Halicmetus granulosus, Ho, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5138.2.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AF4599B6-DBCB-4EE7-A25B-F42C03ED15CC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6556709 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4F45A669-5B1C-45E0-A39B-FE3C0FE8AF6D |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:4F45A669-5B1C-45E0-A39B-FE3C0FE8AF6D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Halicmetus granulosus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Halicmetus granulosus sp. nov.
New English name: Rough Shortnose Seabat
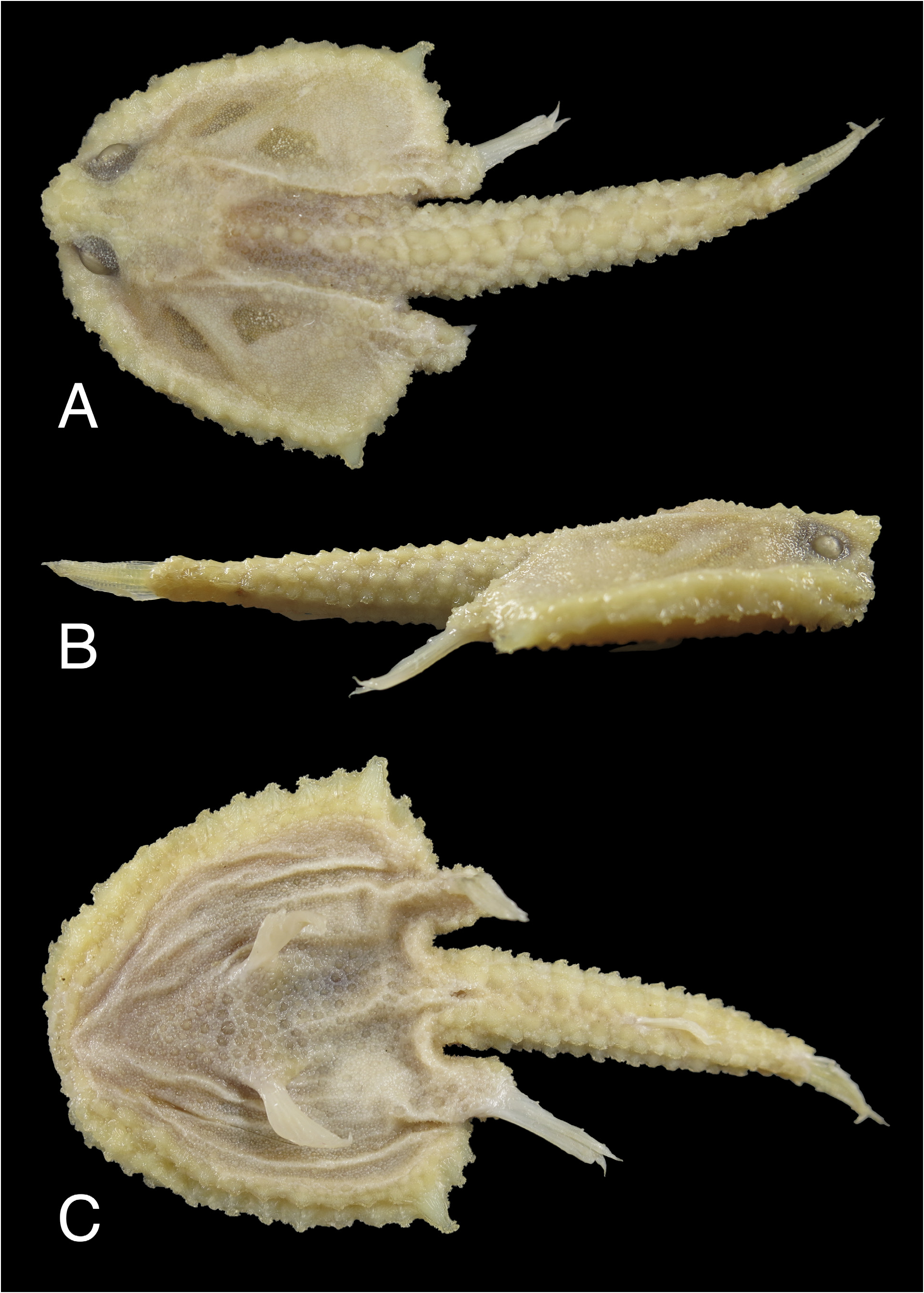
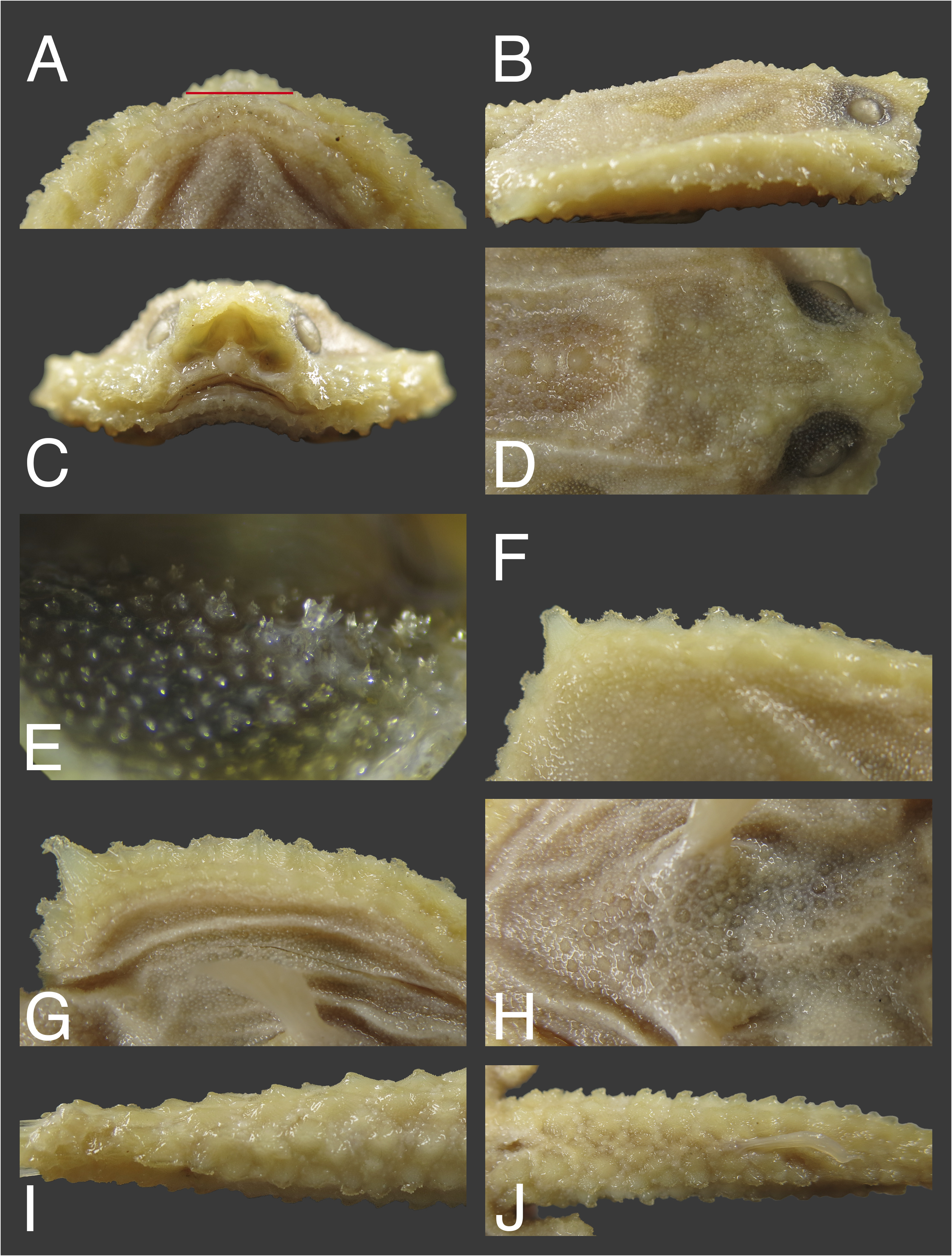
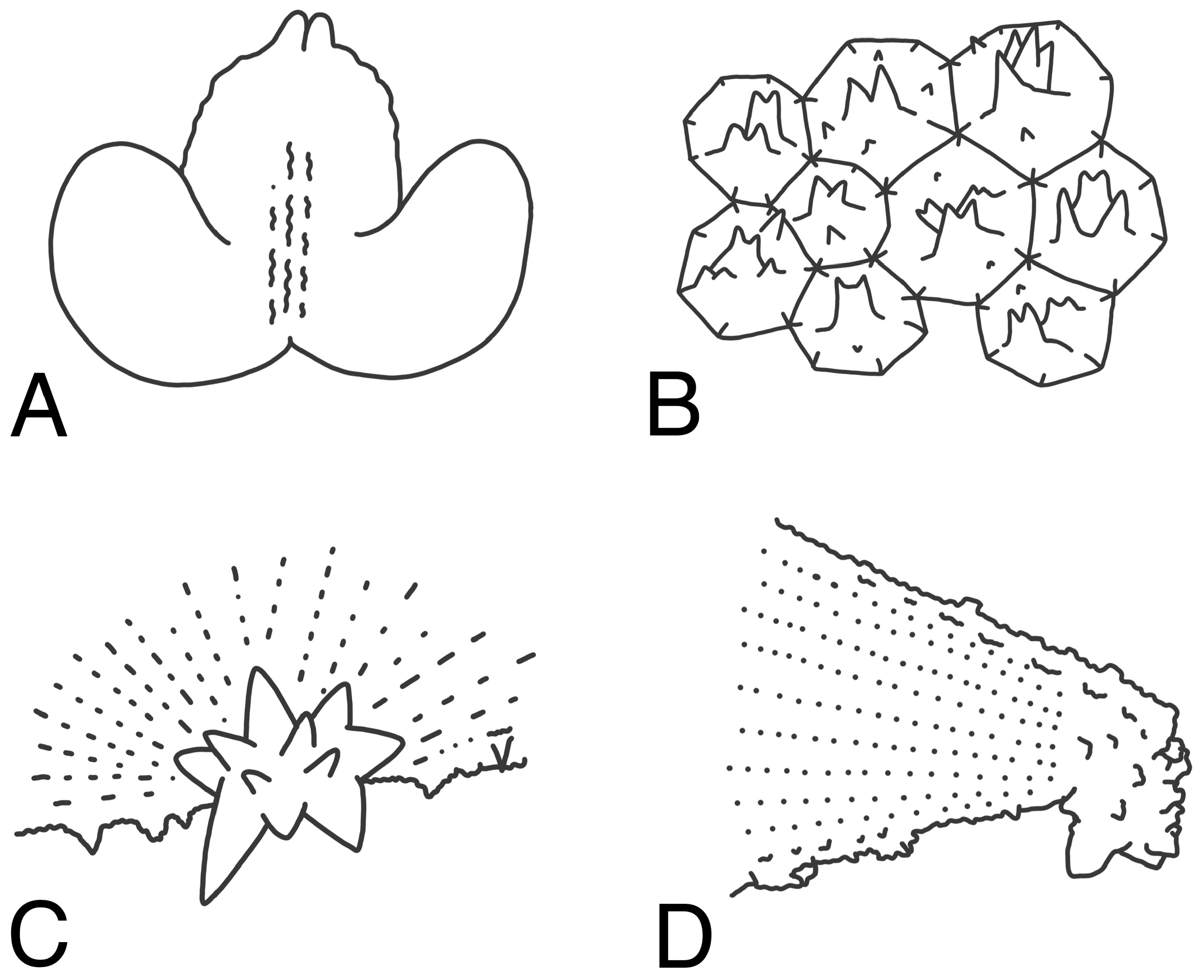
Figures 1‒3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 ; Table 1 View TABLE 1
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:4F45A669-5B1C-45E0-A39B-FE3C0FE8AF6D
Material examined. MNHN IC.1986-0015, R / V Vauban GoogleMaps , sta. ch030, 12°40.2’S, 48°9.6’ E, northern Madagascar, Mozambique Channel, Western Indian Ocean, 595‒605 m, 13 Sep. 1979.
Diagnosis. A species of Halicmetus which is unique in having various-sized bucklers densely covering the body surfaces and that is further distinguished from congeners by the following combination of characters: body disk relatively small, disk width 59.7% SL; orbit small, its diameter 8.3% SL; interorbital moderately wide 7.4% SL; tail length 47.7% SL; illicial trough opening wide and high; dorsal fin absent in adult; pectoral-fin rays 13; uniformly creamy white when preserved; peritoneal membrane pale with dense melanophores and scattered black dots.
Description. Proportional measurements expressed as percentages of SL and meristic data of the holotype are given in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Dorsal-fin rays 0 (no trace of dorsal fin externally); anal-fin rays 4; pectoral-fin rays 13. Body disk depressed, relatively small, its width 1.7 and length 1.9 in SL; disk subtriangular, slightly broader than long, truncated anteriorly ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ); skull slightly elevated anteriorly when viewed in lateral profile, its length 3.9 in SL; orbit small, directed dorsolaterally, diameter 3.1 in skull length (HL).
Rostrum slightly upturned, a small bony plate consisting of several large bucklers, extending beyond mouth ( Figs. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 2A, B View FIGURE 2 ); interorbital space moderately wide, its width slightly smaller than eye diameter, 3.5 in HL; illicial cavity situated entirely beneath rostrum, relatively broad and high ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ), its width 3.7 and width 4.4 in HL; nostrils located on each side of lateroventral margins of illicial cavity, a narrow naked membrane on the border of illicial cavity and nostrils ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ); esca trilobed, two fleshy, oval ventral lobes on each side, and a flap-like dorsal lobe with two short filaments on tip ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Lateral-line canals deep and clear on ventral surface of disk; lateral-line neuromasts on dorsal surface of disk and tail small and not easy to detect, whereas neuromasts on anterior margin of head and disk margin well-defined.
Mouth small, curved and forming an arch ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ); lower jaw slightly beyond upper jaw anteriorly; teeth villiform, small, in wide band on both jaws; quadrangular tooth patches on vomer and palatines. Fifth ceratobranchials bearing large and elongated tooth plates (tongue teeth, sensu Bradbury 1967, 1980).
Gill filaments present only on second and third gill arches; three gill rakers on outer side of second gill arch, four rakers on outer side of third gill arch; gill opening small, at inner portion of pectoral elbow. Dermal cirri present, associated with lateral line system on disk margin and tail. Pectoral fins at outer portion of posterior margin of disk; pelvic fins on ventral surface, slightly closer to mouth than anus; anal fin on ventromedial surface at midlength of tail.
Squamation agreeing well with definition of Ogcocephalus by Bradbury (1980), consisting of close-set of various-sized bucklers, their bases overlapping and forming heavy armor. Bucklers, with sizes ranging from mini to large, covering entire body except for eyes, lips, fins, and anus; large conical bucklers along disk margins, tail, and associated with lateral-line canals and skeleton beneath skin on dorsal surface. Frontal ridge with row of bucklers, anterior two bucklers enlarged, overlapping dorsoanterior border of orbit, fused together with three large bucklers on rostrum and forming a flat bony plate; followed by two smaller bucklers and then two (right) and three (left) slightly taller bucklers along upper margin of orbit ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). Interorbital space densely covered with many small bucklers, except for a slightly larger one anteriorly. Supraocular membranes with three (right) and two (left) slightly enlarged bucklers, each with few spinules on top, right above the margin of eye, elsewhere covered with small, broad-based bucklers ( Figs. 2E View FIGURE 2 , 3B View FIGURE 3 ). Posterior portion of dorsal surface of skull densely covered with mid-sized bucklers, mixed with small spiny bucklers ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). Shoulder evenly covered with mid- and small-sized bucklers ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ), mixed with mini spiny bucklers; a row of large bucklers on midline of posterior portion of disk.
Disk margin with three well-defined rows of bucklers ( Figs. 2F, G View FIGURE 2 ). Uppermost row of bucklers elevated, large, conical with broad base anteriorly, becoming gradually smaller posteriorly; middle and lower rows associated with lateral line. Those in middle row directed laterally, each with a broad, compressed base; tips multifid, each with five or six blunt spinules, which are somewhat arranged in a radiating pattern in lateral view ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ), and row ending with an enlarged, moderately long subopercle buckler extending well beyond disk margin laterally, its tip rather dull, bearing several tiny blunt spines ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ). Bucklers in lower row directed ventrally, relatively small and conical. Four small bucklers along posterior margin of disk between subopercular buckler and pectoral-fin base; outer two large and mutilfid and inner two smaller. Dorsal surface of pectoral-fin base covered with several mid-sized bucklers.
Many mid-sized bucklers on chest, pelvic-fin base, and belly ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ), with the remaining areas densely covered by tiny bucklers, each with a few spinules on top. Tail heavily covered by 12 rows of conical bucklers, with interspaces entirely covered with mini bucklers ( Fig. 2I, J View FIGURE 2 ): two rows on dorsal surface, continuing from the middle row of posterior body disk; two irregular rows on each side above the lateral line; two rows on ventrolateral side associated with lateral line, each with a serrate top which slightly curves backward, and two irregular rows of enlarged bucklers on ventral surface of tail.
Lateral-line canal system with well-developed, lateral-line neuromasts: supraorbital series four; body series eight; premaxillary series one; cheek series eight; preopercular series two; subopercular series seven; dorsolateral branch of subopercular series three; ventral series one (beside anus); tail series nine.
Color. Fresh color unknown. Body uniformly creamy white in preservation; all fins pale without pigment. Oral cavity and gill chamber pale. Peritoneum membrane pale with numerous brown melanophores and scattered black dots.
Distribution. Known only from the holotype collected from off northern Madagascar, Western Indian Ocean, at depth of 595‒ 605 m.
Etymology. The specific name of granulosus derived from the Latin granulis, which means granular, referring to the rough body surface with various-sized bucklers.
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |