Stegana, Meigen, 1830
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00575.x |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/636B87A0-3023-FFE0-7DCD-FC6638E8F88C |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina (2021-04-26 13:13:29, last updated by Plazi 2023-11-02 07:26:17) |
|
scientific name |
Stegana |
| status |
SP. NOV. |
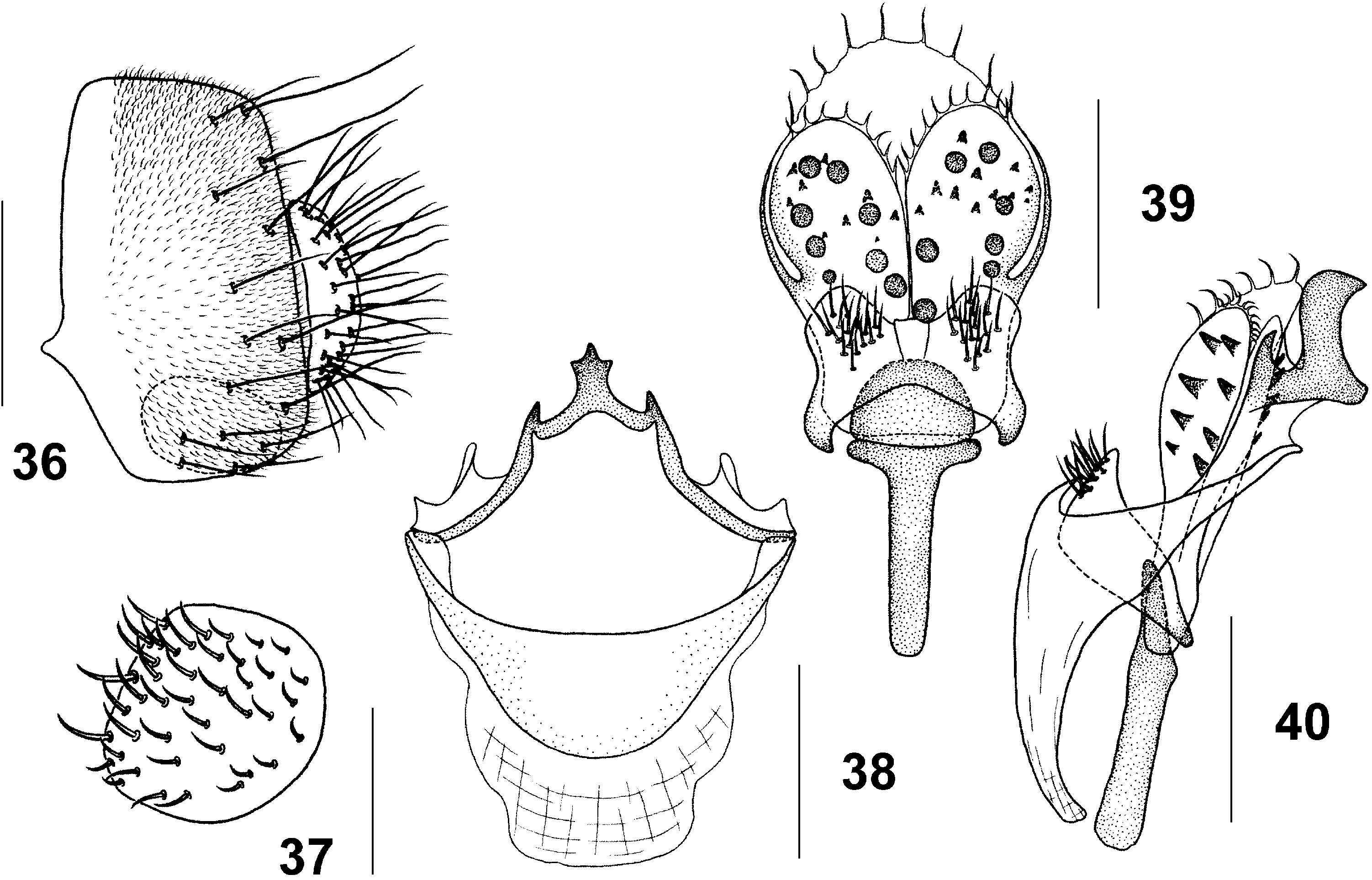
STEGANA View in CoL ( STEGANA ) ROTUNDA CAO & CHEN SP. NOV. ( FIGS 36–40 View Figures 36–40 )
Specimens examined: Holotype male, China: Guangxi, Guilin, Maoershan , 630 m, 21.ix.2006, ex tree trunks, JJ Jiang ( SCAU, no. 120291).
Etymology: From the Latin word rotundus, referring to the aedeagus being slightly rounded apically.
Diagnosis: Katepisternum almost dark brown; paramere with 15–17 strong setae ( Figs 39, 40 View Figures 36–40 ); surstylus without prensiseta ( Fig. 37 View Figures 36–40 ).
Description: Frons, face, and clypeus yellow. First flagellomere yellow on basal third, black on distal two-thirds. Gena brown. Mesonotum yellow, sublaterally with two brown stripes on each side. Scutellum brown. Legs yellowish white, fore leg brown on knee and tibia; mid and hind leg black on femora and basal three-quarters of tibiae. Fore femur with four setae on distal part of ventral surface. Abdomen with all tergites and sternites black. Male terminalia: hypandrium somewhat sclerotized anteromedially ( Fig. 38 View Figures 36–40 ). Gonopods with one curved process posteromedially and two smaller triangular processes submedially ( Figs 39, 40 View Figures 36–40 ). Aedeagus with several tentacle-like setae apically and spine-like processes ventrally, lacking pubescence ( Figs 39, 40 View Figures 36–40 ).
Measurements: BL = 2.46 mm in holotype; ThL = 1.22 mm; WL = 1.88 mm; WW = 0.95 mm. Indices: arb = 7/5, avd = 0.73, adf = 1.67, flw = 2.22, FW/HW = 0.33, ch/o = 0.08, prorb = 1.00, rcorb = 0.80, vb = 0.29, dcl = 0.56, presctl = 0.70, sctl = 1.84, sterno = (damaged), orbito = 2.31, dcp = 0.24, sctlp = 1.50, C = 1.91, 4c = 1.25, 4v = 1.86, 5x = 1.18, ac = 9.26, M = 0.50, C3F = 0.63.
Distribution: China (Guangxi).
RESULTS OF MOLECULAR PHYLOGENETIC ANALYSIS
Data analysis
The alignment of the ND2 sequence was 1029 nucleotide sites in length, coding 342 amino acid residues, containing 183 parsimony-informative characters, with consecutive gaps at sites 267–269 in some sequences. The average base frequencies of the ND2 sequences (including outgroups) calculated in MEGA were 36.6, 45.0, 7.8, and 10.6% for A, T, G, and C, respectively, showing strong bias towards A and T. It was revealed by the Chi-square test that the base composition is not homogeneous among taxa (P = 0.8208) at the third codon position, but homogeneous at the first and second codon positions (P = 1.000 and 1.000, respectively), or even the average data (P = 0.9988). The test of substitution saturation in DAMBE showed that the observed Iss index is 0.1707, significantly lower than the Iss.c
Figures 36–40. Stegana (Stegana) rotunda Cao & Chen sp. nov., male: 36, epandrium, surstylus, and cercus; 37, surstylus; 38, hypandrium and gonopods; 39, paramere, aedeagus, and aedeagal apodeme; 40, hypandrium, gonopods, paramere, aedeagus, and aedeagal apodeme. For orientation, see Figures 1–7. Scale bars = 0.1 mm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |