Hindumanes wayanadensis, Sudhin & Nafin & Sudhikumar, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4350.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:00DC83AE-1754-4065-8BDC-F49B01EA2DDD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5999275 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5B3B3A3C-716E-3E5B-FF3C-AD9AFB84F9C6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hindumanes wayanadensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Hindumanes wayanadensis View in CoL sp. nov.
Figs 4F View FIGURE 4 , 6–7 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7
Type material. Holotype: Female (CATE 8412B) from Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bathery range, 11°45ʹ01.3ʹʹN 76°24ʹ43.2ʹʹE, 746 m asl, P.P. Sudhin & K.S. Nafin, 02.VI.2015.
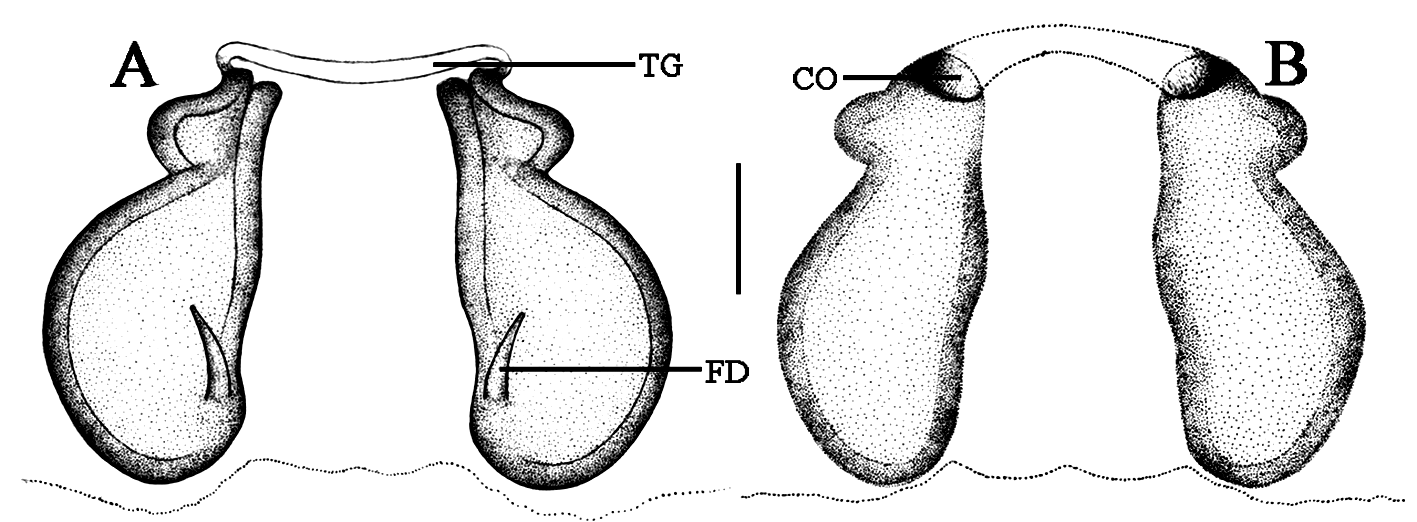
Diagnosis. The female of Hindumanes wayanadensis sp. nov. is similar to that of H. karnatakaensis , but can be separated by the following combination of characters: chelicerae devoid of mid-dorsal spines (two mid-dorsal spines in H. karnatakaensis ); epigyne without posterior outgrowth overhanging the epigastric furrow (present in H. karnatakaensis ); spermathecae almost kidney-shaped, widely separated and anteriorly narrowed with lateral hump (in H. karnatakaensis , it is nearly oblong, close together); copulatory duct is very short and copulatory opening is anteriorly located (in H. karnatakaensis , copulatory duct is moderately long and copulatory opening at the middle of the epigyne) (compare Figs 3C View FIGURE 3 , 4C View FIGURE 4 , 6C View FIGURE 6 , 7A–B View FIGURE 7 ; Logunov 2004: figs 1–2).
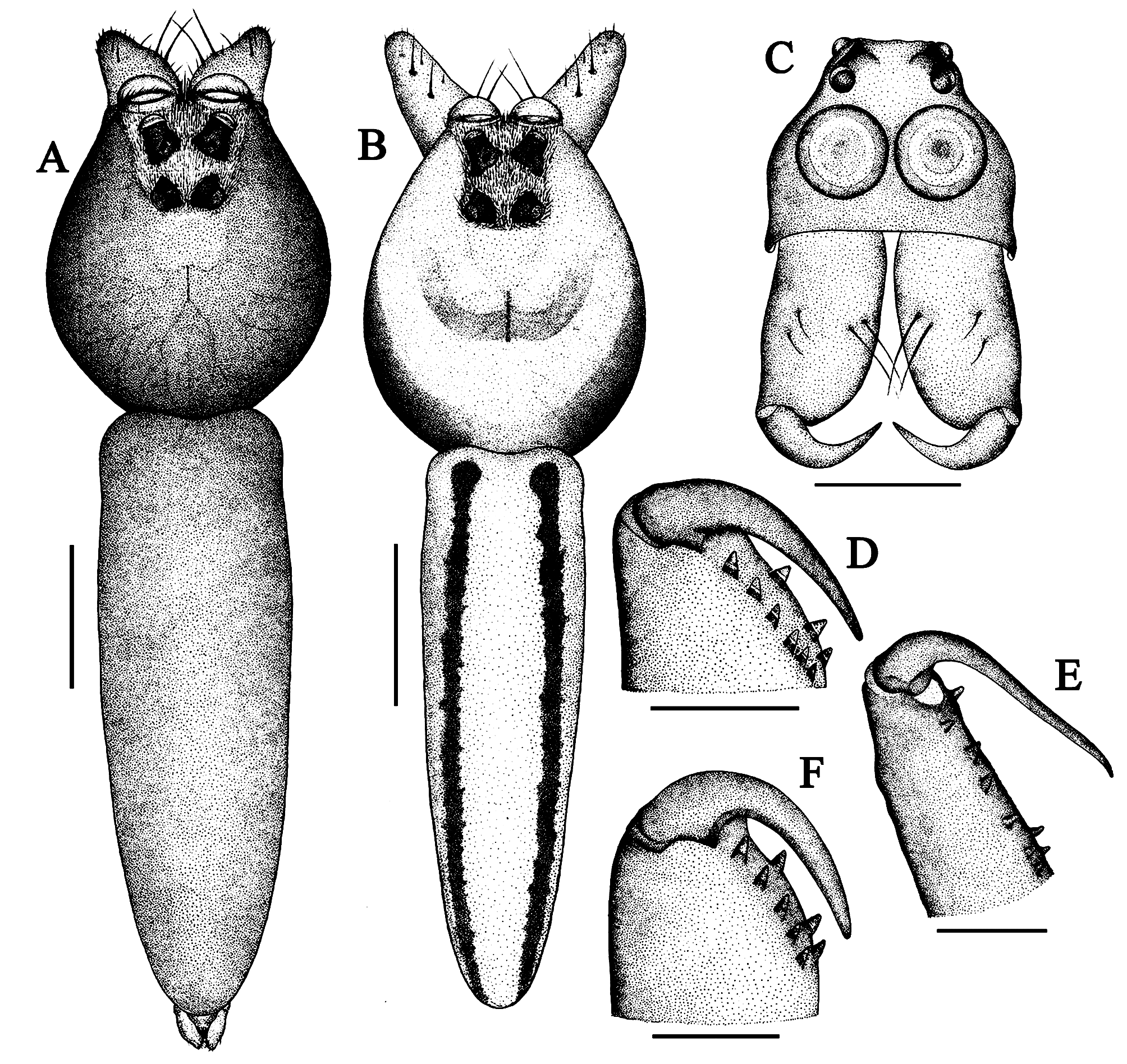
Description. Female. (CATE8412B) ( Figs 4F View FIGURE 4 , 6A–D View FIGURE 6 , 7A–B View FIGURE 7 ) Measurements: body length 6.72. Carapace length 2.68, width (at the middle) 1.98, height at PLE 1.19. Abdomen length 4.04, width (at the middle) 1.53. Ocular area length 0.54, width 0.46. Eye diameters: AME 0.45, ALE 0.18, PME 0.03, PLE 0.13. Eye interdistances: AME–ALE 0.05, PME–PME 0.32, ALE–ALE 0.39, PME–PLE 0.31, PLE–PLE 0.34, ALE–PME 0.08. Clypeus height 0.19. Length of chelicera 0.92. Measurement of palp and legs: Palp 3.57 [1.30, 0.52, 0.7, 1.05], leg I 9.59 [2.84, 1.04, 2.70, 2.43, 0.58], II 7.91 [2.48, 0.84, 2.03, 1.94, 0.62], III 7.01 [2.13, 0.69, 1.74, 1.77, 0.68], IV 7.61 [2.23, 0.54, 2.03, 2.19, 0.62]. Leg formula: 1243.
Spination. Palp: femur pl 1 rl 1, patella do 1, tibia pl 2, tarsus pl 2 rl 2 plv 1 rlv 1 v 1; Legs: femur I–II pl 2 rl 2 do 3, III pl 2 rl 1 do 3, IV pl 1 rl 1 do 3; patellae I–II spineless, III–IV do 1; tibia I plv 4 rlv 4, II pl 1 plv 4 rlv 4, III pl 1 rl 1 plv 2 rlv 1 do 2, IV pl 1 rl 1 do 2; metatarsi I–II plv 3 rlv 3, III pl 1 plv 1 rlv 1, IV spineless.
Carapace green ( Fig. 6D View FIGURE 6 ); fovea distinct and longitudinal, light reddish-brown with indistinct markings radiating from fovea to lateral margins. Eye field slightly raised, covered with golden yellow lustrous appressed scales ( Figs 6A, D View FIGURE 6 ). Clypeus low, vertical, light green. Chelicera medium-sized, light green, sub-vertical, promargin with two spines ( Fig. 6C View FIGURE 6 ); promargin with one medial and two basal teeth, retromargin with five teeth ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ); fangs light greenish-brown. Endites light green. Labium light green. Sternum pale greenish-yellow. Pedicel greenish. Abdomen slender, light green, elongate, ovoid, narrowing posteriorly, clothed with colorless setae ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ). Spinnerets cloudy white, sub-equal in length, posterior spinnerets robust than the rest. Legs and palp light green; tibia I with apical retrolateral black mottling; tibiae I & II with 4 pairs of ventral spines, metatarsi I & II with 3 pairs of ventral spines, patellae I & II distally with one dorsal macrosetae and patellae III & IV with one dorsal spine; tarsi with well-defined claw tufts.
Epigyne ( Figs 7A–B View FIGURE 7 ). Simple, transparent, with an anterior transverse groove, posterior border line with a median invagination ( Fig. 7B View FIGURE 7 ); spermathecae large, almost kidney-shaped, narrowed anteriorly with a lateral hump and widely separated from each other; copulatory opening located on the lateral sides of the anterior transverse groove of the epigyne, entering a very short copulatory duct, which enters ventrally directly into the anterior region of the spermathecae ( Fig. 7B View FIGURE 7 ); fertilization duct small, anterolaterally oriented, located on the inner margin of the posterior spermathecae ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7 ).
Male. Unknown.
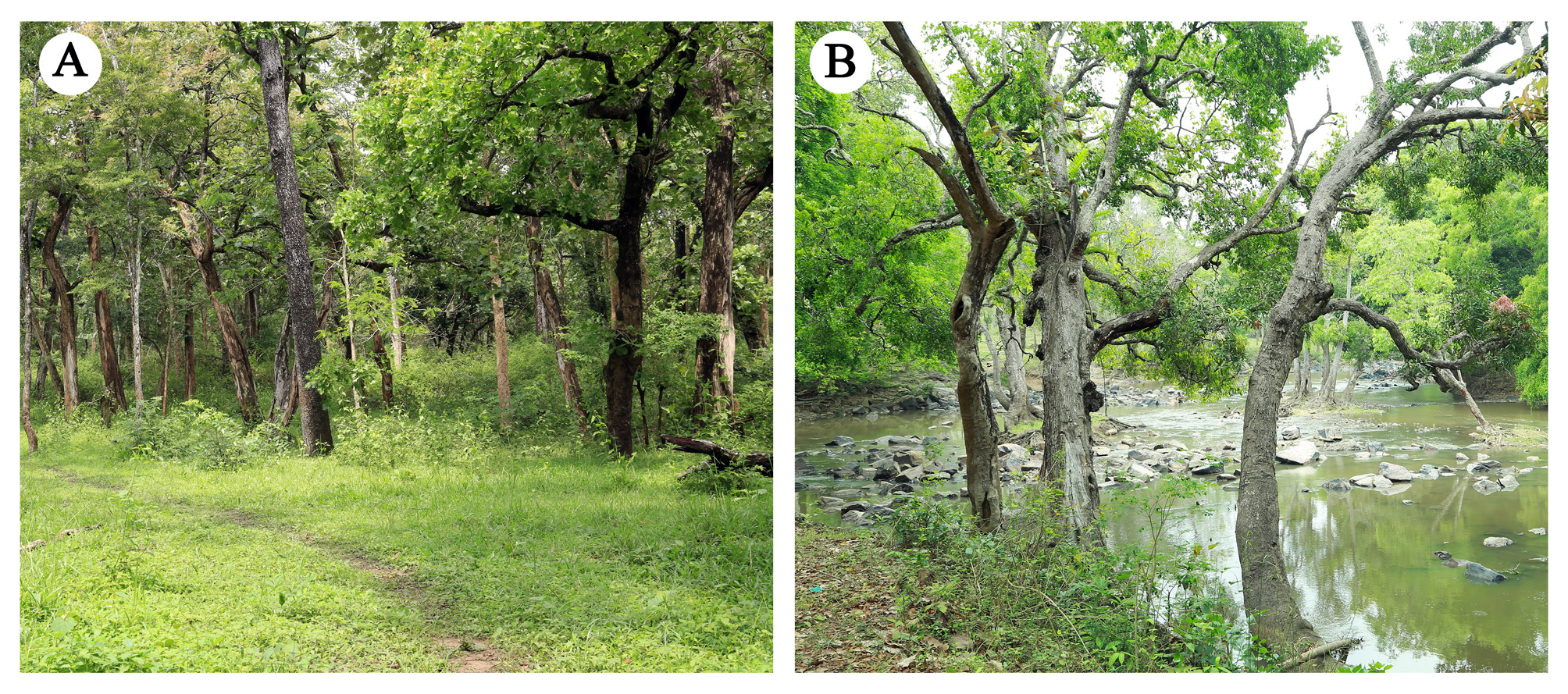
Habitat. Specimens collected from leaves of Chromolaena odorata (Asteraceae) in the riparian habitat of Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Kerala, India ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ).
Etymology. The specific epithet is an adjective derived from the name of the sanctuary from where the species was collected.
Natural history. Mature specimens of H. karnatakaensis and H. wayanadensis sp. nov. were observed/ collected during the late pre-monsoon (April–May) and early monsoon (June–July) seasons. Only juveniles of Hindumanes were spotted during the post-monsoon (October–January) season.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Lyssomaninae |
|
Genus |