Epidorylaimus monhystera, Ahmad, Wasim, Imran, Zarrin & Araki, Masaki, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4072.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AFDF31B2-CA38-4452-891A-824D1E0804FA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5620792 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6D2C87B4-FFB3-FFE6-F2B1-F9C47593FD2A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Epidorylaimus monhystera |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Epidorylaimus monhystera sp. n.
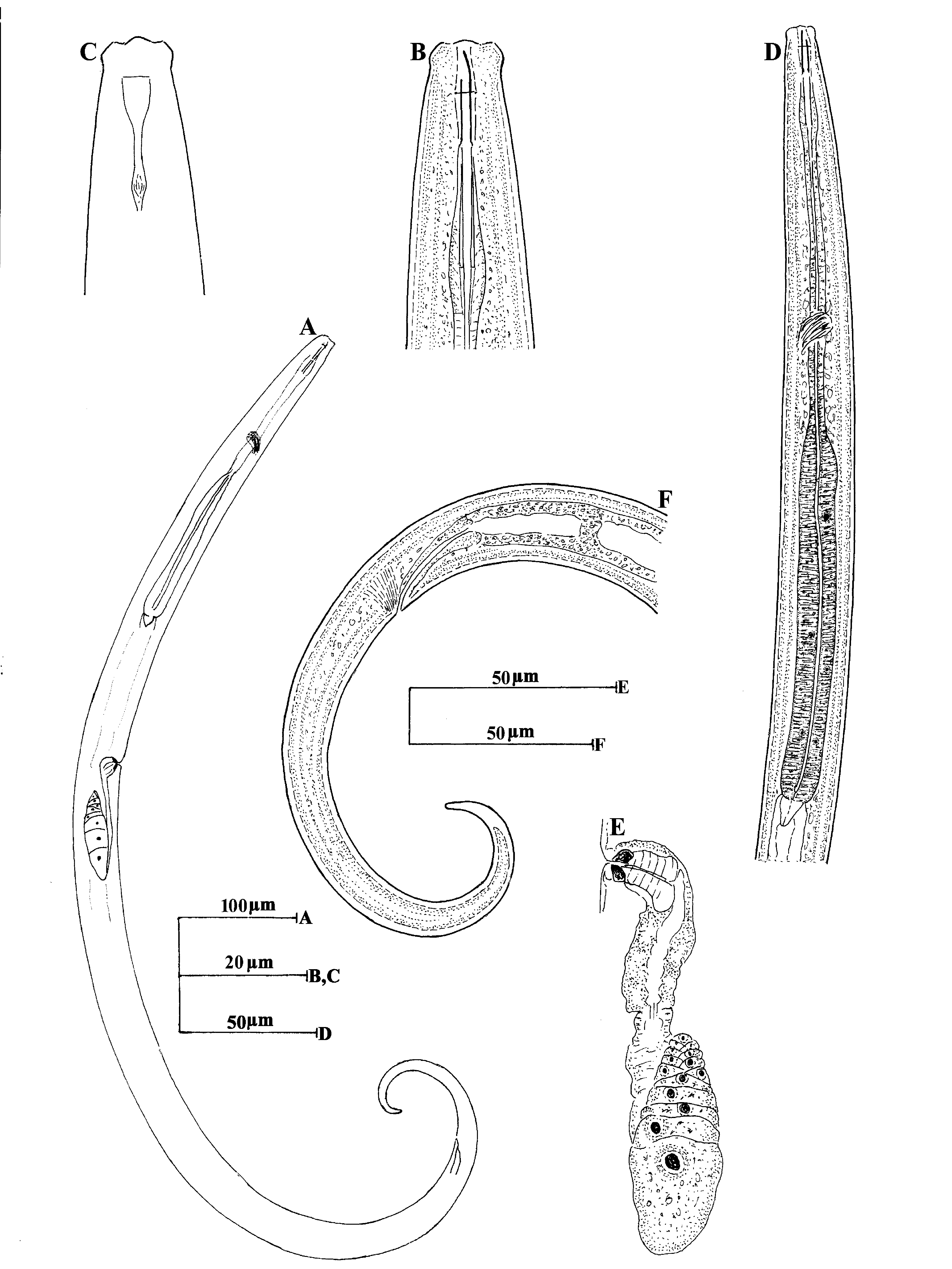
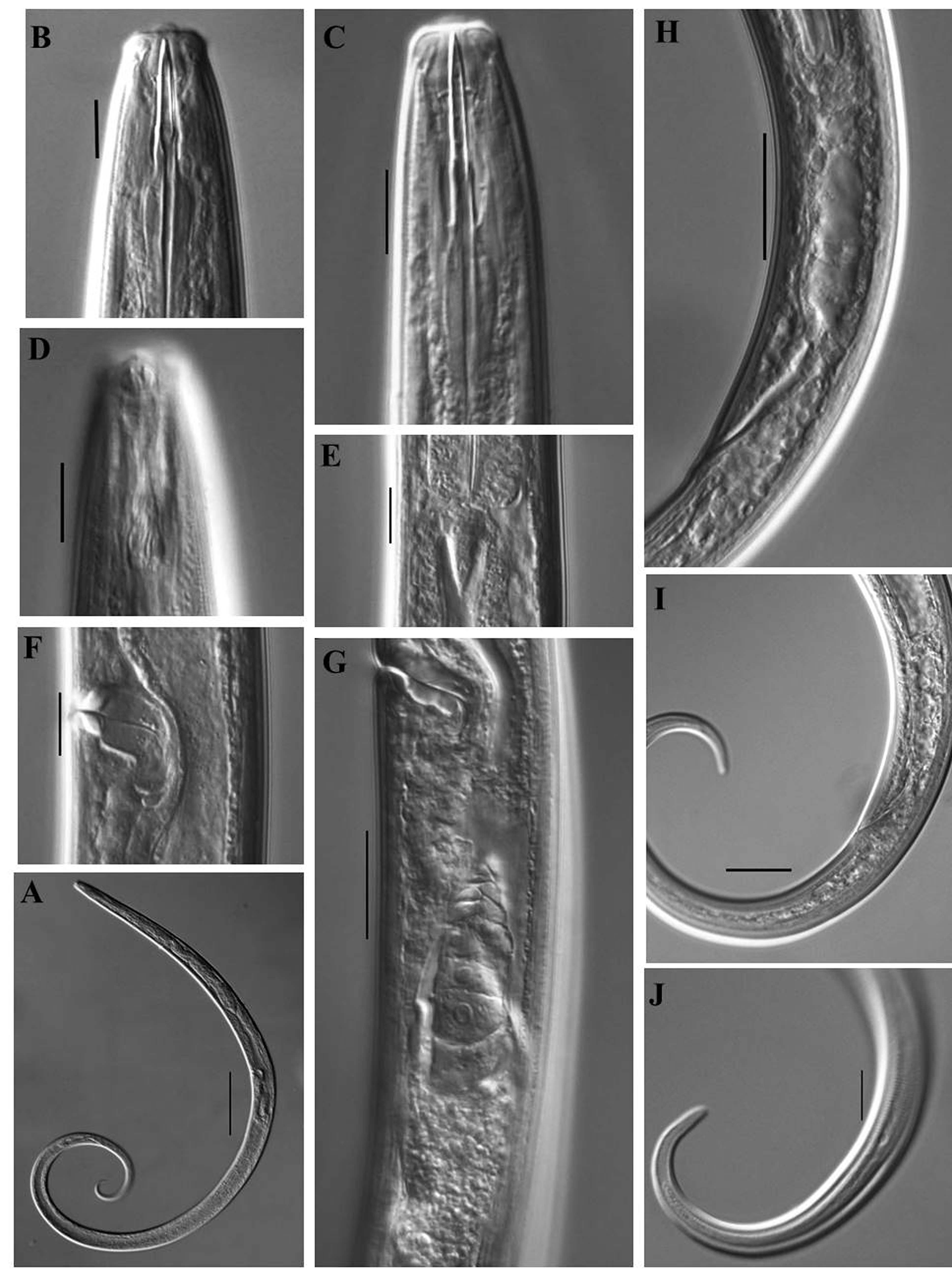
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 & 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Material examined. Twelve females, all in good state of preservation.
Measurements: See table 1.
Description. Female: Body slender, curved ventrad upon fixation, tapering gradually towards posterior extremity. Cuticle with fine transverse striations, 1.0–1.5 Μm thick at mid body and 1.5–2.0 µm on tail. Lateral chords about one-sixth of the corresponding body diameter. Lateral, dorsal and ventral body pores indistinct.
Lip region set-off by slight constriction, about one-third as wide as body diameter at neck base. Lips angular, separate; labial papillae slightly raised. Amphids elongate, wine glass-shaped, their aperture about two-fifths of the corresponding body diameter. Odontostyle dorylaimoid, typical of the family, 1.3–1.6 times lip region diameter long, its aperture about one-fourth to one-third of its length. Guiding ring single, at 0.6–0.7 times lip region diameter from anterior end. Odontophore simple, rod-like, 1.1–1.2 times the odontostyle length. Nerve ring encircling the anterior slender part of pharynx at 37–40% of neck length from anterior end. Pharynx expanding gradually; expanded portion occupying about 41–47% of total neck length. Cardia short, conoid, about one-third of the corresponding body diameter long. Pharyngeal gland nuclei and their orifices located as follows: DO=59–63; DN=63–65; DO-DN= 3.1–4.0; S1N1=72–73; S1N2=77–81, S2N=87–89; S2O= 88–92.
Genital system mono-opisthodelphic. Ovary reflexed, 54–85 Μm long, with oocytes arranged in single row except near its tip. Oviduct joining ovary subterminally, measuring 48–79 Μm. Uterus a simple, undifferentiated tube, 34–44 Μm in length. Oviduct-uterus junction marked by a weak sphincter. Vulva transverse. Vagina posteriorly directed; pars proximalis vaginae 9–12 Μm long encircled by circular muscles; pars refringens vaginae consists of two sclerotized pieces, each measuring, 2– 3 x 4–5 µm; pars distalis vaginae 1.5–3.0 Μm. Prerectum 1.8–2.3 anal body diameters long. Rectum 1.4–2.0 anal body diameters long; Tail elongate, ventrally curved, 10– 11.5 times the anal body diameter in length; hyaline part of tail 8–9% of tail length, caudal pores two on each side.
Male: Not found. No trace of sperms in female genital tract.
Type habitat and locality: Soil around roots of Japanese cypress ( Chamaecyparis obtusa ) from Akazawa FR, Agematsu T, Nagano, Japan; collected in May 1999 by M. Araki.
Type specimens: Holotype female on slide Epidorylaimus monhystera sp. n. /1; paratype females on slides Epidorylaimus monhystera sp. n. /2–10 deposited in the nematode collection of the Department of Zoology, Aligarh Muslim University, India. Two paratype females on slides Epidorylaimus monhystera sp. n. /11–12 deposited with the nematode collection of the National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, Tsukuba, Japan.
Diagnosis and relationships: Epidorylaimus monhystera sp. n. has 1.12–1.33 mm long body, lip region offset by slight constriction, odontostyle 15–16 Μm and odontophore 18–20 Μm long, guiding ring single, pharyngeal expansion gradual, vulva transverse, female genital system mono-opisthodelphic, anterior branch completely absent and tail elongate-conoid, ventrally arcuate, 10–11.5 anal body diameters in length.
The new species is distinctive from all other species of the genus Epidorylaimus in having monoopisthodelphic female genital system. It further differs from all the known species of the genus in having comparatively anterior vulva (V = 34–36) and much longer tail. In none of the other known species of this genus is the vulva so anterior: the value of V is almost always greater than 40%, except only in Epidorylaimus andrassyi Mushtaq & Ahmad, 2007 , where in a few specimens it may be as low as 38.5% (which is still higher than in the new species). The tail also is much longer, with only E. agilis Thorne & Swanger, 1936 (c’ = 7.6) and E. lugdunensis (de Man, 1880) Andrássy, 1986 (c’ = 5.6) coming close, but in both cases with tails still much shorter compared to the new species presented here.
Discussion: The present population is quite enigmatic in having slender body with long ventrally arcuate tail, offset lip region, dorylaimoid odontostyle with aperture about one-third of its length, quite similar to the member of Epidorylaimus but the monodelphic gonad is unusual for this group. In none of the four closely related genera, Eudorylaimus Andrássy, 1959 , Allodorylaimus Andrássy, 1986 , Microdorylaimus Andrássy, 1986 and Epidorylaimus Andrássy, 1986 , has monodelphy ever been reported. Monodelphy is very rare in Qudsianematidae Jairajpuri, 1965 , represented only by the genus Ecumenicus . Thorne (1974) established this genus for the only monodelphic species Eudorylaimus monhystera (de Man, 1880) Andrássy, 1959 known until that time in the family Qudsianematidae . Two further species have been added to this genus since then. However, Ecumenicus is characterized by the anterior migration of amphid, an unusual feature for dorylaims for which Andrássy (2009) Character species n L a b c c̓ lrd ods length Nec length rivalis ♀ 1.5-2.3 20-35 3.1-4.7 11-26 3.5 40-53 - 28-30 - ♂ 1.5-2.2 21-36 3.2-4.2 13-22
monhystera 12♀ 1.1-1.3 31.6-37.7 3.8-4.7 6.9-7.7 10-11 31.8-35.7 11 15-18 270-305 ……continued on the next page TABLE 2 View TABLE 2 . (Cοntinued) = Lip regiοn diameter οds = Οdοntοstyle
. bulb = Pharyngeal bulb Prerect⁄abd. = Prerectum⁄ Anal bοdy diameter vMS = ventrοmedian supplements Geο. distru = Geοgraphical distrubutiοn *) = Calculated measurements frοm illustratiοns
proposed a subfamily Ecumenicinae. This unusual feature is also found in the genus Kochinema Heyns, 1963 of the family Nordiidae . Since the anterior migration of amphid is a very important character and our population has normal post labial position of amphids, it cannot be placed in the genus Ecumenicus . On the other hand, the loss of one genital tract within the same genus is a known evolutionary process in dorylaims, although rare in the superfamily Dorylaimoidea ( Discolaimus Cobb, 1913 , Sicorinema Siddiqi, 1982 , Latocephalus Patil & Khan, 1982 ) but comparatively common in Tylencholaimoidea Filipjev, 1934 ( Tylencholaimus de Man, 1876, Dorylaimoides Thorne & Swanger, 1936 , Basirotyleptus Jairajpuri, 1964 , etc.) and to some extent in Belondiroidea Thorne, 1964 also ( Dorylaimellus Cobb, 1913 ).
With the description of this atypical species with a mono-opisthodelphic female genital system and a transverse vulva, the generic diagnosis of Epidorylaimus needs to be slightly emended as follows:
Diagnosis (emended). Body small to moderately long, 0.6–2.3 mm. Cuticle smooth or with fine transverse striations, especially on tail. Lip region offset, lips separate and mostly angular. Odontostyle one to one-and-a-half times lip region diam. long; its aperture about one-third of its length. Guiding ring single, thin. Pharynx enlarged near middle or posterio-medially. Female genital system amphidelphic, rarely mono-opisthodelphic. Vulva longitudinal, transverse or pore-like, with cuticularised labia. Males rare; spicules dorylaimoid; lateral guiding pieces present and ventromedian supplements four-thirteen. Precloacal space absent between ventromedian row and ad-cloacal pair of supplements. Tail 3.5–11.5 anal body diameters long, ventrally curved with pointed tip, similar in both sexes.
Type species: Epidorylaimus lugdunensis (de Man, 1880) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus lugdunensis de Man, 1880
= Dorylaimus carteri lugdunensis de Man, 1880 ( Micoletzky, 1922)
= Eudorylaimus lugdunensis (de Man, 1880) Andrássy, 1959
= Dorylaimus reisingeri Ditlevsen, 1927
= Eudorylaimus reisingeri ( Ditlevsen, 1927) Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris, 1971
= Dorylaimus curvatus Thorne & Swanger, 1936
= Eudorylaimus curvatus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrássy, 1959
= Eudorylaimus leptus Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris, 1971
Other species:
E. agilis (de Man, 1880) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus agilis de Man, 1880
= Dorylaimus carteri agilis de Man, 1880 ( Micoletzky, 1922)
= Mesodorylaimus agilis (de Man, 1880) Goodey, 1963
= Laimydorus agilis (de Man, 1880) Siddiqi, 1969
= Eudorylaimus agilis (de Man, 1880) Loof, 1969
E. andrassyi Mushtaq & Ahmad, 2007
E.angulosus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus angulosus Thorne & Swanger, 1936
= Eudorylaimus angulosus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrássy, 1959 E. consobrinus (de Man, 1918) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus consobrinus de Man, 1918
= Dorylaimus carteri rotundatus Micotezky, 1922
= Eudorylaimus consobrinus (de Man, 1918) Andrássy, 1959
E. filicaudatus ( Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris, 1971) Andrássy, 1986
= Eudorylaimus filicaudatus Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris, 1971
E.humilior ( Andrássy, 1959) Andrássy, 1986
= Eudorylaimus humilior Andrássy, 1959
E. humilis ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus humilis Thorne & Swanger, 1936
= Eudorylaimus humilis ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrássy, 1959
= Dorylaimus incisus Thorne & Swanger, 1936
= Eudorylaimus incisus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrássy, 1959 E. leptosoma ( Altherr, 1963) Andrássy, 1986
= Eudorylaimus leptosoma Altherr, 1963
E. mellenbachensis ( Altherr, 1974) Andrássy, 1986
= Eudorylaimus mellenbachensis Altherr, 1974 E. muchabbatae ( Tulaganov, 1949) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus muchabbatae Tulaganov, 1949
= Eudorylaimus muchabbatae ( Tulaganov, 1949) Andrássy, 1959 E. muscorum ( Skwarra, 1921) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus muscorum Skwarra, 1921
= Eudorylaimus muscorum ( Skwarra, 1921) Andrássy, 1959 E. pseudoagilis ( Altherr, 1952) Andrássy, 1986
= Dorylaimus pseudoagilis Altherr, 1952
= Mesodorylaimus pseudoagilis ( Altherr, 1952) Andrássy, 1959
= Eudorylaimus pseudoagilis ( Altherr, 1952) Zullini, 1970 E. rivalis Gagarin, 1991
TABLE 2. Mοrphοmetrics οf species belοnging tο the genus Epidorylaimus Andrassy, 1986 (measurements in μm, e cept L in mm).
| agilis | ♀ | 1.3-1.6 | 25-32 | 4-4.5 | 10-14 - | 45 | - | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| andrassyi | 11♀ | 1.05-1.38 | 26-35.5 | 4.2-4.9 | 8.3-11.9 4.7-6.7 | 38.5-46 | 13-14.5 | 14.5-15 | 249-317 |
| angulosus | ♀ | 1.14-1.6 | 23-27 | 4-4.8 | 11-15.3 4 | 42-48 | 15-17 | 15-18 | 275-232 |
| consobrinus | ♀ | 1.4-1.87 | 35-40 | 3.6-4.3 | 16-18 2.7-4.3 | 44-51 | 14-18 | 16-20 | 391 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Epidorylaimus monhystera
| Ahmad, Wasim, Imran, Zarrin & Araki, Masaki 2016 |
E. andrassyi
| Mushtaq & Ahmad 2007 |
E. rivalis
| Gagarin 1991 |
E.angulosus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrassy 1986 |
E. filicaudatus ( Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris, 1971 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris, 1971) Andrassy 1986 |
E.humilior ( Andrássy, 1959 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Andrassy, 1959) Andrassy 1986 |
E. humilis ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrassy 1986 |
E. leptosoma ( Altherr, 1963 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Altherr, 1963) Andrassy 1986 |
E. mellenbachensis ( Altherr, 1974 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Altherr, 1974) Andrassy 1986 |
E. muchabbatae ( Tulaganov, 1949 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Tulaganov, 1949) Andrassy 1986 |
E. muscorum ( Skwarra, 1921 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Skwarra, 1921) Andrassy 1986 |
E. pseudoagilis ( Altherr, 1952 ) Andrássy, 1986
| (Altherr, 1952) Andrassy 1986 |
Eudorylaimus mellenbachensis
| Altherr 1974 |
Eudorylaimus reisingeri ( Ditlevsen, 1927 )
| (Ditlevsen, 1927) Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris 1971 |
Eudorylaimus leptus
| Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris 1971 |
Eudorylaimus filicaudatus
| Tjepkema, Ferris & Ferris 1971 |
Eudorylaimus pseudoagilis ( Altherr, 1952 )
| (Altherr, 1952) Zullini 1970 |
Eudorylaimus leptosoma
| Altherr 1963 |
Eudorylaimus curvatus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936 ) Andrássy, 1959
| (Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrassy 1959 |
Eudorylaimus angulosus ( Thorne & Swanger, 1936 ) Andrássy, 1959
| (Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrassy 1959 |
Eudorylaimus humilior Andrássy, 1959
| Andrassy 1959 |
Eudorylaimus humilis
| (Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrassy 1959 |
Eudorylaimus incisus
| (Thorne & Swanger, 1936) Andrassy 1959 |
Eudorylaimus muchabbatae ( Tulaganov, 1949 )
| (Tulaganov, 1949) Andrassy 1959 |
Eudorylaimus muscorum ( Skwarra, 1921 )
| (Skwarra, 1921) Andrassy 1959 |
Mesodorylaimus pseudoagilis ( Altherr, 1952 )
| (Altherr, 1952) Andrassy 1959 |
Dorylaimus pseudoagilis
| Altherr 1952 |
Dorylaimus muchabbatae
| Tulaganov 1949 |
Dorylaimus curvatus
| Thorne & Swanger 1936 |
Dorylaimus angulosus
| Thorne & Swanger 1936 |
Dorylaimus humilis
| Thorne & Swanger 1936 |
Dorylaimus incisus
| Thorne & Swanger 1936 |
Dorylaimus reisingeri
| Ditlevsen 1927 |
Dorylaimus carteri rotundatus
| Micotezky 1922 |
Dorylaimus muscorum
| Skwarra 1921 |