Gansucossus typicus, Wang, Bo, Zhang, Haichun & Fang, Yan, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.173205 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6255333 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/941187CC-FFE6-7A1D-1A40-FACABFDCFB2F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Gansucossus typicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Gansucossus typicus View in CoL sp. nov.
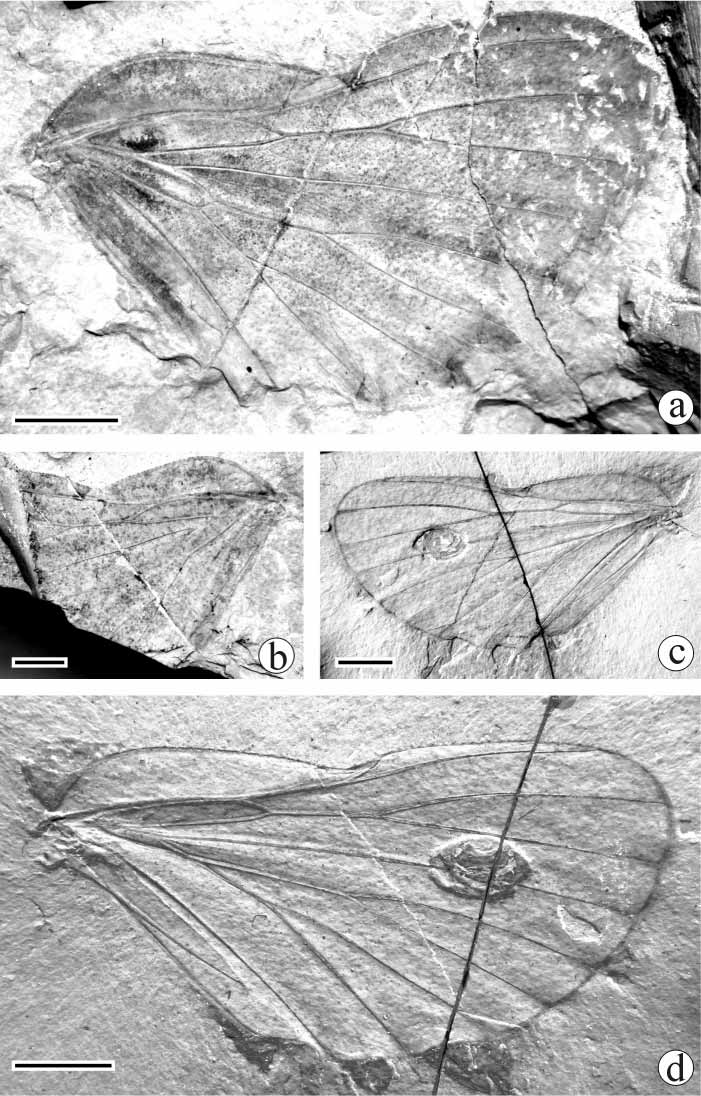
Figs 1a, b View FIGURE 1. a – b , 2 View FIGURE 2
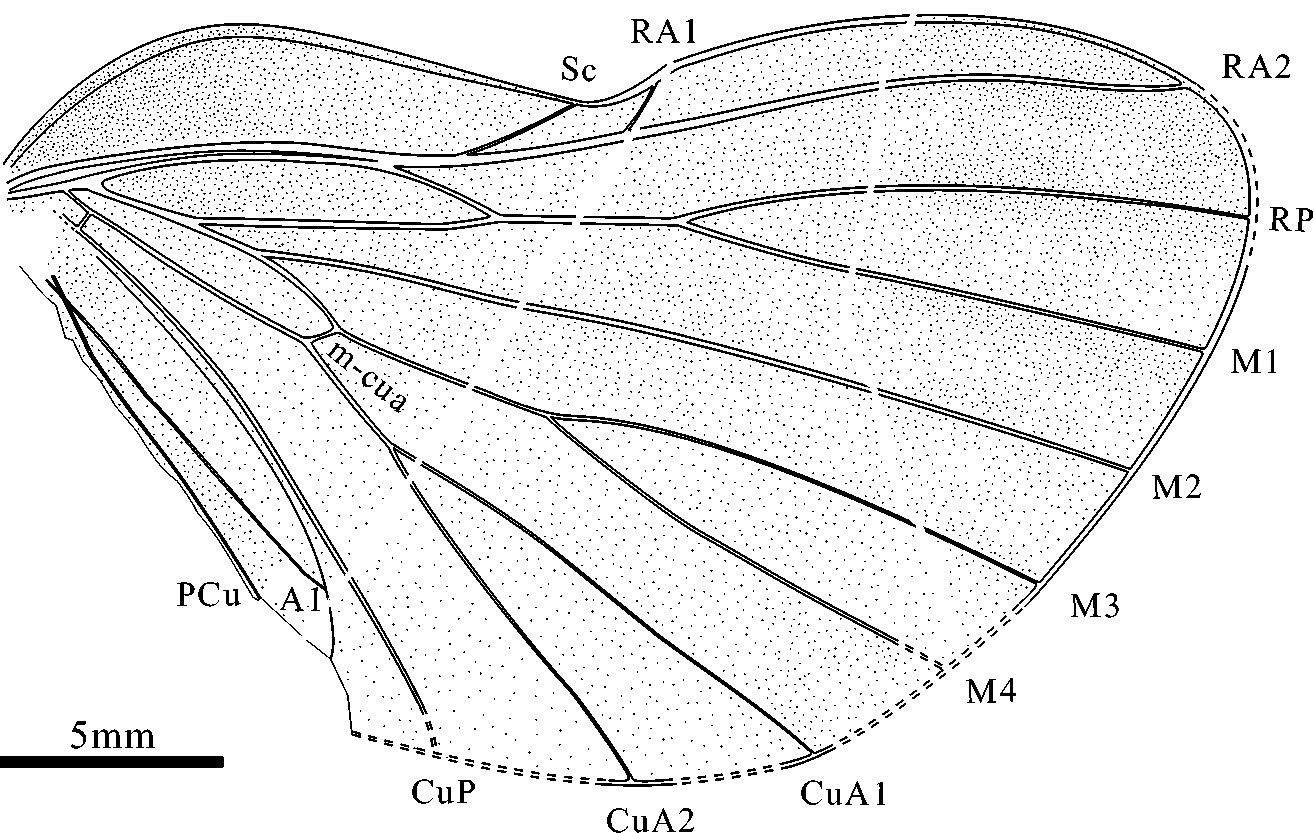
Diagnosis. Hind wing oval, sharp apically, length/width ratio 1.6; costal area length/width ratio 5.0, maximal width in basal half; nodal indentation about midwing; Sc coalesced with base of RA for a short distance; RA1 branching from RA at the level of indentation, and terminating in costal margin just beyond indentation; RA2 ending in costal margin near apex of wing; RP terminating in apex of wing; mcua short and subtransverse.
Differs from the type in having the sharp apex, relatively long costal area, comparatively long and subtransverse mcua and wider media area, and in the location of both the nodal indentation and the apex (M1 terminating in apex in the type).
Differs from G. luanpingensis in the different shape of both the hind wing and the costal area, comparatively short and subtransverse mcua, and in the narrower media area.
Description. Hind wing, part with apex and anal area missing, counterpart with extreme apex destroyed, and anal area folded along PCu. The wing part posterior to PCu is tucked under so that the base of A1 crosses that of PCu. Length 29 mm, width 18 mm (length/width ratio 1.6).
Hind wing oval, sharp apically, infuscate on membrane and with dots in the veins; costal area long, length/width ratio 5.0; nodal indentation about midwing. Sc arising basally, running close to R and coalesced with base of RA for a short distance, and then branching from it, terminating in indentation. R+M forking into R and M at wing base. R a little convex, lying alongside Sc. RA1 dividing from RA at the same level of indentation, ending in costal margin just beyond indentation. RA2 slightly convex, ending in costal margin just above apex of wing. RP branching from R near Sc fusion with R, coalesced with M1 at basal 0.38 wing length, and terminating in apex of wing; Vein RP +M1 length 4 mm. M1 departing from M near wing base, curved anteriorly, and straight for distal half. M2 branching from M2+3+4 and straight for distal half; stem M a little longer than stem M2+3+4. M3+4 connected with CuA by crossvein mcua at basal 0.25 wing length, branching into M3 and M4 at the same level of indentation; stem M3+4 shorter than its branches; M3 and M4 simple. Basal crossvein r+mcua convex, strong and oblique. CuA arising basally from curved stem Cu (the CuA base is a weak concave transverse brace), curved slightly and anteriorly at junction with mcua, and forking at about the same level of RP departing from R. CuP slightly convex. PCu slightly curved. A1 straight, terminating in anal margin. Marginal membrane clear and wider than vein width.
Etymology. Specific epithet is from the Latin typicus , typical, referring to the complete and typical features of the specimen.
Holotype. NIGP 141369 and NIGP 141369a, part and counterpart. Deposited in the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology ( NIGP), Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Age and occurrence. Middle Jurassic; Daohugou Village, Ningcheng County, Chifeng City, Inner Mongolia, China.
| NIGP |
Naking Institute of Geology and Palaeontology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |