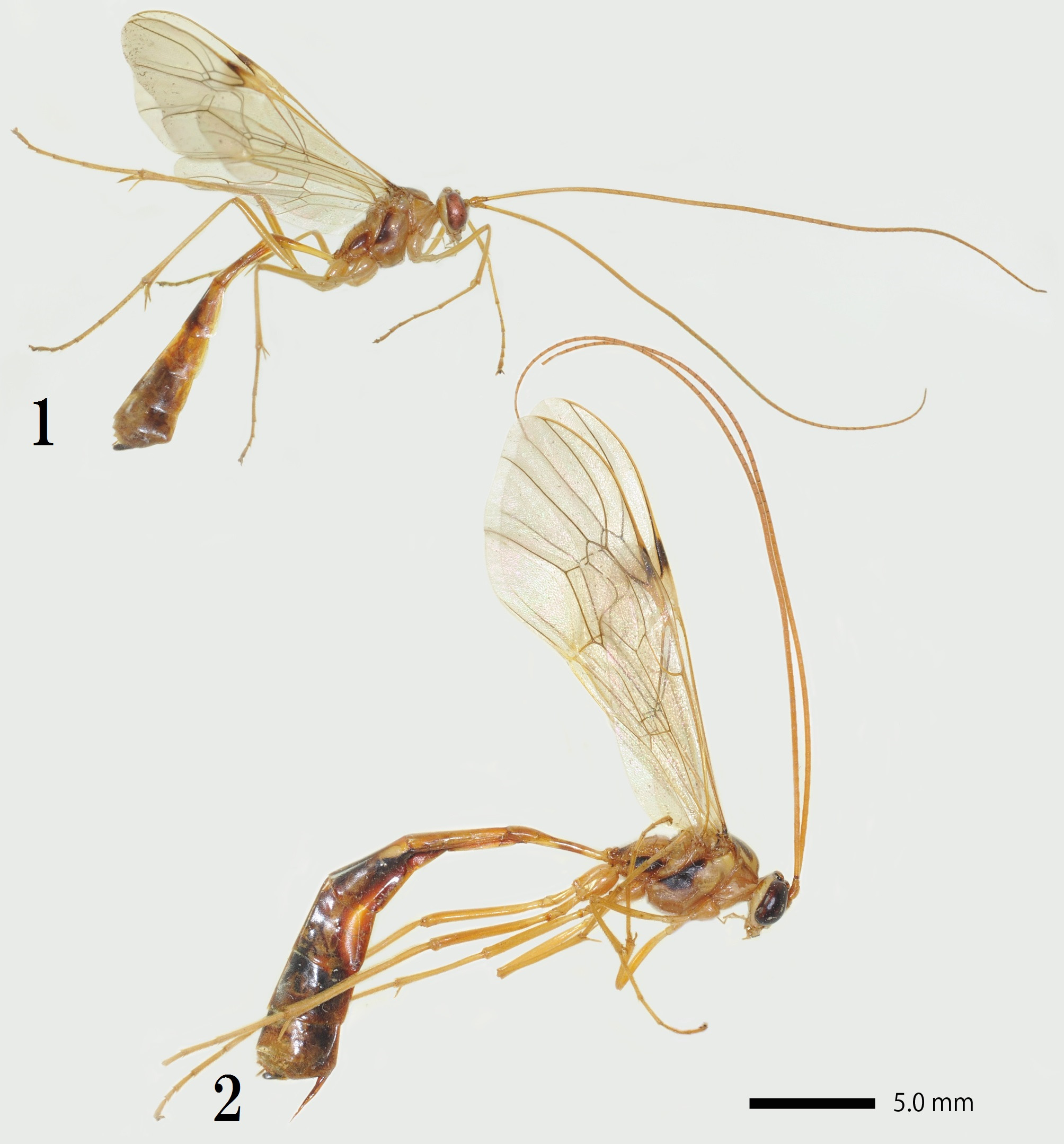
Leptophion Cameron , 1901
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4000.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:10B33B13-6E22-486A-9B85-C08934401B30 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5669751 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6568CF31-FFED-FF88-16AE-FBA2FB58C468 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Leptophion Cameron , 1901 |
| status |
|
Genus Leptophion Cameron, 1901 View in CoL View at ENA
Leptophion Cameron, 1901: 227 View in CoL . Type species: Leptophion longiventris Cameron View in CoL , by monotype. Spilophion Cameron, 1905: 124. Type species: Spilophion maculipennis Cameron , by monotype. Synonymized by Townes et al. (1961: 265).
Coiloneura Szépligeti, 1905: 35. Type species: Coiloneura melanostigma Szepligeti , by subsequent designation. Synonymized by Cushman (1947: 462).
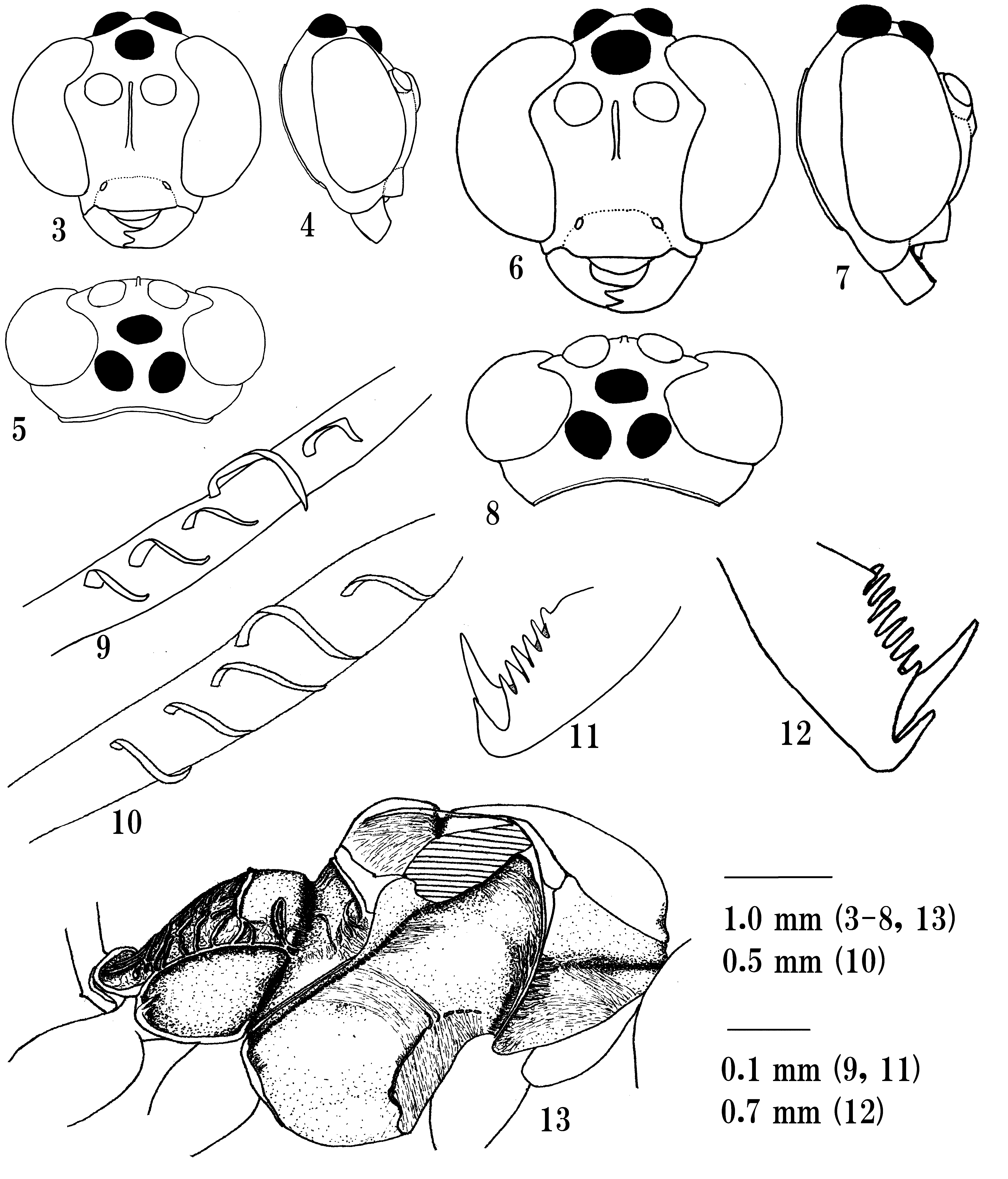
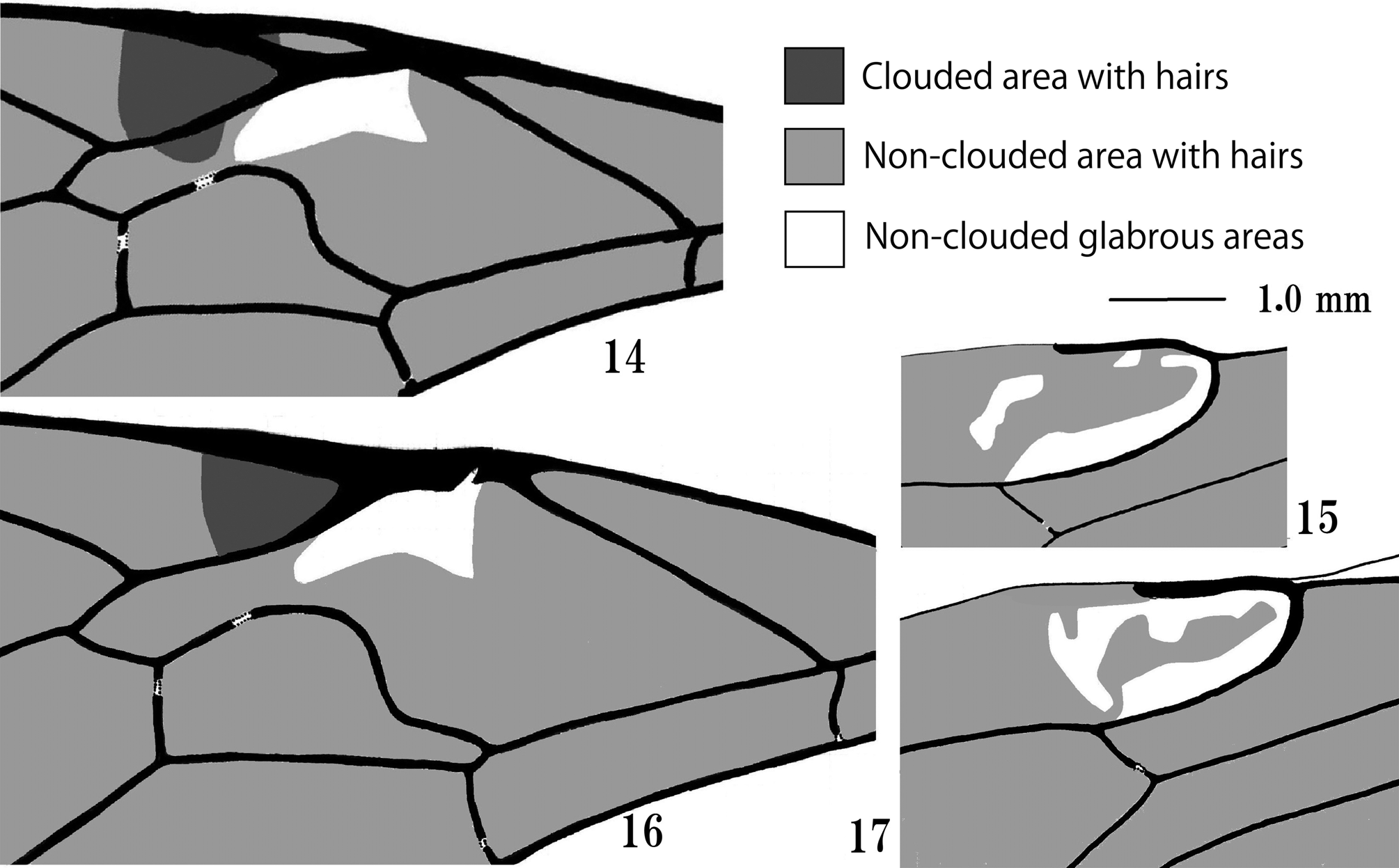
Diagnosis. This genus can be distinguished from other genera of Ophioninae by the following combination of character states: (1) mandible not twisted, barely tapered, with sparsely long hairs, its apex dichotomy of axial symmetric teeth or upper tooth slightly longer than lower one ( Figs 3, 4, 6, 7 View FIGURES 3 – 13 ); (2) clypeus strongly convex, its lateral profile of lower margin nearly straight to slightly convex ( Figs 3, 4, 6, 7 View FIGURES 3 – 13 ); (3) occipital carina complete dorsally and laterally, its lower margin absent, without joined to oral carina ( Figs 4, 5, 7, 8 View FIGURES 3 – 13 ); (4) posterior transverse carina of mesosternum complete ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 3 – 13 ), rarely interrupted in a few Australasian species; (5) tibial spur of fore leg without membranous flange; (6) mid and hind trochanters simple; (7) distal pecten of hind tarsal claws distinctly longer than true apex of claw and other pectens ( Figs 11, 12 View FIGURES 3 – 13 ); (8) fore wing without sclerites ( Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1, 2 , 14–16 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ); and (9) hind wing usually with an apparently elongated penultimate hamulus on R 1 ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 3 – 13 ) ( Townes, 1971; Gauld, 1977; Gauld & Mitchell, 1981).
Distribution. Australasian, Oceanic, Oriental, and Palaearctic (the south of Japan)*, regions. *New record. Bionomics. Host is unknown. Adult wasps are usually collected in light traps.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Ophioninae |
Leptophion Cameron , 1901
| Shimizu, So & Watanabe, Kyohei 2015 |
Leptophion
| Townes 1961: 265 |
| Cameron 1905: 124 |
| Cameron 1901: 227 |