Mongoloraphidia xinjiangana, Shen & Li & Ren & Shali & Liu, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5125.5.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8D3AB961-E2CC-418A-A442-5E849BA1515E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6457433 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A0151E05-8634-FF87-FF17-FD7F18D31FDF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mongoloraphidia xinjiangana |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mongoloraphidia xinjiangana sp. nov.
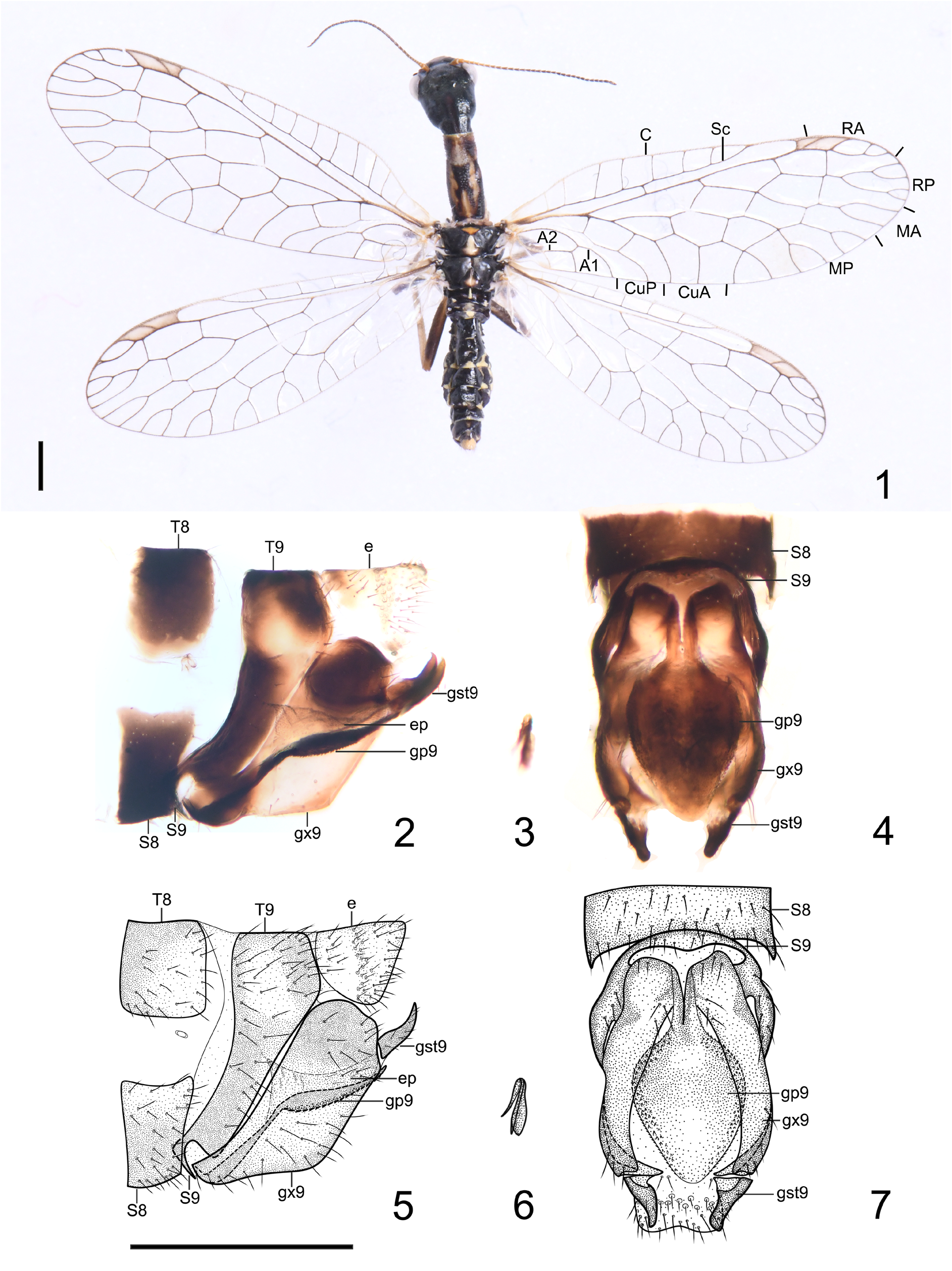
( Figs 1–7 View FIGURES 1–7 )
Diagnosis. The new species is characterized by males with prominent posteroventral margin of gonocoxite 9, which lacks the posterior process, and the gonapophyses 9 (hypovalva) strongly enlarged distally into a heart-shaped plate.
Description. Male. Body length 8.5 mm; forewing length 8.3 mm, hind wing length 7.6 mm.
Head ovoid, black with clypeus blackish brown. Compound eyes pale brown. Antennal sclerite, scape, and pedicel yellow; flagellum yellow, but gradually becoming yellowish brown on distal 2/3 (from 7th flagellomere). Mouthparts brown, but distal 1/2 of mandibles, maxillary and labial palpi dark brown.
Pronotum long, slender, blackish brown, with a median yellowish brown stripe at anterior 1/3; laterally with a pair of narrow hook-like, yellowish brown markings; meso- and metanotum blackish brown, mesonotum anteriorly with a medial subtriangular yellowish brown marking medially, scutellum medially yellow; metanotum with scutellum yellow medially. Legs brown with blackish setae, femur blackish brown, tibia pale brown. Wings hyaline; pterostigma narrow, approximately four times as long as wide, medially crossed by a vein, pale yellowish brown throughout; veins blackish brown; proximal half of C, R and A veins on forewing and bases of most longitudinal veins on hind wing yellow; anterior branch of RP on forewing with two branches, one or two bifurcate to wing margin; anterior branch of RP on hind wing with one simple and one forked vein.
Abdomen blackish brown; pregenital segments with a pair of yellowish vittae laterally, each tergum with a median and posterior yellowish spot posteriorly and each sternum with a transverse yellowish marking posteriorly. Genital segments blackish brown, but ectoproct yellow. Tergum 9 with anterior margin feebly notched. Sternum 9 arcuate, rather narrow, and posteromedially prominent ( Figs 2, 5 View FIGURES 1–7 ). Gonocoxite 9 ( Figs 2, 5 View FIGURES 1–7 ) obliquely directed dorsoventrally, ventral part much broader than dorsal part, posteroventrally prominent into an obtuse angle. Gonostylus 9 ( Figs 2, 5 View FIGURES 1–7 ) short, unguiform, feebly curved. Gonapophyses 9 (hypovalva) ( Figs 2, 4, 5, 7 View FIGURES 1–7 ) directed posterodorsad, largely enveloped by gonocoxites 9, anteriorly separated as a pair of narrow short beams, remaining part flat and slightly inflated in lateral view, and strongly broadened into a heart-shaped plate in ventral view, laterally with numerous small teeth. Ectoproct slightly longer than tergum 9 ( Figs 2, 5 View FIGURES 1–7 ), feebly sclerotized, with posterodorsal corner pointed in lateral view. Fused gonocoxites 11 (gonarcus) reduced. Hypandrium internum trilobate ( Figs 3, 6 View FIGURES 1–7 ), lateral lobes slightly wider but shorter than median lobe, posterior end strongly narrowed.
Female. Unknown.
Type material. Holotype ♂ [preserved in alcohol], CHINA: Xinjiang, Urumqi, Shayibak District [ 乌ã木λ, 沙ff-克区], Xinjiang Agricultural University , 87°34′11.99″E, 43°48′36″N, 787.21 m, 2021.V.13, Bingchen Li ( CAU). GoogleMaps
Distribution. China ( Xinjiang).
Etymology. The new species is named after Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region where the holotype was collected.
Remarks. The new species appears to be closely related to Mongoloraphidia alaica H. Aspöck, U. Aspöck & Rausch, 1997 from Kyrgyzstan in having similar male gonocoxite 9 lacking posteroventral projection and generally flat male gonapophyses 9 (hypovalva) posteriorly strongly enlarged. However, it can be distinguished from the latter species by the male gonocoxite 9 posteroventrally produced into an obtuse angle, and the male gonapophyses 9 (hypovalva) posteriorly enlarged into a heart-shaped plate. In M. alaica , the male gonocoxite 9 is not produced on posteroventral margin, and the male gonapophyses 9 (hypovalva) is posteriorly enlarged into a broad, pentagonal plate (see H. Aspöck et al. 1997: figs 26–28).
| CAU |
China Agricultural University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |