Asphondylia callicarpae Felt
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4847.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1F8E3DED-6EA9-4D8A-8DA9-CD8C0CC9147F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4407438 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A32D87D4-1C41-537B-55DE-FF0D226BE7CF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2020-12-31 14:54:00, last updated 2024-11-26 01:04:37) |
|
scientific name |
Asphondylia callicarpae Felt |
| status |
|
Asphondylia callicarpae Felt View in CoL
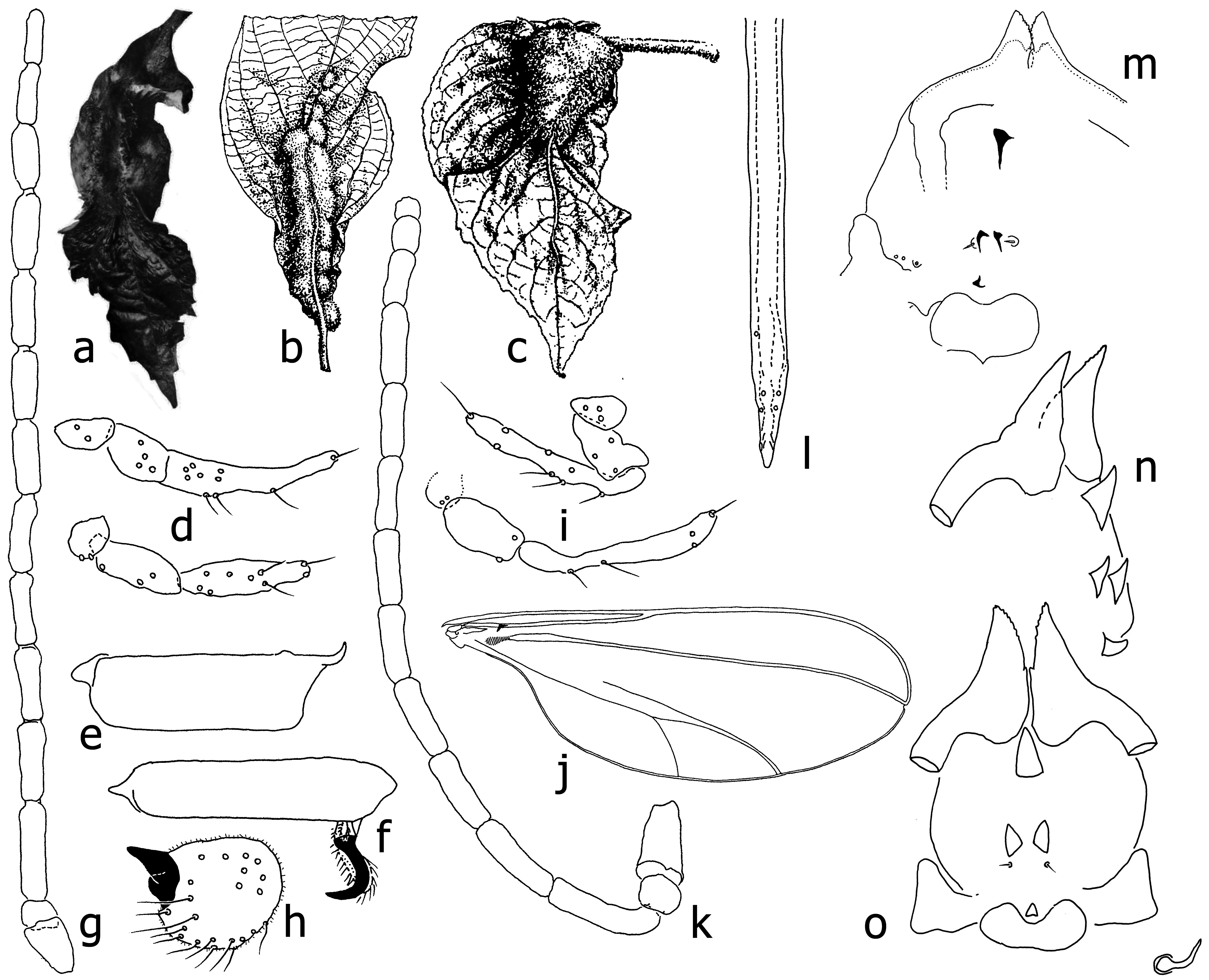
[ Figs 3 View FIGURES 3 a–o]
Asphondylia callicarpae Felt, 1918: 285 View in CoL .
Material examined. Syntypes, male, 3 females, and a pupal exuviae [fragment], Felt #a2843, reared from leaf galls on Callicarpa erioclona Schauer ( Verbenaceae [now Lamiaceae ]), Mt Makiling, Laguna Province, Luzon, the Philippines, collected at altitude 200–300 m viii-1917 and reared by L.B. Uichanco 3-ix-1917. One slide bears a male missing an antenna, another slide with a complete female except with its head inside an anterior fragment of a pupal exuviae, and the two other females are still pinned and well-preserved. Three years after the original description, Felt (1921d) described one female and two pupae reared by DvL from a leaf gall on Callicarpa longifolia Lam. collected at Mt Ungaran, Java, iv-1914, and concluded that they belonged to this species. We examined those specimens also: an uncleared female and pupa and a pupal exuviae, are on a single slide (Felt #a3102).
Description. Male. Wing length 2.3 mm, width 1.0 mm. Antenna: scape 2x longer than wide, pedicel slightly wider than long, flagellomeres slightly progressively shorter [ Fig. 3g View FIGURES 3 ]. Palpus 3-segmented, division between second and third may be indistinct, segments progressively longer [ Fig. 3d View FIGURES 3 ]. First tarsal segment with apicoventral spur short, robust, curved at basal third [ Fig. 3e View FIGURES 3 ]. Tarsal claws robust, curved at midlength, empodia as long as claws, pulvilli minute [ Fig. 3f View FIGURES 3 ]. Gonostylus as wide as long in posterior view, one tooth long and pointed, one short and blunt [ Fig. 3h View FIGURES 3 ].
Female. Wing length 2.6 mm, width 1.0 mm, vein R 5 joining C at wing apex, R 1 2/3 wing length [ Fig. 3j View FIGURES 3 ]. Flagellomeres 1–9 progressively slightly shorter, 10–12 progressively much shorter, first flagellomere 5x longer than wide [ Fig. 3k View FIGURES 3 ]. Palpus 3-segmented, segments progressively longer [ Fig. 3i View FIGURES 3 ]. Needle-like protrusible part of ovipositor 2.4x longer than seventh sternite [ Fig. 3l View FIGURES 3 ].
Pupa. The anterior end of the pupal exuviae fragment collected in 1917 in the Philippines and mounted by Felt has large antennal horns with finely serrated inner edges, one large anterior frontal horn and three smaller posterior frontal horns placed in the shape of an isosceles triangle, the posteriormost, situated adjacent to the labella, recurved and rugose [ Fig. 3m View FIGURES 3 ].
Larva unknown.
Remarks. The pupa has serrated inner edges of the antennal horns, and the posteriormost of the three lower frontal horns is somewhat removed from the other two and uniquely rugose. We note that the frontal horns of the Javan specimens [ Figs 3m, n View FIGURES 3 ] are noticeably larger than those seen on the Philippine pupa [ Fig. 3m View FIGURES 3 ]. We defer to future study, possibly until larvae can be compared, whether that difference is a specific one.
Biology. Uichanco (1919) reared the type specimens in the Philippines from leaf galls on Callicarpa erioclona Schauer (gall No. 18147, Plate X Fig. 2 View FIGURES 2 [ Fig. 3a View FIGURES 3 ]) and described the gall as about 30 mm, width 15 mm, thickness 16 mm, polythalamous, consisting of an enlargement of the midrib and forming with the atrophied leaf lamina a single mass of succulent tissue. The enlarged portion is tomentose, concave above and convex on the nether surface. The petiole, usually the leaf apex, and a small portion at the base are sometimes unaffected. The hair covering is long, dark brown and concolorous with the normal short pubescence of the plant. Larval chambers are subellipsoid, their size variable and arranged irregularly in close proximity to the upper, concave surface. The deformation is confined to younger, subterminal leaves. Galls were abundant at the type locality and present most of the year ( Uichanco 1919). DvL (1921, Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8 [ Fig. 3c View FIGURES 3 ]) and DvLR & DvL (1926, gall No. 1291, Fig. 927 [ Fig. 3b View FIGURES 3 ]) reported a similar gall on Callicarpa longifolia from several localities in Indonesia. The insects reared from the Indonesian galls were examined by Felt who considered them conspecific with the insects from the Philippine galls ( Felt 1921b; DvLR & DvL 1926).
Geographical distribution. This species is known from its type locality at Mt Makiling, Laguna Province, Luzon , in the Philippines where it was reared from Callicarpa erioclona viii-1917 ( Felt 1918) and from several localities in Indonesia (DvLR & DvL 1926) where the galls were found on Callicarpa longifolia on Java at Mt Muria , alt. 500 m, x-1912 ; Ciharum, near Cibeber ,, alt. 1000 m, vi-1916 ; Cadas Malang, near Cibeber , alt. 1000 m, iv-1917 ; Mt Gede, Cibodas , alt. 1500 m, ix-1918 ; Pesewahan, south of Cibadak, near Bogor , alt. 600 m, viii-1918 ; Mt Ungaran , alt. 1200 m, xi-1919 ; Wanayasa, near Purwakarta , alt. 1000 m, vii-1920 and in Sumatra at Rimbo Pengadang vi-1916 .
Felt, E. P. (1918) New Philippine gall midges, with a key to the Itonididae. The Philippine Journal of Science, 13, 281 - 325, pl. I.
Felt, E. P. (1921 d) New Javanese gall midges. Treubia, 2, 89 - 92.
Felt, E. P. (1921 b) Javanese gall midges. Treubia, 1, 139 - 151.
Uichanco, L. B. (1919) A biological and systematic study of Philippine plant galls. The Philippine Journal of Science, 14 (5), 527 - 554, pls. I-XV. https: // doi. org / 10.5962 / bhl. part. 14568
FIGURES 2a–j. Actilasioptera falcaria: a–d, galls on Avicennia marina: a, leaf upper side on top, gall cross section on bottom (Figs 51a, b of DvLR & DvL 1910); b (Fig. 2 of DvL 1921); c (Fig 921 of DvLR & DvL (1926)); d, leaf underside (Fig. 2 of Gagné & Law 1999); e–f, male: e, tarsal claw with empodium and pulvillus; f, terminalia (somewhat misshapen in the preparation), from left to right: cerci (ce), mesobasal lobe (ml), aedeagus (ae), hypoproct (hy), gonocoxite (gc), gonostylus (gs); g–k, female: g, end of abdomen (lateral); h, palpi; i, sixth flagellomere (ventral); j, same (dorsal). Figs 2k-n. Actilasioptera sp.: k, palpi; l, wing; m, galls on Avicennia marina, drawn to same scale as Fig. 2a, leaf underside on left, upper side on right (Fig. 3 of DvL (1921); n, gall cross section (Fig. 51c of DvLR & DvL 1910).
FIGURES 3a–o. Asphondylia callicarpae: a, gall on Callicarpa erioclona from the Philippines (Fig. X-2 of Uichanco (1919)); b, gall on Callicarpa longifolia from Java (Fig. 927 of DvLR & DvL (1926)); c, gall on Callicarpa longifolia from Java (Fig. 8 of DvL 1921); d, male palpi; e, male first tarsal segment; f, male last tarsal segment with claw, empodium and pulvillus; g, male antenna; h, gonostylus in posterodorsal view; i, female palpi; j, female wing; k, female antenna (within pupal exuviae); l, end of ovipositor in ventral view; m–o, anterior part of pupa: m, o, ventral; n, lateral. Insect drawings d–m are based on types reared from C. erioclona in the Philippines, n–o from C. longifolia in Java.
FIGURES 8a–i. Asphondylia vitea: a–b, galls on Cayratia trifolia from the Philippines (Figs VIII-4 & VIII-6 of Uichanco (1919)); c, gall on C. trifolia from Indonesia (Fig. 636 of DvLR & DvL (1926)); d, palpus; e, first tarsomere; f, male terminalia (dorsoposterior); g, 6th male flagellomere (only part of circumfila visible in type specimen); h, wing; i, tarsal claw of front leg with empodium. Insect drawings made from types reared in the Philippines.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Asphondylia callicarpae Felt
| Kolesik, Peter & Gagné, Raymond J. 2020 |
Asphondylia callicarpae
| Felt, E. P. 1918: 285 |
1 (by plazi, 2020-12-31 14:54:00)
2 (by ExternalLinkService, 2020-12-31 15:19:50)
3 (by ExternalLinkService, 2020-12-31 17:12:57)
4 (by diego, 2021-01-28 17:51:22)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-01-28 18:13:22)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-09-20 00:52:31)
7 (by plazi, 2023-11-01 02:06:35)