Acomys russatus lewisi Atallah, 1967
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4397.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DAB14765-7C9C-41FF-9ECF-563B82B9D258 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5991783 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C32887CB-FF8D-BA7E-FF3D-FF60FE87E981 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Acomys russatus lewisi Atallah, 1967 |
| status |
|
Acomys russatus lewisi Atallah, 1967
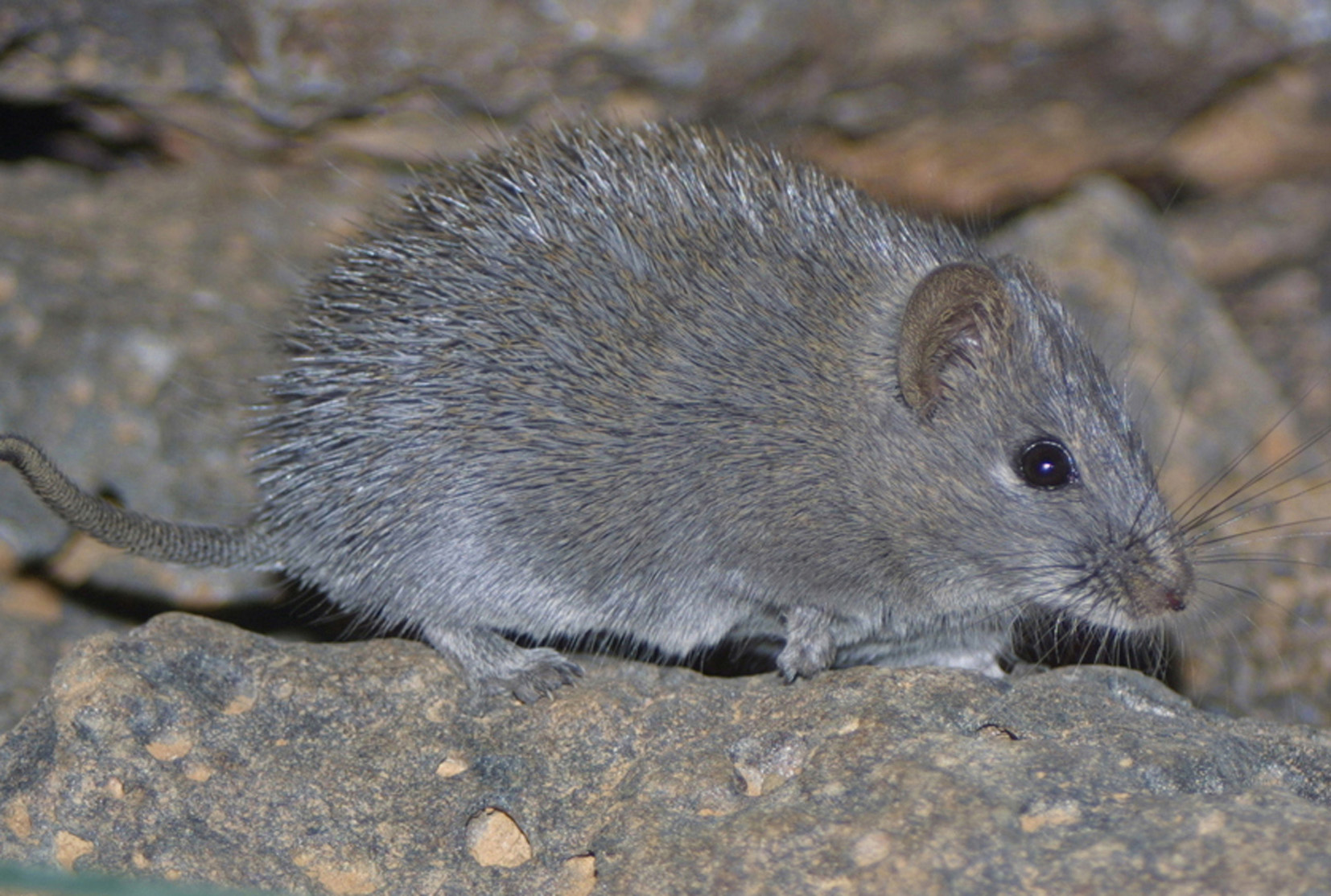
Common name: Melanistic or Lewis’ spiny mouse.
Diagnosis: This is a melanistic form of A. r. russtaus , similar in size and form, but covered with black spines on the back and dark gray fur on the ventral side ( Figure 30 View FIGURE 30 ). Skul morphology is shown in Figure 31 View FIGURE 31 .
Localities: Previous records. Azraq ( Atallah, 1967a); Wādī Rajil near Jāwá (Searight, 1987); Buqay’awiyah, Wādī Salma ( Abu Baker & Amr, 2003a). New records. Ernbeh, Marab Omish ( Figure 32 View FIGURE 32 ).
Habitat: This subspecies is confined to the black lava desert of eastern Jordan. It occupies rocky areas around Azraq and extends throughout the black lava desert into Syria and northern Saudi Arabia.
Biology: Individuals of this species were successfully kept in captivity; they were fed sunflower seeds and supplied with water. The activity peak in the laboratory was seen in the early morning hours of the day. The ability of interbreeding between the two forms of this species ( A. r. russatus and A. r. lewisi ), was tested in the laboratory with an adult A. r. russatus male from Wādī Ramm and an adult A. r. lewisi female from Azraq ed Duruz. No signs of any aggressive behavior were seen during the time of the experiment. The animals were kept together for several months, however, they failed to reproduce, while controlled groups of A. r. lewisi gave birth to 3–5 young ( Abu Baker & Amr, 2003b).
Remarks: Bates (1994) considered the species A. lewisi as a synonym for A. russatus . A. lewisi is darker in color and apparently is confined to the black lava deserts of Azraq and Jāwá ( Atallah, 1967a; Searight, 1987).The karyotype for specimens collected from Jordan yielded a diploid chromosome number of 66 and a fundamental number was 76–92. The autosomal set consists of 12 biarmed pairs (subtelocentric) and 20 pairs of acrocentric chromosomes. The X chromosome is subtelocentric, and the Y chromosome is acrocentric (Qumsiyeh et al., 1986; Sözen et al., 2008).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.