Dioclerus Distant, 1910
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2021.745.1311 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6C85E664-6DE6-442A-9410-D94254E429F5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4695056 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/BE301C0D-F867-FF88-FD06-88637438F878 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Dioclerus Distant, 1910 |
| status |
|
Dioclerus Distant, 1910 View in CoL
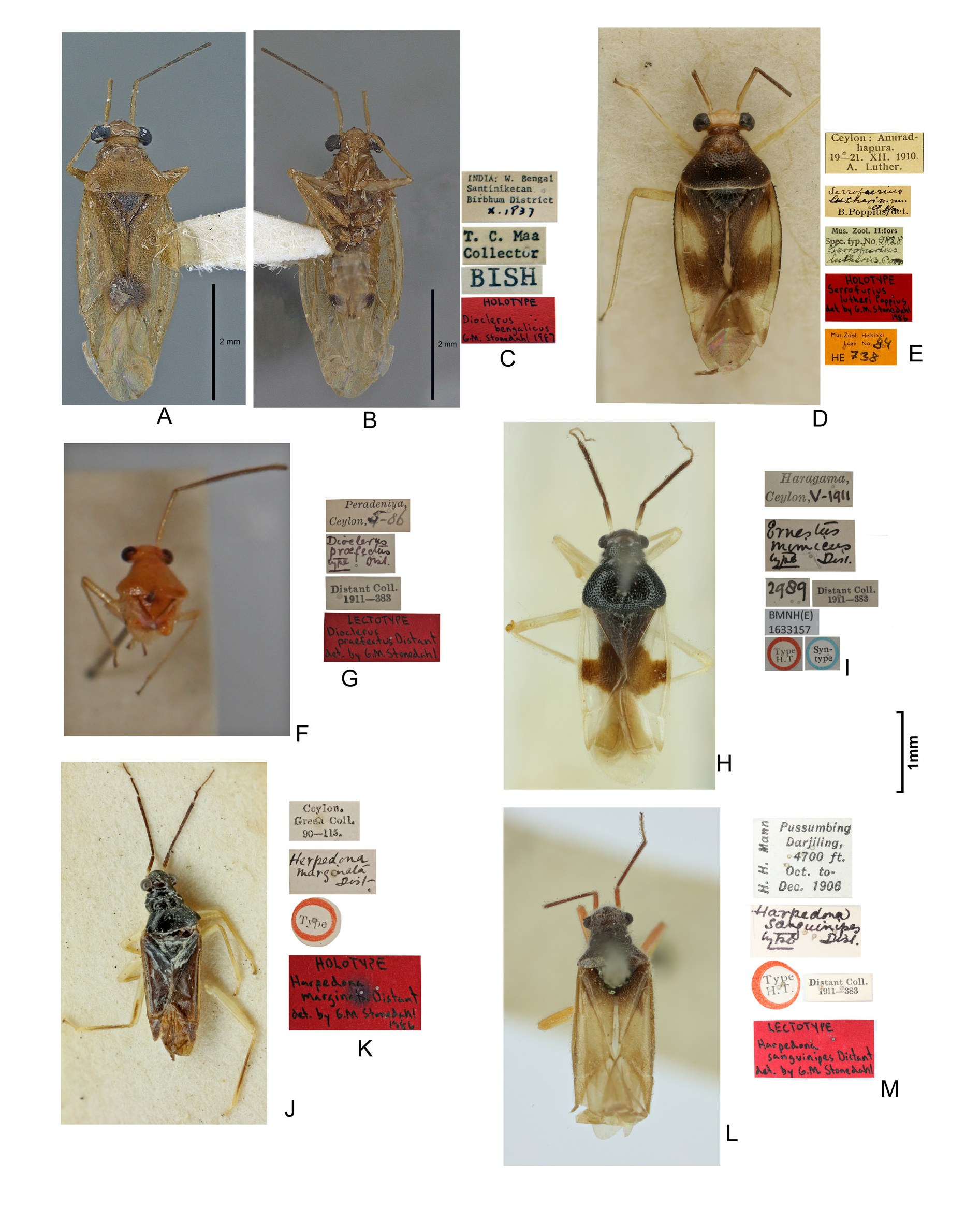
Figs 1 View Fig , 5A–G View Fig , 11 View Fig
Dioclerus Distant, 1910: 12 View in CoL (original discription).
Serrofurius Poppius, 1912: 23–24 (syn. by Carvalho 1952: 55).
Dioclerus View in CoL – Distant 1911b: 278–279, fig. 151 (description). — Stonedahl 1988: 7–16 (revision).
Type species
Dioclerus praefectus Distant, 1910 View in CoL (by monotypy; Distant 1910).
Diagnosis
Easily recognized among other eccritotarsines by the distinctly punctate dorsum, posteriorly carinate vertex, well-delimited pronotal collar, basally serrate costal margin of hemelytron, broadly triangular scent-efferent system, twin-celled membrane, and relatively simple male genitalia with the right paramere being smaller than the left.
Host
Unknown. All specimens with known collection method were attracted at light.
Distribution
Sri Lanka, northeastern India, Thailand, and Malaysia.
Remarks
The genus belongs to a group of eleven genera, viz. Campyloneura Fieber, 1861 , Bunsua Carvalho, 1951 , Bryocorellisca Carvalho, 1981 , Carinimiris Carvalho, 1981 , Crassiembolius Carvalho, 1981 , Diocleroides Stonedahl & Hernandez, 1996 , Dioclerus , Gunadhya Distant, 1920 , Michailocoris Štys, 1985 , Paramichailocoris Yasunaga & Duwal, 2007 , and Sinevia Kerzhner, 1988 that apparently form a sister clade to all remaining eccritotarsines ( Konstantinov et al. 2018). In addition to the characters given in the diagnosis, these taxa have inflated and medially confluent calli, symmetrical parempodia and pulvilli devoid of pulvillar combs ( Konstantinov & Zinovjeva 2016). The characteristic serration of costal margin at base of hemelytron is a unique feature of the genus. Dioclerus contains seven described species ( Stonedahl 1988; Yasunaga & Ishikawa 2016) and three of them occur in India and Sri Lanka.
Key to species of the genus Dioclerus View in CoL of India and Sri Lanka
1. Pronotum and clavus dark brown, corium dirty yellow with a large brown spot on medioapical area ( Figs 1C View Fig , 5D View Fig ) ............................................................................................ D. lutheri ( Poppius, 1912) View in CoL
– Pronotum and clavus pale brown to golden yellow, corium uniformly yellow or with a small dark spot near claval apex ( Figs 1A, D View Fig , 5A–B View Fig ) ........................................................................................ 2
2. Antennal segment II subequal to posterior width of pronotum. India (West Bengal, Andaman and Nicobar Islands) ................................................................................. D. bengalicus Stonedahl, 1988 View in CoL
– Antennal segment II distinctly longer than posterior width of pronotum. Sri Lanka......................... ................................................................................................................. D. praefectus Distant, 1910 View in CoL
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Dioclerus Distant, 1910
| Yeshwanth, H. M. & Konstantinov, Fedor V. 2021 |
Serrofurius
| Carvalho J. C. M. 1952: 55 |
| Poppius B. 1912: 24 |
Dioclerus
| Stonedahl G. M. 1988: 7 |
| Distant W. L. 1911: 278 |
Dioclerus
| Distant W. L. 1910: 12 |