Leptotyphlops boulengeri (Boettger)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6789060 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6789082 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A77887C2-FFCC-FFE8-FF02-83FA44D1B64F |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Leptotyphlops boulengeri (Boettger) |
| status |
|
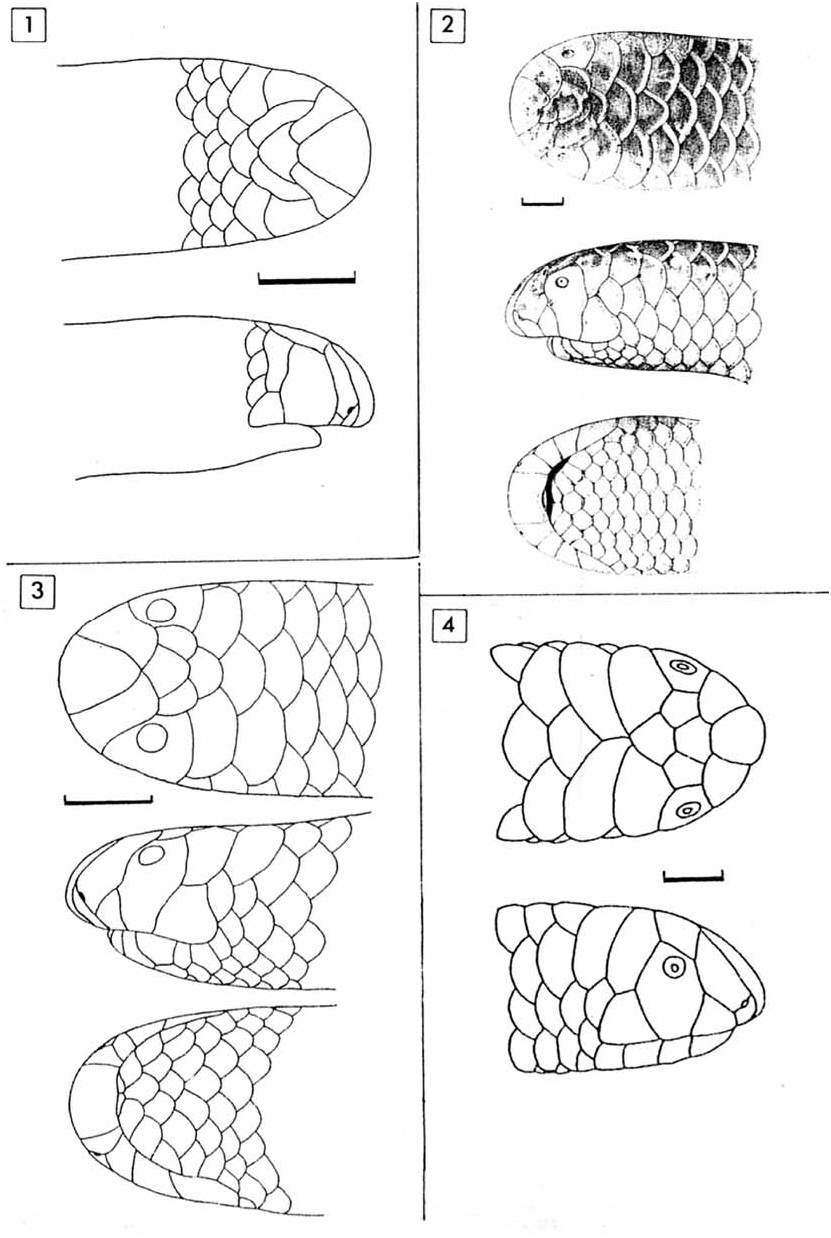
Leptotyphlops boulengeri (Boettger) ( Plate 6 View PLATE 6 , Fig. 3)
Lamu worm-snake
Glauconia boulengeri Boettger, 1913 , Reise in Ostafrika, 3: 354, pl. 25, fig. 1. Type locality: Manda Island, Kenya ( 02°18’S, 40°58’E, near sea level), holotype SMF 16700 (formerly SMF 7066a), collected by A. Voeltzkow, 10–14 February 1903; Boulenger, 1915b: 617; Loveridge, 1924: 4.
Leptotyphlops boulengeri — Loveridge, 1936: 230, 1957: 246; Hahn, 1978: 479, 1980: 8; Spawls, 1978: 2; Meirte, 1992: 16; Broadley & Wallach, 1996: 162; Wallach, 1996: 426; McDiarmid et al., 1999: 23; Spawls et al., 2002: 300.
Diagnosis. A member of the Leptotyphlops reticulatus species group, differing from the other species in its low middorsal and subcaudal counts and colouration.
Description. Body cylindrical, with head and neck broadened and flattened, distinct from body, the short tail tapers abruptly to a thorn-like apical spine, recurved ventrally.
Snout rounded, rostral moderate (0.29–0.38 head width, mean = 0.35), subequal to the nasals anteriorly, tapering to a blunt point posteriorly and not reaching the level of the eyes, a deep preoral groove present ventrally but rostral not extending below lip level. Behind rostral, upper lip bordered by infranasal (nostril midway between rostral and supralabial along nasal suture), moderate anterior supralabial that extends dorsally to a point level with the nostril and its width along lip 1.5–2 times that of infranasal, large ocular with eye at upper anterior edge, and moderate posterior supralabial. Supraoculars small, pentagonal, anteriorly wedged between upper nasal and ocular, posteriorly wedged between frontal and postfrontal, the former lozengeshaped, the latter subhexagonal, both much smaller than the broader and deeper hexagonal interparietal and interoccipital. Parietals transverse, subequal to the enlarged occipitals, in contact with the posterior supralabials. Temporal single. No mental, five infralabials.
Body covered with 14 rows of smooth, imbricate, subequal scales. Reduction to 10 rows on the tail takes place lateral to the crescent-shaped cloacal shield. Total middorsals 179–192; subcaudals 18–22.
Total length/tail ratio 10.3–12.7; total length/diameter ratio 29–37.
Dorsum light brown, each scale beige or pink with a brown border, venter slightly paler. Flesh pink in life ( Loveridge, 1936).
Size. Largest specimen ( MCZ 40085 — Lamu Island , Kenya) 187 + 16 = 203 mm .
Habitat. Beneath rotting grass lying on red soil at the edeg of one of the native gardens ( Loveridge, 1936).
Distribution. Endemic to Manda and Lamu Islands off the northern coast of Kenya, near sea level ( Plate 5 View PLATE 5 ).
Localities. KENYA. Lamu Island MCZ 40084–85 About MCZ , 40087 About MCZ *; Manda Island ( Boettger, 1913) MCZ 40088 .
| MCZ |
Museum of Comparative Zoology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Leptotyphlops boulengeri (Boettger)
| Published, First 2007 |
Leptotyphlops boulengeri
| Spawls, S. & Howell, K. & Drewes, R. & Ashe, J. 2002: 300 |
| McDiarmid, R. W. & Campbell, J. A. & Toure, T. A. 1999: 23 |
| Broadley, D. G. & Wallach, V. 1996: 162 |
| Meirte, D. 1992: 16 |
| Hahn, D. E. 1980: 8 |
| Hahn, D. E. 1978: 479 |
| Spawls, S. 1978: 2 |
| Loveridge, A. 1936: 230 |