Elaphoidella longiramus, Watiroyram & Janpong & Sanoamuang, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5138.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C18EFDC5-AD6B-479D-AB4D-138BC6454E91 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6560594 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9582C0D8-03CC-4A52-9CD7-C3A1F051CAE3 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:9582C0D8-03CC-4A52-9CD7-C3A1F051CAE3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Elaphoidella longiramus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Elaphoidella longiramus sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:9582C0D8-03CC-4A52-9CD7-C3A1F051CAE3
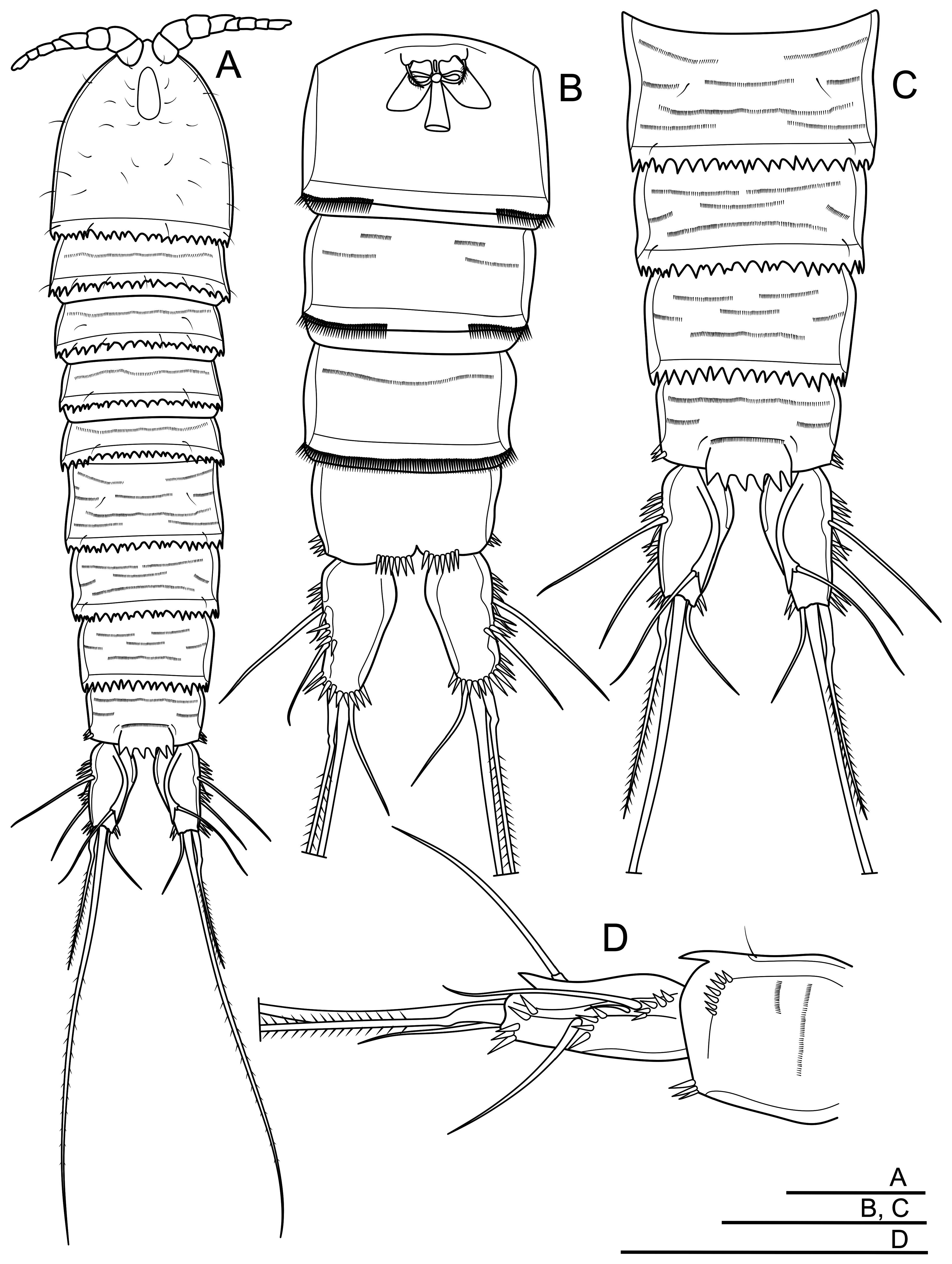
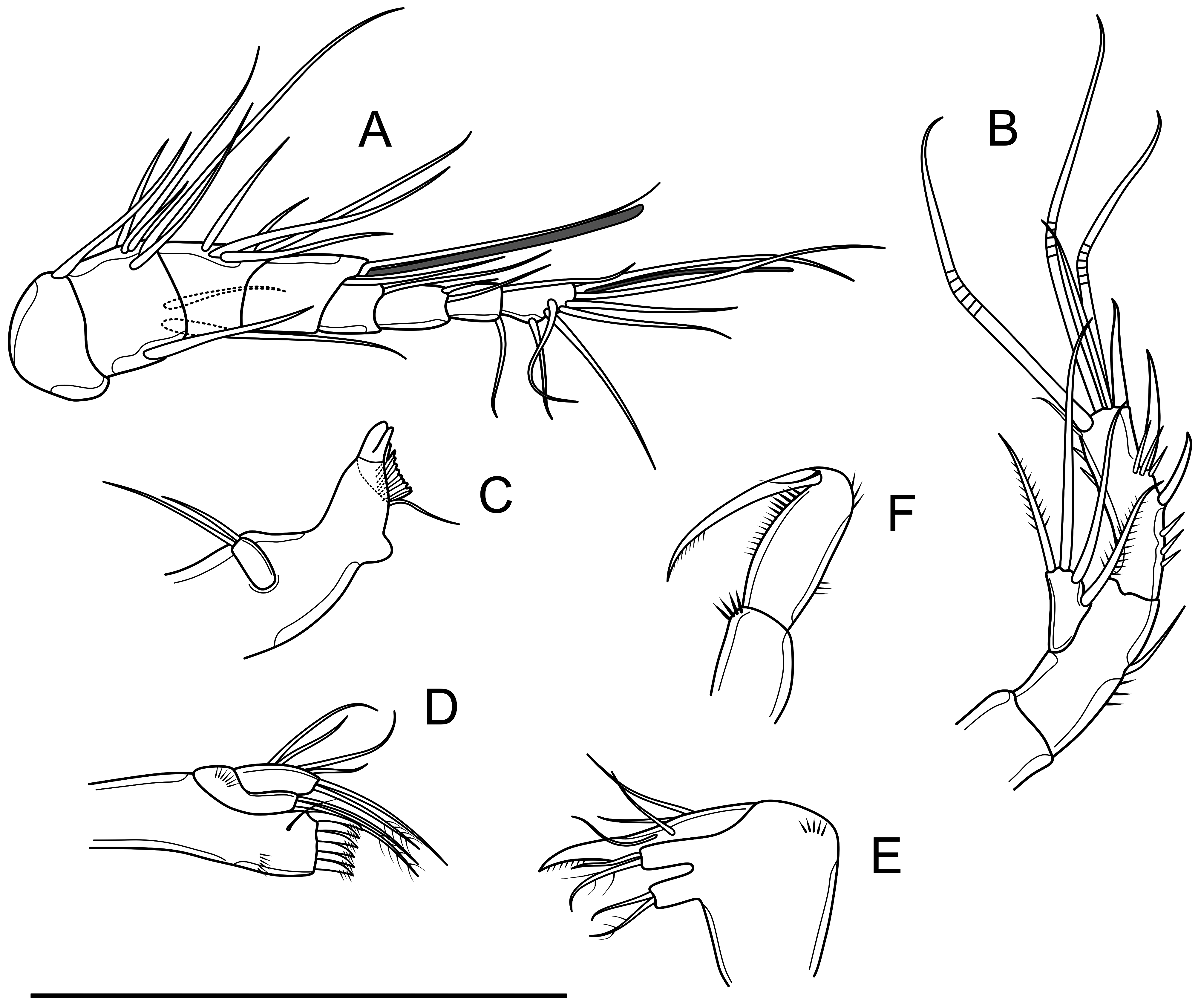
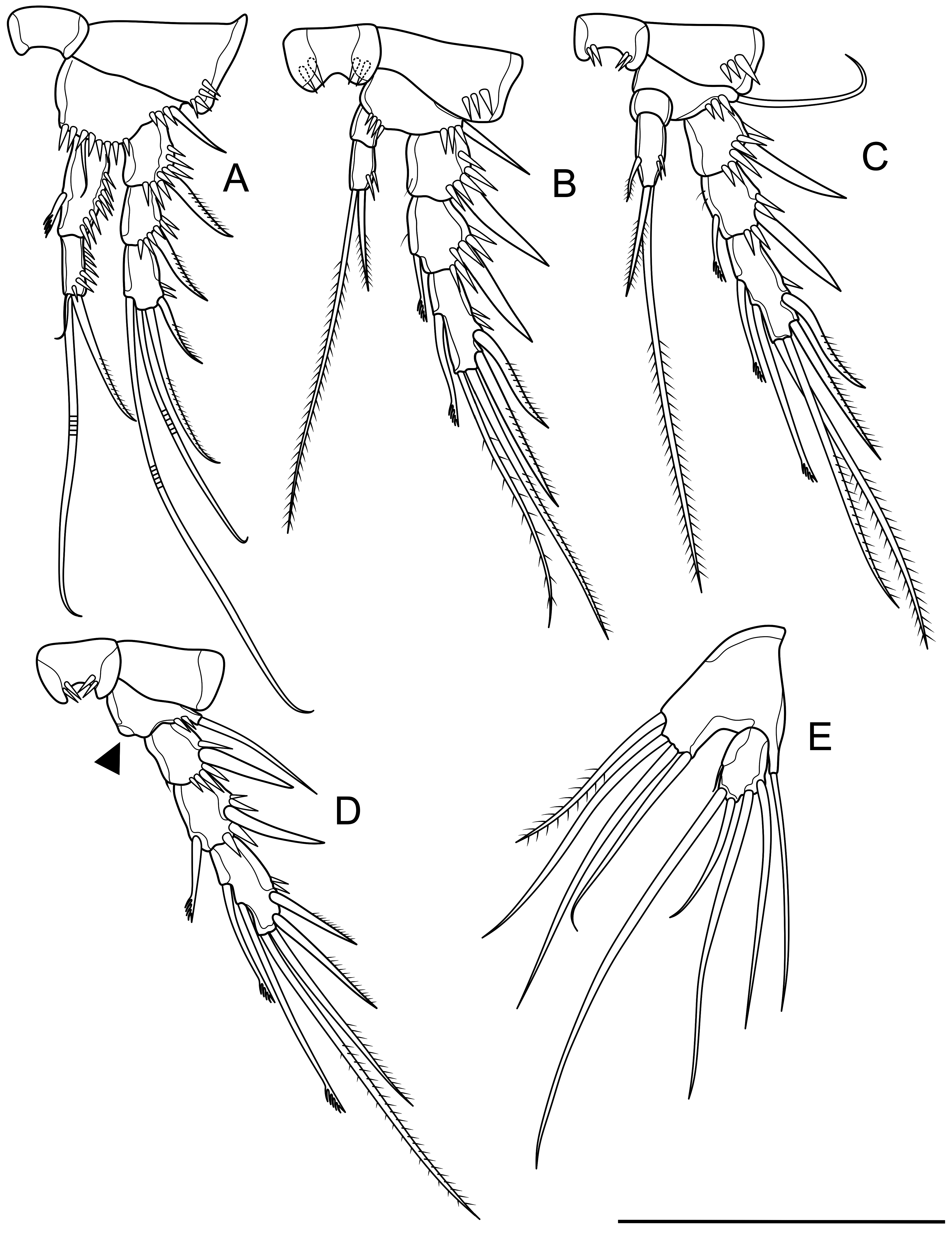
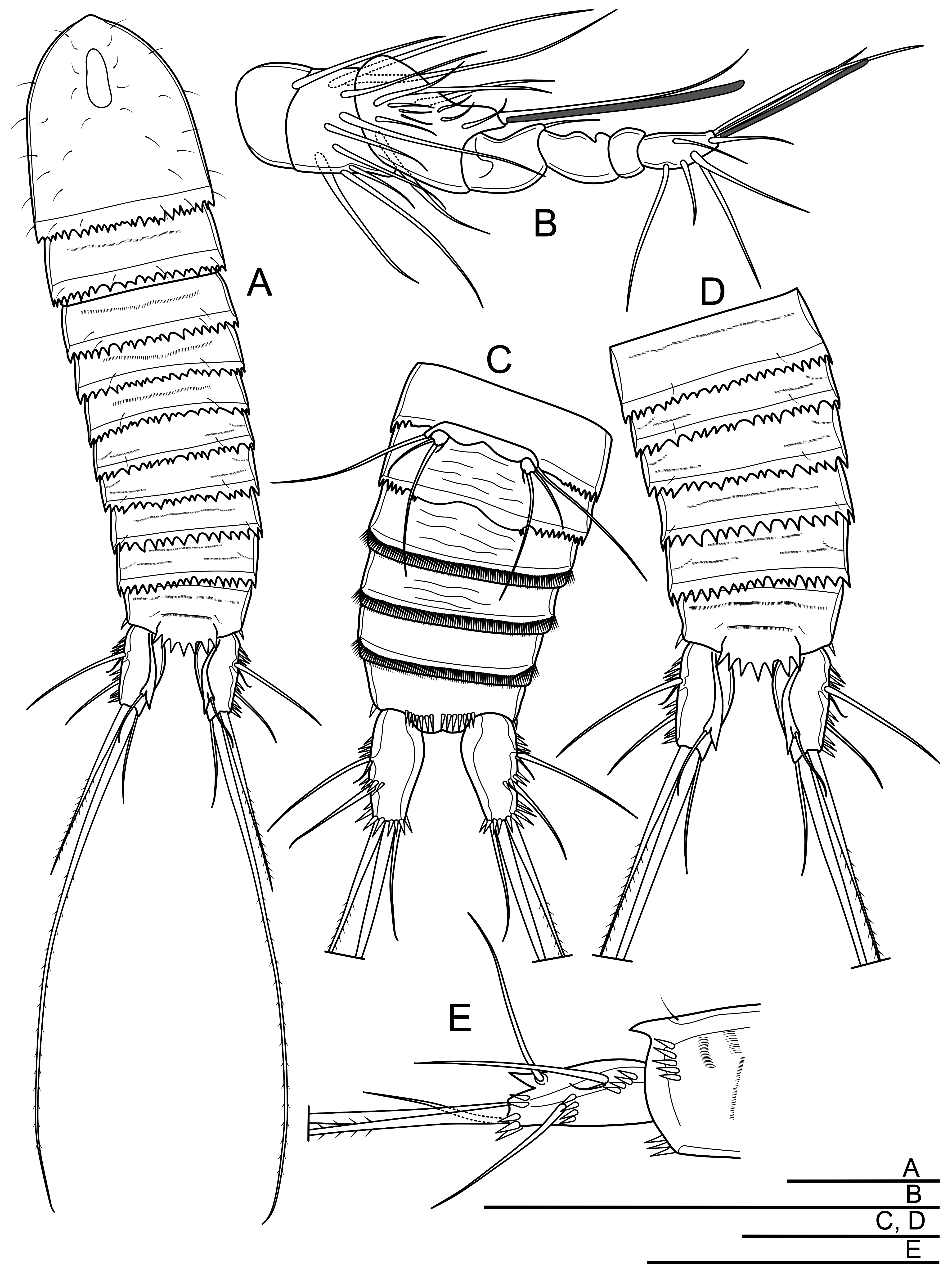
( Figs. 2-6 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 )
Type locality. Thae Wa Phithak Cave , Chong Sarika Subdistrict , Patthana Nikhom District, Lopburi Province, central Thailand. Cave entrance coordinates: 14° 47' 39.2" N, 100° 52' 35.0" E, elevation 267 m a.s.l. GoogleMaps
Species diagnosis.− Elaphoidella longiramus sp. nov. has the following characteristics: 1) urosomites with deeply serrated-free posterior margins; 2) anal somite with seven ventral spinules at the base of the caudal ramus; 3) anal operculum with 6-7 teeth on the free margin; 4) caudal ramus long, 2.0 times as long as wide; 5) P1 has a two-segmented Enp; 6) P4 has a highly reduced Enp, which is represented by a segmental vestige; 7) P2–P4 Exp-3 with armature formula 5.6.6. Female with armature formula on P2-P4 Enp-2 as 2.3.0, P5 with four setae on Exp and baseoendopod, and P6 with a single seta. Male with only single seta on P2 Enp-2, with transformed P3-P4 (P3 with three-segmented Enp, Enp-3 with two long setae; P4 Exp-3 with one transformed spine), P5 with three exopodal setae, and P6 with two tiny spines.
Material examined. Holotype: one adult female, dissected and mounted on a slide (THNHM-Iv-18769). Allotype: one adult male, dissected and mounted on a slide (THNHM-Iv-18770). Paratypes: three adult females (THNHM-Iv-18771) and three adult males (THNHM-Iv-18772), stored in 70% ethanol. The material was collected from the type locality by W. Janpong on December 10, 2019.
Etymology. The new species name " longiramus " is an adjective, referring to the two elongated caudal rami, the longest caudal rami in the genus Elaphoidella recorded from Thailand.
Description of adult female. Body length, measured from anterior edge of rostrum to posterior edge of caudal rami, 460-600 µm (mean = 550 µm, n = 5). Habitus ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ) elongated, cylindrical, preserved specimens colorless. Naupliar eye not discernible. Rostrum small. Cephalothorax with dorsally deeply-serrated posterior margin, with numerous pairs of sensilla, integumental window oval-shaped. Prosomites 2-4 and urosomites have several rows of longitudinal small spinules, and a deeply and irregularly serrated posterior margin dorsally ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Genital double-somite about 0.8 times longer than wide, with two pairs of sensilla and several rows of tiny spinules dorsally ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ), with a discontinuous row of spinules on posterior margin ventrally ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). Genital complex with a single large median copulatory pore and a bell-shaped copulatory duct, seminal receptacles symmetrically, well-developed ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). Urosomite 3 has one pair of dorsal sensilla and a discontinuous row of spinules ventrally. Urosomite 4 with a latero-ventral row of distal spinules. Anal somite with seven ventral strong spinules at base of each caudal ramus ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ), and 6−7 transverse rows of strong spinules laterally ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). Anal operculum with a row of tiny spinules basally, six large triangular teeth on free distal margin, slightly overreaching posterior end of anal somite, and one pair of sensilla dorsally near anal operculum basally ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ).
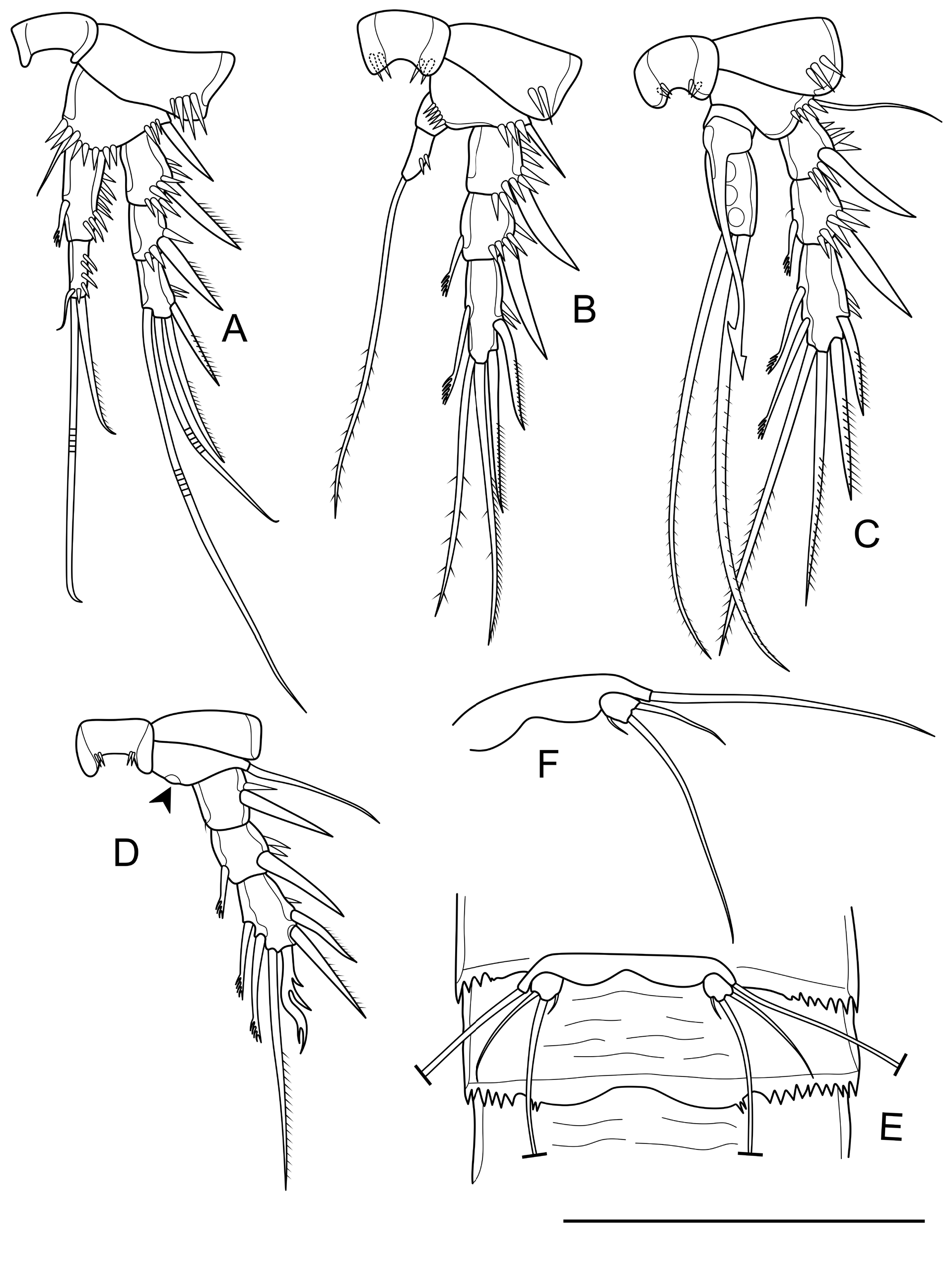
Caudal rami ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A-D) relatively conical, flattened dorsoventrally, about 2.0 times as long as wide, with a dorsal keel well-developed and with an acute distal tip, with several strong ventral spinules on distal margin and a few strong lateral spinules at insertion of setae II-III. Each ramus armed with seven setae (setae I, II, III, VI and VII bare). Anterolateral accessory seta (I) small and thin, inserted below seta II. Anterolateral seta (II) inserted at about one-third of ramus length with an oblique line of 4-5 spinules near its insertion. Posterolateral seta (III) slightly shorter than seta II, inserted laterally at about two-third of ramus length, with four strong spinules close to its insertion. Outer terminal seta (IV) about 1.5 times as long as caudal ramus, spiniform-shaped, without breaking plane. Inner terminal seta (V) longest, pinnate, and about two-third of its length, with no visible breaking plane. Inner accessory seta (VI) about as long as caudal ramus. Dorsal seta (VII) as long as seta II, inserted dorsally at about two-third of caudal ramus length.
Antennule ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ) relatively short, eight-segmented, not reaching posterior margin of cephalothorax. Aesthetasc on segment 4, cylindrical, with a rounded tip surpassing distal segment. Second aesthetasc on segment 8, long and thin. Each aesthetasc fused with one seta at its base. Setal formula: 1, 8, 5, 1+(1+A), 1, 2, 2, 6+(1+A).
Antenna ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ) comprised of coxa, allobasis, one-segmented Exp and Enp. Coxa shorter than wide, unarmed. Allobasis with one seta and three tiny spinules on abexopodal margin. Exp with two apical setae and two subapical setae. Enp with two strong inner spines and several spinules of various lengths. Distal margin of Enp with one strong spine, normal seta, and three geniculate setae. Outer margin of Enp with two spinules and one short seta on distal corner.
Mandible ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ) with one short seta at the corner dorsally and two strongly chitinized teeth on gnathobase. One-segmented mandibular palp, with two smooth setae on distal margin.
Maxillule ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ) comprised of praecoxa, coxa and basis. Praecoxal arthrite with six strong spines, a bare seta and tiny spinules on anterior part. Coxa and basis, each with one bare seta and one pinnate seta on endite distally. Exp and Enp reduced to four bare setae.
Maxilla ( Fig. 3E View FIGURE 3 ) with a row of outer spinules. Syncoxa with two endites, each with one normal and one pinnate setae distally. Allobasis drawn out into a slightly curved claw distally, with one seta on median margin. Enp reduced to three smooth setae.
Maxilliped ( Fig. 3F View FIGURE 3 ) composed of syncoxa, basis and one-segmented Enp. Syncoxa with four spinules on distal margin. Basis about twice as long as wide, with one group of spinules at about one-third, and one distal on outer margin, and row of several spinules along inner margin. Enp as long as basis, drawn out into a unipinnate claw, with one small seta on its base.
P1-P4 Exp three-segmented, Enp two-segmented (except P4 without Enp). Armature formula of legs 1-4 as follows (inner-outer seta/spine; inner-apical-outer seta/spine; Arabic numerals represent setae, Roman numerals represent spines):
P1 ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ) intercoxal sclerite smooth. Coxa with a few strong spinules at outer distal margin. Basis with one robust outer spine and one slender inner seta. Two-segmented Enp, with several spinules on outer margin. Enp-1 long, reaching to end of corresponding Exp-2, with a robust inner spiniform seta. Enp-2 shorter than Enp-1, reaching slightly below end of corresponding Exp-3, with three apical setae; outermost seta unipinnate, middle seta geniculate, about 1.5-2.3 times as long as outermost seta, innermost seta bare and shortest. Three-segmented Exp, each segment with one robust outer unipinnate spine and several lateral spinules. Exp-3 with one inner subapical geniculate seta, two apical geniculate setae, and one outer unipinnate spine.
P2 ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ) intercoxal sclerite with a coupler of two strong spinules on anterior surface. Coxa with a few strong spinules at outer distal margin. Basis with a robust outer spine. Enp two-segmented. Enp-1 small and short, unarmed. Enp-2 with 2-3 spinules on inner margin and one slender spine apically and a pinnate seta about 3.0 times as long as outer spine. Exp-1 as long as Exp-2, each segment with outer robust spine. Exp-2 with an additional inner feather-like seta. Exp-3 about 2.5 times as long as wide, with one inner feather-like seta. Exp-3 has two strong outer spinules and two outer unipinnate spines sub-distally, two pinnate setae apically, and one inner feather-like seta.
P3 ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ) intercoxal sclerite and coxa similar to P2. Basis with a long outer seta. Enp-1 bare, shorter than wide. Enp-2 twice as long as wide, with a short inner spiniform seta, two outer spinules, one pinnate seta and one spiniform seta apically (spine slender, about 1.5 times as long as Enp-2; seta about 6.0 times as long as Enp-2). Exp- 1 as long as Exp-2, with a robust outer spine. Exp-2 with one short inner feather-like seta and one robust outer spine. Exp-3 with two inner apically feather-like setae, two outer unipinnate spines, and two apical pinnate setae.
P4 ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ) intercoxal sclerite similar to P2, coxa unornamented. Basis with a long outer seta. Enp reduced, represented by a segmental vestige. Three-segmented Exp, Exp-1 with a robust outer spine, Exp-2 with a robust outer spine and one additional inner feather-like seta. Exp-3 with spinules and two spiniform spines on outer margin; two unipinnate and pinnate setae apically; and two inner feather-like setae.
P5 ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ) intercoxal sclerite small and unornamented. Baseoendopod and Exp separated. Basoendopod welldeveloped, overreaching one half of Exp, with four long setae: innermost seta pinnate, remaining setae bare; second outermost longest. Exp small, oval-shaped, with four bare setae of unequal lengths: second innermost seta shortest, about 2.2-2.5 times as long as Exp length; with one seta-like spinule on inner margin of Exp.
P6 ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ) fused into a small single plate, with a short pinnate seta on each side of copulatory pore.
Egg sac: not found.
Description of adult male. Body length slightly shorter than in female, 470-560 µm (mean = 510 µm, n = 5), measured from anterior edge of rostrum to posterior edge of caudal rami. Body colorless, naupliar eye not discernible. Cephalothorax and prosomites 2-4 similar to female ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Genital somite with serrate posterior margin laterally. Urosomites 3-5 have smooth posterior margins ventrally; with each having a row of continuous spinules on disto-ventral margin ( Fig. 5C View FIGURE 5 ). Anal somite ( Fig. 5D View FIGURE 5 ), caudal rami ( Fig. 5C, D, E View FIGURE 5 ), antenna, mouthparts and P1 ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 ), P2 and P3 intercoxal sclerite, coxa, basis and Exp similar to female. Anal operculum with 7-8 triangular teeth, slightly surpassing posterior margin of somite bearing it.
Antennule ( Fig. 5B View FIGURE 5 ) 7-segmented. Geniculation between segments 4 and 5. First aesthetasc long and cylindrical, surpassing posterior margin of distal segment. Second aesthetasc cylindrical and smaller than first one. Both aesthetascs fused into a seta at their bases. Setal formula as 1, 9, 11+(1+A), 1, 0, 0, 7+(1+A).
P2 ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ) with two-segmented Enp. Enp-1 without inner seta, unornamented. Enp-2 with two spinules on outer margin and one apical pinnate seta, as long as segment bearing it.
P3 ( Fig. 6C View FIGURE 6 ) with three-segmented Enp, Enp-1 shortest and bare. Enp-2 with inner apophysis with a harpoonlike tip, slightly surpassing end of Exp-3. Enp-3 about 2.0 times as long as wide, with two sub-equally long pinnate setae apically.
P4 ( Fig. 6D View FIGURE 6 ) basis with a long, bare outer seta. Enp absent, represented only by a segmental vestige. Three-segmented Exp, Exp-1 as long as Exp-2, each with one outer robust spine. Exp-2 with a short, feather-like seta at distal inner margin. Exp-3 twice as long as wide, with shorter setae than in female: two inner feather-like setae, two outer unipinnate spines, one apical unipinnate seta and one apical transformed spine, antler-like shaped.
P5 ( Fig. 6E, F View FIGURE 6 ) with Exp and baseoendopod completely separated. Baseoendopod with a long and bare outer seta. Exp small, with three bare setae; inner seta very short, inner apical seta about 2.5 times as long as outer apical seta.
P6 ( Fig. 6E View FIGURE 6 ) reduced to a round and shallow plate, with two tiny spines fused to somite.
Variability. The number of teeth on the anal operculum ranged from 5-8 in males (n = 17) and 6-8 in females (n = 12). Ventral spinules on the anal somite ranged from 7-8 in males (n = 17) and 7-9 in females (n = 12).
Differential diagnosis. Elaphoidella longiramus sp. nov. clearly fits into the genus Elaphoidella for the armature of P5 and the segmentation of P1-P4 and the armature of P2-P4 Exp-3. The new species belongs to group VIII (i.e., the sewelli group Lang, 1948) based on the presence of a transformed spine on the male P4 Exp-3, and the armature formula and shape of the female P5. The new species is most similar to E. thailandensis due to the lack of P4 Enp and the presence of a two-segmented Enp of P1, in both sexes. However, the new species can be distinguished from E. thailandensis by several characteristics: (1) E. longiramus sp. nov. has a slender spinule at the inner margin of the female P5 Exp, whereas E. thailandensis lacks such a spinule; (2) the setal formula of the Exp-3 of P2-P 4 in both sexes of the new species is 5, 6, 6, whereas it is 4, 5, 6 in both sexes of E. thailandensis ; (3) in both sexes of E. longiramus sp. nov., the caudal ramus is about 2.0 times as long as wide, with a smooth inner margin, whereas in E. thailandensis , it is about 1.5 times as long as wide, with spinules along the inner margin; (4) the anal operculum of E. longiramus sp. nov. has six teeth in the female and 7-8 teeth in the male, whereas E. thailandensis has 10-11 teeth in both sexes; and (5) the anal somite of E. longiramus sp. nov. frequently has seven ventral spinules in both sexes, whereas that of E. thailandensis has four ventral spinules in both sexes.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |