Kalidos balstoni (Angas, 1877)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.2462.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6413F378-FFCF-6A52-F28B-76FCFEAEF9BA |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Kalidos balstoni (Angas, 1877) |
| status |
|
Kalidos balstoni (Angas, 1877) View in CoL
Figures 23G–H View FIGURE 23 , 29E View FIGURE 29 , 31M–O View FIGURE 31 , 33B View FIGURE 33 , 35A View FIGURE 35
Material examined. Madagascar: AM C205303 (two specimens dissected, one radula examined), 15km SW of Andringitra Reserve, 55 km SE of Ambalabao , SW Madagascar, dense mountain rainforest, 1997 .
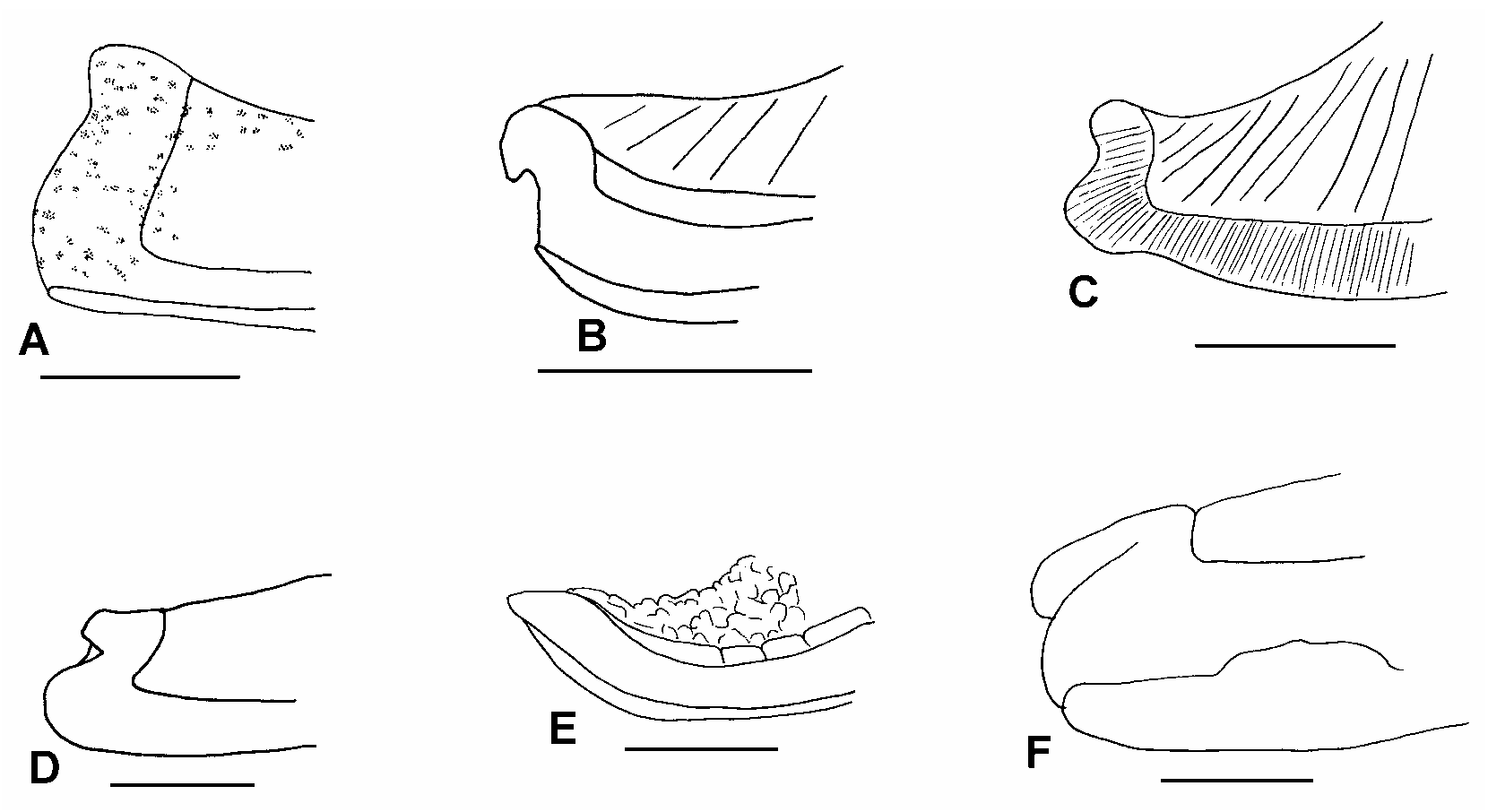
Description. External morphology: Shell 5.9 whorls, orange brown, spire and apex slightly raised. Protoconch sculptured with spiral ribs and irregular radial ribs; teleoconch with radial ribs. Whorl profile flattened above and below an angular periphery. Internal walls of early whorls complete; umbilicus open, very narrow U-shape. Animal ( Figure 35A View FIGURE 35 ) light brownish-yellow with grey spots. Mantle laps absent. Right mantle lobe small, left and median mantle lobes very small. Sole of foot and caudal apparatus as for family; caudal horn small; caudal foss vertical slit in tail.
Mantle cavity: As for family. Mantle with no visible minor blood vessels, pigmentation of black and white spots.
Digestive system: Oesophageal crop absent.
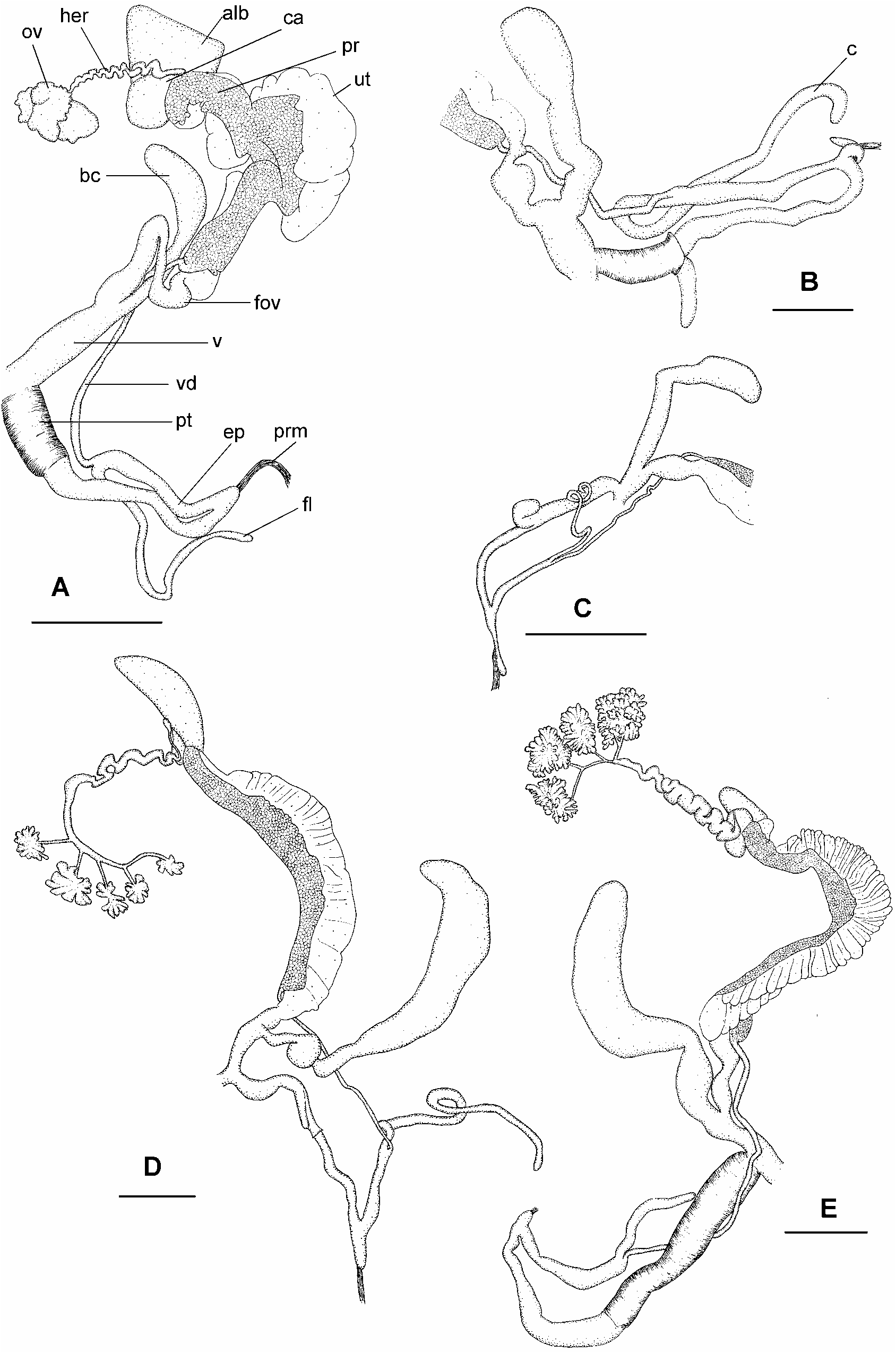
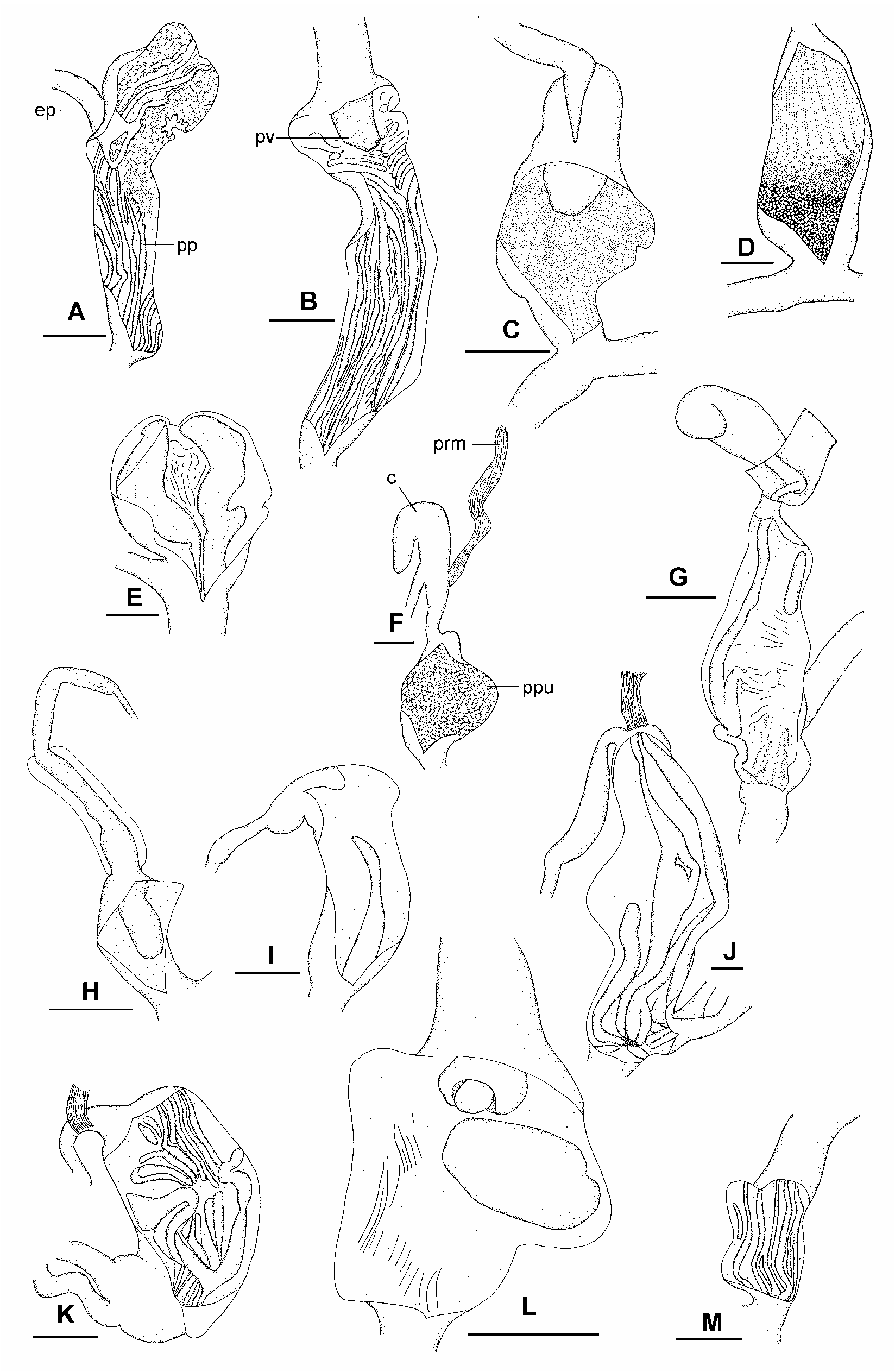
Genital system ( Figures 23G–H View FIGURE 23 , 29E View FIGURE 29 , 33B View FIGURE 33 ): As for family. Carrefour and talon both not embedded in albumen gland. Free oviduct of medium length; capsular gland present; internal longitudinal pilasters absent. Bursa copulatrix inserted on vagina, moderately short, about half spermoviduct length; duct of bursa copulatrix narrow, very short, distinguishable from bursa copulatrix, internally with pustules. Vagina internally with longitudinal pilasters. Penis long; epiphallus enters penis through short verge; penis internally smooth, twelve longitudinal penis pilasters present, penial diverticulum absent. Penial sheath present, very thick, enclosing only penis; muscle connecting top of penial sheath to epiphallus present; penis retractor muscle attached to epiphallus. Epiphallus approximately equal to penis length, internally with longitudinal pilasters. Epiphallic retractor caecum absent. Flagellum present; flagellum and distal part of epiphallus without internal cryptae and externally smooth and slender. Spermatophore soft capsule with firm tail pipe open at one end; tail pipe long, sculptured with longitudinal rows of tiny teeth.
Radula ( Figure 31M–O View FIGURE 31 ): Relatively long and narrow. Central tooth with small ectocones; mesocone lanceolate, similar in length to tooth base. Lateral and marginal tooth fields distinguishable. Lateral teeth with endocone much smaller than central tooth ectocones; ectocone equal in size to those on central tooth; mesocone shorter than tooth base. Marginal teeth with endocones absent; ectocones absent, not subdivided into extra teeth. Radular formula (69.12.1.12.69) × 105 rows.
Remarks. Kalidos is a large genus endemic to Madagascar containing about 60 species ( Schileyko 2002b). No anatomical data are available for the type species, K. ekongensis (Angas, 1877) . The genus was traditionally included in Ariophantinae (Ariophantidae) ( Zilch 1959) but has been more recently regarded as a member of Ereptinae (Ariophantidae) ( Schileyko 2002b). Kalidos balstoni diverged from the base of Helicarionidae in the present phylogenetic analysis ( Figures 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 ). In the molecular analysis of Hyman et al. (2007) its position was poorly resolved, but it diverged basally from Helicarionidae when other problematic taxa were removed.
| AM |
Australian Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.