Kumba japonica (Matsubara, 1943)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/megataxa.3.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B711B23F-FF36-86F0-D99D-C6E3FAC37B95 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Kumba japonica (Matsubara, 1943) |
| status |
|
Kumba japonica (Matsubara, 1943) View in CoL
[Japanese name: Kagami-hige]
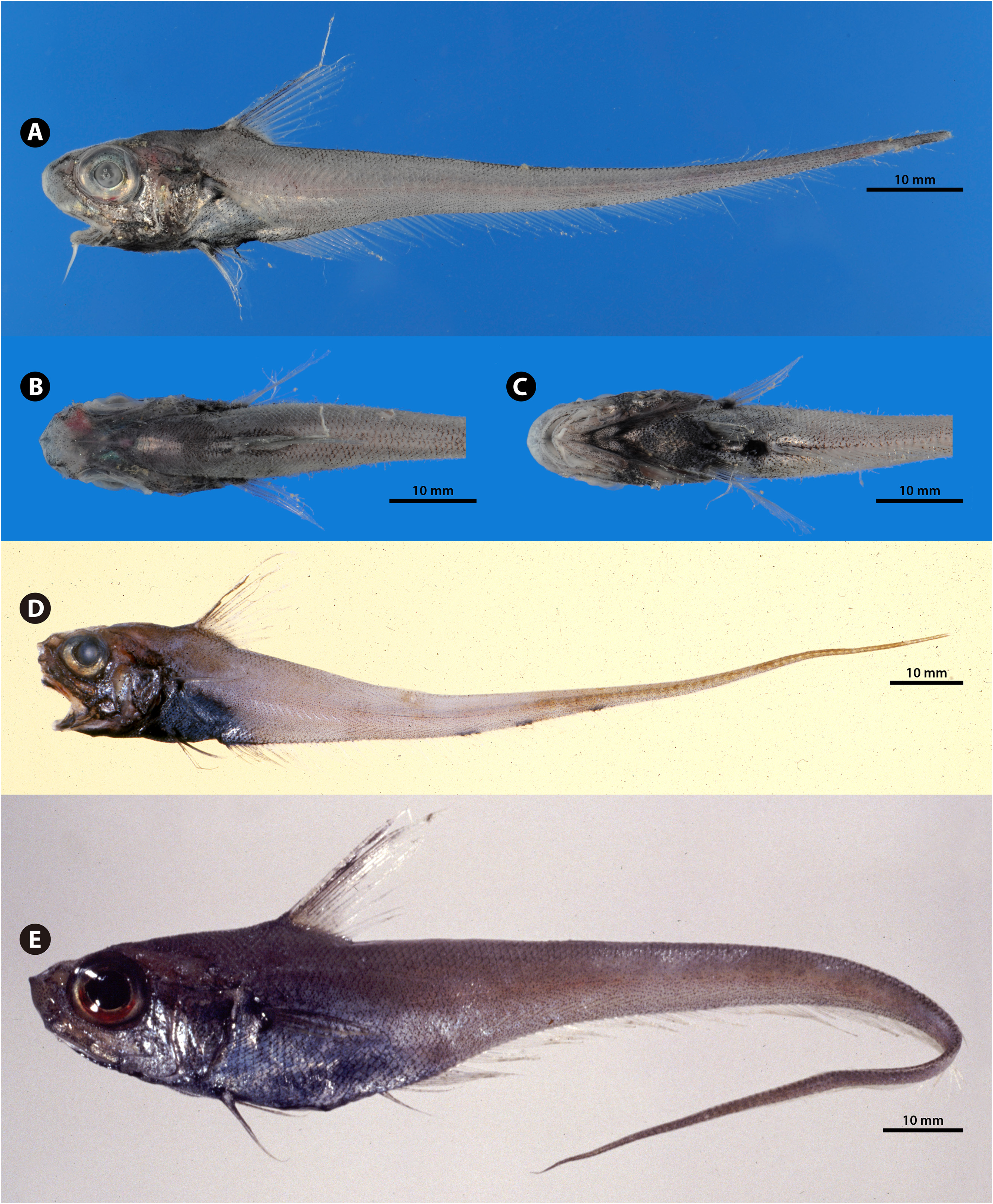
( Figs. 148–149 View FIGURE 148 View FIGURE 149 ; Appendix 3-9B)
Lionurus japonicus Matsubara, 1943:149 , fig. 9 [original description; holotype: FAKU 1951 (ex. Sigenkagaku Fish Collection no. 8), from Kumano-nada; 1 paratype probably collected with holotype; new Japanese name: “Kagamihige”]; Matsubara 1955:1316 (in key; Japan); Okada et al. 1959:83 (listed; Kumano-nada); Kamohara 1964:96 (listed; Kochi Pref.).
Nezumia japonicus: Okamura 1970a:88 View in CoL , pl. XIX, text-fig. 39 (new combination; description; 5 spec. from Kumano-nada and Tosa Bay).
Nezumia japonica: Okamura 1970b : table 1 (listed; Japan); Kataoka & Tomida 1981:78 (listed; Mie Pref.); Tominaga & Uyeno 1981:489 (listed; Japan); Ozawa 1983:13 (listed; off Makurazaki, Kagoshima Pref., East China Sea).
Ventrifossa japonica: Okamura 1982:147 View in CoL , 349, fig. 91 (brief description; 10 spec. from Kyushu-Palau Ridge; photo based on BSKU 29332); Okamura 1984b:93, pl. 81, fig. F (compiled); Okamura 1988:93, pl. 81, fig. F (compiled); Nakabo 1993:357 (in key; Japan); Okamura 1997:128, fig. 8 (compiled); Nakabo 2000:421 (in key; Japan); Shinohara et al. 2001:306 (listed; Tosa Bay); Nakabo 2002:421 (in key; Japan); Kitagawa et al. 2008:39, unnumbered fig. (compiled; Pacific off Tohoku); Shinohara et al. 2009:709 (listed; Pacific off Tohoku).
Kumba japonica: Iwamoto & Sazonov 1994:231 View in CoL , fig. 7 (Kyushu- Palau Ridge and Tosa Bay); Chiou et al. 2004a:45, fig. 14, table 1 (brief description; 2 spec. from Dong-gang; first record from Taiwan); Shao et al. 2008b: table 2 (3 spec. listed from northeastern and southwestern Taiwan); Nakabo & Kai 2013:497 (in key; Japan); Iwamoto et al. 2015:80 (brief description; 10 spec. from northeastern and southwestern Taiwan, and Japan); Motomura 2020:39 (listed; Japan).
Diagnosis. A species of Kumba with 11–13 pelvic-fin rays; naked area dorsally on head restricted anterior to line connecting lateral angles of snout; anus separated from anal-fin origin, situated posterior 1/3 of pelvicanal distance; head firm, not inflated; cephalic sensory pores present along all canals, those on infraorbital and mandibular canals larger; chin barbel long, length 21–30% HL; snout length 25–32% HL; orbit diameter 33–40% HL; upper-jaw length 35–39% HL; interorbital width 23–28% HL; 3 (rarely 4) small, black pigmented areas near mid-length of anal-fin base (only found in smaller specimens).
Material examined. 12 specimens. Japan : BSKU 101176 View Materials (1, 25.1 mm HL, 159+ mm TL), Tosa Bay , 300 m, FRV Kotaka-maru, 4 Dec. 1997 ; * BSKU 117558 View Materials (1, 16.3 mm HL, 91+ mm TL), off mouth of Niyodo River , Tosa Bay, 300 m, FRV Tosa-Kaiyo-maru, coll. T. Ohkawa, 24 Mar. 2015 ; BSKU 99318 View Materials (1, 27.9 mm HL, 170+ mm TL), Tosa Bay , 400 m, 20 Mar. 1989 ; BSKU 43817 View Materials (1, 24.9 mm HL, 168 mm TL) , BSKU 43818 View Materials (1, 25.6 mm HL, 169+ mm TL), Tosa Bay , 400 m, FRV Kotaka-maru, 11 Jun. 1987 ; FAKU 204496 View Materials (1, 24.1 mm HL, 150+ mm TL), Tosa Bay , Mimase fish market, F/ V Tsukasamaru, bottom trawl, coll. N. Nakayama, 4 Mar. 2017 ; BSKU 44189 View Materials (1, 20.9 mm HL, 140 mm TL), Mimase fish market, 7 Nov. 1987 ; NSMT-P 114948 (1, 29.9 mm HL, 187 mm TL), southwest of Cape Omaezaki , Enshu-nada, 34.3816ºN, 138.0010ºE, 475–488 m, R/ V Tansei-maru, cr. KT-95-17, sta. EN1-4, 3-m ORE beam trawl, 10 Dec. 1995 GoogleMaps ; NSMT-P 104114 (1, 28.3 mm HL, 158+ mm TL), Kumano-nada , 420–425 m, R/ V Tansei-maru, cr. KT-95- 17, sta. KN-01(2), 3-m ORE beam trawl, date unknown ; BSKU 32216 View Materials (1, 22.1 mm HL, 136+ mm TL) , BSKU 32217 View Materials (1, 20.3 mm HL, 128+ mm TL) , BSKU 32220 View Materials (1, 20.5 mm HL, 133+ mm TL), Kyushu-Palau Ridge , 28.1117ºN, 134.6656ºE, 550–600 m, F/ Vs Shinsei-maru, No. 53 and Kyoyo-maru, No. 2, tr. 9, bottom trawl, coll. O. Okamura et al., 19 Dec. 1979 GoogleMaps .
Counts and measurements. Based on 11 specimens (20.3–29.9 mm HL, 128+– 187 mm TL). Counts: first dorsal-fin rays II,10–12; pectoral-fin rays i18–i23; pelvicfin rays 11–13; gill rakers on first arch (outer/inner) 8–11/11–13, on second arch 11–14/11–13; longitudinal scales 34–40; transverse scale rows below first dorsal-fin origin 10–11, below first dorsal-fin midbase 6.5–8, below second dorsal-fin origin 6.5–8.
The following measurements are in % of HL, followed by those in % of PRL in parentheses: snout length 25–32 (32–43); orbit diameter 33–40 (44–52); postorbital length 37–43 (50–58); postrostral length 73– 79; orbit–preopercle distance 29–37 (39–48); suborbital width 13–15 (17–20); upper-jaw length 35–39 (46–51); length of rictus 28–34 (36–46); length of premaxillary tooth band 18–22 (24–28); preoral length 20–23 (27–32); distance between tip and lateral angle of snout 14–18 (18– 25); snout width 24–31 (31–42); internasal width 19–22 (25–30); interorbital width 23–28 (30–38); body width over pectoral-fin bases 37–48 (47–65); body depth at first dorsal-fin origin 71–85 (97–111); body depth at anal-fin origin 62–74 (79–98); prepelvic length 95–105 (124– 142); preanus length 126–142 (160–187); preanal length 143–170 (190–220); isthmus–pelvic distance 34–47 (46– 60); isthmus–anus distance 67–91 (86–115); isthmus–anal distance 85–120 (116–155); pelvic–anal distance 46–76 (62–99); anus–anal distance 17–29 (23–38); pelvic-fin length 49–59 (62–79); pectoral-fin length 54–68 (72–86); predorsal length 110–121 (148–161); height of first dorsal fin 88–103 (116–131); length of first dorsal-fin base 28– 37 (37–49); interdorsal length 50–84 (67–108); length of gill slit 14–19 (20–26); length of posterior nostril 6–11 (8–15); barbel length 21–30 (28–40).
Size. To about 19 cm TL ( NSMT-P 114948, 187 mm TL, Enshu-nada, Japan).
Variation. The unique pigmentation of K. japonica , consisting of three (or rarely four) small, black spots along the anal-fin base, has been considered to be one of the diagnostic features of this species ( Iwamoto 1990; Iwamoto & Sazonov 1994). However, these spots are often obsolete and barely discernible in large specimens ( Fig. 148E View FIGURE 148 ).
Distribution. Known only from the northwestern Pacific from the east of Tohoku southward to the northern South China Sea off southern Taiwan, including the Kyushu-Palau Ridge, at depths of 213–710 m (Iwamoto et al. 2015; this study; Appendix 3-9B).
Remarks. This species was well described in the original description (Matsubara 1943) and by Okamura (1970a; as Nezumia japonicus ), and these should be referred to for further details. It was previously allocated to Lionurus G̹nther, 1887, Nezumia Jordan in Jordan & Starks, 1904, or Ventrifossa Gilbert & Hubbs, 1920 (see the synonymy of this species). However, based on the work of Iwamoto & Sazonov (1994:232), the extensive naked areas on the head and the distinctive spinulation of the head scales support its placement in Kumba .
Comments on type specimens. Kumba japonica was originally described by Matsubara (1943) as a new species of Lionurus based on two specimens collected from the Kumano-nada, Japan. Unfortunately, the holotype was destroyed during WWII (see the Comments on holotype of C. hige ). The paratype was not found in the FAKU collection during the author’s visits in 2009 and 2010, and has been presumed to be lost (see also Iwamoto et al. 2015:80).
Comparisons. Kumba japonica is distinctive within the genus, and readily differs from any other congeners in having 3–4 black spots along the anal-fin base (but often obscure in large specimens vs. completely absent) and a longer chin barbel (21–30% HL vs. ±21%). It further differs from all but K. gymnorhynchus Iwamoto & Sazonov, 1994 and K. musorstom Merrett & Iwamoto, 2000 in its higher counts of pelvic-fin rays [11–13 (usually 12) vs. 8–9]. [Meristic and morphometric data for the other species are based on Iwamoto & Sazonov (1994: table 1) and Merrett & Iwamoto (2000:762).]
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Kumba japonica (Matsubara, 1943)
| Nakayama, Naohide 2020 |
Kumba japonica
| : Iwamoto & Sazonov 1994: 231 |
Ventrifossa japonica:
| Okamura 1982: 147 |
Nezumia japonicus
| : Okamura 1970: 88 |
Nezumia japonica:
| Okamura 1970 |
Lionurus japonicus
| Matsubara 1943: 149 |