Camptotheca SLAS
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112626 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8302364 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8D608791-DF67-1365-FFCD-2E6BFE38B484 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Camptotheca SLAS |
| status |
|
2.4. In vitro analysis of Camptotheca SLAS View in CoL View at ENA activities in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
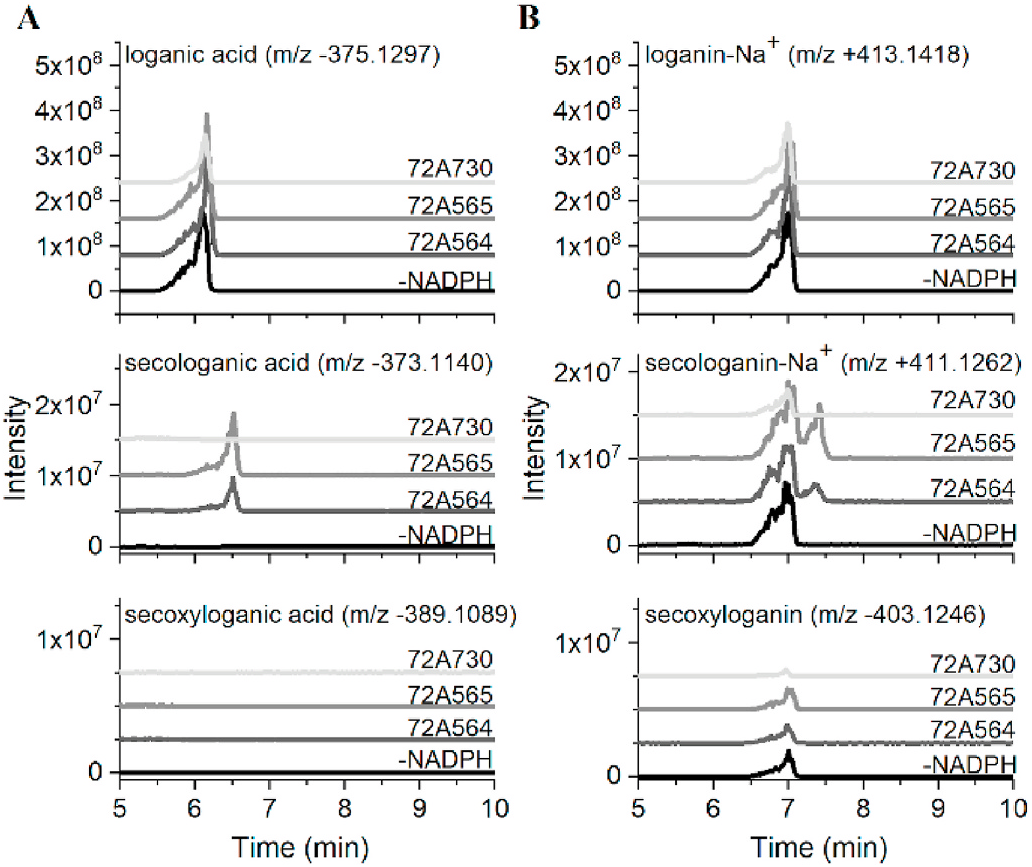
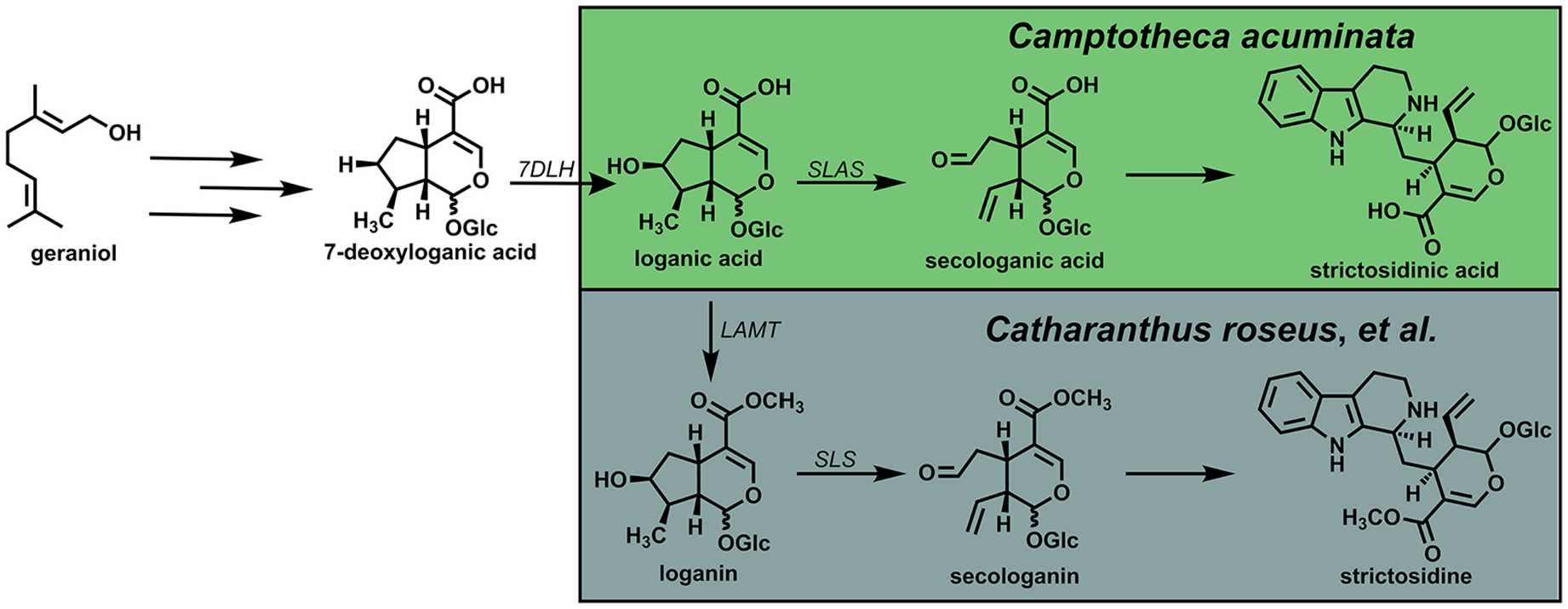
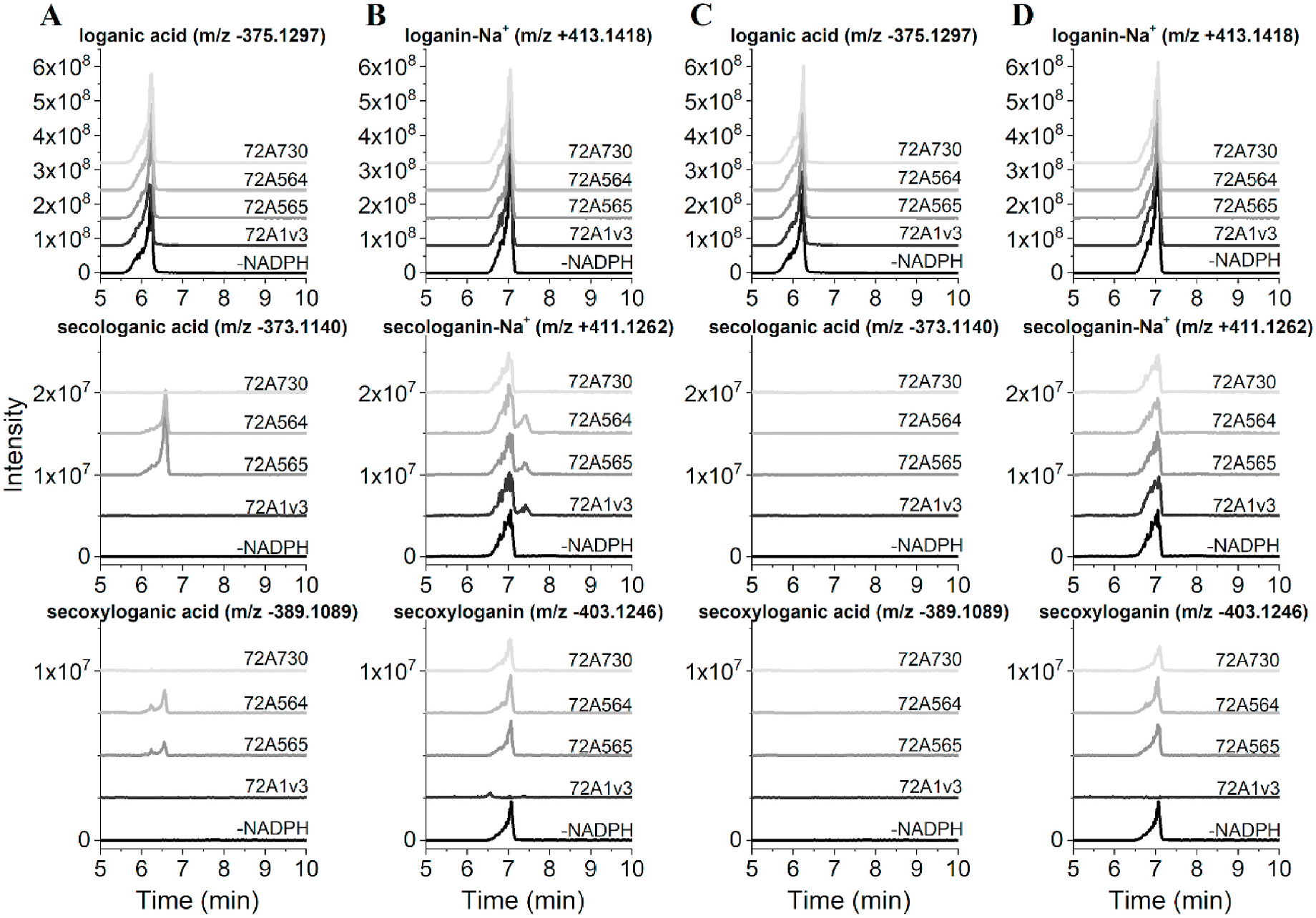
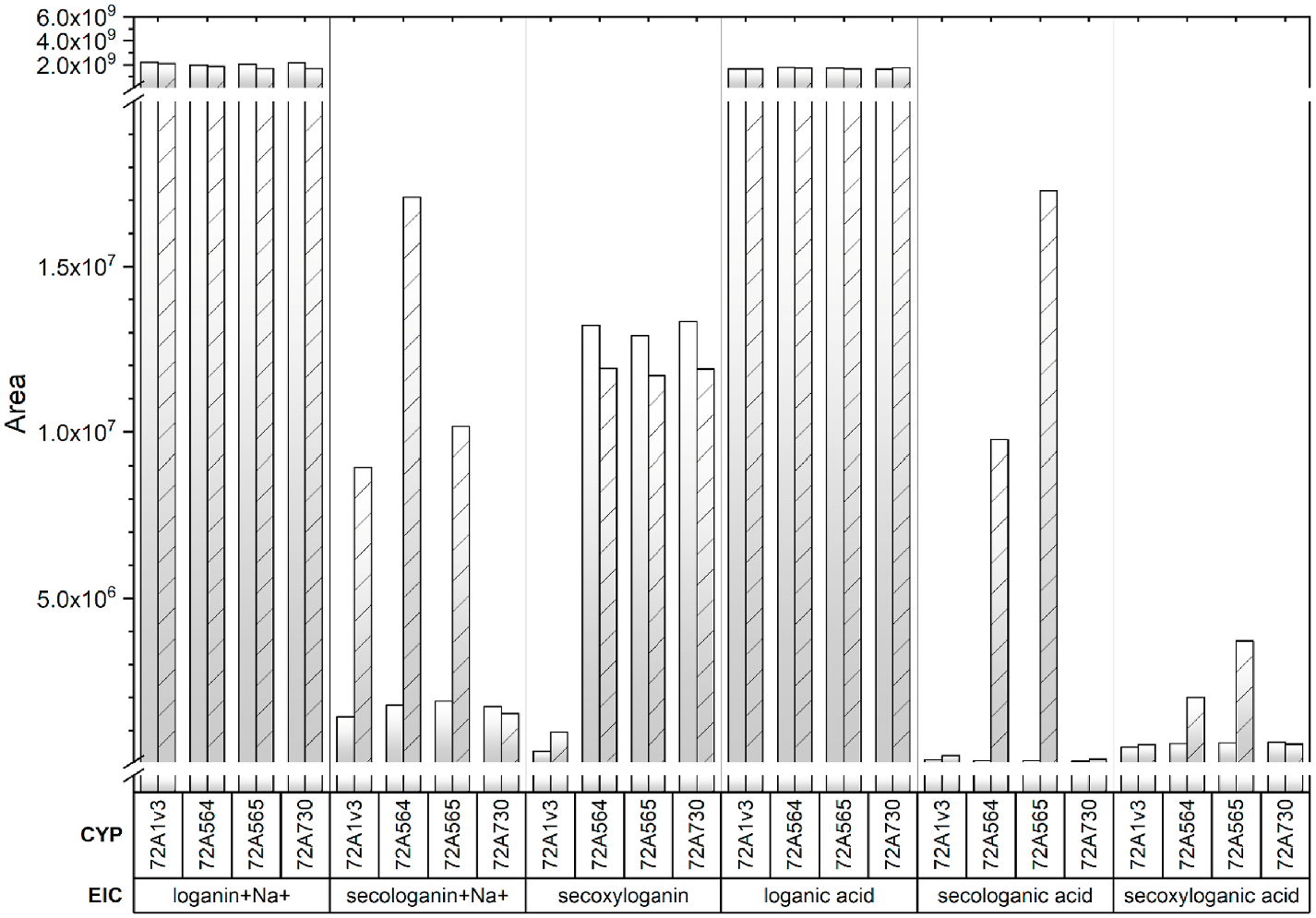
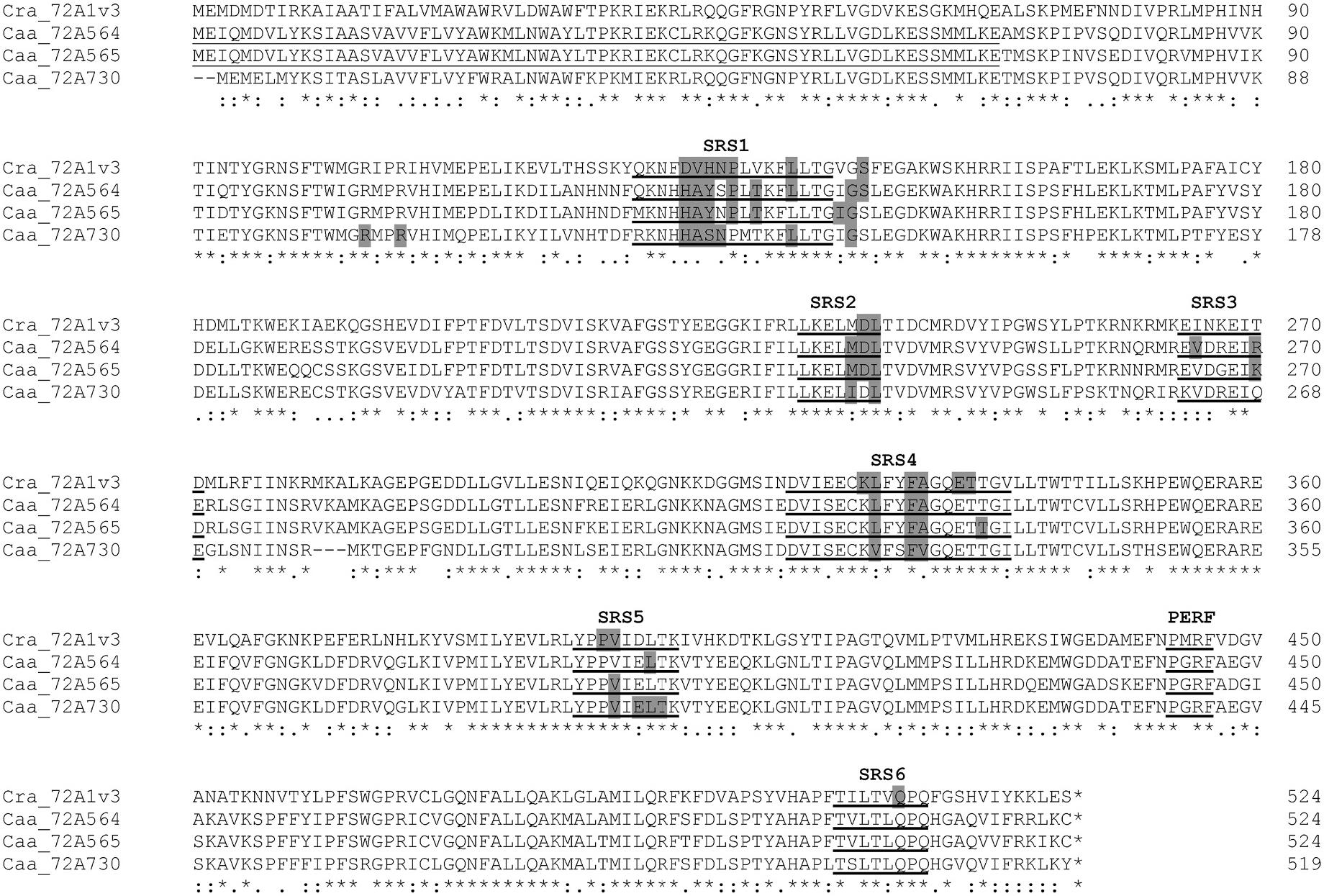
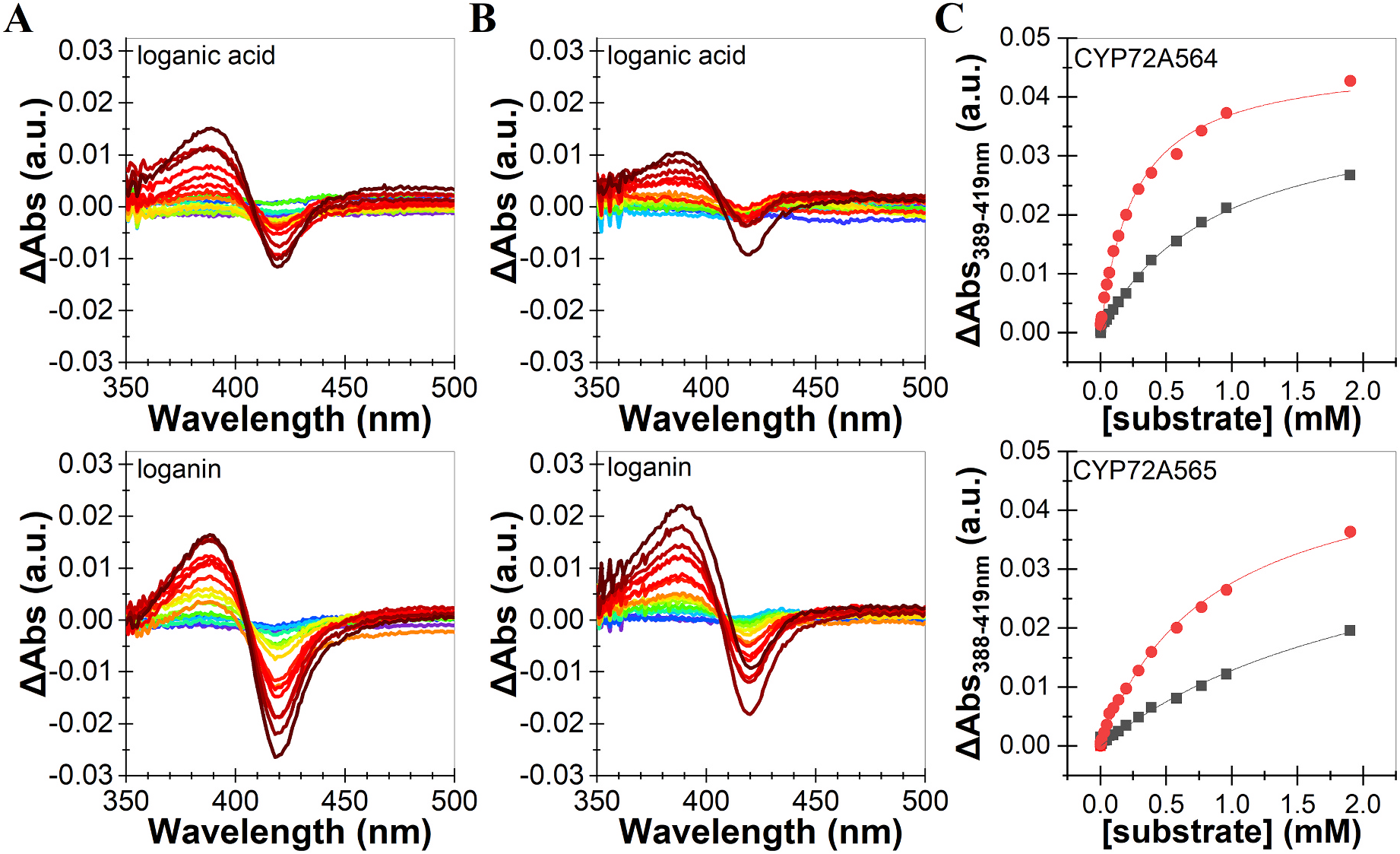
For initial analyses, the Camptotheca CYP 72A564, CYP72A565, CYP72A730 and Catharanthus CYP 72A1v3 were expressed in the WAT11 and WAT21 yeast strains, which have been engineered to constitutively express ATR1 or ATR2, respectively ( Urban et al., 1997). HPLC analyses of in vitro assays conducted with yeast microsomes followed by LC-MS analyses indicated that, not unexpectedly, both Camptotheca CYP 72A564 and CYP72A565 expressed in the WAT11 and WAT21 yeast strains converted loganic acid into secologanic acid ( Fig. 3 View Fig , S 1 View Fig , S 4 View Fig , S 5 View Fig ). In addition, both of these Camptotheca enzymes also converted loganin into secologanin (detected as its sodium salt). Catharanthus CYP 72A1v3 expressed in the WAT11 and WAT21 strains converted only loganin into secologanin and secoxyloganin ( Fig. S1 View Fig , S 2 View Fig , S 3 View Fig ). In contrast, the more divergent Camptotheca CYP 72A730 expressed in the WAT11 and WAT21 strains failed to metabolize either loganic acid or loganin ( Fig. 3 View Fig , S 1 View Fig , S 6 View Fig ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |