Pisacha baculiformis, Meng, Rui, Wang, Menglin & Wang, Yinglun, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3866.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6202FA35-AF83-4F98-82EE-F089EA7ACC35 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6143309 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8E3287F1-C23D-F949-FF6C-1B95FD8CF981 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pisacha baculiformis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pisacha baculiformis View in CoL sp. nov.
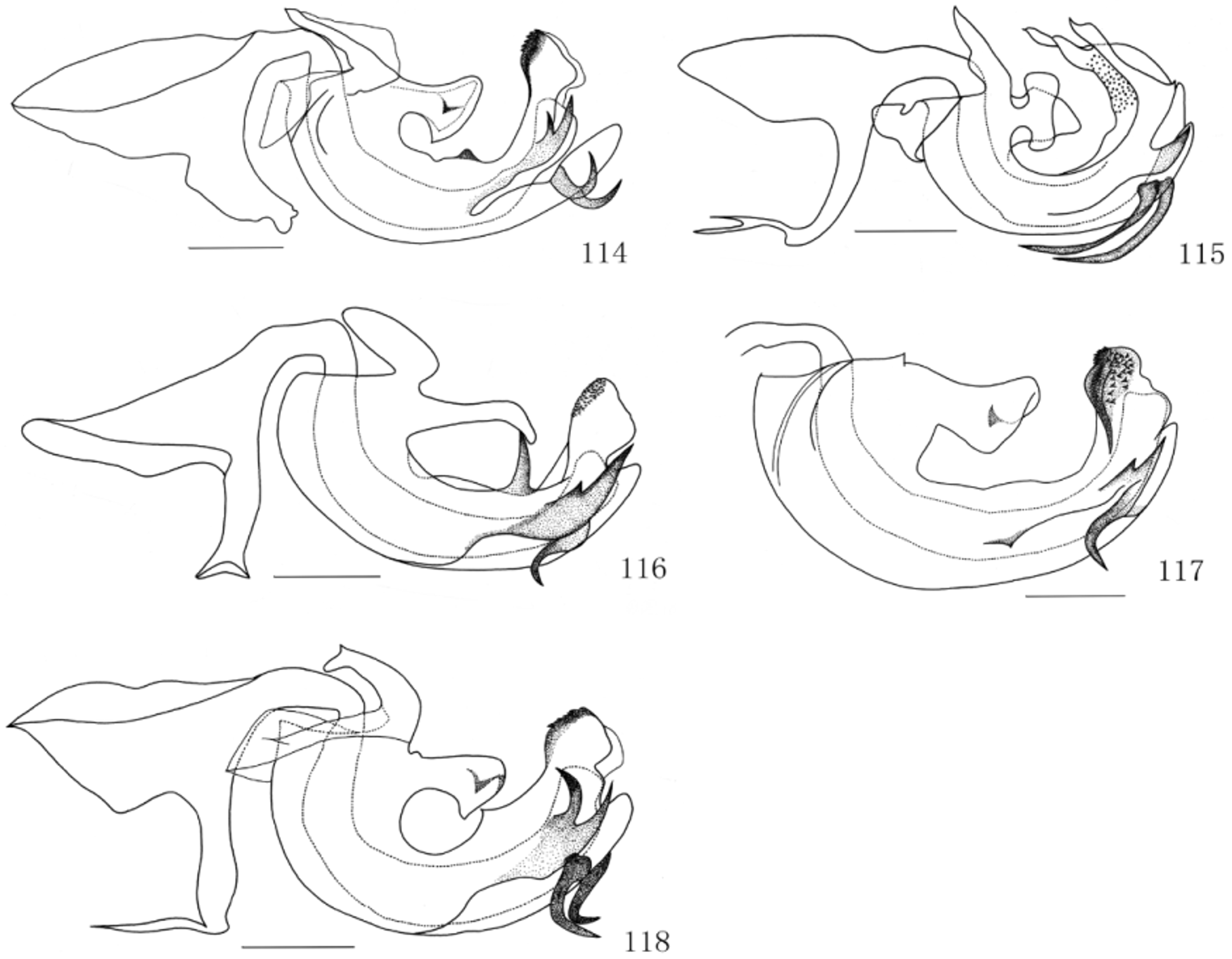
( Figs 70–78 View FIGURES 70 – 78 , 116 View FIGURES 114 – 118 , 121 View FIGURES 119 – 123 )
Description. Length, male (N=1) (including tegmen): 13.8 mm, length of tegmen:12.0 mm; female (N=1) (including tegmen):15.0 mm, length of tegmen: 12.9 mm.
General color brown. Vertex dark brown, median carinae and lateral margins pale yellow. Frons yellow, median area somewhat dark brown, lateral area with numbers of dark brown dots, median carina pale yellow, lateral carinae and margins black, with six small spots along lateral carinae, apical angles black, near upper margin with two black spots. Clypeus yellow, median carina yellow. Ocelli red. Eyes black brown. Antenna dark brown. Gena light brown, with a big black mark at apical angle and a dark brown mark at middle. Pronotum brown, pale yellow. Mesonotum fuscous at median area, light brown laterally, median carina pale yellow, and lateral carinae black. Tegmina transparent, slightly yellow, venation dark brown.
Vertex 3.2 times wider than long in middle line, anterior margin angularly convex, posterior margin obtusely concave ( Figs 70, 72 View FIGURES 70 – 78 ). Frons long, 1.4 times longer than wide at widest part; upper margin angularly concave, median carina indistinct, disappeared near apical one-third ( Fig. 73 View FIGURES 70 – 78 ). Pronotum about 1.4 times longer than vertex in middle line; anterior margin obtusely convex, almost reaching the level of top of eye ( Fig. 72 View FIGURES 70 – 78 ). Mesonotum large, 2.7 times as long as vertex and pronotum combined in middle line, lateral carinae almost reaching posterior margins ( Fig. 72 View FIGURES 70 – 78 ). Tegmina transparent, clavus with 7 transverse veinlets between the suture and its longitudinal vein, one transverse veinlet between two claval veins. Spinal formula of hind leg 13(11)–11–2.
Male terminalia. Anal tube relatively narrow in dorsal view, 2.6 times longer than widest part, apical margin weakly convex, with ventral margin slightly sinuate ( Figs 74, 77 View FIGURES 70 – 78 ). Phallobase with dorso-basal portion elongate, baculiform, deflexed near apex. Dorso-lateral phallobase lobes with a pair of long vertical clavate processes on dorsal margins near middle, apical portion strongly sclerotized and short in lateral view, with about 35 small spikes on each side surface; lateral sides with a pair of bifurcate processes, upper branches tiny and under branches relatively long and thick ( Figs 75, 78 View FIGURES 70 – 78 , 116 View FIGURES 114 – 118 ). Ventral phallobase lobe round and small at median part, apical portion long, nearly rectangular, apical margin weakly concave medianly ( Figs 76 View FIGURES 70 – 78 , 121 View FIGURES 119 – 123 ). Phallus with a pair of short processes directed cephalad, but curved deflexed near middle, two processes far away from each other in ventral view ( Figs 76, 78 View FIGURES 70 – 78 , 116 View FIGURES 114 – 118 , 121 View FIGURES 119 – 123 ). Pygofer with posterior margin distinctly convex at middle ( Fig. 74 View FIGURES 70 – 78 ).
Type material. Holotype: male, China, Zhejiang Province, Qingliangfeng Mountain, 450m, 9 August 2008, coll. Lei Zhang.
Paratypes: 1 female, China, Zhejiang Province, Baishanzu nature reserve, Wulingkeng Mountain, 567m, 13 August 2003, coll. Dai Wu, collected by light trap.
Diagnosis. This species is similar to P. kwangsiensis by vertex with anterior margin angularly convex and tegmina transparent without any stripe, but can be differentiated from it by the following features: 1) frons 1.4 times longer than wide at widest part; median carina indistinct, disappeared near apical one-third, “V” lateral carinae clear, with 6 clear black spots along lateral carinae, in P. kwangsiensis , frons longer than wide in widest part about 1.6 times; median carinae clear, presented at apical fourth, “V” lateral carinae unclear but darkened at base, with 5 obscure black spots along lateral carinae; 2) the processes of phallobase lobes and phallus is quite different between these two species, it can be seen from Figs 44–46 View FIGURES 42 – 55 and Figs 75, 76, 78 View FIGURES 70 – 78 .
Etymology. The specific epithet derived from the Latin “ baculiformis ”, referring to dorso-basal processes of phallobase baculiform in lateral view.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |