Myopegma midatlantica, Monniot, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.2864.1.5 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A86387B3-FFC7-5E37-FF33-C9F632DE719B |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Myopegma midatlantica |
| status |
|
Myopegma midatlantica View in CoL n. sp.
Figures 1 –3
Material: Mid-Atlantic ridge, Kane Fracture zone, 23°27’ N – 45°03’W, 2087m, 07/07 / 1988, dive 18. (MNHN P6 MYO 2: tunic and P 6–46: slide)
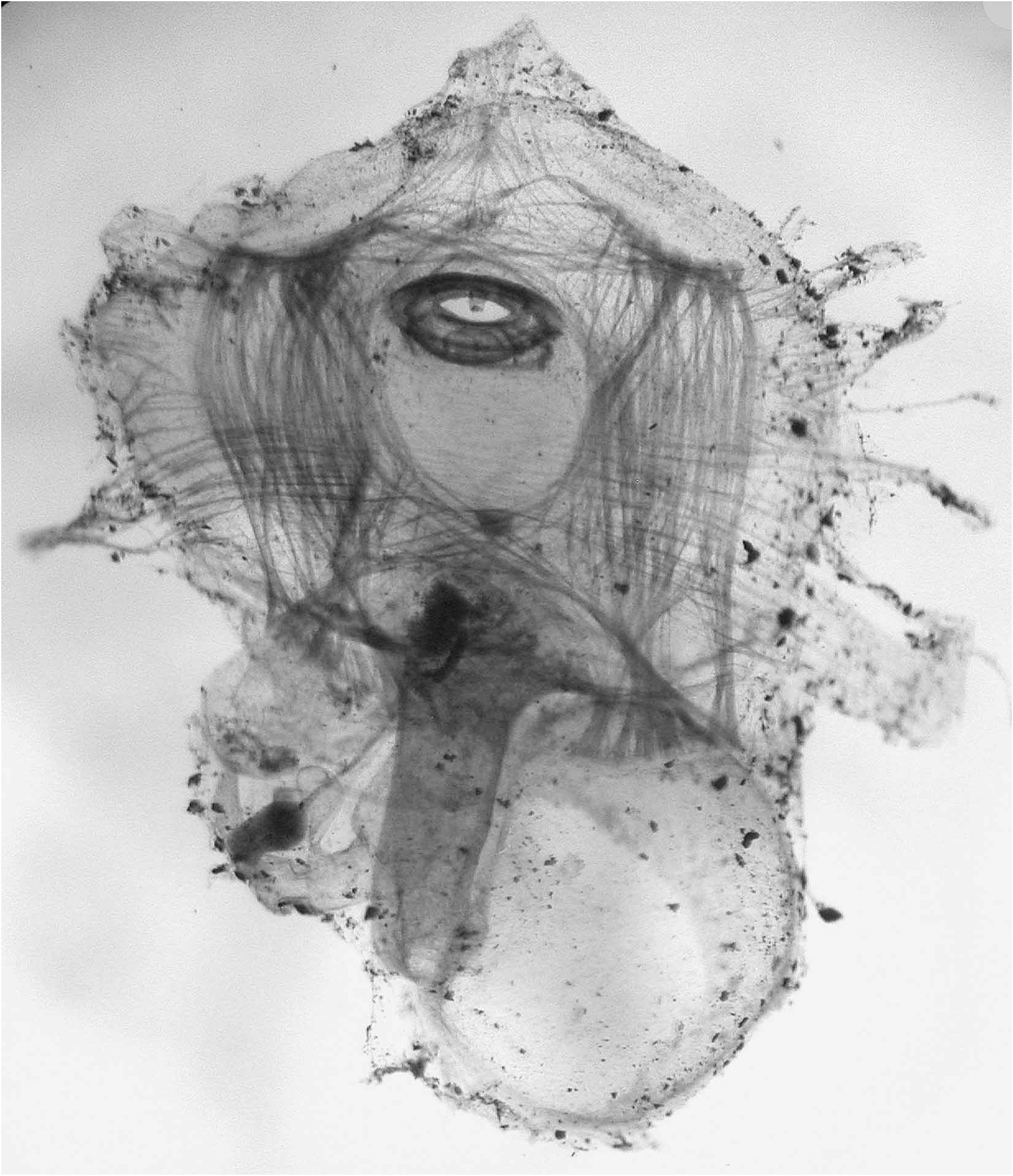
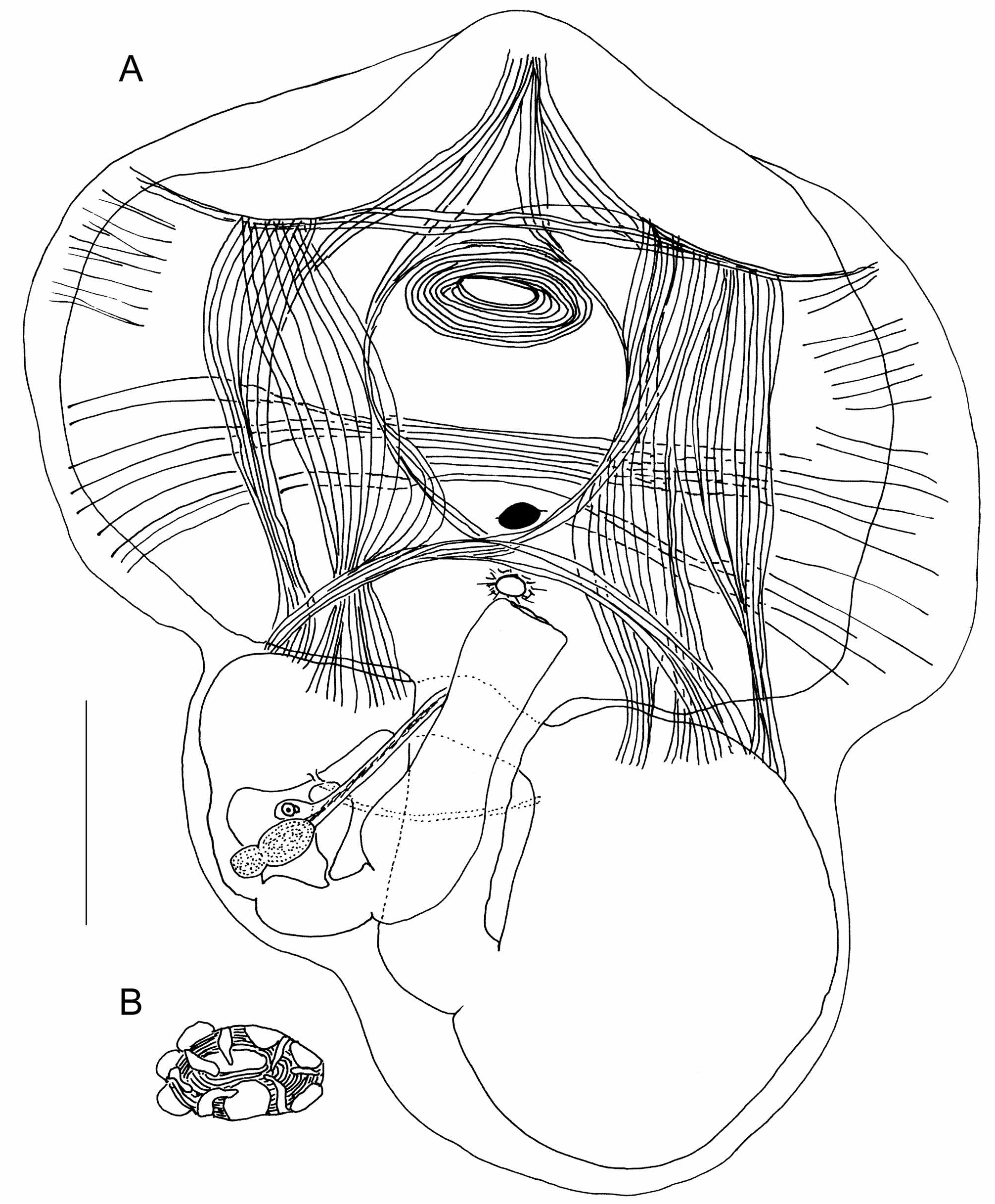
The single specimen, flat, 5mm in maximum length, was attached to the substratum by its whole ventral side ( Fig. 1).The tunic has a paper-like consistency and is thin and transparent, with tiny concentric superficial ridges. Both siphons open at the upper surface of the body. The oral siphon is sessile in a slit. The atrial siphon opens in a round hole in the middle of the body length. The tunic spreads out on the substrate around the body wall. Extracted from the tunic, the body appears in two parts enclosed in a very thin transparent body wall ( Fig.2 View FIGURE 2 ). The thoracic part comprises a large pharyngeal cavity lined by a thin membrane with no trace of branchial sac ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ) The abdomen, below the thorax, contains the gut loop and the gonad Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). The neural ganglion is round (Figs 2,3A) close to the atrial aperture; no neural gland has been detected. The oral aperture has 6 round membranous introverted lobes and between the lobes arise 6 simple tentacles ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ); a ring of circular muscles forms a strong sphincter crossed by a few weak short radiating fibres. The cloacal aperture has a smaller sphincter ( Fig.3A View FIGURE 3 ). The dorsal side of the body wall over the pharyngeal cavity is the only part containing muscles (Figs 2,3A). The musculature is made of flat ribbons delimiting a square mesh. Two ribbons of long fibres, one on each side, are parallel to the dorsal line. They are crossed perpendicularly by 2 transverse ribbons, one anterior to the oral aperture and the other close to the atrial aperture. The latter ribbon gives off a few fibres starting from its middle part and directed anteriorly in 2 arcs converging on the dorsal line behind the oral siphon. In addition and deeper, a transverse band of long parallel fibres crosses the body width. Some other short transverse fibres are limited to the lateral margins of the body wall ( Fig.3A View FIGURE 3 ). There are no muscles on the ventral side of the thorax and none above the gut loop.
The abdominal part of the body is filled with the digestive tract (Figs 2,3A). A long oesophagus originates from the middle of the posterior part of the pharynx. The large spherical stomach has a thin smooth wall. The first segment of the intestine is tubular, applied against the pharynx. It gives into an enlarged section (post-stomach), followed by a narrow tube. After a constriction another short segment opens into a large straight rectum ( Fig.3A View FIGURE 3 ). The anus has a smooth edge. The last intestinal compartment before the rectum wears a large drop-like ampulla ( Fig.3A View FIGURE 3 ) with a narrow duct (pyloric?) that unites the post-stomach to the intestine ( Fig.3A View FIGURE 3 ). The whole digestive tract forms a closed loop in which lies the gonad composed of a single testis lobe and a small ovary at its side ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). The sperm duct is long and parallel to the rectum.
The new species likely belongs to the genus Myopegma Monniot & Monniot, 2003 collected off New Calédonia at 450m depth, and never subsequently recollected later. M. midatlantica n. sp. from the mid-Atlantic station is deeper than M.melanesium the only until now described species of the genus. M. midatlantica n. sp. lacks the strong rods of aggregated muscle fibres found in M. melanesium and the intestinal compartments have a different shape. It confirms the generic characters: body dorso-ventrally flattened, absence of branchial sac, musculature in strong ribbons crossed at right angles and restricted to the dorsal area, a single hermaphrodite gonad in the gut loop on the left body side.
The carnivorous diet of the genus is confirmed as fragments of digested small crustaceans have been found in the stomach, intestine and rectum.
The genus Myopegma differs from all other Octacnemidae ( Benthascidia , Cibacapsa , Cryptia , Dicopia, Hypobythius , Kaikoja , Megalodicopia , Octacnemus , Polyoctacnemus , Situla ), by the total absence of branchial structures, a small oral aperture without lips, and the musculature design.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.