Prosadenoporus Bürger, 1890
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222930802130286 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/816E8F49-2206-FFBB-3102-FB4FFD6C21B3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Prosadenoporus Bürger, 1890 |
| status |
|
Neonemertes Girard, 1893 . New synonymy. Type species Tetrastemma agricola Willemoes-Suhm, 1874 by monotypy.
Pantinonemertes Moore and Gibson, 1981 (part). New synonymy. Type species Pantinonemertes winsori Moore and Gibson, 1981 by original designation.
Type species
Prosadenoporus arenarius Bürger, 1890 , by subsequent designation ( Moore and Gibson 1988).
Etymology
‘‘Pro’’5before, forward, in front of, L.; ‘‘adeno, adenos’’5gland, G.; ‘‘poros’’5hole, G. Likely refers to the presence of well-developed frontal organ [anterior pore] through which mucus cephalic glands discharge.
Diagnosis
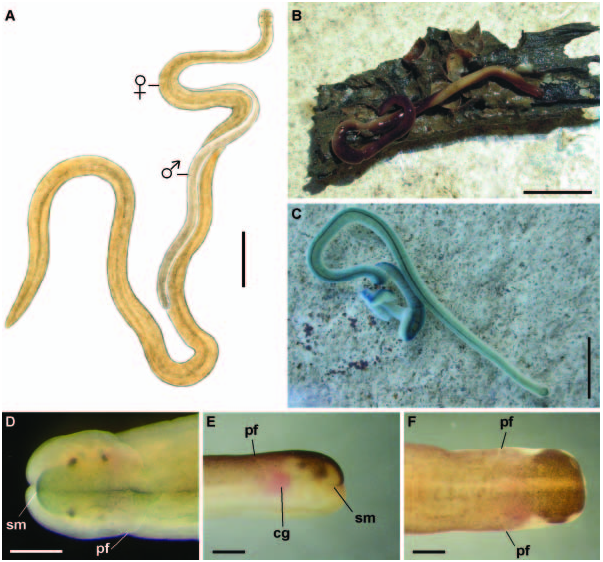
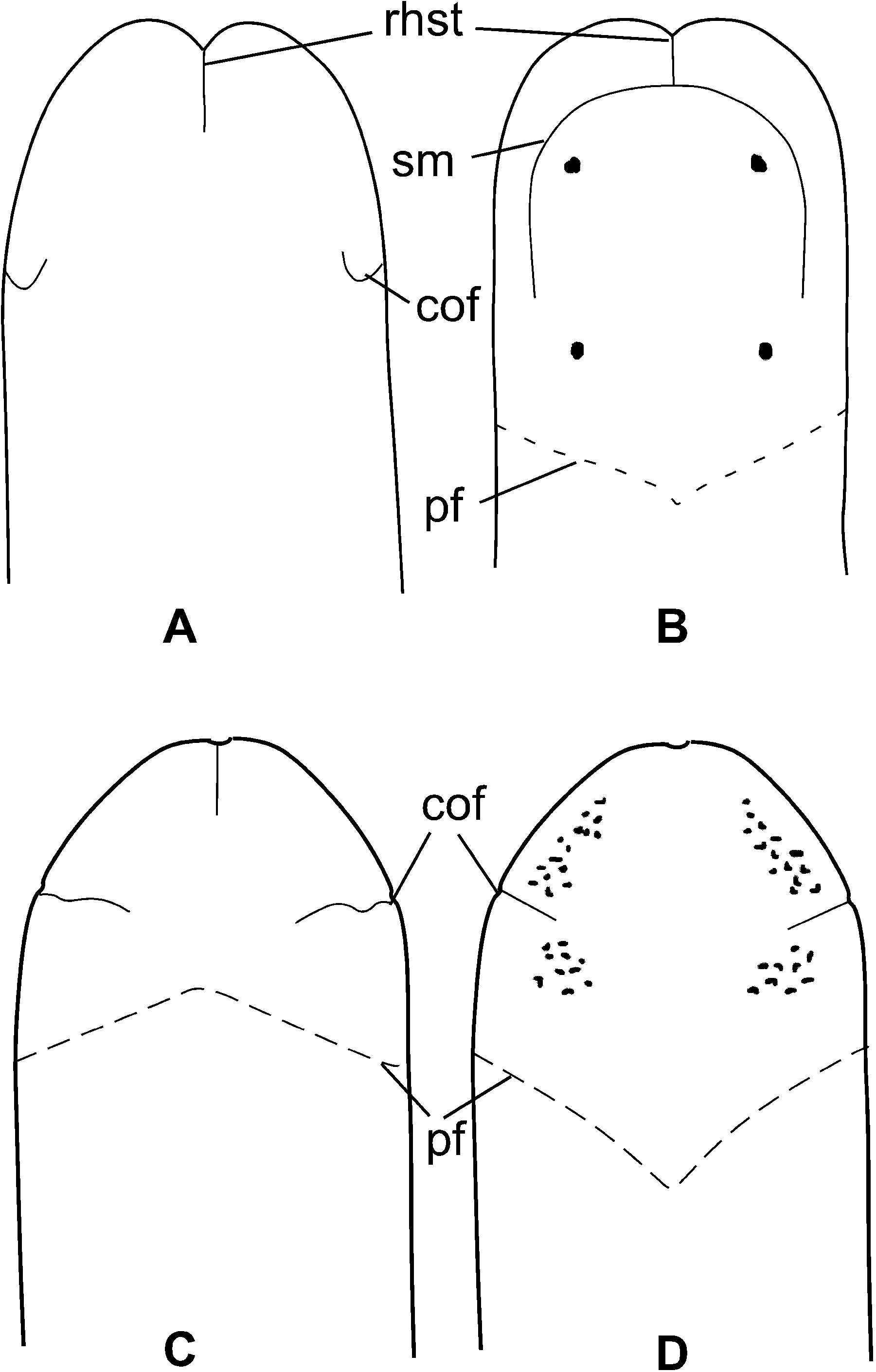
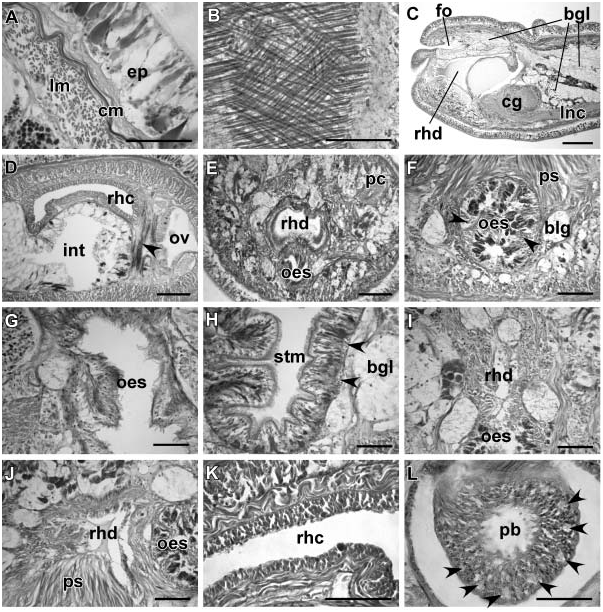
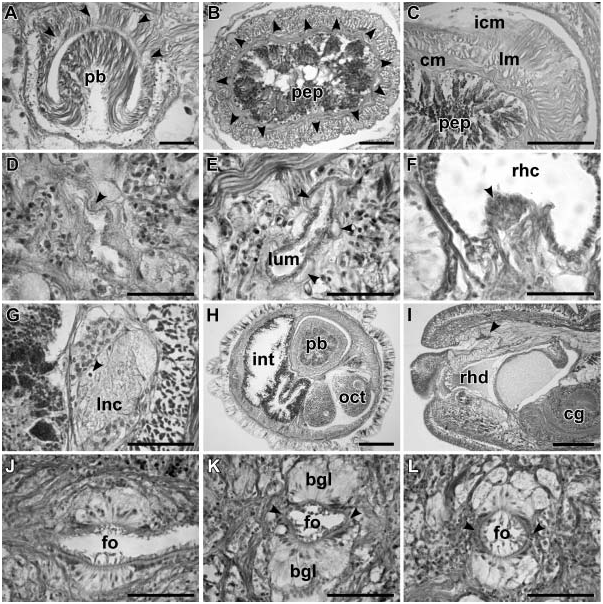
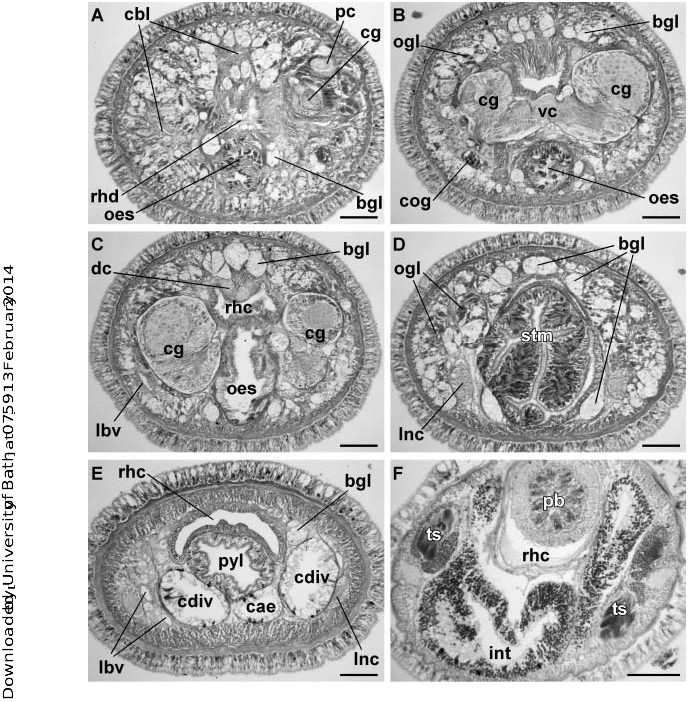
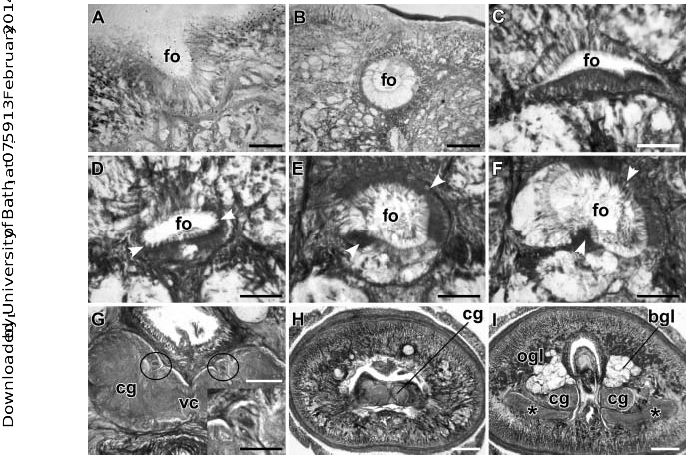
Monostiliferous marine, brackish-water, semi-terrestrial or terrestrial hoplonemerteans with a horizontal cephalic epithelial fold (prosorhochmid smile) ( Figures 1D, 1E View Figure 1 and 2B View Figure 2 ). Four eyes ( Figures 1A, 1D, 1E View Figure 1 and 2B View Figure 2 ). Body-wall musculature well developed with a delicate layer of diagonal muscles between outer circular and inner longitudinal muscle layers ( Figures 3A and 3B View Figure 3 ). Rhynchocoel full body-length, with wall composed of distinct outer circular and inner longitudinal muscle layers ( Figure 3K View Figure 3 ). Proboscis small or massive, may be used for rapid locomotion. If massive, proboscis often with increased number of proboscis nerves and accessory stylet pouches, longer stylet (S) and basis (B) and decreased S:B ratio ( Table 3). Tubular frontal organ is long and exceptionally well developed, with laterally differentiated epithelium ( Figures 3C View Figure 3 , 4 View Figure 4 I–L, 5G–I, 7A–I, 7L, 8A–D and 9C–F). Cephalic glands extensive, reaching into stomach-pylorus region and containing basophilic (mucus) components ( Figure 3C View Figure 3 ) discharging through frontal organ and via improvised epidermal ducts and acidophilic (proteinaceous) components, staining red (red glands) ( Figure 5H) and orange with Mallory trichrome and its modifications (orange-G glands) ( Figures 5J, 6B and 6D View Figure 6 ). Proteinaceous cephalic glands discharge via improvised ducts scattered throughout epidermis. Cerebral sensory organs small, anterior or antero-lateral to brain, with simple un-forked canal, opening ventro-laterally into reduced cerebral organ furrows ( Figures 2A View Figure 2 , 5A, 5B and 5J). Neurochord cells and neurochords present in some species ( Figures 5E, 5F, 7J View Figure 7 , 8E, 8F View Figure 8 and 9G View Figure 9 ), but not necessarily together. Lateral nerve cords without accessory nerves (e.g. Figures 4G View Figure 4 and 7J View Figure 7 ). Oesophagus divisible into anterior region supplied with acidophilic glands ( Figures 3F, 3I, 3J View Figure 3 , 5J, 6A and 6B View Figure 6 ), and posterior non-glandular region ( Figures 3G View Figure 3 and 6C View Figure 6 ). Caecum long, anteriorly bifid, with numerous lateral diverticula on each side ( Figure 6E View Figure 6 ). Blood system with three main longitudinal vessels, without transverse connectives; mid-dorsal blood vessel with single vascular plug ( Figure 4F View Figure 4 ); cephalic vascular loop recurved. Extracellular matrix (parenchyma) may be very extensive, especially in large species. Excretory system well developed, with binucleate terminal nephridial cells reinforced by transverse support bars ( Figures 5C, 5D and 7K View Figure 7 ), thin-walled canals and large number of inconspicuous nephridiopores. Gonochoric or hermaphroditic. Oviparous or viviparous.
Composition
Prosadenoporus includes nine species: P. agricola ( Willemoes-Suhm, 1874) comb. nov., P. arenarius Bürger, 1890 , P. spectaculum ( Yamaoka, 1940) comb. nov., P. winsori ( Moore and Gibson, 1981) comb. nov., P. enalios ( Moore and Gibson, 1981) comb. nov., P. mooreae ( Gibson, 1982b) comb. nov., P. mortoni ( Gibson, 1990) comb. nov., P. fujianensis ( Sun, 2001) comb. nov., and P. floridensis sp. nov.
Geographic distribution
Atlantic coast of the USA (FL) and Bermuda; Caribbean ( Belize); Pacific coast of USA (Puget Sound, WA to CA); Hong Kong, China (Fujian Province), north-eastern coast of Australia (Queensland), Indonesian Islands (Noordwachter
Island off Sulawesi and Ambon Island [Amboina]), Palau Bidan (Kedah Province) off Malay Peninsula, Laccadive Islands.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Prosadenoporus Bürger, 1890
| Maslakova, Svetlana A. & Norenburg, Jon L. 2008 |
P. agricola ( Willemoes-Suhm, 1874 )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. spectaculum ( Yamaoka, 1940 )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. winsori ( Moore and Gibson, 1981 )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. enalios ( Moore and Gibson, 1981 )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. mooreae ( Gibson, 1982b )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. mortoni ( Gibson, 1990 )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. fujianensis ( Sun, 2001 )
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
P. floridensis
| Maslakova & Norenburg 2008 |
Pantinonemertes
| Moore and Gibson 1981 |
Pantinonemertes winsori
| Moore and Gibson 1981 |
Neonemertes
| Girard 1893 |
Prosadenoporus Bürger, 1890
| Burger 1890 |
Prosadenoporus arenarius Bürger, 1890
| Burger 1890 |
Prosadenoporus
| Burger 1890 |
P. arenarius Bürger, 1890
| Burger 1890 |
Tetrastemma agricola
| Willemoes-Suhm 1874 |