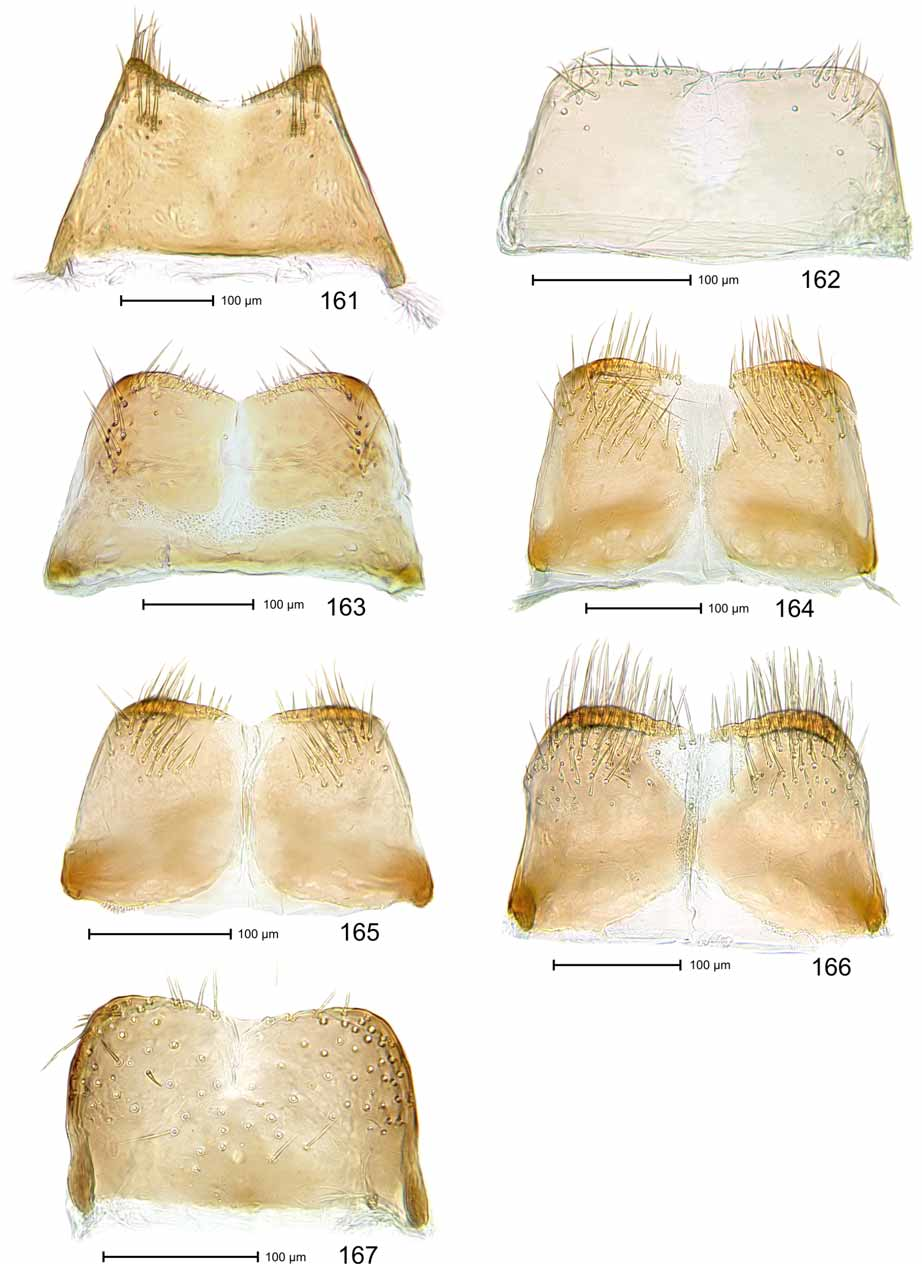
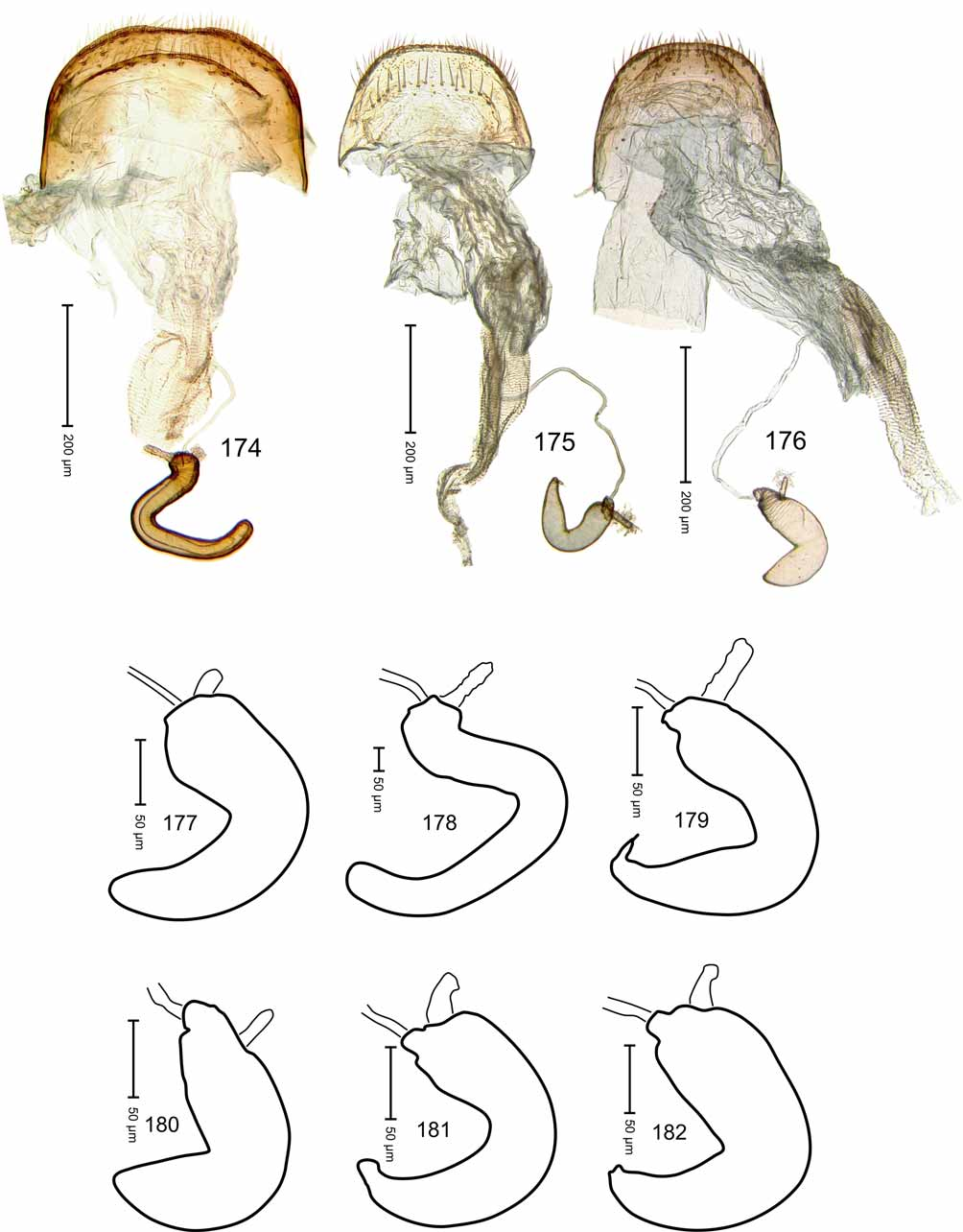
Terminalia. Sternite VIII ( Fig. 164 View FIGURES 161 – 167 ) medially subdivided by membrane connecting lateral sclerotised areas; apex broadly bilobate, densely setose with long setae; base medially with marked constriction. Tegminal plate as in Fig. 157 View FIGURES 153 – 157 . Aedeagus with sclerotised sides of pedon widening mesoapicad, connected to subtriangular plate fused with its short side to apical scoop, the latter ( Fig. 156 View FIGURES 153 – 157 ) ca. 1.14 x longer than wide, sides sinuate and converging, apex pointed; tectum with sides converging, apically pointed; TA ( Figs. 154–155 View FIGURES 153 – 157 ) flagelliform, insertion of ductus ejaculatorius ventral; basal sclerite long, narrow, folded dorsoapicad, dorsally fitting to basal half of long, C-shaped flagellum formed by fusion of extended transferprocesses. Endophallus with cuticle densely minutely denticulate.
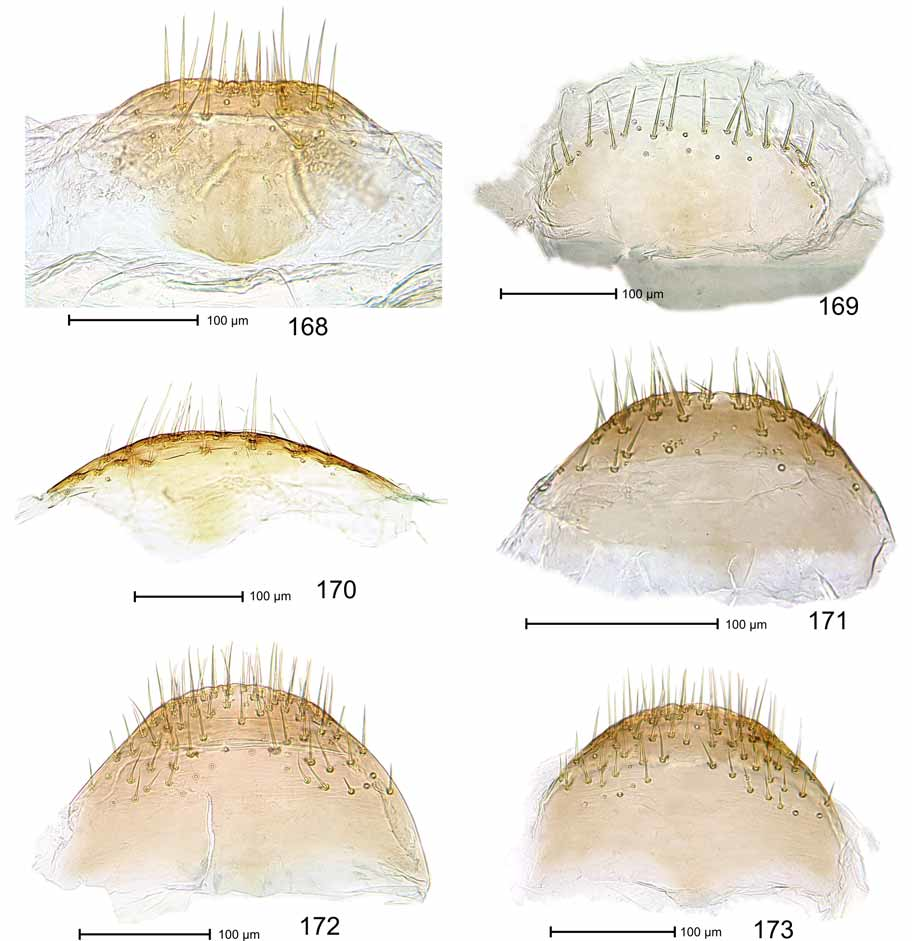
Female. As holotype except: Length 2.26 mm. Head as in Fig. 115 View FIGURES 110 – 115 . Gena 0.65 x as long as width of head behind eyes. Rostrum 1.69 x longer than mouthparts. Prothorax 0.75 x as long as wide. Elytron 2.14 x longer than wide. Protibia ( Fig. 135 View FIGURES 130 – 135 ) with dorsal contour evenly convex; ventral contour evenly sinuate; uncus median. Abdomen with venter flat. Pygidium 1.05 x wider than long. Sternite VIII as in Fig. 172 View FIGURES 168 – 173 . Spermatheca ( Fig. 181 View FIGURES 174 – 182 ) with body moderately tapering apicad.
Intraspecific variation. Size: length 1.68–2.30 mm (n=20, x =2.12 ± 0.17); prothorax 0.75–0.81 x as long as wide (n=20, x =0.77 ± 0.02);. elytron 2.00–2.21 x longer than wide (n=20, x =2.10 ± 0.05); height of pterothorax 0.83–0.92 x length of elytron (n=20, x =0.87 ± 0.02); abdomen with patch of modified setae in female 1.19–1.90 x longer than wide (n=10, x =1.39 ± 0.23); pygidium 0.89–1.08 x wider than long in males (n=10, x =0.98 ± 0.05), 0.94–1.07 x in females (n=10, x =1.02 ± 0.05). Coloration ranging from goldencoppery to greenish-bronze and bluish-bronze. Flagellum C-shaped (as in holotype) or S-shaped.
Material examined. Holotype: INDIA, Tamil Nadu, 15 km SE Kotagiri, Kunchappanai, 11°22´N, 76° 56´E, 900m, leg. D. Hauck ( SMNK). Paratypes: INDIA, Karnataka: 11 males, 12 females, Goa, 25 km E Ponda, Molem, 15° 23´N, 74° 16´E, leg. D.Hauck, 2–4.V.2000 ( ARC in SMNK, SMNK, ZSM); 4 males, Karnataka, W Ghats, 20 km W Talguppa, Jog Falls, N 14°14´E 74° 44´, 500± 200m, leg. P. Pacholátko, 22–28.V.2002 ( ARC in SMNK); Tamil Nadu: 10 males, 9 females [including selected female paratype], same as holotype ( ARC in SMNK); 2 males, 1 female, Tamil Nadu, 11 km SE Kotagiri, Kunchappanai, 11°24´N, 76° 56´E, 1100± 100m, leg. P. Pacholátko, 3.–15.V.2002 ( ARC in SMNK); 1 male, 4 females, Tamil Nadu, 15 km SE Kotagiri, Kunchappanai, 11°22´N, 76° 56´E, leg. L. Dembický & P. Pacholátko, 17.–22.V.1997 ( RDCP); 1 female, Kunchappanai, 11°20´N, 77° 00´E, leg. R. Sauer, 12.–22.V.1994 ( ARC in SMNK); 1 female [ paratype of E. indicus Legalov ], 15 km SE Kotagiri, Kunjappanai env., 900m, 11°22´N, 76° 56´E, 22–30.V.1999, leg Z. Kejval & M. Trýzna (PKC); 4 males, 1 female, Kerala, Thekkady, Peryar Lake, N 9,34° E 77,10°, 900–1000m, 19–27.IV.1997, leg. Dembický & Pacholátko ( NHMB).
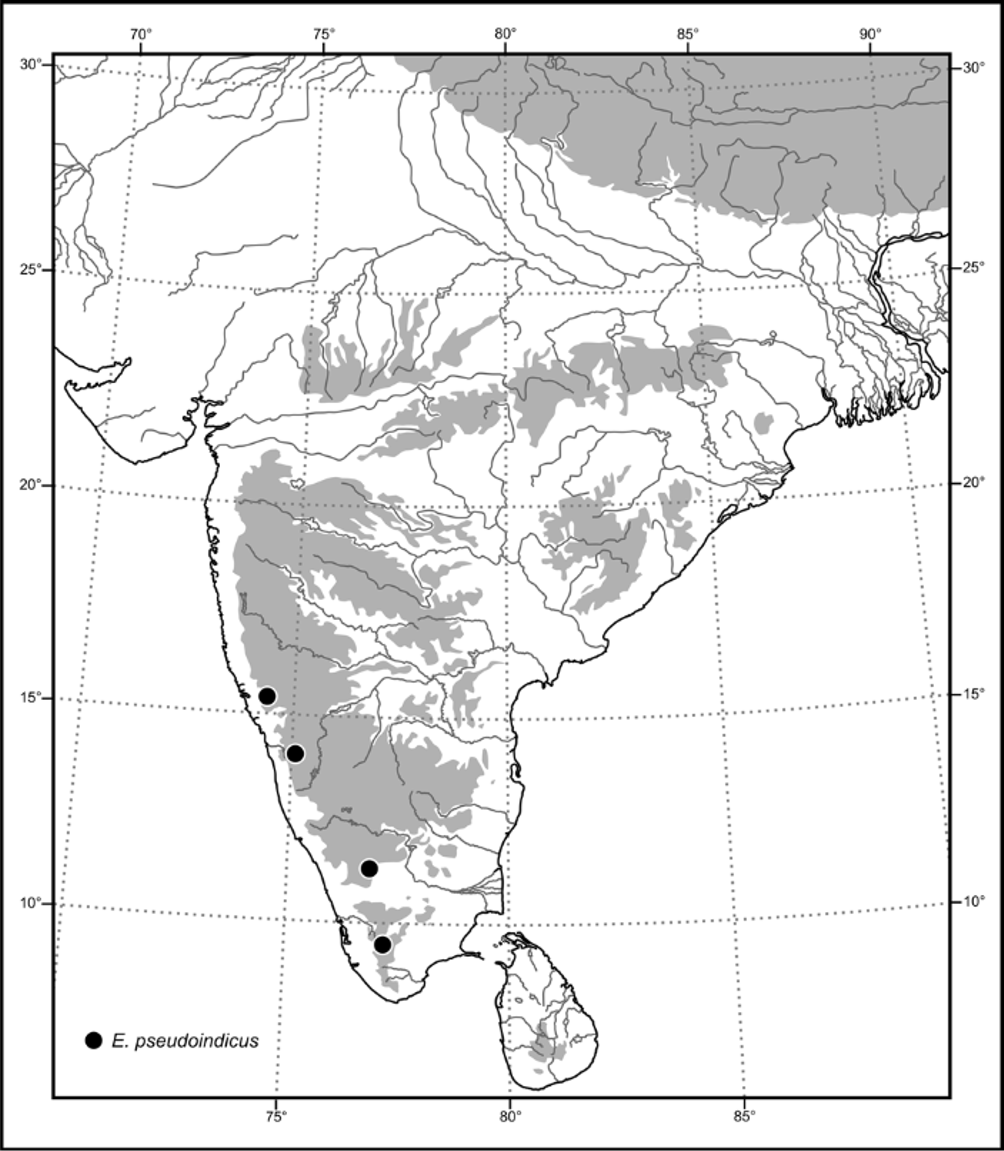
Distribution ( Fig. 188 View FIGURE 188 ). INDIA, Karnataka (Molem), Tamil Nadu (Nilgiri Hills). Elevation: 900–1000 m.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Curculionoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |