Heth, Cobb, 1898
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4861.4.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8B330C85-5B40-48EF-8C17-48332637C1C9 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4426640 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8569BD6C-FF84-1279-31A9-1DDAFA5EFB35 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Heth |
| status |
|
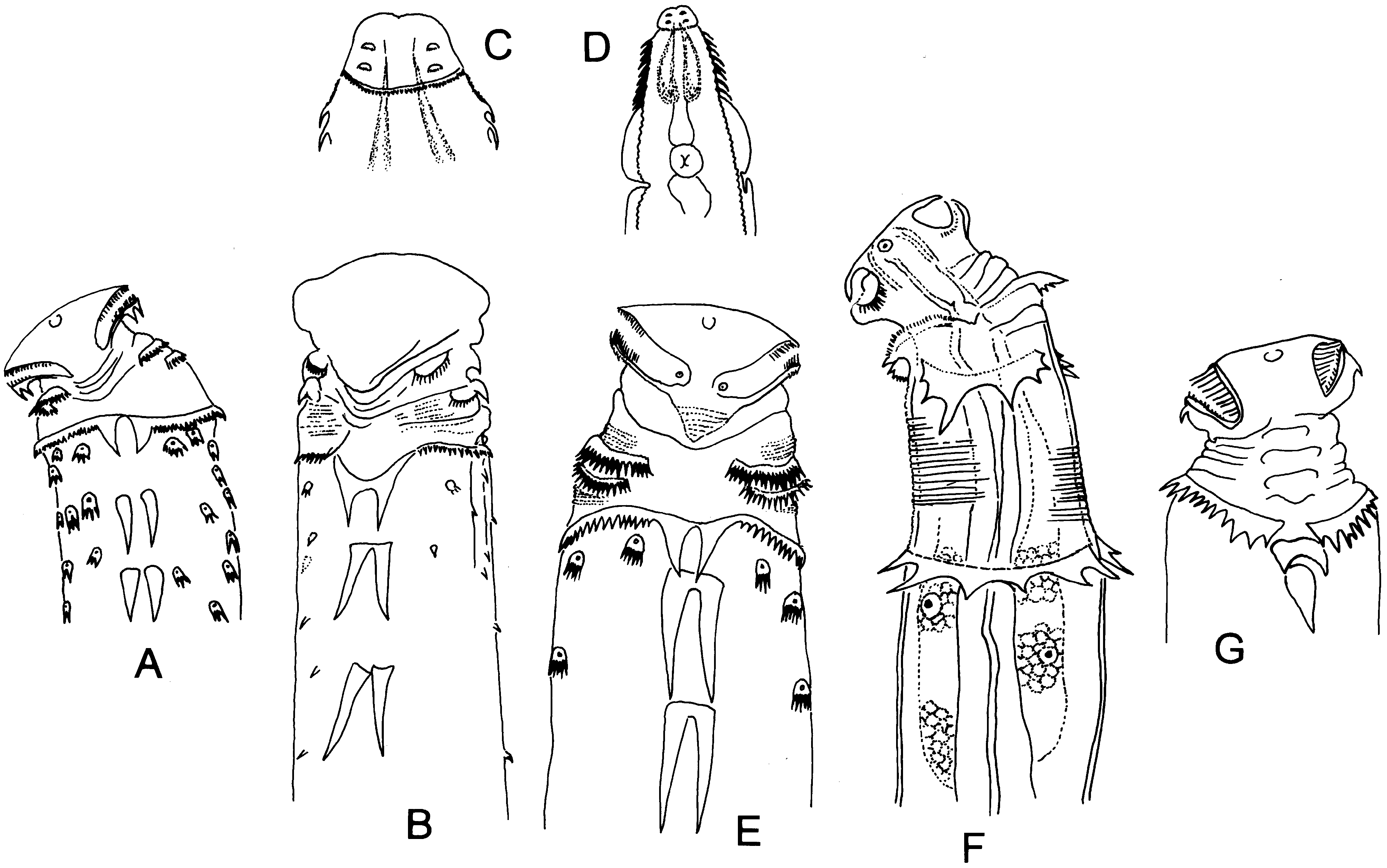
Key to group 1 Heth spp.
1. With one continuous cervical collar of spines around circumference of neck, usually with interruption by lateral cervical spines.............................................................................................. 2
- With two continuous cervical collars around circumference of neck; rows of eight similar-sized spines extending from cervical collar to level of esophageal isthmus ( Fig. 9E View FIGURE 9 ); lateral alae originating from posteriormost cervical spines and ending at base of tail; female length 1,326 –1,440 µm .................................................................. H. coyi
2. Lateral spines absent; cervical collar spines continuous, not interrupted laterally; numerous multi-cusped sensory papillae anterior and posterior to cervical collar ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9 ); length of female 1,070 –1,210 µm .......................... H. albertoi
- Lateral spines present; cervical collar interrupted or deeply notched laterally, often by prominent cervical spines.......... 3
3. One or two pairs of lateral spines present, posterior lateral spines sometimes single................................. 4
- Numerous lateral spines (>8 pairs) extending half the length of the esophagus; lateral alae wing-like.................. 15
4. Single posterior lateral spine............................................................................ 5
- Posterior lateral spines paired or absent.................................................................... 7
5. Cervical collar interrupted laterally ( Fig. 10G View FIGURE 10 ); length of female 1,550 –1,920 µm ...................... H. zeuglocantha
- Cervical collar notched or slightly produced laterally as two small, pointed lobes................................... 6
6. Cervical collar notched ( Fig. 9I View FIGURE 9 ); female length 1,730 -2,240 µm ....................................... H. konoplevi
- Cervical collar slightly prolonged as two small, pointed lobes ( Fig. 11D View FIGURE 11 ); females 1,420 –2,500 μm long....... H. hamatus
7. Lateral spine pairs broad, outer edges coarsely toothed....................................................... 8
- Lateral spine pairs slender, outer edges smooth............................................................. 9
8. Cervical collar with about 92 spines; two broad, strongly serrated pairs of lateral spines, their length and width about equal; length of female 2,600 –3,200 µm ( Fig. 9F View FIGURE 9 )......................................................... H. gordae
- Cervical collar with about 60 spines; anterior and posterior lateral spines much wider than long, posterior spines nearly encircling the body; female length 1,400 –1,700 µm ( Fig. 10F View FIGURE 10 )............................................. H. xarochae
9. With continuous anterior and posterior series of discontinuous spines around the circumference of the esophageal region ( Fig. 9J View FIGURE 9 ); length of female 1,731 –2,482 µm ........................................................... H. maicuru
- Post-collar spines confined to lateral region............................................................... 10
10. Cervical collar densely serrated and expanded away from body; posterior spines apparently absent; length of female 1,820 – 2,070 µm ( Fig. 9G View FIGURE 9 )....................................................................... H. hexaspinosum
- Cervical collar not expanded away from body; posterior lateral spines present.................................... 11
11. Large multi-cusped papillae (2–4 per side) only present anterior to cervical collar................................. 12
- Papillae present both anteriorly and posteriorly to cervical collar; with transverse rows of small spines in cervical folds... 13
12. Cervical, anterior and posterior lateral spines narrow, about equal in size ( Fig. 10B View FIGURE 10 ); length of holotype 2,800 µm ................................................................................................ H. perarmatum
- Cervical, anterior and posterior lateral spines progressively larger, broader and overlapping one another ( Fig. 9B View FIGURE 9 ); lateral winglike alae extending from posterior region of esophagus to anus; female length 1,753 –1,973 µm .......... H. amazonensis
13. Collar interrupted by long, slender cervical spines nearly reaching base of anterior lateral spines; anterior and posterior lateral spines long and slender ( Fig. 10E View FIGURE 10 ); female length 1,610 –1,990 µm .................................... H. spinosum
- Cervical collar interrupted by larger lateral spines not reaching base of anterior lateral spines........................ 14
14. Anterior and posterior spine pairs not sharing common bases ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 10A View FIGURE 10 ); female length 1,750 –1,830 µm .... H. mauriesi
- Anterior and posterior spine pairs with common bases....................................................... 15
15. Anterior lateral spines not reaching base of posterior spines ( Fig. 9D View FIGURE 9 ); female length 2,960 –3,090 µm ........... H. clunyi
- Anterior pair of lateral spines overlapping base of posterior pair; ( Fig. 9C View FIGURE 9 ); female length 1,880 –2,080 µm H. bifidispiculum
16. Prominent spines extending from posterior cervical collar to beginning of lateral alae ( Fig. 10C, D View FIGURE 10 ); lateral alae extending from posterior esophagus to tail; length of female 1,155 –1,165 µm ........................................ H. pinnatum
- Somatic spines extending from cephalic extremity to isthmus with first three spines small and remaining spines long and curved ( Fig. 9H View FIGURE 9 ); female length 1,740 –2,000 µm ...................................................... H. hispaniolae
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
InfraOrder |
Rhigonematomorpha |
|
SuperFamily |
Ransomnematoidea |
|
Family |