Virgilia imuganensis Soulier-Perkins, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4415.1.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FE0C98F6-E952-4FE9-82DE-37F13BD1C703 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5946532 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B20A87EC-FFCA-FFD4-D785-864FFD9CFBD2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Virgilia imuganensis Soulier-Perkins |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Virgilia imuganensis Soulier-Perkins View in CoL sp. nov.
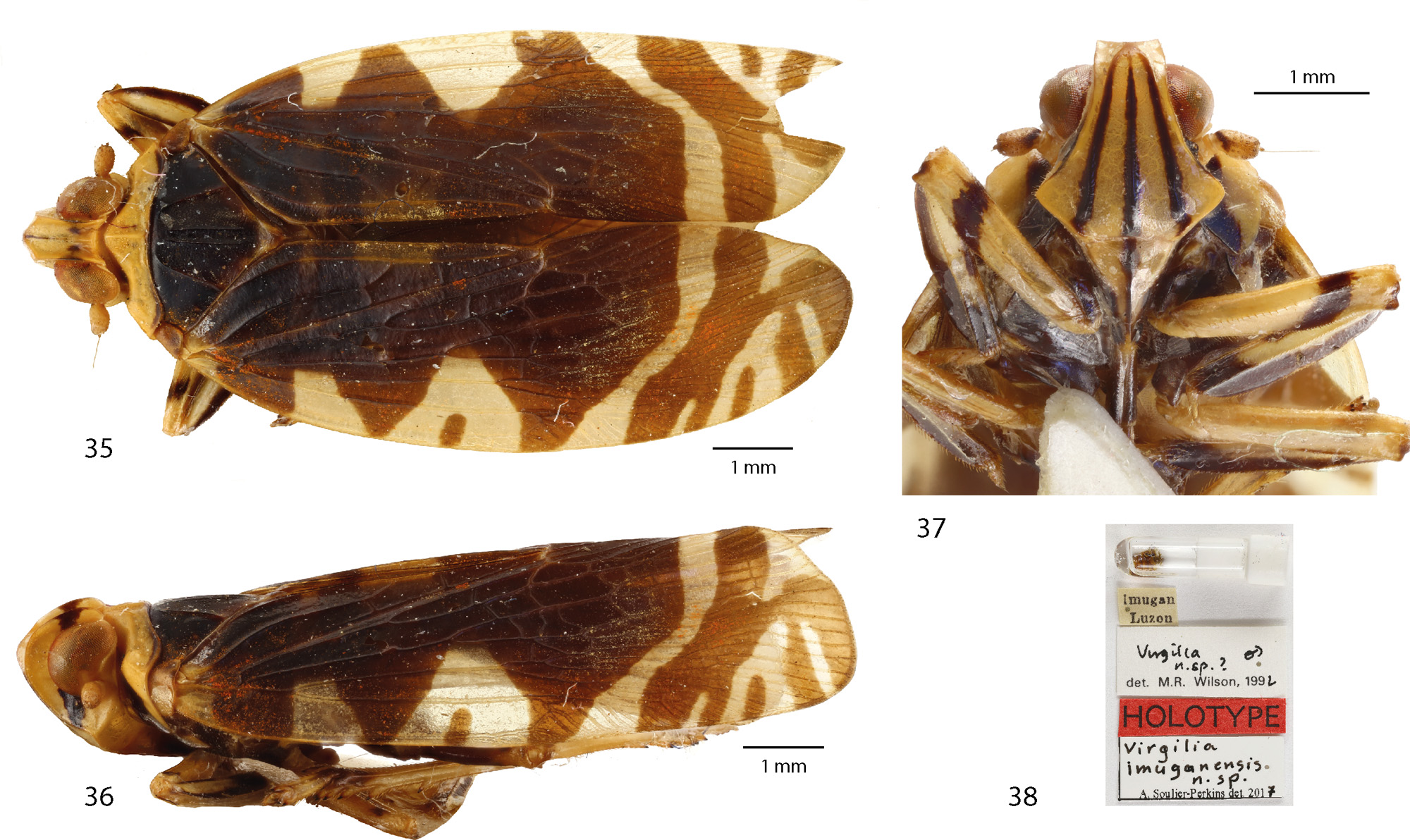
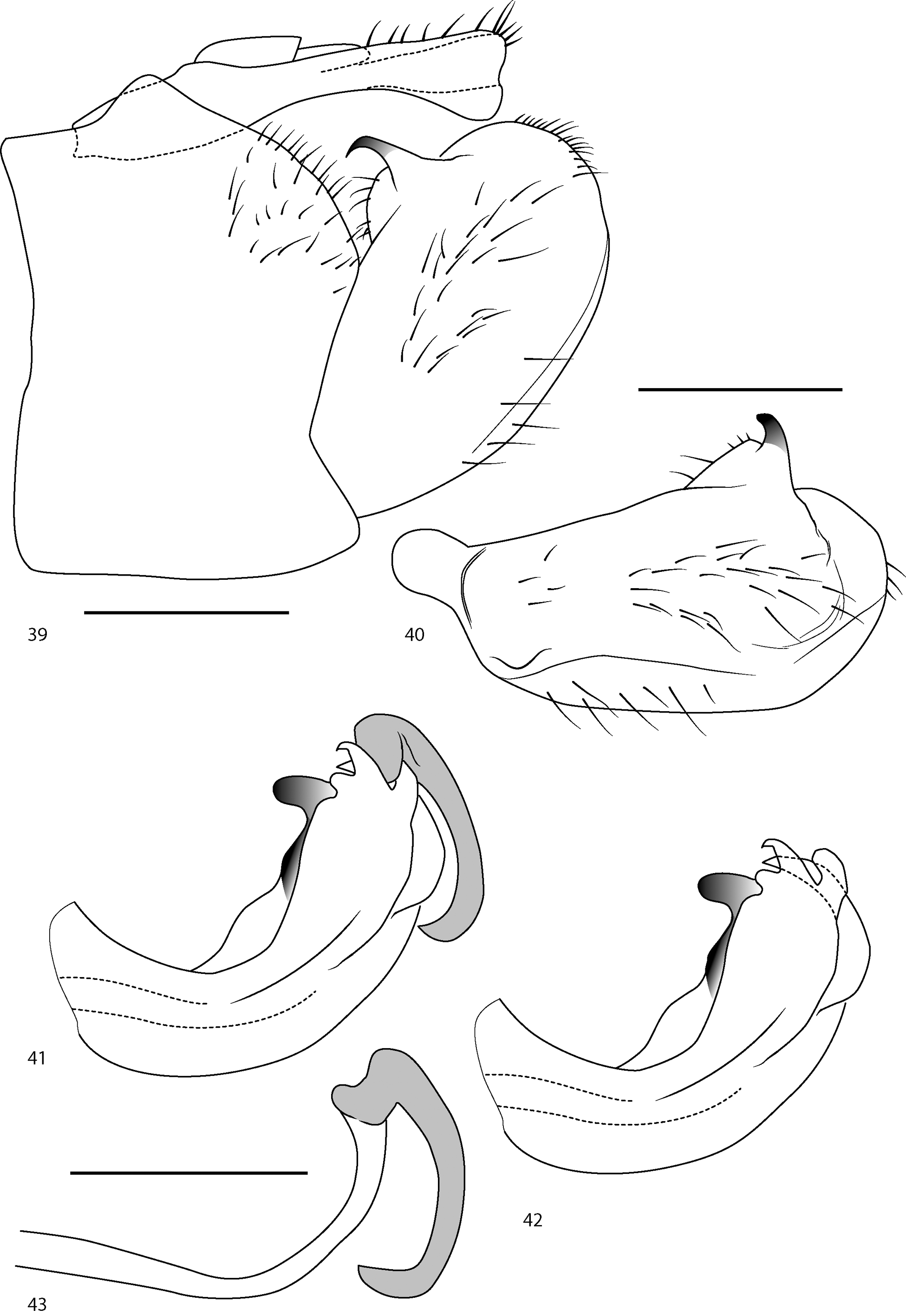
( Figs 35–43 View FIGURES 35–38 View FIGURES39–43 )
Type material. Male holotype: Philippines: Luzon, Imugan MNHN (EH)23937 ( MNHN).
Paratype: 1♂?. [Imugan Luzon], [coll. Dr D. Mac Gillavry], [Zoology Museum collection Amsterdam], 1♂? (ZMA).
Distribution. Philippines, Luzon Island ( Fig. 65 View FIGURE 65 )
Diagnosis. Easy to recognise from the other three Virgilia by the coloration of its frons, it bears line of brown colour only along the median and the sub-lateral carinae (Fig. 4), the three running stripes meet at the edge of the fronto-vertex margin, when V. cocovora bears six brown spots ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–3 ), V. luzonensis has two patches and a stripe ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–3 ) and V. nigropicta a single large patch, half–moon shaped, touching the fronto-clypeal margin ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–3 ).
Description. Total length of male holotype: 1.08 cm (tegmina included)
Head. In dorsal view, head 1.7 times wider across eyes than long in midline. Vertex 1.68 longer than wide, posterior margin concave, anterior margin V shaped, lateral margins posterior curving slightly at the eyes level and lateral margins elevated ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 35–38 ). In frontal view, frons 1.02 wider across the widest part at gena level than long in midline, fronto-vertex margin slightly concave, fronto-clypeal margin almost straight, lateral margins regular and underlining the pear-shaped frons, the widest area is sharply curved, sub-lateral and median carinae present but not reaching the fronto-clypeal suture ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 35–38 ). In lateral view, ocellus present located below compound eye and anteriorly to antennae, ocellar carinae absent, genal carinae present ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 35–38 ). Prothorax larger than head and 4.41 times wider than long in midline. Mesothorax 1.55 times wider than long in midline. Tegmina 2.7 longer than wide at midline, ScP+R(+MA) forking first, then CuA and finally MP, all forking before the end of clavus and respectively around 1/6, 1/3 and 2/5 of the total tegmina’s length. Metatibiae bearing 3 lateral and 9 stout apical spines, first metatarsal segment bearing a series of apical spines organised in a triangular area, longer than cumulative length of second and third metatarsal segment, second segment reduced to a lobe without any spine.
Male terminalia. In lateral view, anal tube elongated posteriorly, 5.14 times longer than its biggest thickness measured just before the epiproct insertion, narrowing at epiproc and paraproc level, ventral margin developed before the apex into a regular rounded extension pointing ventrally ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES39–43 ). Pygofer with dorsal margin elevated medially, hiding the anterior part of anal tube then truncated posteriorly, posterior margin indented anteriorly in its third lowest portion, posterior and ventral margin meeting in a rounded angle, anterior margin almost straight ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES39–43 ). Gonostylus with dorsal margin developing on its 3/4 posterior length a dorsal extension rounded anteriorly and hook shaped, posterior to the hook, the dorsal and posterior margin rounded regularly, ventral margin gently rounded ( Figs 39–40 View FIGURES39–43 ). Periandrium with dorsal margin curving up and finishing in its median part apically by a thumb shaped extension oriented anteriorly and on both sides by two extensions, the first, hook shaped and oriented median anteriorly and the second rounded and hidden by the aedeagus ventral process, ventral margin very regularly curved and finishing apically by a pair of sharp processes oriented dorso-anteriorly ( Figs 41–42 View FIGURES39–43 ). Aedeagus bearing a ventral anterior process curving down and with its apex pointing anteriorly, ventral posterior process absent ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES39–43 ).
Colour. Generally brownish and cream. Head cream with: on the vertex, median carina underlined in brown on its 1.3 anterior part and two brown patches on the half posterior area ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 35–38 ); on the frons, 3 brown-black stripes underlining the median and sub-lateral carinae; clypeus cream bearing medially a brown longitudinal stripe ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 35–38 ); on each gena, a large brown patch stretches from bellow the compound eye down to the frontal suture, symmetrically a brown patch stretches from above the compound eye to the vertex carina ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 35–38 ). Prothorax cream with only the posterior margin slightly underlined in brown, meso- and metathorax browns. Tegmina with basal 2/3 dominantly dark brown with 2 cream lunula shaped areas along the costal margin, posterior margin of this area cut toward the start of the radial margin; last third of the tegmina dominantly cream with a large brown band crossing from the areola postica to the radial margin plus a series of 4 brown patches of stripes starting on the margin and reaching or not this band. Profemur with 1 dark brown transversal stripe, mesofemur cream, pro- and mesotibias brown along the external margins and apically, metafemur brownish and metatibia cream except for the tips of spines.
Etymology. The species is named after the place where it was found: Imugan located South-East in the Cagayan Valley region on Luzon.
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |