Homalopsis nigroventralis Deuve, 1970
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.209953 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6169959 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C2337B59-FFEA-FFE5-DC91-471BFB19B105 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Homalopsis nigroventralis Deuve, 1970 |
| status |
|
Homalopsis nigroventralis Deuve, 1970
Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 d, 8d, 9
Homalopsis buccata — Taylor & Elbel 1958: 1159; Taylor 1965: 923; Gyi 1970: 136. Homalopsis buccata nigroventralis Deuve, 1970 . Type Specimen: none, Deuve’s specimens presumed lost in a fire. Type locality: Ngum River Valley, Laos.
Homalopsis nigroventralis Stuart et al. 2006:149 .
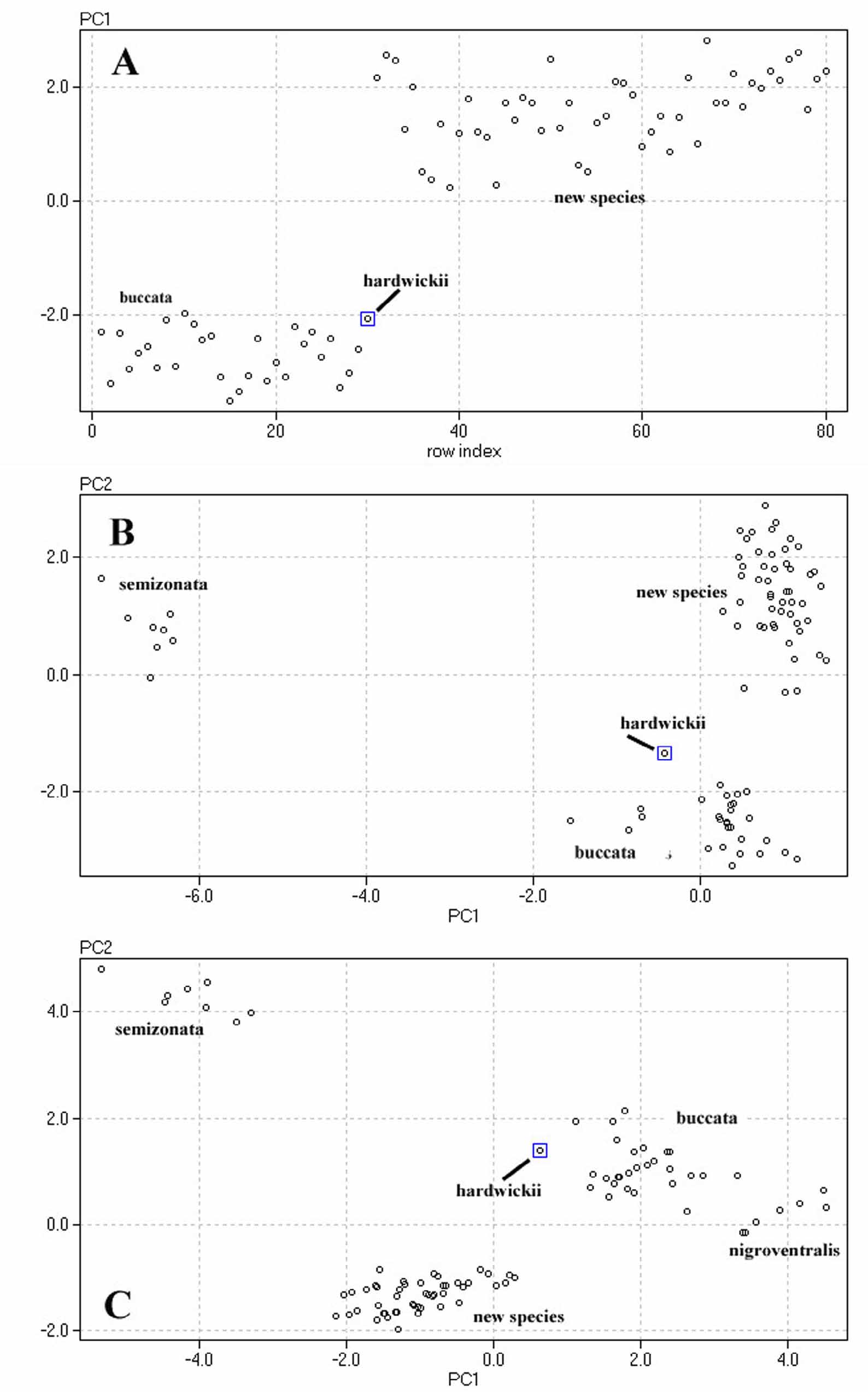
Comment. Deuve (1970) described this snake from the Ngum River Valley, Laos and reported 35–39 scale rows at midbody, 152–164 ventrals and 75–94 subcaudals. The specimens examined here fall within these parameters, except for the subcaudal counts. Homalopsis nigroventralis may use a different habitat than other Homalopsis – streams with a moderate current, and sand and rock substrate as opposed to slow moving or stagnant water with mud substrates. Because we have not examined specimens from Laos we have not established a neotype or restricted the type locality. Photographs of this snake can be found in Taylor & Elbel (1958: 1066) and Murphy (2007: 201-203). Field observations on this snake can be found in Deuve (1970), Stuart et al. (2006), and Bezuijen et al. (2009).
Diagnosis. Homalopsis nigroventralis has upper labials 1–3 contacting the loreal; two prefrontals; 35–39 dorsal scale rows at midbody, reduced to 30 or less; one or two postocular scales plus one postsubocular scale; 10–12 upper labials; 159–167 ventrals; and a reverse color pattern on the venter (dark olive-gray with white spots). Homalopsis buccata has upper labials 1–4 contacting the loreal; one postocular scale plus a postsubocular scale; a ventral pattern that is light with dark spots. Homalopsis hardwickii has a divided loreal contacting upper labials 1– 4; one postocular scale and no presubocular scale. Homalopsis semizonata has a divided or fragmented loreal contacting upper labials 1–4 or 1–5; three prefrontals; 39–44 dorsal scale rows at midbody, reduced to more than 30 posteriorly; one postocular and one postsubocular. The new species, H. mereljcoxi has a single loreal contacting upper labials 1–4; 40–47 scale rows at midbody, reduced to 30 or more posteriorly; 13 (12–14) upper labials; and ventral counts that are usually greater than 165.
Distribution. This species is known from the Mekong River in Laos, Cambodia, and Thailand. Deuve (1970) reported it in the Ngum River Valley of Laos. Taylor & Elbel (1958) describe specimens from Thailand’s Phan Phu Mountain, and Stuart et al. (2006) reported it from Siem Pang and Ta Veng in eastern Cambodia in bamboo mixed with evergreen forest between 100 and 170 m ASL. Two specimens were taken during the day, others were found in gill nets. The streams were described as having a moderate current, and a sand and rock substrate; one had a closed canopy, others were open and had grass lined banks. All of these localities are peripheral to the Mekong. However, Bezuijen et al. (2009) report it from the Mekong River in Kratie Province, Cambodia. They describe four specimens, one in a market, and three others at Koh Kapeung and Koh Khlap Islands, the largest was 104 cm in total length. One of these snakes was on a mud substrate.
Material Examined. CAMBODIA – Ta Veng FMNH 263029 (Virachey National Park, O Lopeung stream, 14°10'39.2" N, 107°17'25.1" E, 150 m); Siem Pang FMNH 263030 (Virachey National Park, O Kanome stream, 14°13'33.7" N, 106°36'16.0" E, 170 m), FMNH 2630301-32 (Virachey National Park, O Kanome stream, 14°15'08.0" N, 106°37'58.8" E, 175 m), FMNH 263033 (Virachey National Park, 14°12'53.8" N, 106°35'51.3" E, 100 m); Nong Khai FMNH 265801 (Phu Wua Wildlife Sanctuary, Houay Sod waterfall, 18°15'51.4" N, 103°54'22.1" E, 160 m), MNHN 1988.2104; THAILAND – Phan Phu Mt. FMNH 179239, 117858-60.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Homalopsis nigroventralis Deuve, 1970
| Murphy, John C., Voris, Harold K., Traub, Joshua & Cumberbatch, Christina 2012 |
Homalopsis nigroventralis Stuart et al. 2006 :149
| Stuart 2006: 149 |
Homalopsis buccata
| Gyi 1970: 136 |
| Taylor 1965: 923 |
| Taylor 1958: 1159 |