Anaxibia folia, Sankaran & Sebastian, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4363.3.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:15B32E25-7BCD-4AA3-9610-9B6E9AD5500B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5999298 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/854687F2-FF9C-FFDF-7DC8-FA11FF00AEC1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Anaxibia folia |
| status |
sp. nov. |
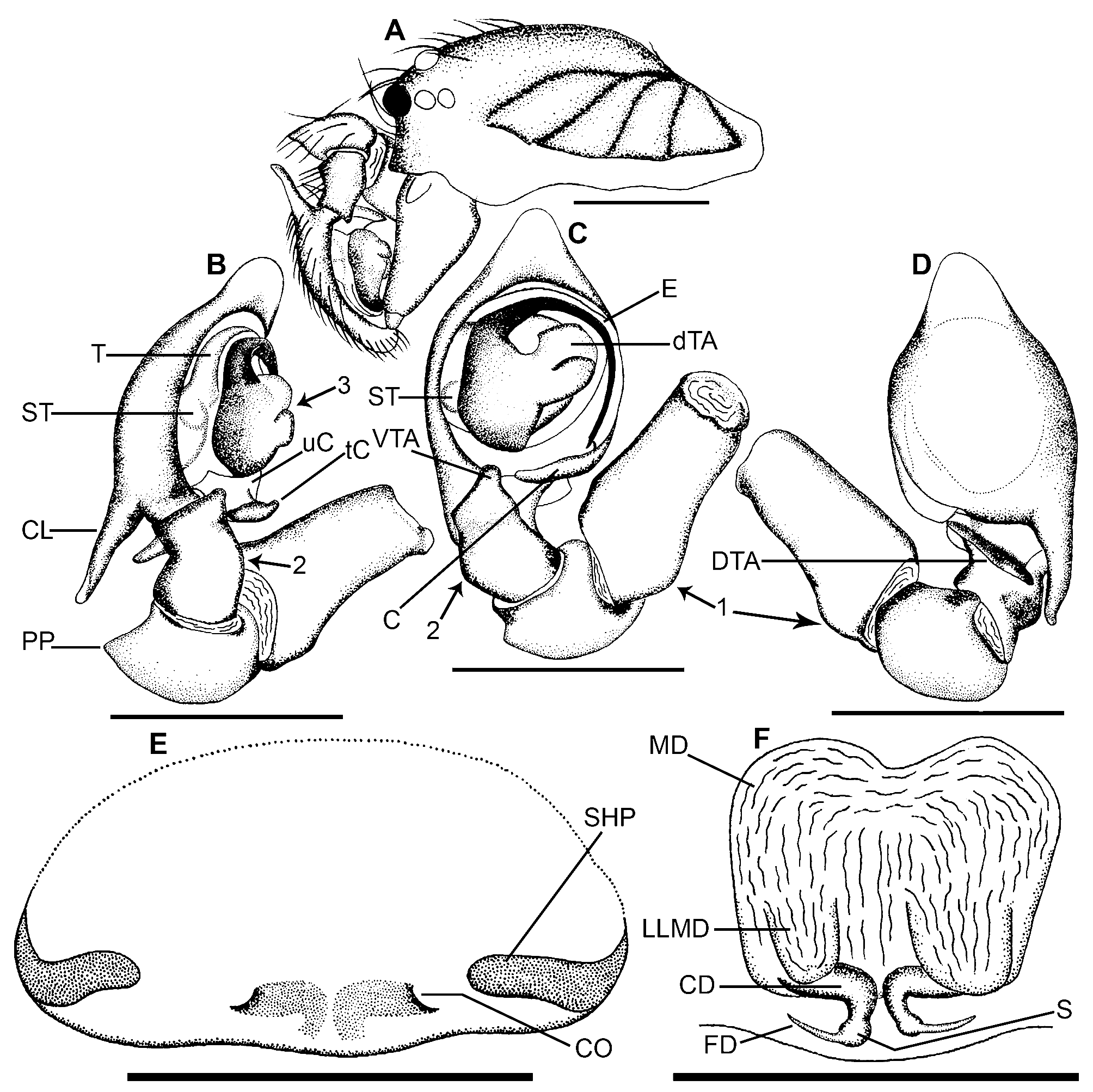
Anaxibia folia View in CoL spec. nov. ( Figs 1– 3 View FIGURES 1 View FIGURES 2 View FIGURE 3 )
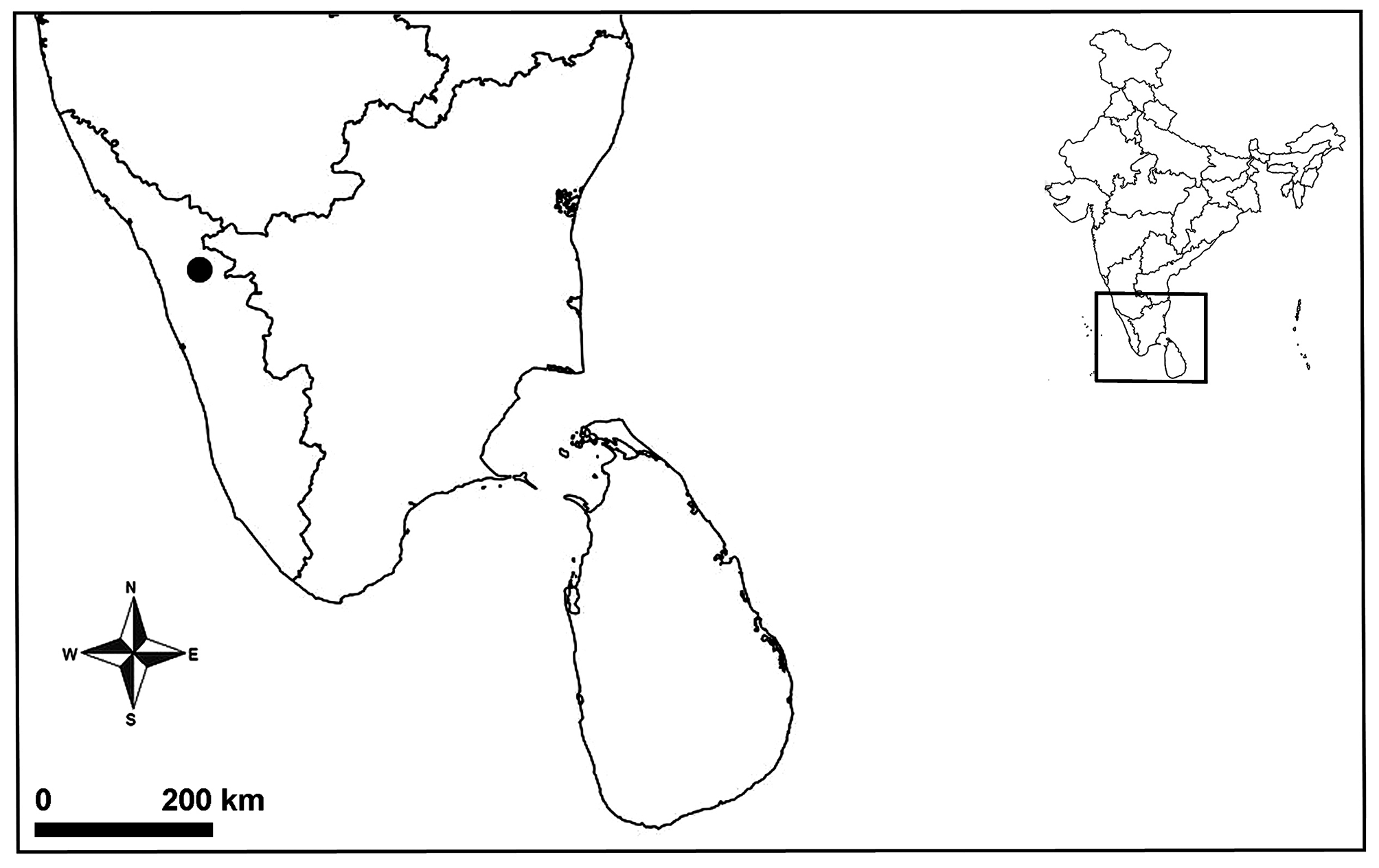
Type material: Holotype: Male ( ADSH2831 View Materials A), INDIA: Kerala: Malappuram, Nilambur , Canolly’s Plot , 11o16'06.17''N, 76o12'22.21''E, 20 m alt., 16 May 2013, P.M. Sankaran leg., from forest litter, by hand GoogleMaps . Paratypes: 1 male, 2 females, 1 juvenile ( ADSH2831 View Materials B), same data as for holotype GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The specific epithet is a neuter plural in apposition, derived from the leaf litter-dwelling habit of the new species. Latin: folium = leaf.
Diagnosis. Anaxibia folia spec. nov. is most similar to Anaxibia pictithorax ( Kulczyński, 1908) , but can be separated from the latter by the following combination of characters: cymbial caudal lobe (CL; Fig. 2B, D View FIGURES 2 ) almost straight and remaining covered by tibia in ventral view (cymbial caudal lobe of A. pictithorax with strong baso-prolateral bend and visible in ventral view), tibia with ventral bulging (tibia of A. pictithorax lacks ventral bulging), dorsal tibial apophysis (DTA; Fig. 2D View FIGURES 2 ) short and distant from cymbial caudal lobe ( A. pictithorax with broad DTA lying close to cymbial caudal lobe) and epigyne with sclerotised horizontal plates (SHP; Fig. 2E View FIGURES 2 ) and without lateral foveae (epigyne of A. pictithorax with lateral foveae and without sclerotised horizontal plates) (compare Figs 2B–E View FIGURES 2 with Kulczyński 1908: plate 23, figs 27–29). Females of A. folia spec. nov. can be separated from the females of A. rebai , the only Indian congener by lacking paired brown or black patches on the posterior half of mid-dorsal opisthosoma and epigyne with sclerotised horizontal plates and without lateral foveae, whereas the posterior half of mid-dorsal opisthosoma of A. rebai with paired conspicuous deep brown or black patches and epigyne with lateral foveae and lacks sclerotised horizontal plates (compare Figs 1B View FIGURES 1 , 2E View FIGURES 2 with Tikader 1966: figs 1a–b).
Description. Male ( holotype, Figs 1A, C, E View FIGURES 1 , 2A View FIGURES 2 ). Carapace brownish with dark brown striae, with cephalic region elevated more than thoracic region ( Figs 1A View FIGURES 1 , 2A View FIGURES 2 ). Fovea absent. Ocular area, clypeus, chelicerae, fangs, labium, maxillae, sternum brownish. AER recurved, PER straight; AME black, all others pearly white ( Fig. 1A View FIGURES 1 ). Boss prominent. Cheliceral promargin with three teeth, retromargin with one. Maxillae with reduced scopulae. Sternum covered with black hairs, weak medially; truncate between coxae IV, with blunt tip. Opisthosoma widely oval, creamy white with inconspicuous broad greyish patches, covered with a uniform mat of fine greyish hairs; dorsum provided with two pairs of sigillae ( Fig. 1A View FIGURES 1 ). Anal tubercle prominent ( Fig. 1C View FIGURES 1 ). Cribellum reduced ( Fig. 1C View FIGURES 1 ). Spinnerets creamy white with greenish shades only on posterior lateral spinneret; anterior lateral spinneret widest, posterior lateral spinneret longest ( Fig. 1C View FIGURES 1 ). Legs slender, spineless, setaceous, brownish with green shades; metatarsus IV with reduced calamistrum ( Fig. 1E View FIGURES 1 ). Body length 1.35. Prosoma length 0.56, width 0.50. Opisthosoma length 0.79, width 0.58. Eye diameters: ALE 0.03.
AME 0.04. PLE 0.02. PME 0.02. Eye interdistances: AME–AME 0.02. AME–ALE 0.02. AME–PME 0.02. PME–PME 0.05. PME–PLE 0.06. Clypeus height at AMEs 0.07, at ALEs 0.08. Chelicerae length 0.23. Measurements of pedipalp and legs. Pedipalp 0.60 [0.17, 0.11, 0.09, 0.23], I 1.73 [0.50, 0.18, 0.44, 0.36, 0.25], II 1.57 [0.46, 0.16, 0.37, 0.34, 0.24], III 1.35 [0.40, 0.14, 0.30, 0.30, 0.21], IV 1.52 [0.46, 0.15, 0.35, 0.36, 0.20]. Leg formula: 1243. Pedipalp ( Figs 2B–D View FIGURES 2 ): Palpal segments uniformly brownish, spineless; femur disto-dorsally with a short bulging ( Figs 2C–D View FIGURES 2 , 1 View FIGURES 1 st arrow ); patella retrolaterally with a short, triangular process (PP; Fig. 2B View FIGURES 2 ); tibia with ventral bulging ( Figs 2B–C, 2 View FIGURES 2 nd arrow), distoventrally with short, knob-like ventral tibial apophysis (VTA; Fig. 2C View FIGURES 2 ), with an obliquely oriented, plate-like dorsal tibial apophysis (DTA; Fig. 2D View FIGURES 2 ). Cymbium proximo-prolaterally with a moderately long caudal lobe (CL; Fig. 2B, D View FIGURES 2 ). Tegulum moderately large. Dictynid terminal apophysis stout, medio-retrolaterally placed (dTA; Fig. 2C View FIGURES 2 ), disto-ventrally with a horizontal ridge ( Fig. 2B View FIGURES 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 rd arrow). Subtegulum small, globular (ST; Figs 2B–C View FIGURES 2 ). Embolus originating prolaterodistally from tegulum, moderately long, with wedge-shaped proximad tip resting near base of conductor (E; Fig. 2C View FIGURES 2 ). Conductor originating retrolatero-proximally from tegulum, unmodified, smoothly curved (C; Figs 2B–C View FIGURES 2 ), with straight basal part and prolaterad apical part (uC, tC; Fig. 2B View FIGURES 2 ).
Female ( paratype, Figs 1B, D, F View FIGURES 1 ). Like male except the following. Carapace, ocular area, clypeus, chelicerae, fangs, maxillae, labium, sternum, legs, spinnerets, palps straw coloured ( Fig. 1B View FIGURES 1 ). Opisthosoma lacking greyish patches ( Fig. 1B View FIGURES 1 ). Cribellum well marked, unipartite ( Fig. 1D View FIGURES 1 ). Calamistrum prominent, uniseriate ( Fig. 1F View FIGURES 1 ). Palpal tibiae and tarsi bear spine-like macrosetae. Body length 1.59. Prosoma length 0.60, width 0.51. Opisthosoma length 0.99, width 0.65. Eye diameters: ALE 0.03. AME 0.03. PLE 0.02. PME 0.02. Eye interdistances: AME–AME 0.03. AME–ALE 0.02. AME–PME 0.02. PME–PME 0.05. PME–PLE 0.05. Clypeus height at AMEs 0.05, at ALEs 0.06. Chelicerae length 0.21. Measurements of palp and legs. Palp 0.53 [0.15, 0.08, 0.10, 0.20], I 1.88 [0.57, 0.19, 0.46, 0.41, 0.25], II 1.75 [0.54, 0.18, 0.41, 0.38, 0.24], III 1.54 [0.49, 0.17, 0.33, 0.34, 0.21], IV 1.82 [0.59, 0.19, 0.42, 0.40, 0.22]. Leg formula: 1423. Copulatory organ ( Figs 2E–F View FIGURES 2 ): Epigyne simple, hirsute, widely flat, laterally with distinct, sclerotised, smoothly curved horizontal plates (SHP; Fig. 2E View FIGURES 2 ). Copulatory openings crescent-like, widely separated, lying near to the posterior border of epigyne (CO; Fig. 2E View FIGURES 2 ). Copulatory ducts short, sclerotised, basally wide, basal part remains contiguous with an enlarged sac-like median diverticulum (CD; Fig. 2F View FIGURES 2 ); median diverticulum roughly squarish with anterior concavity, postero-laterally with paired, broad lobes overhanging to the basal part of copulatory ducts (MD, LLMD; Fig. 2F View FIGURES 2 ). Spermathecae small, sclerotised, circular (S; Fig. 2F View FIGURES 2 ). Fertilization ducts narrow, angular, originating postero-laterally from spermathecae (FD; Fig. 2F View FIGURES 2 ).
Distribution. Only known from the type locality ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ).
Note. Males of A. rebai are misidentified and belonging to Nigma shiprai ( Tikader, 1966) (World Spider Catalog 2017).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |