Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) axinus Zhang, Liu & Shi, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4942.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4B0F7A80-97E8-4C32-8228-0CA2B63F1601 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4644192 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7E30424C-AC4F-A77E-C5BD-FE633770DBA5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) axinus Zhang, Liu & Shi, 2017 |
| status |
|
Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) axinus Zhang, Liu & Shi, 2017
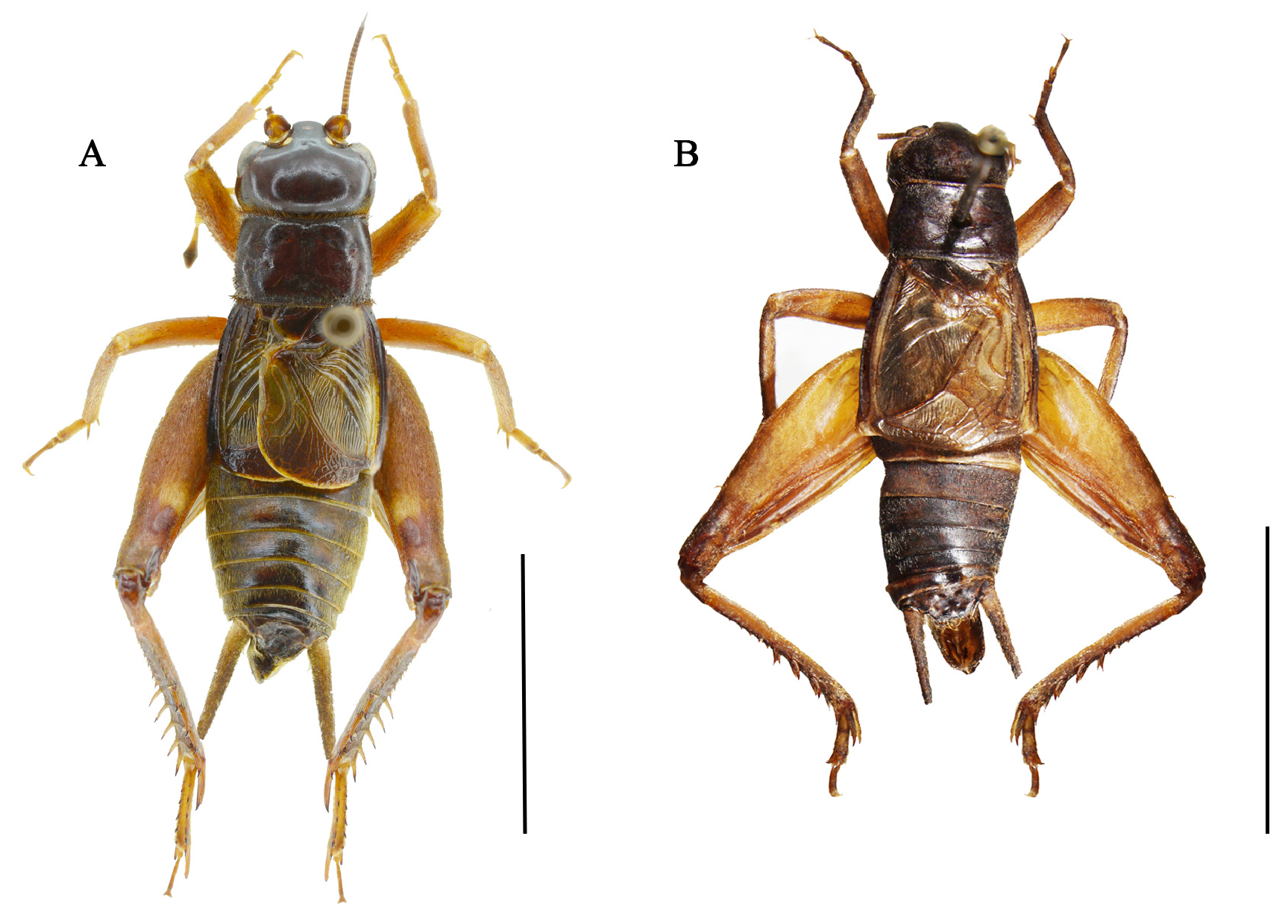
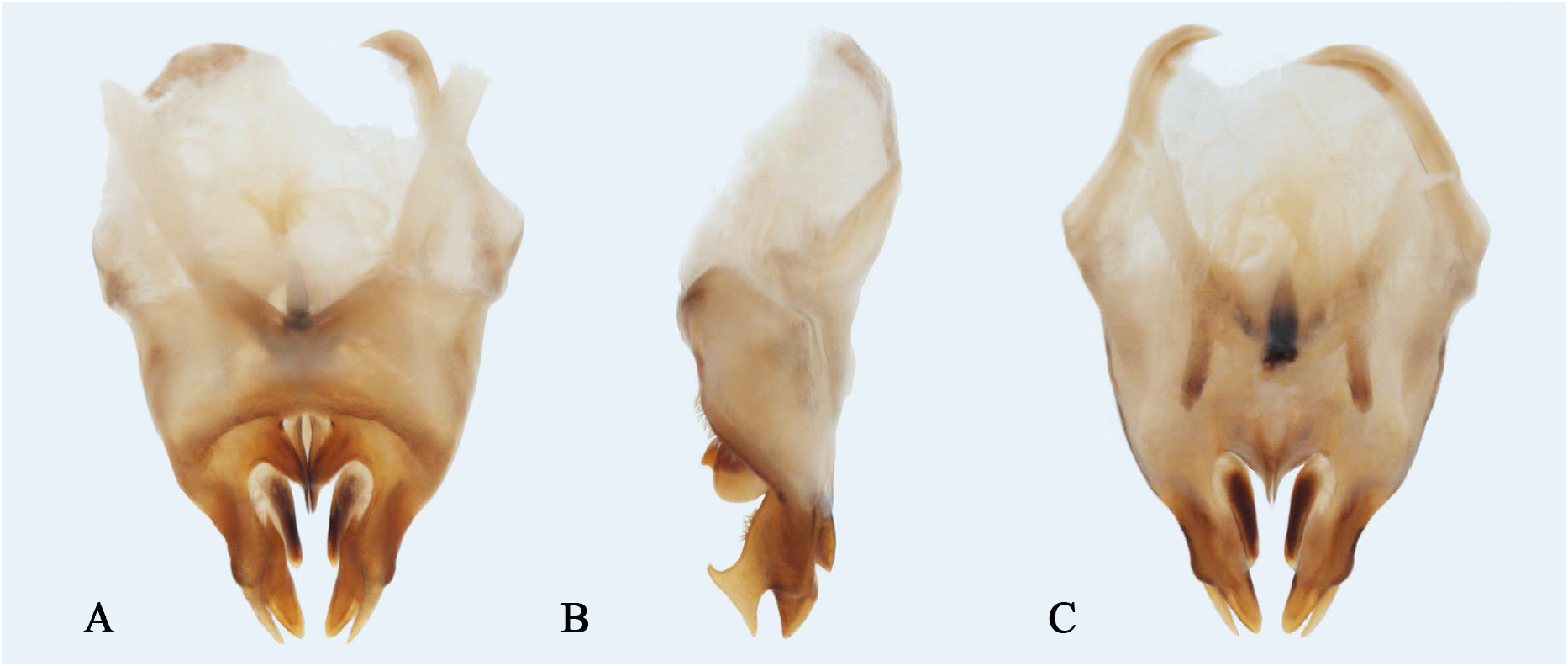
( Fig 3–4 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) axinus Zhang , et al., 2017: 316; Chen, et al., 2019: 553
Examined materials. 2 males. China: Hannan , Yinggeling, Aug. 22, 2019, coll. He, Zhixin ( SNNU) ; 2 males. China: Hannan , Wuzhishan, Aug. 16, 2019, coll. He, Zhixin ( SNNU) .
Measurements (mm). Male: BL 20.11±2.12; HL 3.48±0.53; HW 5.10±0.57; PL 2.82±0.24; PW 5.00±0.33; FWL 6.78±0.45; HFL 9.18±0.02; HTL 6.66±0.08.
Description. Male: Head smooth and light, conspicuously wider than pronotum. Vertex broad and flattened, weakly inclined. Frontal rostrum slightly convex in frontal view, slightly wider in dorsal view, almost equal to the width of antennal scape. Face transversely broad, area of antennal socket and area of lower side of eye distinctly depressed, between two areas ridged; cheek shiny and plump. Median ocellus small and transversely ovoid; lateral ocelli large and rounded. Clypeus extremely small, distal narrowed portion is short. Eyes ovoid, situated at middle of head side, about 1/3 length of head. Labrum rhombus-like, with angle lateral margins and concave apically. End section of maxillary palpi as long as the third, depressed and widened, with rounded apex; end section of labial palpi longer than remainder sections, depressed and widened.
Pronotum widened and depressed; anterior margin concave and arch-like, posterior margin straight, about 1.7 times as long as wide; middle of both lateral edges slightly convex. Hind wings aplasia, small (reaching posterior margin of metanotal gland) and entirely covered by forewings. Tegmina reaching the fifth abdominal tergite. The basal region of forewing elevated and slightly higher than the rest of the forewing surface. Oblique veins five; diagonal vein forked, not connected to CuA veins. Chord veins three, second and third chord veins basally connected, converging on CuA veins; second or third chord vein distally forked, connected to CuA veins. Mirror inconspicuous, replaced by multiple irregular wing cells, of them, most of proximal ones somewhat larger than the apical ones. A chord vein and wing cells are connected by veins numbered from two to four. Apical field armed with reticulated veins. Lateral field bearing five branches Sc vein.
Both inner and outer tympanum ovoid and the inner slightly larger than outer one. Hind tibiae equipped with spines on the one half of proximal portion and spurs on distal part (numbered 4:4); and with five apical spurs, of them, the inner numbering three, and the ventral one shorter than the dorsal two; and the outer apical spur numbering two, the ventral one shorter than the dorsal, but longer than 1/2 its length; as a whole, outer apical spurs longer than the inner ones. First tarsus of hind leg armed with six spines respectively on sides. Supper-anal plate trapezoid-like. Subgenital plate pike-like.
Genitalia ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ): Genitalia tapering distallyin dorsal view. Middle lobes of epiphallus short and thick. Lateral lobes of epiphallus about two times longer than the middle lobe; its tip apically bifurcate and included angle between branches formed as flat angle, and each branch armed with acute apex, and the lower branch slightly longer than the upper one. Epiphallus ventrally possessing two lateral projections, the anterior one short and somewhat as long as epiphallic middle lobe, and the posterior one about two times longer than the anterior. Ectoparameres acute, about two times longer than epiphallic middle lobe.
Coloration: Body colored brown. Femora light brown. Tegmina surface yellowish brown, lateral field brown. Cercus yellow-brown proximally and apically brown.
Female unknown.
Remark. This species is similar to Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) hainanensis Liu, He & Ma, 2015 , but the lateral lobes of the epiphallus are different; in Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) axinus , both anterior and posterior edge of epiphallus lateral lobe sharp, but in Duolandrevus (Eulandrevus) hainanensis , anterior edge of epiphallus sharp, posterior one obtuse. Body size as well as number and size of wing cells which replacing mirror are varied among individuals of this species. And most literature note that this species does not possess hind wings ( Chen et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2017a). After observing some specimens, we discovered it bears hind wings. These wings are undeveloped, rather small (slightly longer than posterior margin of metanotal gland) and entirely covered by forewings.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Landrevinae |
|
Tribe |
Landrevini |
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Eulandrevus |