Leucodellus albidus Reuter, 1906
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.176797 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5466291 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7F4B7A7C-FFB7-956E-B3E8-181FFD9CFE27 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Leucodellus albidus Reuter, 1906 |
| status |
|
Leucodellus albidus Reuter, 1906 View in CoL
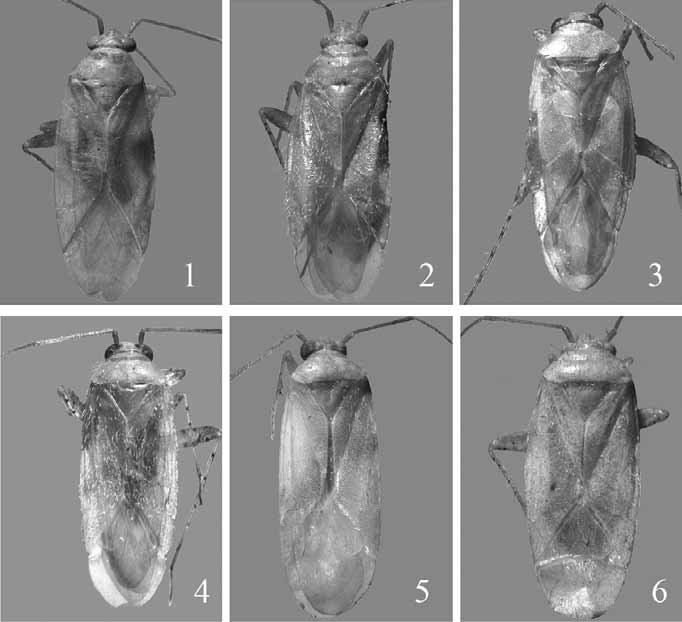
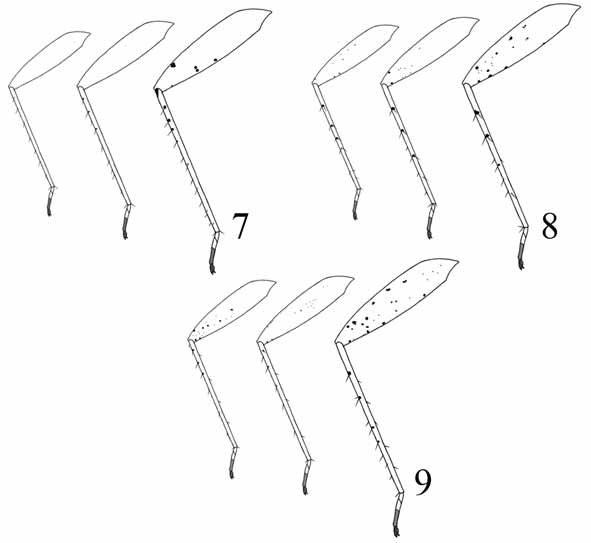
( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 , 7 View FIGURES 7 – 9 , 10–13 View FIGURES 10 – 21 , 22 View FIGURES 22 – 24 )
Leucodellus albidus Reuter, 1906: 69 View in CoL .
Diagnosis: Large, total length 3.98–4.52 (male), 3.75–4.51 (female); pale coloration; vestiture with pale simple setae only; fore and middle femora without dark spots ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 9 ); tibial spines pale, fore tibia without dark spots at bases of spines; vesica sigmoid with spicules on dorsal surface near secondary gonopore ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 10 – 21 ), anterior spine much longer than posterior. Most similar to L. pallescens in body shape and coloration. Distinguished from L. pallescens by larger size and structure of vesica. The shape of the male genitalia is similar to that of L. amygdali ; but, in L. amygdali , the two apical spines of vesica are all very long. The coloration of tibial spines also differs.
Description: Male ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 6 ): Body elongate, elliptical.
Coloration: Head, pronotum, scutellum, hemelytra, abdomen, appendages unicolourous pale, membrane transparent; vestiture always with pale simple setae; with 4 or 5 black spots on venter of hind femur ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 9 ); tibial spines pale, fore tibia without dark spots at bases of spines, basal portion of hind tibia black; tarsal segment III and claws slightly darkened. Structure: Dorsum smooth, covered with recumbent, shining simple setae; clypeus visible from above; antenna inserted below ventral margin of eye, antennal segments III and IV more slender than II, combined total length shorter than segment II; labium just reaching abdomen; hemelytra nearly parallel-sided, only slightly deflexed at fracture; genital capsule rather large, occupying nearly 1/2 length of abdomen.
Male genitalia ( Figs. 10–13 View FIGURES 10 – 21 ): Vesica sigmoid with spicules dorsally near secondary gonopore, two spines at apex of vesica, anterior spine much longer than posterior one, strongly bent, sharply attenuated apically. Female ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 6 ): Coloration and structure similar to those of male, but interocular distance greater. S pecimens Examined: CHINA: 13 males, 14 females, Xiaojin (30°59'N, 102°21'E), Sichuan Province, alt. 2350m, 26.viii.1963, Le-yi Zheng leg.; 1 male, Xiaojin (30°59'N, 102°21'E), Sichuan Province, alt. 2350m, 25.viii.1963, Huan-guang Zou leg. (paratype of Plagiognathus pallescens Zheng and Li, 1991 ); 1 male, 2 females, Xiaojin (30°59'N, 102°21'E), Sichuan Province, alt. 2350m, 25.viii.1963, Huan-guang Zou leg..
Distribution: China (Sichuan).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Leucodellus albidus Reuter, 1906
| Li, Xiao-Ming & Liu, Guo-Qing 2007 |
Leucodellus albidus
| Reuter 1906: 69 |