Asphondylia viticola Kieffer & Docters van Leeuwen-Reijnvaan
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4847.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1F8E3DED-6EA9-4D8A-8DA9-CD8C0CC9147F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4407471 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A32D87D4-1C59-5362-55DE-F9792740E33F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Asphondylia viticola Kieffer & Docters van Leeuwen-Reijnvaan |
| status |
|
Asphondylia viticola Kieffer & Docters van Leeuwen-Reijnvaan View in CoL
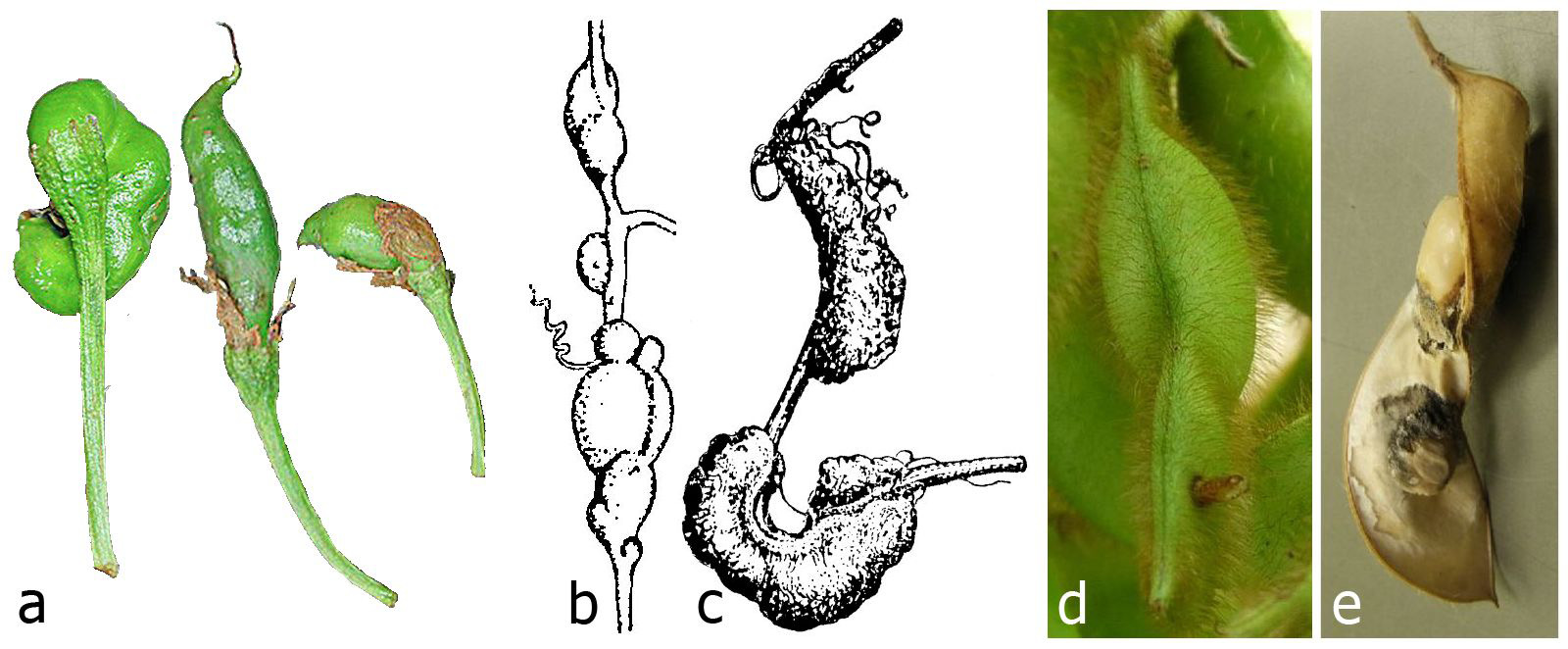
[ Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 b–c]
Asphondylia viticola Kieffer & DvLR, 1910: 124 View in CoL .
Material. Syntypes, male, female and pupal specimens reared from stem and leaf stalk galls on Vitis trifolia L. [now Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen, previously also known as Cayratia trifolia (L.) Domin] ( Vitaceae ) collected at Salatiga, Java, [before] x-1910 (Kieffer & DvLR 1910; DvLR & DvL 1909b). The types are presumed lost.
Description (based on Kieffer & DvLR (1910), some insignificant characters omitted). Adult. Palpus 3-segmented, first and second segments as wide as long, third twice as long as first and second together. Flagellomeres cylindrical; in male about 5x longer than wide, with looped circumfila typical for Asphondylia ; in female progressively shorter, first flagellomere about 6x longer than wide, tenth 2.5x, eleventh 1.5x, twelfth round.
Pupa. Antennal and frontal horns exceptionally strong, antennal horns long and pointed, one anterior frontal horn, two closely placed upper posterior horns and one lower posterior horn. Cephalic papillae with setae half the length of antennal horns. Prothoracic spiracles slightly shorter than posterior horns, thin, curved.
Larva unknown.
Remarks. The types are presumed lost ( Gagné & Jaschhof 2017) so any distinction between this species and A. vitea , both gallformers on the same host, cannot be ascertained. DvLR & DvL (1941) found a similar stem gall on Causonis japonica (Thunb.) Raf. in Java at Cipanas, near Cisolok, alt. 50 m, xi-1927.
Biology. Galls were described by Kieffer & DvLR (1910), DvLR & DvL (1909b, Fig. 48 [ Fig. 4b View FIGURE 4 ], young gall] and DvLR & DvL (1926, Fig. 637 [ Fig. 4c View FIGURE 4 ], mature gall). Asphondylia viticola causes galls on stems and sometimes on leaf stalks of Causonis trifolia . Galls are brown, lopsidedly developed, 10–50 mm long and 6–12 mm wide, the infested part of the stem is often curved, inside are one to several larval chambers. The gall is succulent and covered with a red-brown corky layer. Adults emerged at the end of October at Salatiga, Java [before 1910].
Geographical distribution. Asphondylia viticola was found in Java: Salatiga (in October of an unrevealed year as stated in 1910 publication), Sumber Pitu , near Weleri ; Sukamangli , near Weleri , alt. 500 m, ii-1909 ; Madura island , v-1910 ; Kuripan, near Pekalongan , vii-1911 , Semarang , i-1912 ; Jrakah, near Semarang , iii-1913 ; Pegangsaan , Jakarta; v-1915 ; Depok , x-1918 ( Kieffer & DvLR 1910, DvLR & DvL 1909b, 1926) .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Asphondylia viticola Kieffer & Docters van Leeuwen-Reijnvaan
| Kolesik, Peter & Gagné, Raymond J. 2020 |
Asphondylia viticola
| Kieffer & DvLR 1910: 124 |