Neotonchinae
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3692.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F9EC43F2-F82E-4E8C-A735-ECA4DFF7CA00 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6154049 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/707787ED-FFE5-2F10-FF73-F98DFD1AF80C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Neotonchinae |
| status |
|
Subfamily Neotonchinae Wieser & Hopper, 1966
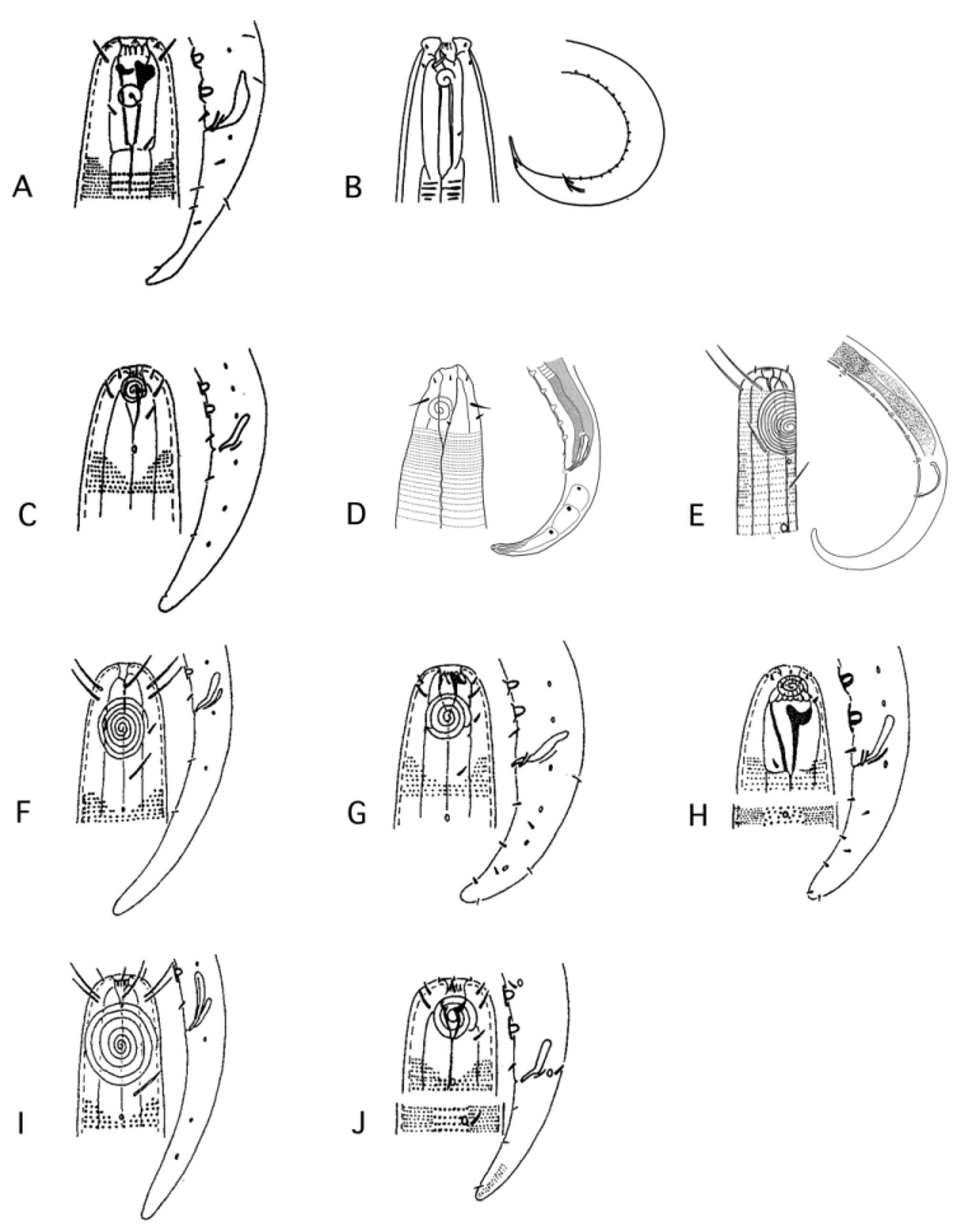
Diagnosis. Ethmolaimidae (originally Cyatholaimidae ): buccal cavity elongate, depth greater than width; armed with very small to medium or large dorsal tooth located midway in the buccal cavity and with or without small subventral teeth. Cephalic sense organs 6+6+4. Pharynx with well-developed terminal bulb. Spicula of highly characteristic shape, proximal two-thirds fairly straight and nearly uniform thickness, distal third narrowed, cylindroid and with a slight S-shaped curvature. Precloacal supplements large, well-developed, cup-shaped. Tail plump, conoid, with bluntly rounded terminus.
Marine. (Platt, 1982; Lorenzen 1994) (Type genus: Neotonchus Cobb, 1933 )
Genera belonging to Neotonchinae : Comesa Gerlach, 1956 , Dystomanema gen. nov., Filitonchoides Jensen, 1985 , Filitonchus Platt, 1982 , Gomphionchus Platt, 1982 , Gomphionema Wieser & Hopper, 1966 , Nannolaimus Cobb, 1920 , and Neothonchus Cobb, 1933. ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 )
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |