Lathrobium baiyunense Peng and Li
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3780.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A391A8BD-B89F-4C9C-8DF0-5206F3435B2D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6133434 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/952C0935-FFFD-C858-D5E9-DD4F8A711BDA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lathrobium baiyunense Peng and Li |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Lathrobium baiyunense Peng and Li View in CoL , new species
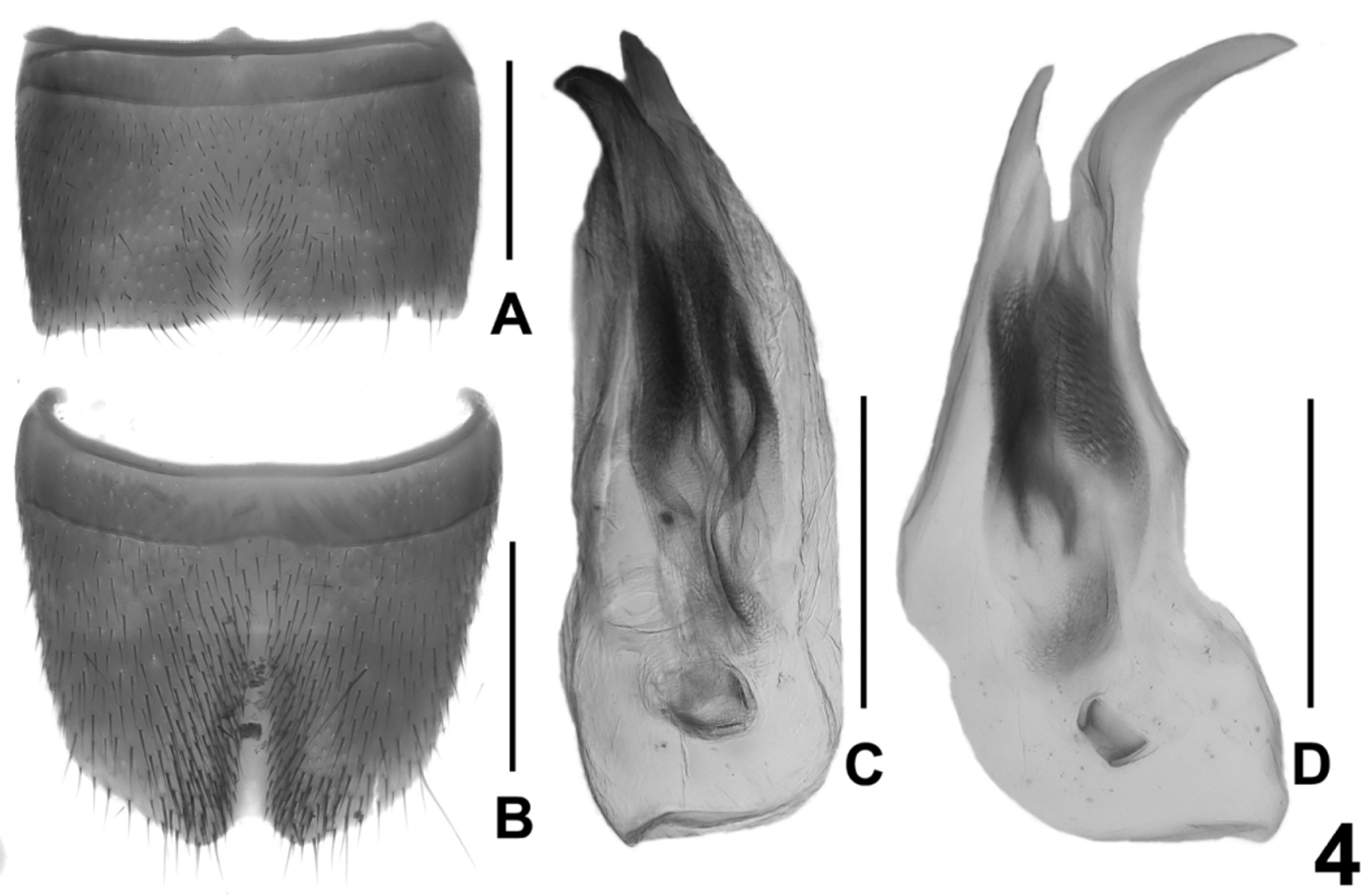
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 C, 4)
Type material. (2 ♂♂). HOLOTYPE: ♂, labelled ‘ CHINA: Henan Prov., 120km SW Luoyang City, Baiyun Shan, 33°40'N, 111°50'E, 18.viii.2008 alt. 1,500 m, Li-Zhen Li leg.’ ( SNUC). PARATYPES: 1 ♂ [teneral], same label data as holotype ( SNUC).
Description. Measurements (in mm) and ratios: BL 7.06–8.34, FL 3.61–3.73, HL 0.93–0.94, HW 1.00–1.02, AnL 1.88–1.90, PL 1.30–1.31, PW 1.02–1.04, EL 0.83, AL 1.31, HL/HW 0.92–0.93, HW/PW 0.98, HL/PL 0.72, PL/PW 1.26–1.27, EL/PL 0.63–0.64.
Habitus as in Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C. Body dark brown with paler apex, legs brown to light brown, antennae brown.
Head weakly transverse; punctation coarse and dense, somewhat sparser in median dorsal portion; interstices with very shallow microreticulation. Eyes 0.26–0.28 times as long as postocular region in dorsal view and composed of 50 ommatidia.
Pronotum nearly parallel-sided; punctation sparser than that of head; impunctate midline moderately narrow; interstices without microreticulation.
Elytra moderately short; punctation dense, coarse, and moderately defined. Hind wings completely reduced.
Abdomen with fine and dense punctation, that of tergite VII somewhat sparser than that of anterior tergites; interstices with very shallow microsculpture; posterior margin of tergite VII without palisade fringe.
Male. Posterior margin of tergite VIII truncate; sternites III–VI unmodified; sternite VII ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A) strongly transverse, with shallow median impression posteriorly, this impression with weakly modified, short and dark setae, posterior margin indistinctly concave in the middle; sternite VIII ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 B) weakly transverse, with shallow median impression posteriorly, middle of this impression narrowly without setae, on either side of middle with cluster of dense dark setae, posterior excision small, concave, and in symmetric position; aedeagus as in Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 C, D, ventral process long, evenly arched, apically acute in lateral view, and with median carina ventrally; dorsal plate long and slender; internal sac with dark membranous structures, but without sclerotized spines.
Female. Unknown.
Comparative notes. Based on the similarly derived morphology of the aedeagus, particularly the shape of ventral process and the presence of membranous structures in the internal sac, and on the shapes and chaetotaxy of the male sternites VII and VIII, Lathrobium baiyunense belongs to the L. varisternale group ( Assing 2013a), which was previously represented by thirteen species distributed in the Qinling Shan, the Daba Shan and adjacent mountain. The new species is distinguished from the other representatives of this group by the slender habitus, by the morphology of the aedeagus (shape of ventral process and dorsal plate, dark membranous structures in internal sac). For illustrations of the species of the L. varisternale group see Assing (2013a) and Peng et al. (2013a).
Distribution and biological notes. The type locality is situated in the Baiyun Shan to the southwest of Luoyang, western Henan. The specimens were sifted from leaf litter and grass from the floor of a pine forest at an altitude of 1,500 m.
Etymology. The species is named after its type locality.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |