Mucillnata rava, Qin, Dao-Zheng & Zhang, Ya-Lin, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.195125 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6198300 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/BA2787C2-FFA6-FC50-FF16-FBB3C9F0FF08 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mucillnata rava |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mucillnata rava View in CoL sp. nov.
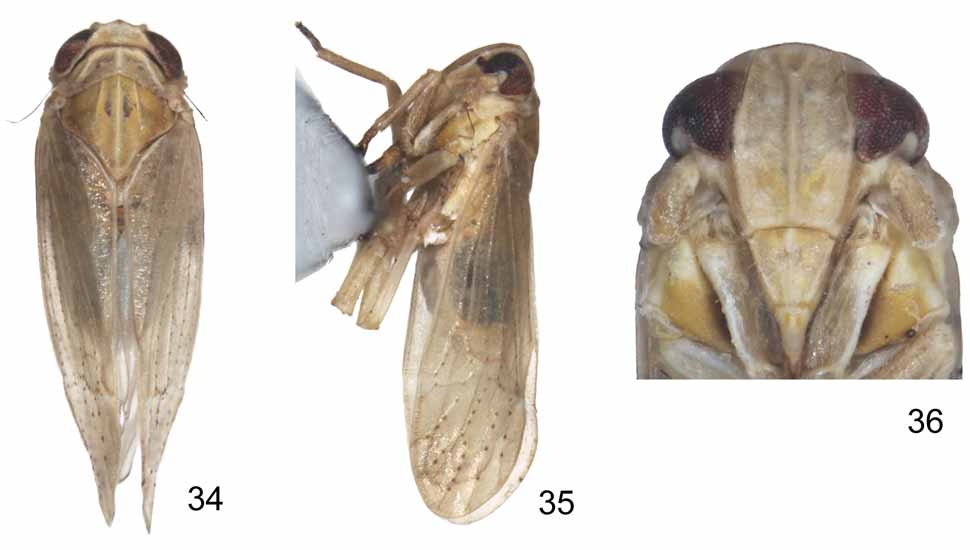
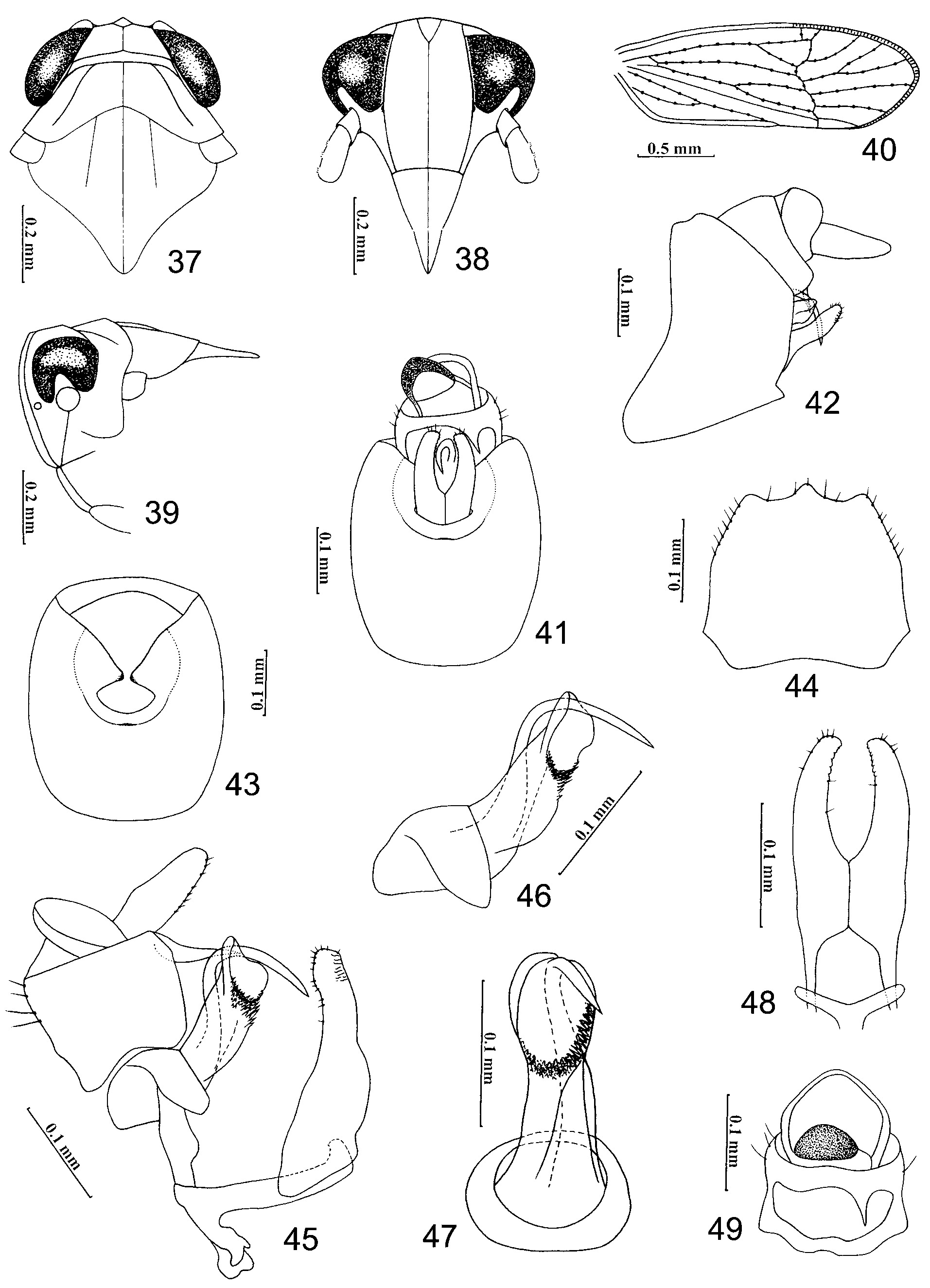
( Figs. 34–49 View FIGURES 34 – 36 View FIGURES 37 – 49 )
Type material. Holotype male (macropterous), China: Hainan Province, Qixianling, 30 April 2008, coll. Qiulei Men ( NWAFU). Paratypes. 5 males, 1 female (macropterous), same data as holotype ( NWAFU).
Description. Body length: male (macropterous, n=6) 1.74-1.77 mm; female 2.01mm (macropterous, n=1), Total length (including tegmen): male (macropterous) 2.73-2.86 mm, female (macropterous) 3.21 mm.
Color. General color yellowish. Eyes reddish brown. Ocelli reddish black. Pronotum ochreous to brownish. Tegmina translucent with pale yellowish veins, speckled with yellowish to brownish flecks, wings greyish, subhyaline. Dorsum of male abdomen blackish except laterally yellowish white, venter of abdomen yellow, ornamented with tiny brownish spots sublaterally on each tergite. Rostrum brownish, apex black. Legs yellow to brownish yellow, protarsi brownish, tips of apical teeth on hind tibiae and tarsi black. Male pygofer yellow. Parameres brownish. Female with the same color as male. Ovipositor brownish.
Head. Including eyes slightly narrower than pronotum (about 0.96: 1) ( Figs. 34 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 37 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Vertex trapeziform, short, at base about 3.20 times as broad as long in midline; distinctly narrower at apex than at base (about 0.66: 1), anterior margin transverse, somewhat incised caudad in middle, slightly projecting in front of eyes, lateral carinae ridged, slightly convex, distinctly converging anteriorly and diverging apically to lateral carinae of frons; posterior margin ridged, slightly concave and incised medially, vertex truncated in lateral view ( Figs. 34, 35 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 37, 39 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ); Y-shaped carina with common stem prominent ( Figs. 34 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 37 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ), areas of basal compartments shallowly concave. Frons ca. 1.52 times higher than its maximum width, widest at middle level of frons, lateral margins convex and ridged, median carina distinctly convex, very shortly forked at base, area within fork apparently depressed, frontal areas between carinae shallowly concave, at apex slightly shorter than at base (about 0.92: 1), apical frontal margin slightly curved medially ( Figs. 36 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 38 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Rostrum with apex reaching mesotrochanters. Postclypeus at base apparently wider than frons at frontoclypeal suture, less than half the length of frons (about 0.41: 1) and ca. 1.27 times longer than anteclypeus, post- and anteclypeus together approximately 0.76x length of frons, postclypeus with median carina apparently convex, lateral carinae developed, in profile nearly in the same plane as frons at base ( Figs. 36 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 38, 39 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ), Antennal segments short, cylindrical, slightly surpassing frontoclypeal suture, segment I slightly widening distad, almost as long as apical width, segment II about 2.5 times longer than I ( Figs. 36 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 38 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ).
Thorax. Pronotum in midline longer than vertex (about 1.30: 1), anterior margin transverse, anterior lateral areas strongly sloping laterad, posterior margin concave inwardly, lateral carinae developed, slightly sinuate and diverging posterolaterally, not attaining hind margin, pronotum width 0.70-0.79, length 0.13-0.15 ( Figs. 34 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 37 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Mesonotum gently vaulted, medially ca. 2.10 times longer than vertex and pronotum together, lateral carinae straight, slightly diverging posterolaterad but not reaching hind margin, median carina reaching end of scutellum except where obscure subapically ( Figs. 34 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 37 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Tegmina 2.28-2.68 mm long, surpassing tip of abdomen more than one third of total length, apical margin acutely rounded, row of crossveins almost in apical third ( Figs. 35 View FIGURES 34 – 36 , 40 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Legs relatively short and stout, hind tibiae 0.66-0.71 mm long, bearing 2 lateral teeth on outer edge and 5 teeth at apex (grouped 2 at inner side and 3 at outer side), metabasitarsus (0.23-0.25) slightly shorter than tarsomere II (0.10-0.13) + III (0.18-0.22) combined, metabasitarsus joint distally with 6 black teeth in a transverse row, tarsomere II with 4 teeth. Post-tibial spur (0.20-0.22) nearly the same length as metabasitarsus, solid, thick, without teeth along lateral margin but with a rigid apical tooth.
Male genitalia. Male pygofer rounded in caudal aspect, ventrocaudal margin smooth, with single median process on the midventral margin ( Figs. 41, 43 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ), in lateral view posterior margin concave medially, much longer than the anterior margin, ventral margin slightly wider than dorsal margin, laterodorsal angle angulate but not produced caudad, caudoventral angle triangularly produced ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ); in ventral view ventrocaudal margin shallowly concave, apically with a rather developed projection in middle ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Diaphragm narrow, centrally open and connecting with the opening for parameres ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Parameres moderate, directed dorsocaudad in lateral view, in caudal aspect with bases broad and contiguous, then slightly narrowing towards apex, distally slightly converging and with small teeth along inner margins, apices rounded ( Figs. 41, 42, 48 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Aedeagus tubular, broad, thick at base, in middle slightly broadened, gonopore apical on left side, subapically surround gonopore with notches and membraneous teeth ventrally to laterally; basal aedeagal process slender, apparently longer than aedeagus, arising basally, apical third strongly curved caudoventrad ( Figs. 45, 46, 47 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Opening for parameres relatively small, ventral margin evenly concave ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ). Male anal segment ring-like, caudoventral margin produced caudoventrad into single and spinose process on right side ( Figs. 41, 49 View FIGURES 37 – 49 ).
Etymology. The name of the species alludes to the yellowish brown body color of the species. Distribution. Known only from the type locality in southern China (Hainan Province).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |