Macrotomoderus boops, Telnov, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2022.797.1667 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8DF57743-9C53-4265-BCB5-743276A3A16C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6317915 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/417E7988-84CC-4F48-B177-778AB3339ACA |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:417E7988-84CC-4F48-B177-778AB3339ACA |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Macrotomoderus boops |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Macrotomoderus boops sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:417E7988-84CC-4F48-B177-778AB3339ACA
Differential diagnosis
This species falls in a group of species from continental China with pronotum wider than head across eyes. Among them, the males of M. mirabilis Telnov, 2018 and M. monstrificabilis Telnov, 2018 both have distinct triangular median projection at the head base (not present in M. boops sp. nov.), while the head base in the male M. monstratus Telnov, 2018 is slightly medially impressed (truncate in M. boops sp. nov.), the front margin of the anterior pronotal lobe in male with pointed, triangular mesal projection in M. hengduan sp. nov. (see description below) and M. monstratus (the anterior pronotal projection not present in M. boops sp. nov.). Macrotomoderus boops sp. nov. is also conspicuous due to its nonobsolete shoulders and in antennal asymmetry (in males only?).
Etymology
From the Ancient Greek “βοῶΠΙΣ” (‘having large, full eyes’), referring to the comparatively large compound eyes of this species.
Type material
Holotype CHINA • ♂; “CHINA, Sichuan Prov., Emeishan Mt., 9.VI. 2014, Leidongping env., 2410 m, 29°32′49″N 103°20′22″E, // sift #9, bamboo groove, debris under rock abyss, near steep track to temples below, J. Hájek & J. Růžička leg.”; NMP. GoogleMaps
Description
MEASUREMENTS. Holotype, total body length 3.76 mm; head 0.75 mm long, across eyes 0.8 mm broad, pronotum 1 mm long, maximum width 0.9 mm, minimum width 0.23 mm, elytra 2 mm long, 1.1 mm combined wide.
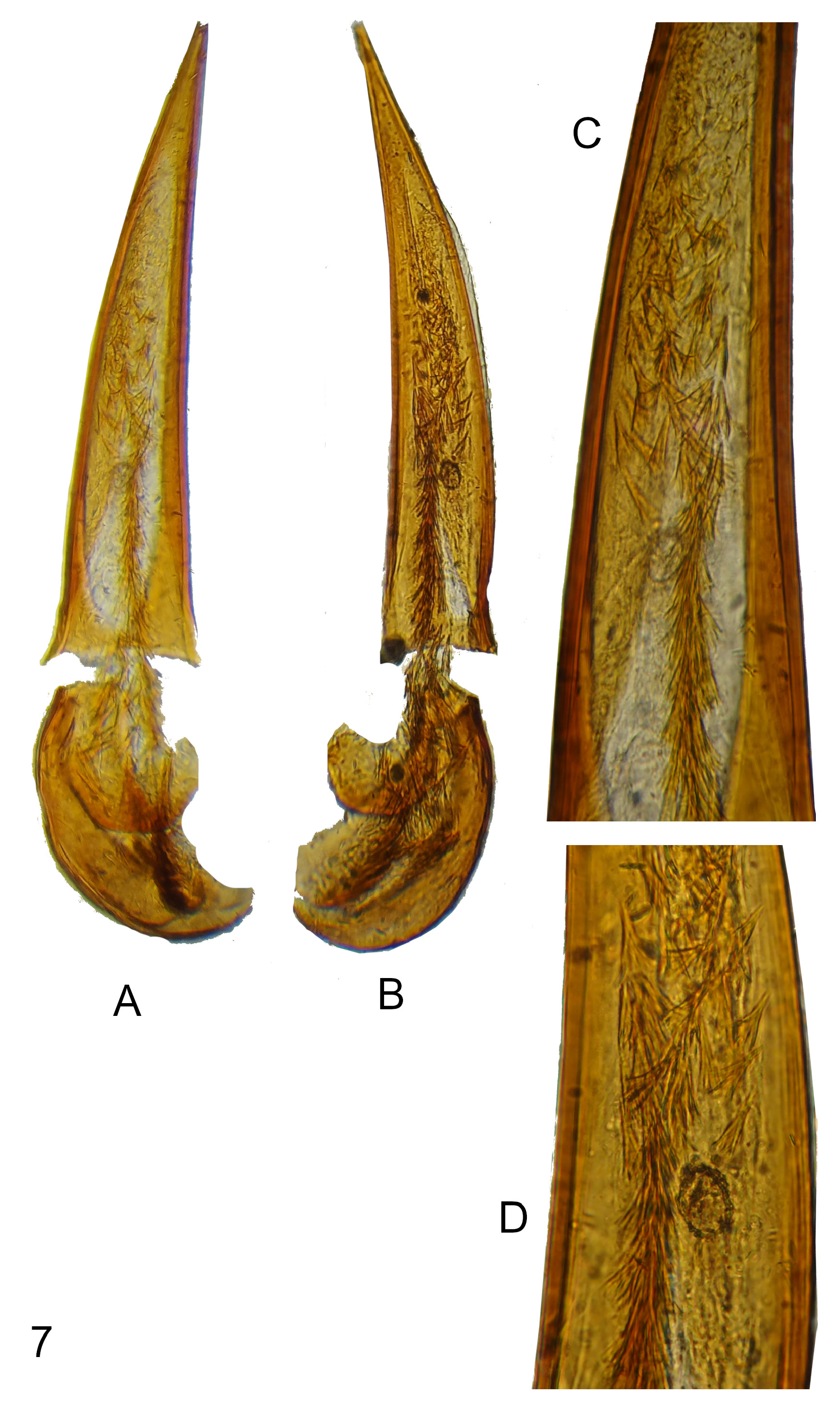
Dorsum and venter uniformly pale brown, head slightly darker. Mouthparts, antennae, palps and legs yellowish-brown. Head subtriangular with large, ovoid compound eyes, which are protruding beyond head outline laterally. Tempora slightly converging towards head base, distinctly shorter than eye length. Temporal angles broadly rounded, head base truncate. Head dorsal punctures minute and inconspicuous. Head dorsal setae inconspicuous and sparse, denser on head base. Antennae long, extending towards anterior third of elytra. Antennomere three about 1.3× as long as antennomere two, in male somewhat slightly bulged distally at one edge, insertion of male antennomere four is therefore not exactly medial and male antennomere four positioned slightly asymmetrical with regard to antennal axis. Male antennomere four shortened and near spherical, shorter than antennomere three. Antennomeres 9–10 slightly transverse. Terminal antennomere elongate triangular with pointed apex, about twice as long as penultimate antennomere. Terminal maxillary palpomere slightly securiform. Pronotum broadly hourglass-shaped with anterior lobe significantly wider than posterior and wider than head across eyes. Postmedian lateral constriction broad and medially broadly and deeply notched. Front margin of anterior lobe very broadly rounded, slightly impressed mesally, dorsally without anterior rim. Anterior lobe large and broad, inverted triangular; posterior lobe about one third length of anterior lobe, much narrower. Front margin of anterior lobe at place of mesal impression with a group of golden, curved, very dense, anterolaterally directed setae touching head base ( Fig. 6B–C View Fig ). Anterior lobe convex in lateral view ( Fig. 6C View Fig ). Lateral constriction continues onto disc in lateral view, shallow ( Fig. 6C View Fig ). Lateral pronotal fovea broad at lower external margin of pronotum, widens upwards towards pronotal disc in lateral view, external margins protruding into a pair of strongly obtuse (in lateral view), widely separated denticles (in lateral view). Cavity in lateral wall of pronotum between lateral denticles large, elliptical. In dorsal view, lateral pronotal fovea broad and deep, anterior and posterior pair of denticles appear rectangular to obtuse angulate, fully concealed by dense appressed setae of adjacent portions of fovea ( Fig. 6B View Fig ). Pronotal punctures minute on disc; lateral constriction dorsally with inconspicuous, median longitudinal carina and few sparse, moderately large punctures around it ( Fig. 6B View Fig ). Dorsal pronotal setae inconspicuous, moderately long. Scutellar shield minute, rounded apically. Elytra dorsally elliptical, slightly convex in lateral view, widened laterally around midlength, lateral margins evenly broadly rounded. Shoulders rounded but prominent (metathoracic wings present). Elytral punctures moderately large, rather dense, becoming slightly smaller and sparser towards apices. Elytral setae long and sparse, suberect. Male tergite and morphological sternite VII broadly rounded at posterior margin. Aedeagus as in Fig. 7 View Fig , large and rather slender, apicale and median portion of basale filled with elongate, dense spineshaped gonopore armature. Armature spines closely attached to one another in basal half of aedeagus, arranged into ‘garland’, becoming irregularly directed in apical half of aedeagus. Armature spines significantly smaller at apex of aedeagus compared to those in median and basal parts of it.
Sexual dimorphism
Female is unknown.
Ecology
Collected by sifting leaf litter in a bamboo grove at 2410 m elevation.
Distribution
Known only from Mount Emei in Sichuan Province, central China.
| NMP |
National Museum (Prague) |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Polyphaga |
|
SuperFamily |
Tenebrionoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Tomoderinae |
|
Genus |