Folsomides mediterraneus, Arbea, Javier I. & Jordana, Rafael, 2002
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.156067 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6277511 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6531BB0A-F158-FF97-4D1D-F9CC155C806D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Folsomides mediterraneus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Folsomides mediterraneus n. sp.
( Figs. 19 View FIGURES 1 6 View FIGURES 7 9 )
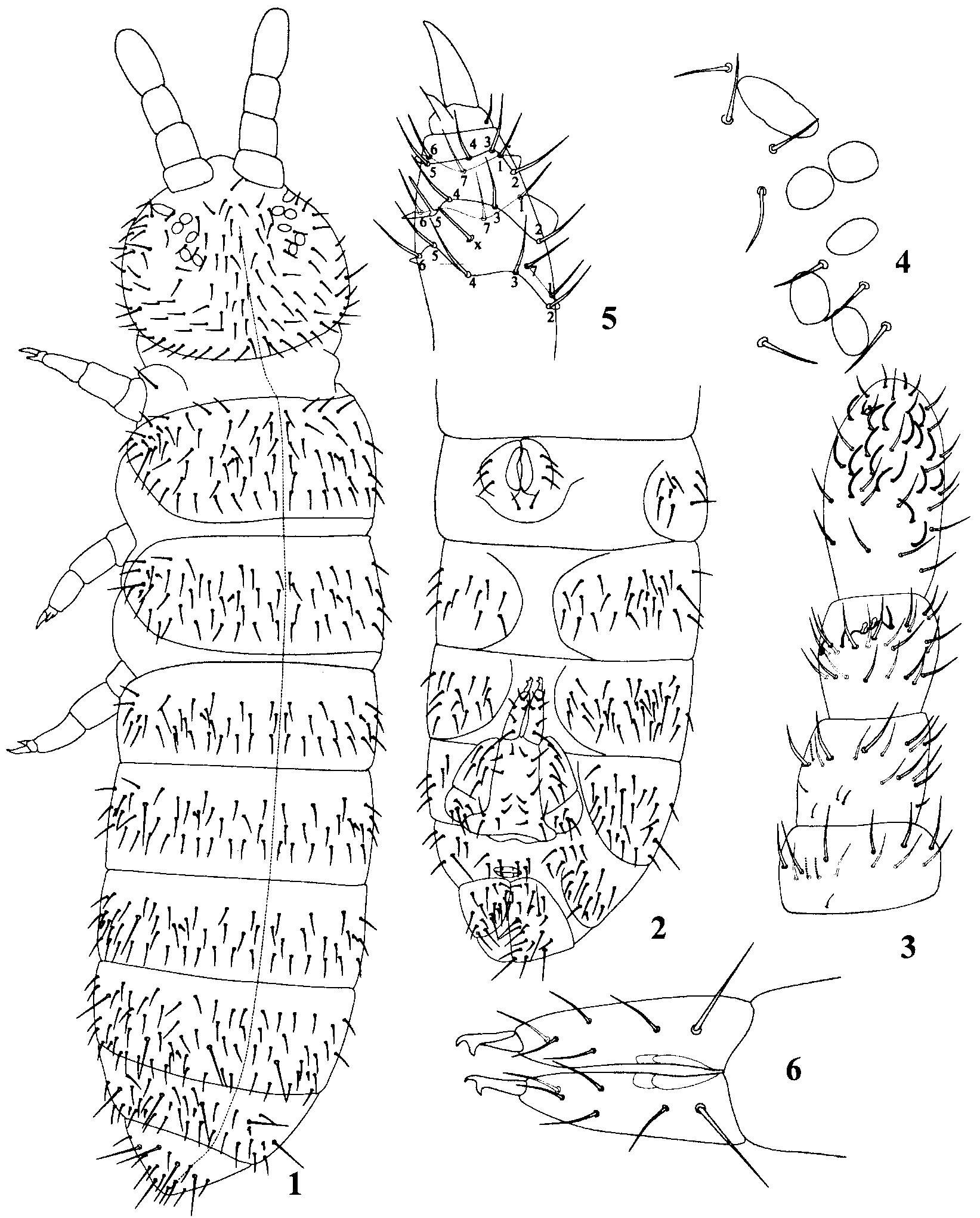
Size: 0.70.9 mm males, 0.81.0 mm females. Colour: blue greyish; pigment more concentrated in eye fields. Body long and slender ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 9 ). Dorsal mesochaetae smooth and pointed. Subaxial SA macrochaeta on abdominal tergite IV 0.4 times tergite length ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 6 ).
Antennae shorter than cephalic diagonal. Antennal segment IV with some 21 dorsal cylindrical sensilla, a dorsoexternal microsensillum and a subapical pit organ. Sensory organ of antennal segment III with a pair of small and rounded microsensilla and two short sensilla, one on each side. Another sensillum found in a ventrolateral location. Antennal segment III with 22 normal chaetae. Antennal segment II with a small subcylindrical ventral sensillum and 18 normal chaetae, and some of the basal ones short and fine. First antennal segment with two subcylindrical ventral sensilla and 12 normal chaetae; one of the basal chaetae smaller than the others ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 6 ).
Five corneola on each side of head. Postantennal organ long and narrow, 2.5 times corneolae diameter and width of a corneola, with two posterior chaetae ( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1 6 & 8 View FIGURES 7 9 ). Clypeolabral chaetae formula: 2/5,5,4. Maxillary palp bifurcate with three sublobal chaetae.
Dorsal chaetotaxy represented in Figure 1 View FIGURES 1 6 . Axial chaetotaxy of thoracic tergites IIIII and abdominal tergites IV have 5,3/3,3,3,4,2 pairs of mesochaetae respectively. Macrochaetotaxy: 1,1/0(1),1,1,3,3; type 3 of Fjellberg (1993), but lateral macrochaeta (L) of abdominal tergite I similar in length to normal chaetae. Microsensillar chaetotaxy: 1,1/ 0,0,0. Sensilla short, smooth and blunt ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7 9 ), half as long as mesochaetae. Two lateral sensilla on abdominal tergite V subequal, slightly smaller than the two medial sensilla.
Tibiotarsi of legs I, II and III with 20, 20 and 22 pointed chaetae respectively. Chaetae A1A7, B1B7, C1C7 and x present on tibiotarsus of leg III. Tibiotarsi of legs I and II with single chaeta B4/5. B5 and x chaetae of legs III in males rodlike modified ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 6 ). Claw with no teeth on inner edge. Empodial appendage sharp; its length less than half internal edge of claw.
Ventral abdominal chaetotaxy represented in Figure 2 View FIGURES 1 6 . Ventral tube with 3+3 distal chaetae and 1+1 basal ones. The retinacle with 3+3 teeth and one chaeta on corpus. Subcoxa of furca with six chaetae on anterior side and five on posterior side.
Furca well developed. Manubrium usually with 9+9 dorsal and no ventral chaetae. Dens with five dorsal chaetae and one chaeta in ventroapical location ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1 6 ). The mucro with two teeth, with a small lateral lamella from base to subapical tooth.
Types Locality: Caparroso, Bardenas (Navarra), Spain. Mediterranean shrub of RosmarinetoLinetum of the association of RosmarinoEricion. Soil on gypsy rock (torriorthent typical), altitude 300 m, UTM: 30TXM1184, date: 20VII1982. leg. Jordana.
which are present in Europe, north Africa and the Canary Islands.
Species ms Mc Dens Mucro Retinacle maxillary Distribution (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Palp.
F. petiti (Delamare, 1951) 10/000 11/11133 2/0 2 3/0 bifurcate Iberian Peninsula,
sensu Fjellberg, 1993 Canary Islands, France
F. pocosensillatus Fjellberg, 1993 10/000 11/11133 2/1 2 3/1 simple Iberian Peninsula,
Canary Islands (1): Number of microsensillae from Thor. II to Abd. III. (2): Macrochaetae from Thor. II to Abd. V. (3): Dens:
Number of dorsal chaetae/ventroapical. (4): Mucro: 1 or 2 (with 1 or 2 tooth). (5): Retinacle: Number of
tooth/chaetae.
Holotype female on slide CA014405. Number of paratype specimens in the slides: 5 in CA014406, 1 in CA014407, 1 in CA014409, 7 in CA0144 10, 5 in CA0144 11, 2 in CA0144 12, 7 in CA0144 13, 3 in CA014504, 1 in CA014505 and 196 in ethyl alcohol. All specimens are deposited in the Zoology Museum at the University of Navarra.
Other specimens: Specimens from the same locality and biotope: 234 from 27X1982 (samples CA0276 & CA0279). 27 from 1III1983 (samples CA0539 & CA0542). Specimens from the same locality and biotope but occurring in Pinus halepensis litter: 1 from 20VII1982 (sample CA0147), 3 from 27X1982 (sample CA0282). All these specimens were cited as Folsomides angularis ( Jordana et. al., 1987).
Madrid: Aranjuez, grass on soil of gypsy Serosem, HA, 21III1954, leg. W. Steiner (sample T72a). Vallecas, UTM: 30TVK4770, soil of gypsy Serosem, HA, 4IV1954, leg. W. Steiner (sample T73), deposited in the Museo de Ciencias Naturales in Madrid, labelled by Steiner as Folsomides n. sp.
Zaragoza: Retuerta de Pina, Pina de Ebro, UTM: 30TYL75, Mediterranean shrub of the Ononidetum tridentatae association, on moss ( Pleurochaete squarrosa ) and gypsy soil, numerous specimens of different dates between 19871992, leg. J. Blasco Zumeta. Deposited in the private collection of J.I. Arbea.
Discussion: Following Fjellberg (1993), Folsomides mediterraneus n. sp. belongs to the species group of Folsomides angularis (Axelson, 1905) as it has 5+5 corneolae and dens with mucro. The new species is close to F. t e r r u s Fjellberg, 1993 which has identical microsensillar chaetotaxy (11/000), but it is very different according to some other characteristics ( Table 1). According to its dental chaetotaxy (5/1) it is close to F. portucalensis Gama, 1961 , but it differs in the microsensillar distribution.
The main diagnostic characteristics are summarised in Table 1.
Biology: Folsomides mediterraneus n. sp, lives in a very dry area of Spain characterised by gypsy soils, and typical mediterranean shrub.
Derivatio nominis: Its name refers to the broad distribution of the specimen in the Mediterranean area of Spain.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Folsomides mediterraneus
| Arbea, Javier I. & Jordana, Rafael 2002 |
F. pocosensillatus
| Fjellberg 1993 |