Pterygosoma pseudotrapelus, Bochkov, Andre V. & Melnikov, Daniel A., 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.190303 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6226915 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C31E8799-FE44-9813-DAE4-FD5AA74EFAF6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pterygosoma pseudotrapelus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pterygosoma pseudotrapelus sp. nov.
( Figs. 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
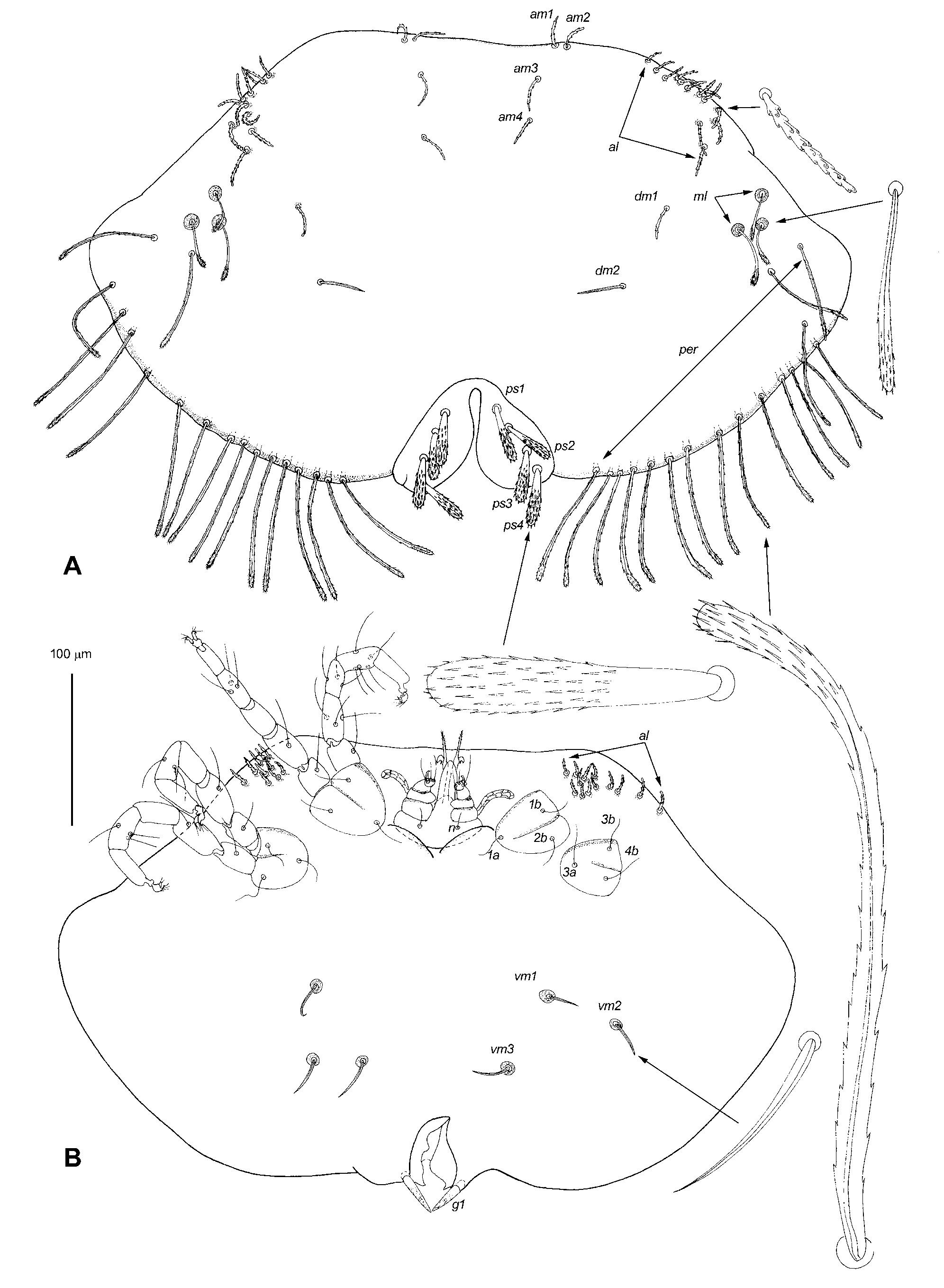
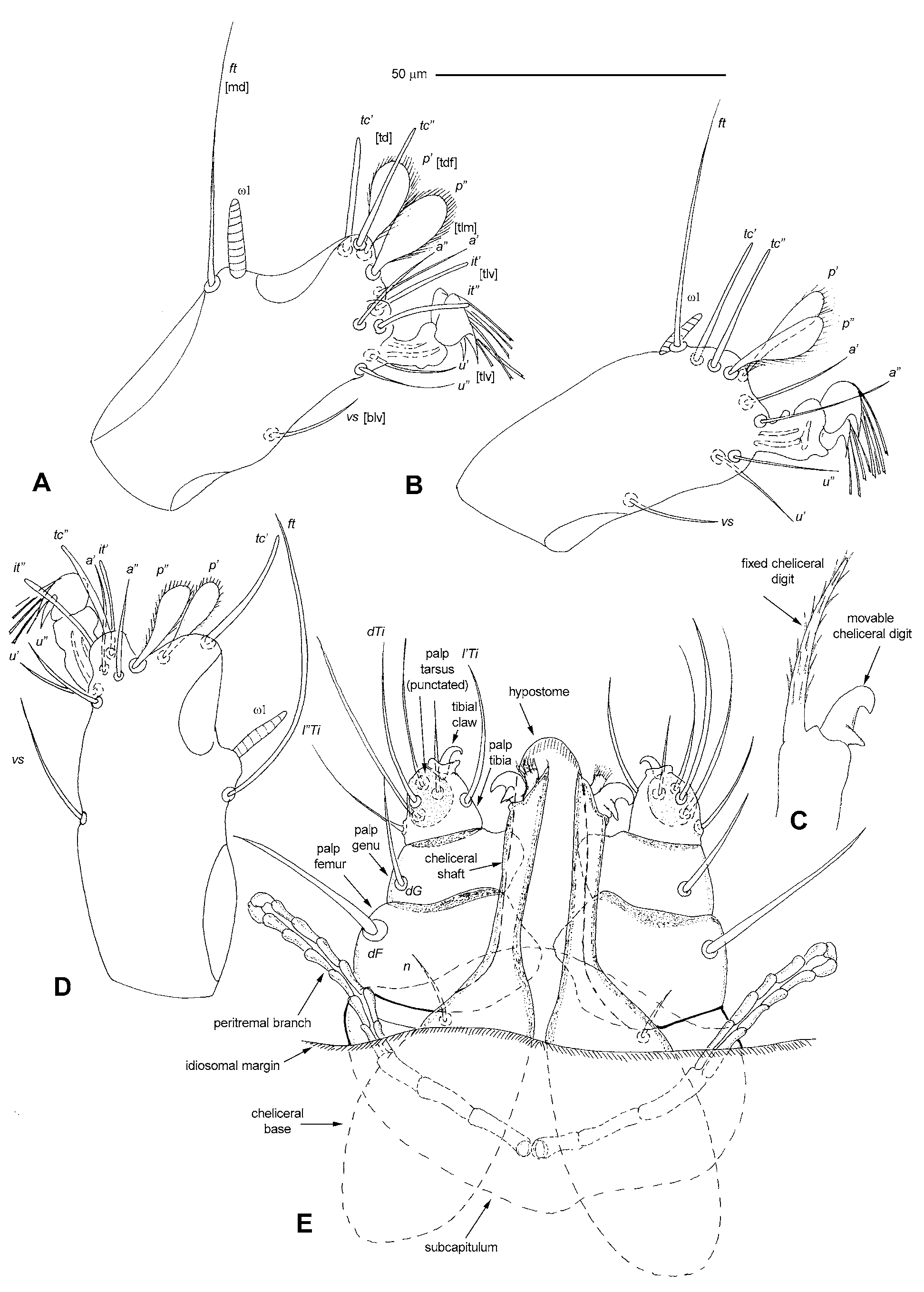
Description. FEMALE (holotype, Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 and 3 View FIGURE 3 A–C). Gnathosoma strongly displaced to ventral idiosomal surface and invisible from dorsal side. Cheliceral base 60 long, cheliceral shaft 50 long. Fixed cheliceral digit 30 long, barbed ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C). Movable cheliceral digit with basal spur. Palpal femur and genu with smooth and stout dorsal seta each. Palpal tibia with 3 setae and short claw; palpal tarsus with 3 setae. Subcapitulum with 1 pair of setae n. Free lateral part of peritremal branch 30 long. Hypostome reaching level of movable cheliceral digits, with smooth rounded apex. Idiosoma 530 long (480–560 in 10 paratypes) and 840 wide (820–860). Idiosomal dorsum ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) with 5 groupings of setae: 4 pairs of antero-median and 23–28 pairs of filiform antero-lateral barbed setae 35–45 long (12–16 pairs of antero-lateral setae replaced ventrally); 2 pairs of filiform dorso-median setae: dm1 barbed and dm2 slightly serrate; 3 pairs of filiform medio-lateral setae with slightly expanded and serrated apices 55–60 long; 16–18 pairs of uniform barbed peripheral setae 100–150 long with slightly expanded tips. Idiosomal venter ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) with 3 pairs of smooth filiform ventro-median setae vm1-vm3, 15–25 long. Pseudoanal (genital sensu Jack [1962]) setae 4 pairs. All of them located dorsally, 60–70 long and about 10 wide in apical part, serrated in distal half. Genital setae (genital spines sensu Jack [1962]) represented by 1 pair of 30–35 long, serrate spurs situated ventro-terminally. Genital-anal slit about 110 long. Leg setation (trochanters-tibiae) corresponding to group 4 of Jack (1964): tibiae I–IV 5–3 –3–3, genua 3–0–0–0, femora 3–1–1–1, trochanters 1–1–1–1. Setation of tarsi corresponding to group B of Jack (1964): I 12 setae (ft, tc ’, tc ”, p ’, p ”, a ’, a ”, it ’, it ”, u ’, u ”, vs) and solenidion ω 1 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A), II 10 setae (ft, tc ’, tc ”, p ’, p ”, a ’, a ”, u ’, u ”, vs) and solenidion ω 1 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B), II and IV with 10 setae each. Setae tc ’, tc ”, it ’, it ” represented by eupathidia, setae p ’ and p ” fan-like with numerous tines.
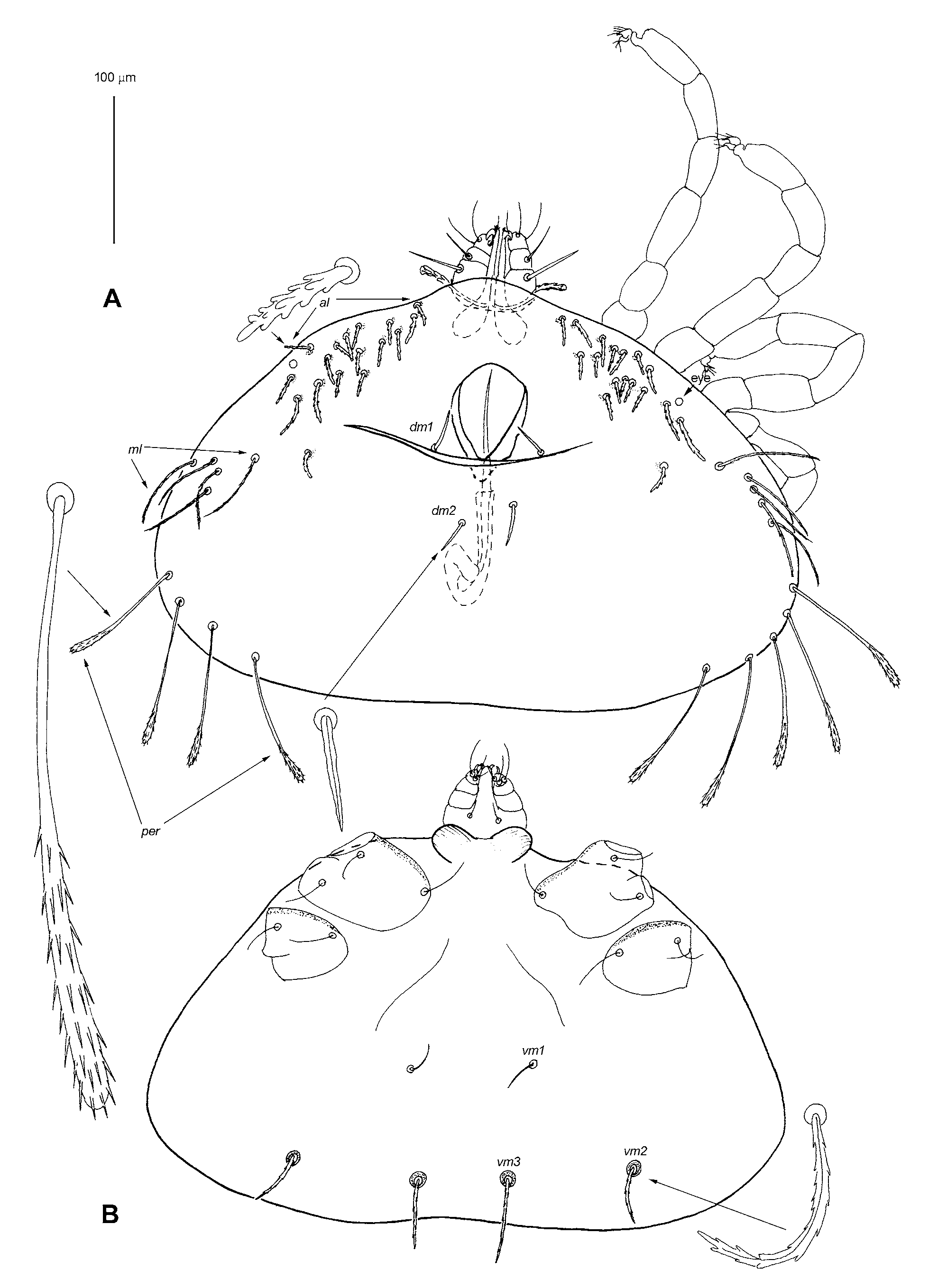
MALE (10 paratypes, Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 D, E). Gnathosoma as in female but inserted subterminally at ventral surface of idiosoma. Cheliceral base 50–55 long, cheliceral shaft 30–35 long. Fixed cheliceral digit short with numerous apical tines. Free lateral part of peritremal branch about 30 long. Idiosoma 270–290 long and 420– 450 wide. Idiosomal dorsum with 4 groupings of setae: antero-lateral setae 15–19 pairs, all filiform barbed, about 18–30 long, located dorsally; 5–6 pairs of filiform serrate medio-lateral setae, 45–80 long; 2 pairs of slightly serrate dorso-median setae, dm1 and dm 2 15–25 long; 4–5 pairs of filiform, serrate peripheral setae with slightly expanded tips, 100–120 long. Eyes present. Aedeagus about 150 long, directed forward; genital anal opening located in anterior half of idiosoma. Idiosomal venter with 3 pairs of filiform ventro-median setae, vm1 smooth, vm2 and vm3 serrate. Leg setation as in female, but setae tc” situated near it” on common antaxial tubercle.
Type material. Female holotype (T-Pt-003), 20 female and 20 male paratypes ex Pseudotrapelus sinaitus (Heyden) ( Squamata : Agamidae ), JORDAN: Aqaba Province, Ram village, Wadi Rum Desert, tourist desert Camp, alt. 1446 m, 29°34’N, 35°25’E, 23 October 2008, coll. R.A. Nazarov and D.A. Melnikov [mites were removed by DAM).
Type deposition. Holotype and most paratypes in ZISP, 2 female and 2 male paratypes in UMMZ, 2 female and 2 male paratypes in IRSNB.
Etymology. The species name is derived from the host generic name and is a noun in apposition.
Remarks. Jack (1962) established six species groups for the African species of the genus Pterygosoma s.str.: transvaalense, hirsti, armatum, fimbriata, melanum, and neumanni. Some these species, however, occur in Asia. Diagnoses of these groups are based on the five following characters of females: length ratio of the cheliceral base and shaft (i), number of the pseudoanal setae (genital sensu Jack) (ii), location of the pseudoanal setae (iii), number of the genital setae (genital spines sensu Jack) (iv), and length/width ratio of the genital setae (v). According to these characteristics, the new species does not belong to any of these groups. In Pterygosoma pseudotrapelus , the cheliceral base is slightly (1.1 times) longer than the shaft (feature of the transvaalense, hirsti, and armatum groups); four pairs of the pseudoanal setae are present (feature of the hirsti, armatum and melanum groups); all the pseudoanal setae (p1-ps4) are situated dorsally (feature occurring in fimbriata, melanum, and neumanni groups); one pair of the genital setae are present (characteristic of the hirsti and armatum groups); and the pseudoanal setae are much longer than broad (the feature of transvaalense and neumanni groups).
According to the leg setation, this species belongs to group 4 established by Jack (1964) and based on setation of trochanters-tibiae I–IV. This group includes three other species, – all from agamids: P. sinaita Jack ex Pseudotrapelus sinaitus from South West Arabia and Egypt, and ex Trapelus mutabilis (Merrem) (Agaminae) from Egypt and Libya; P. rhipidostichata Bertrand et al. ex Trapelus pallidus (Reuss) from Israel; P. foliosetis Jack ex Psammophilus dorsalis (Gray) (Draconinae) from India. Females of Pterygosoma pseudotrapelus are close to P. sinaita and differ from females of this species by the presence of 15–18 pairs of long peripheral setae (vs. three-four pairs) and by the presence of one pair of strong and stout genital setae (vs. three short spine-like setae). The new species (females) differs from P. rhipidostichata by the number of antero-lateral setae, 23–28 pairs (vs. more than 50 pairs), peripheral setae slightly expanded apically (vs. pointed setae), presence of a pair of stout genital setae (vs. lacking setae), and the presence of four pairs of pseudoanal setae uniform in shape (vs. five pairs of setae of different shape). It differs from P. foliosetis by the long peripheral setae with slightly expanded tips (vs. strongly expanded setae), barbed filiform anterior-lateral setae (vs. smooth expanded setae), and pseudoanal setae being much longer than wide (vs. setae as long as wide).
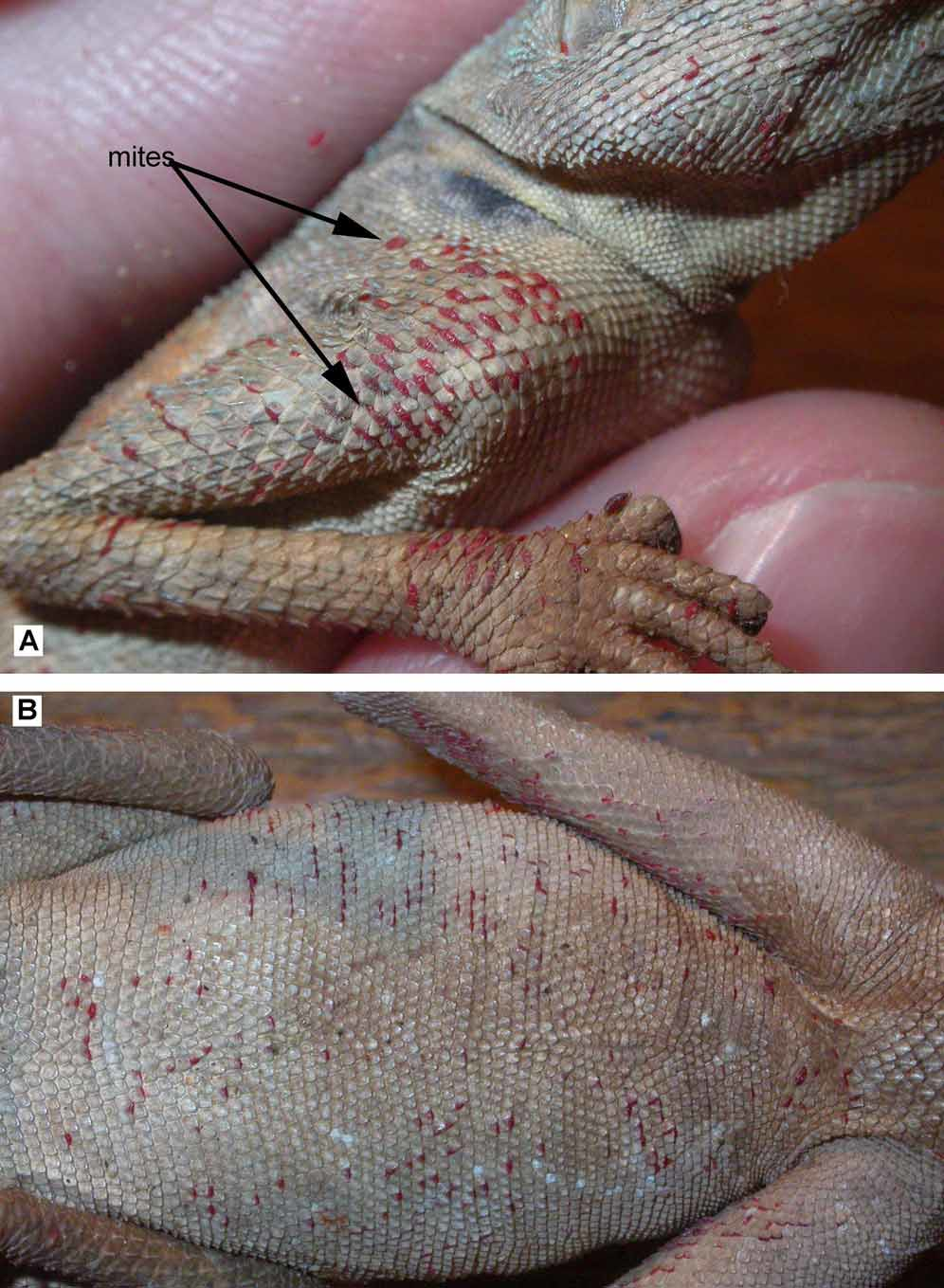
Mites were removed by DAM from two alive individuals six month after capturing. Lizards were evidently weaked. Mites occupied limbs all ventrall surface of the host, excluding the tail. A few specimens were collected from the head ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
SuperOrder |
Acariformes |
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Pterygosoma |