Eungarion mcdonaldi Stanisic, 1993
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.2462.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6413F378-FFA0-6A3D-F28B-7554FC01F91F |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Eungarion mcdonaldi Stanisic, 1993 |
| status |
|
Eungarion mcdonaldi Stanisic, 1993 View in CoL
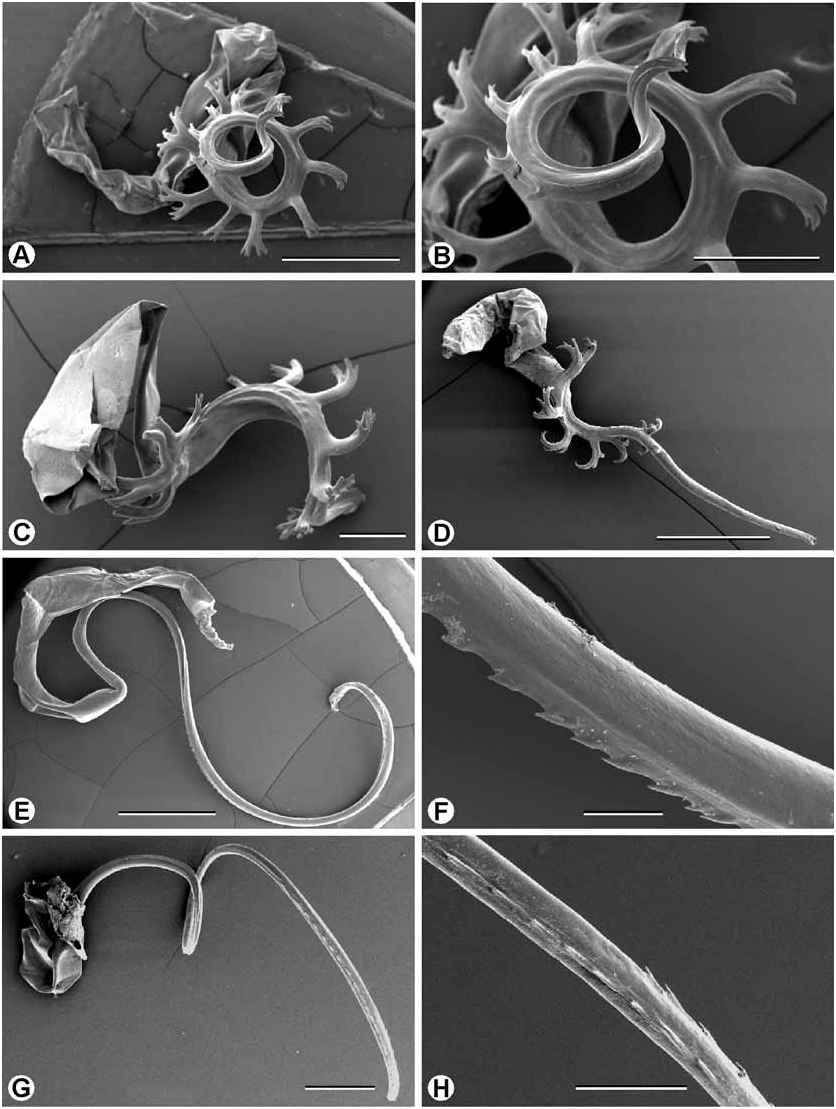
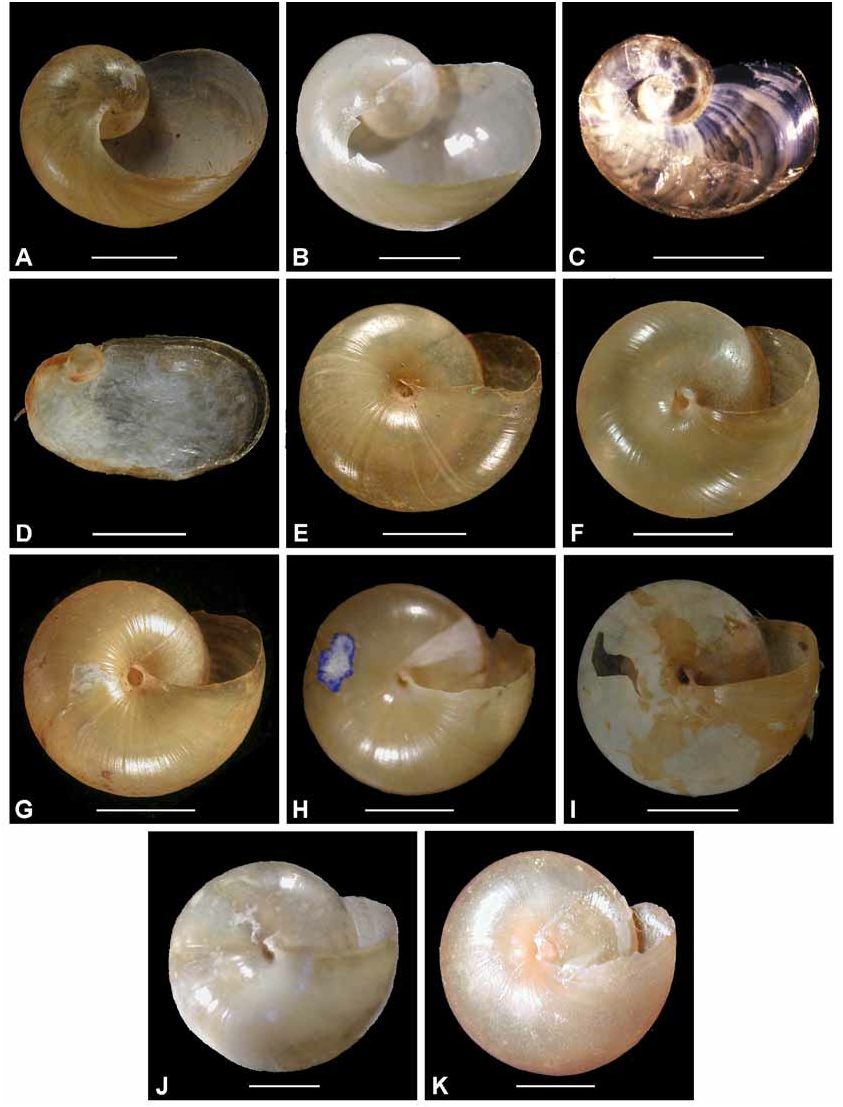
Figures 6L–M View FIGURE 6 , 13K View FIGURE 13 , 14E–F View FIGURE 14 , 18C View FIGURE 18 , 19C View FIGURE 19 , 21C View FIGURE 21
Eungarion mcdonaldi Stanisic, 1993a: 28 View in CoL , figs 1–4.
Material examined. Queensland, Australia: AM C438760 (one specimen dissected), Mt. William National Park , N of Mackay (21º1' S, 148º36' E), 27 Apr. 1975, W.F. Ponder, P.H. Colman, J.B. Burch GoogleMaps ; QMMO35628 (one shell photographed, measured), Mt. Macartney , middle east Queensland .
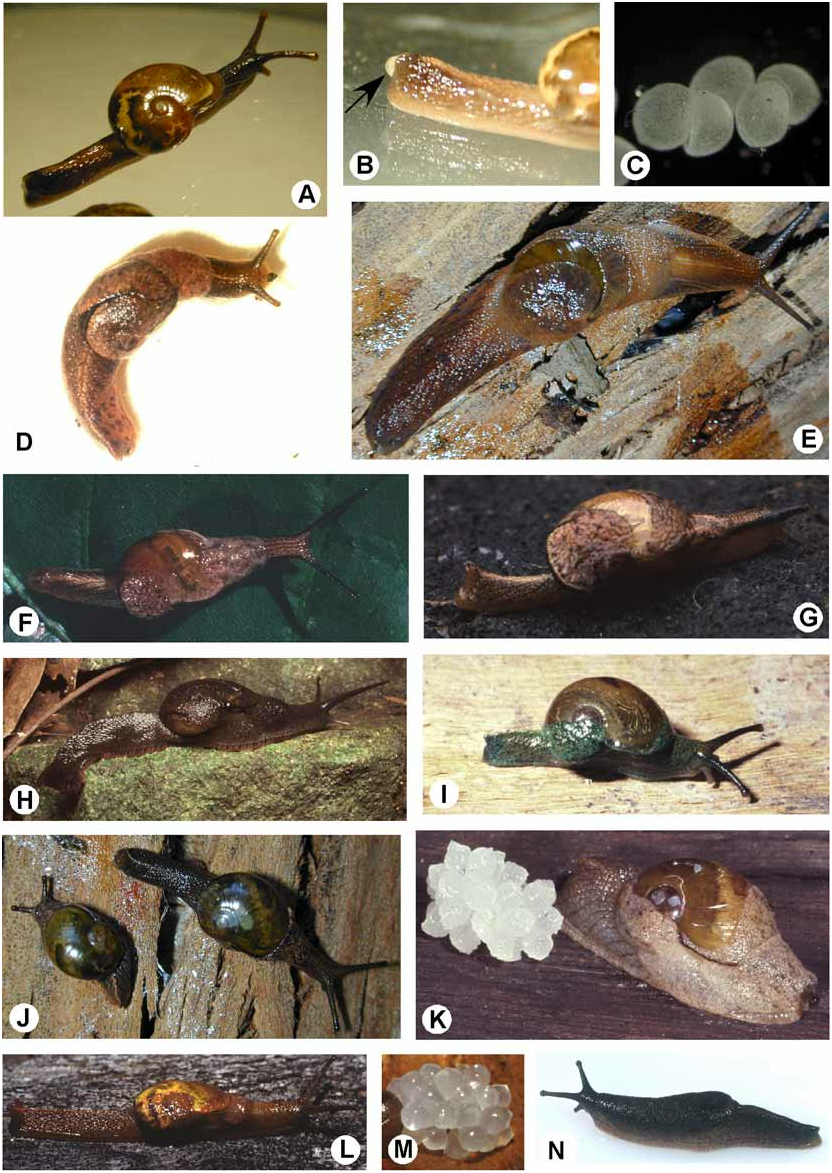
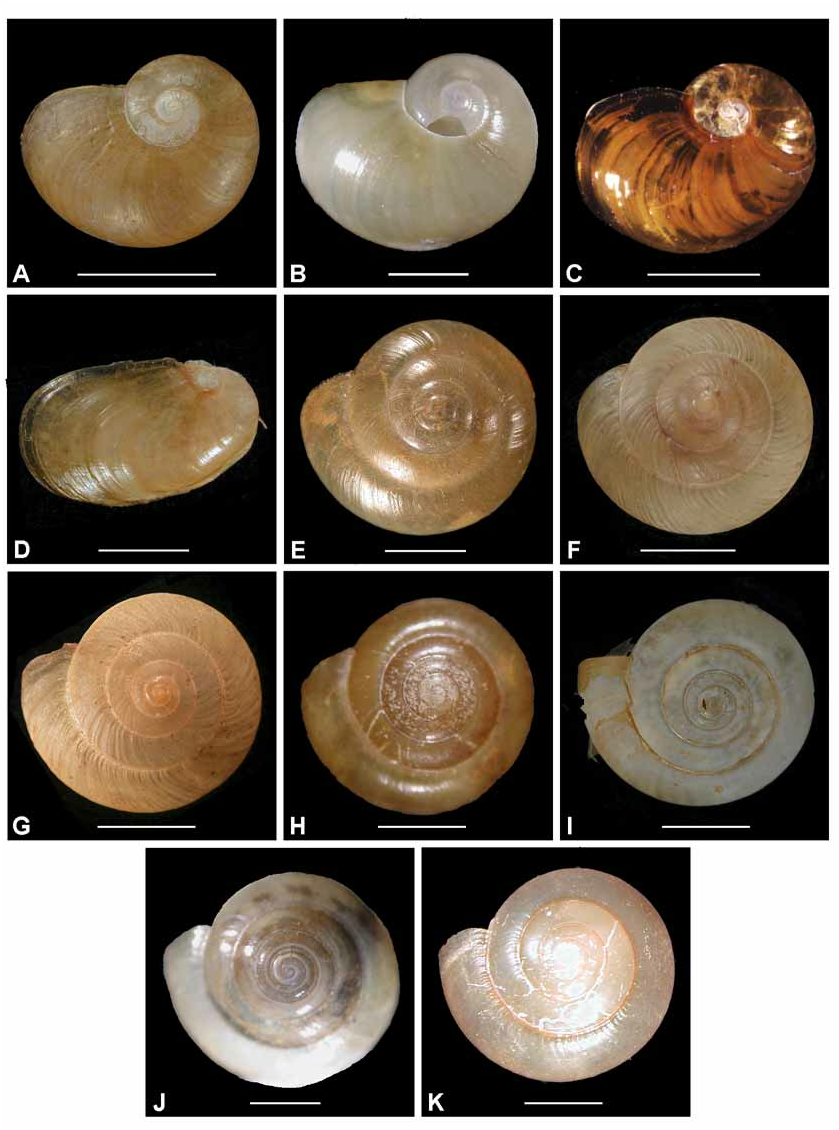
Description. External morphology: Shell ( Figures 19C View FIGURE 19 , 21C View FIGURE 21 ) reduced; about 2.7 whorls, orange-brown, shape and sculpture as for genus. Animal ( Figure 6L View FIGURE 6 ) cream in ethanol. Mantle laps large, rounded, fused at base, uniform in colour. Mantle lobes of medium size, left and median lobes fused. Caudal apparatus as for genus; caudal horn small; caudal foss vertical slit in tail.
Mantle cavity and digestive system: As for genus.
Genital system ( Figures 13K View FIGURE 13 , 14E–F View FIGURE 14 , 18C View FIGURE 18 ): As for genus. Penis moderately long; epiphallus enters penis through two fleshy lips; penis internally covered in pustules, four longitudinal penis pilasters present. Epiphallus longer than penis, internally with longitudinal pilasters. Spermatophore soft capsule with firm tail pipe open at one end; tail pipe sculptured with longitudinal rows of tiny teeth.
Radula (based on Stanisic 1993a): As for genus. Radular formula (140.11.1.11.140) (number of rows not recorded).
Range and habitat. Eungarion mcdonaldi appears to be restricted to the simple notophyll vine forests on the summits or near-summits of the Clarke Ranges in mideastern Queensland. The semislugs are usually found in dead palm fronds and on leaves on the ground ( Stanisic 1993a).
| AM |
Australian Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Eungarion mcdonaldi Stanisic, 1993
| Hyman, Isabel T. & Ponder, Winston F. 2010 |
Eungarion mcdonaldi Stanisic, 1993a: 28
| Stanisic, J. 1993: 28 |