Corononema vulgare, Phuong & Long & Thanh & Tu, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5380.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1F31D83F-BDFD-4832-8858-4F9A0A0ACA8A |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10249157 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B44E87FE-3B11-FFAA-FF25-C2D3FC0AF922 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Corononema vulgare |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Corononema vulgare View in CoL sp. n.
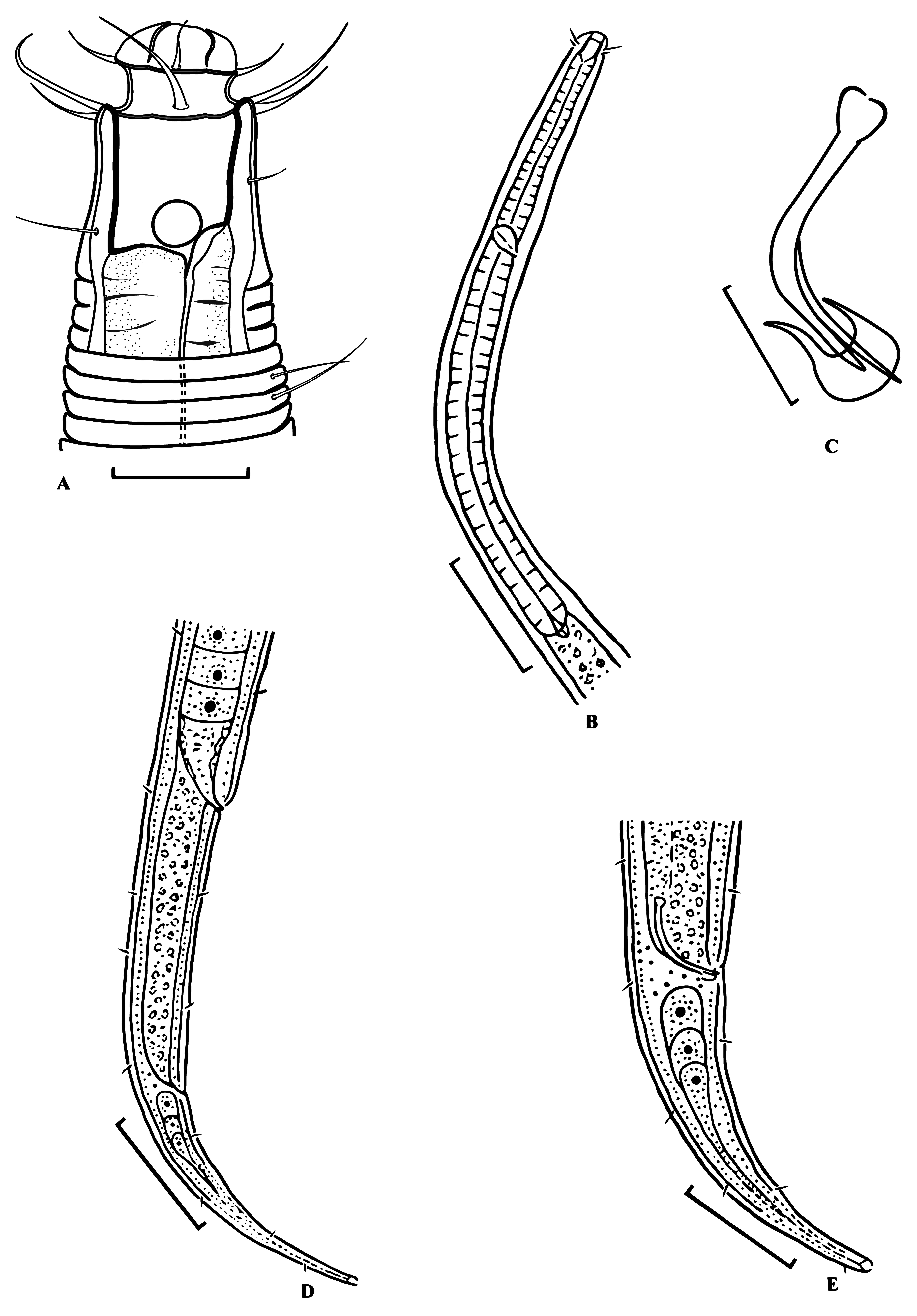
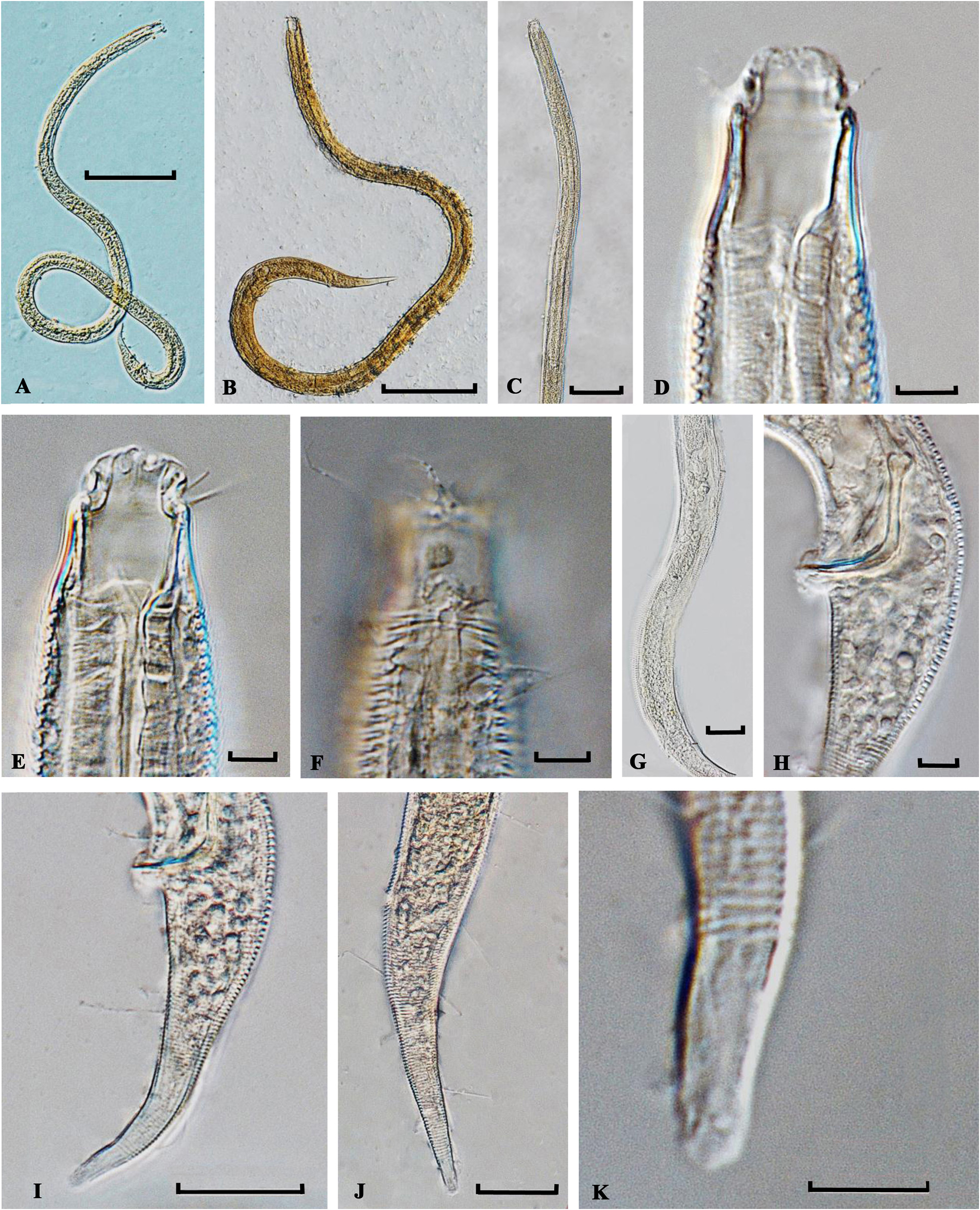
( Figures 1 View FIGURE 1 and 2 View FIGURE 2 , Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Type material. Holotype male, inventory slide number NSS-SH 2, 6; deposited in the Vietnam National Museum of Nature, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (Hanoi, Vietnam).
Paratypes: 10 ♂, slide number CD-2020-1 (4 specimens) and CD-2020-2 (6 specimens), and 10 ♀, slide number CD-2020-3 (5 specimens) and CD-2020-4 (5 specimens); deposited in the collection of nematodes of the Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (Hanoi, Vietnam) .
Type locality. Shallow area off the coast of Vietnam. Coral reefs from Hon Ba Island , Con Dao Archipelago , Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province. Coordinates : 8038 ʹ52ʹʹN, 106033 ʹ10ʹʹE. Depth : 2m. Water salinity: 32 ‰.
Etymology. The specific epithet means “ordinary”, “usual”.
Descriptions.
Males. Body slender, medium size. Head end narrowed. Cuticle coarse annulated, especially at the anterior body end, annules 1–2 µm, without longitudinal ridges. Somatic setae short and rare, 3–4 µm long. Labia relatively high; labial region well separated from the rest of the body by cuticular mouth ring. Deep groove located between the inner labial setae and outer labial and cephalic setae. Six inner labial setae 2–3 µm long, six outer labial setae 3–5 µm long, four cephalic setae 2–3 µm long. Four cervical setae, 2–3 µm long and located at level of posterior half of pharynx length. Cheilostoma narrow, set off from the pharynx with two strong cuticle rings. Pharyngostoma spacious, in the shape of a short cylinder 8–11 µm long and 6–8 µm wide. Amphidial fovea circular, 4–5µm diameter, and located at 9–11 µm from the anterior body end. Pharynx cylindrical and muscular. Cardia small, triangular, protruding into the lumen of intestine. Cardial glands not observed.
Two opposed testes. Anterior testis straight, located to the left of the intestine. Posterior testis curved, short, barely visible. Spicules thin, comparatively short, curved with head. Spicules 25–28 µm long. Gubernaculum surrounds spicule tips, 3 µm long. Precloacal ventromedial supplements absent.
Tail elongated-conical. Annulation at tail end and terminal setae absent. Caudal glands and spinneret present.
Females. General morphology similar to that of males. Structure of cuticle and anterior body end as in males. Cuticle annulated. Labial region separated from rest of the body by cuticular mouth ring. Six internal labial setae 2–3 µm long; outer labial setae and cervical setae 3–5long; cephalic setae 2–3 µm long. Cheilostoma thin, set off from pharyngostoma with two cuticular rings. Pharingostoma in the shape of short cylinder, 8–10 µm long, 6–8 µm wide. Amphidial fovea circular, located 10–12 µm from anterior body end. Pharynx muscular and equally thickened along its entire length.
Ovary single, anterior, straight, relatively long and located to the left of intestine. Vulva post- equatorial, in the form of transverse slit. Vulva lips only slightly protruding from the contours of body. Vagina short, thin-walled and situated obliquely towards the posterior end of the body. Uterus spacious, filled with numerous spermatozoids. Distance from vulva to anus just slightly longer than the tail. Tail elongated-conical. Subterminal setae absent. Caudal glands and spinneret present.
Differential diagnosis. At the present, the genus Corononema Nicholas & Stewart, 1995 includes two valid species. Corononema parvum Nicholas & Stewart, 1995 found in the coastal shallow water sea area off the coast of Australia and C. thai Nicholas & Stewart, 1995 found in coastal sea area off the coast of Thailand ( Nicholas & Stewart 1995). The new species is morphologically similar to C. thai , but differs from it by the absence of longitudinal ridges on the cuticle (eight longitudinal ridges on the cuticle in C. thai ), shorter outer labial setae (3.0–5.0 µm long vs 6–10 µm long in C. thai ), and a different shape of gubernaculum.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |