Boiga flaviviridis Vogel & Ganesh, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4981.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:99295692-0941-4073-B10D-9DEC79A51767 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5047175 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7510136E-C65E-9468-FF39-D4BDFE05FEF2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Boiga flaviviridis Vogel & Ganesh, 2013 |
| status |
|
Boiga flaviviridis Vogel & Ganesh, 2013
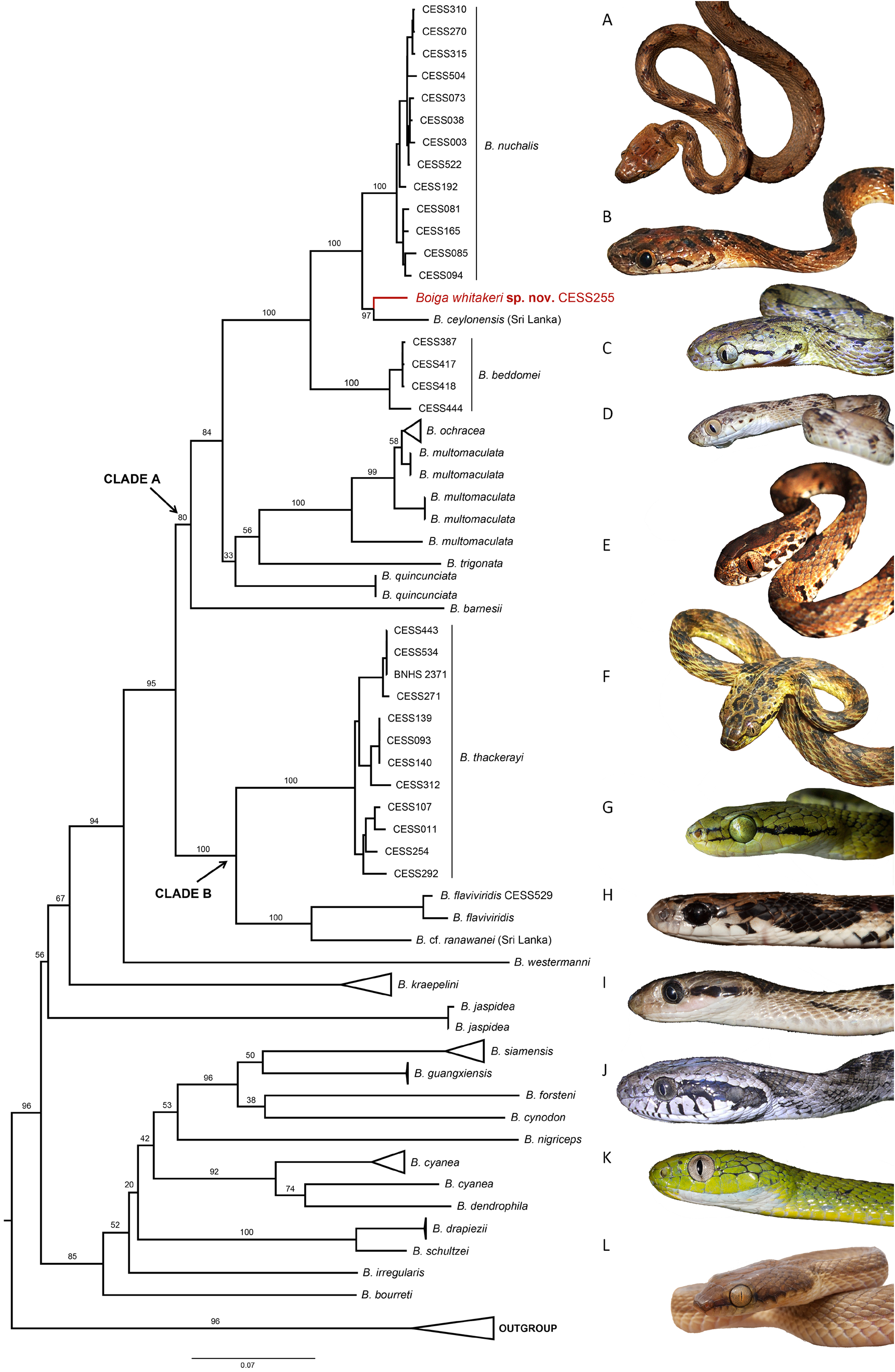
( Fig. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 ; Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Suggested common name: Yellow-green cat snake.
Boiga beddomei (non Wall, 1909)—Chaitanya et al. 2019
Boiga cf. flaviviridis — Giri et al. 2019
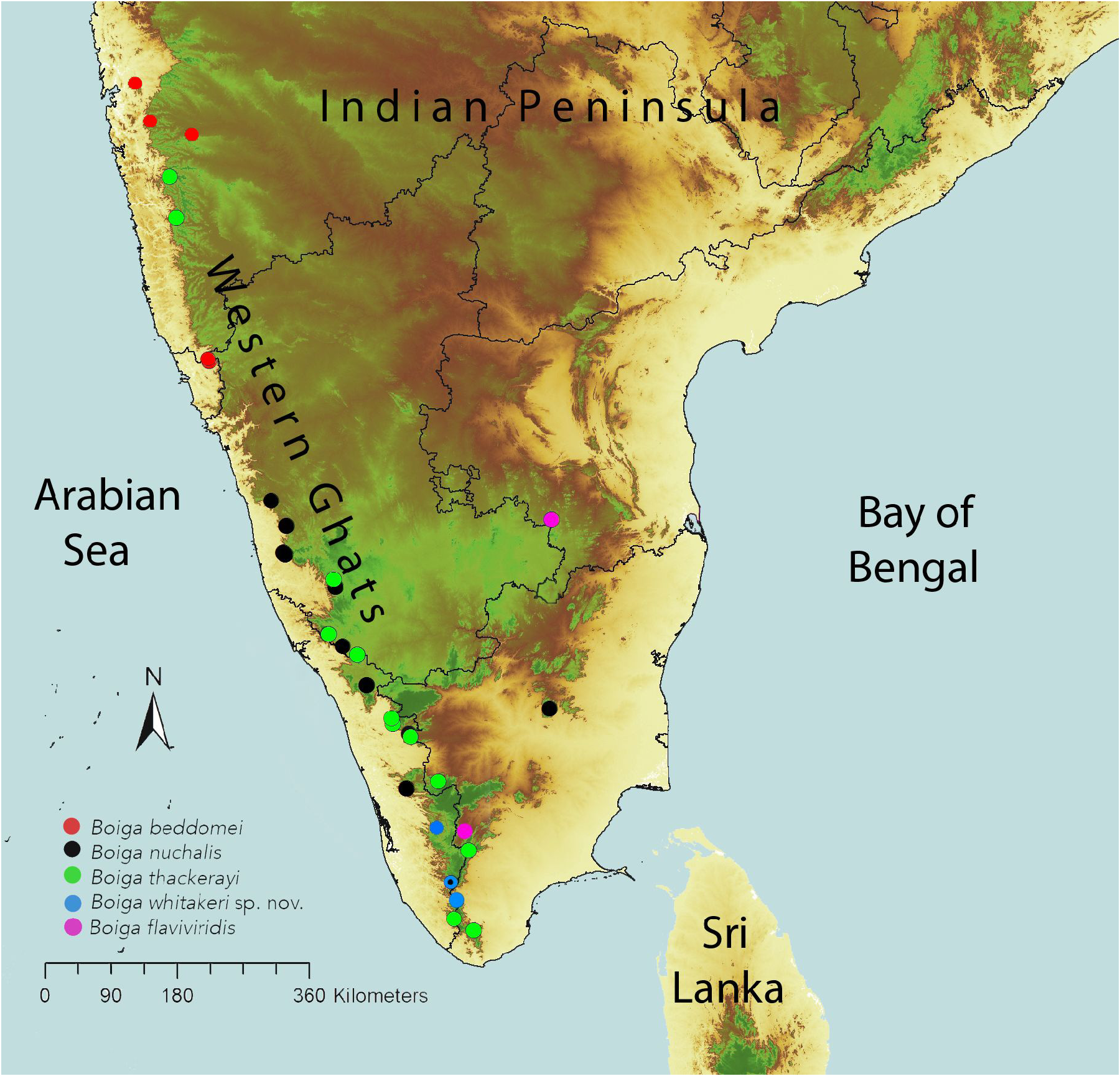
Additional specimens examined. (n=1). INDIA. CESS 529 , an adult female from Horsley Hills, Chittoor dt., Andhra Pradesh, Eastern Ghats .
Complementary Diagnosis. Boiga flaviviridis is phylogenetically sister (node support 100%) to the Sri Lankan Boiga cf. ranawanei . These two taxa are closely related to B. thackerayi (node support 100%). Boiga flaviviridis is 9.1–9.5% genetically divergent from its sister species B. cf. ranawanei and has 2.2% intraspecific divergence between specimens from Horsley hills and Meghamalai at cyt b.
Comments. Boiga flaviviridis is a poorly known species for which phylogenetic data of well-identified vouchers are provided herein for the first time. The Giri et al. (2019) sequence represented as B. cf. flaviviridis is from leeward slopes of Western Ghats, a region not previously known to harbor this species (see Vogel & Ganesh, 2013). The present sequence from Horsley Hills is close to the referred material’s locality: Kaigal, both situated in Chittoor hills of the Eastern Ghats.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.