Stenopsocus externus Banks
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4057.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:89E858EB-2E3B-47FC-B2F0-35B2A3ED6EBB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6122749 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5764C334-124B-FFF5-A4B7-FB333664FF36 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenopsocus externus Banks |
| status |
|
Stenopsocus externus Banks View in CoL
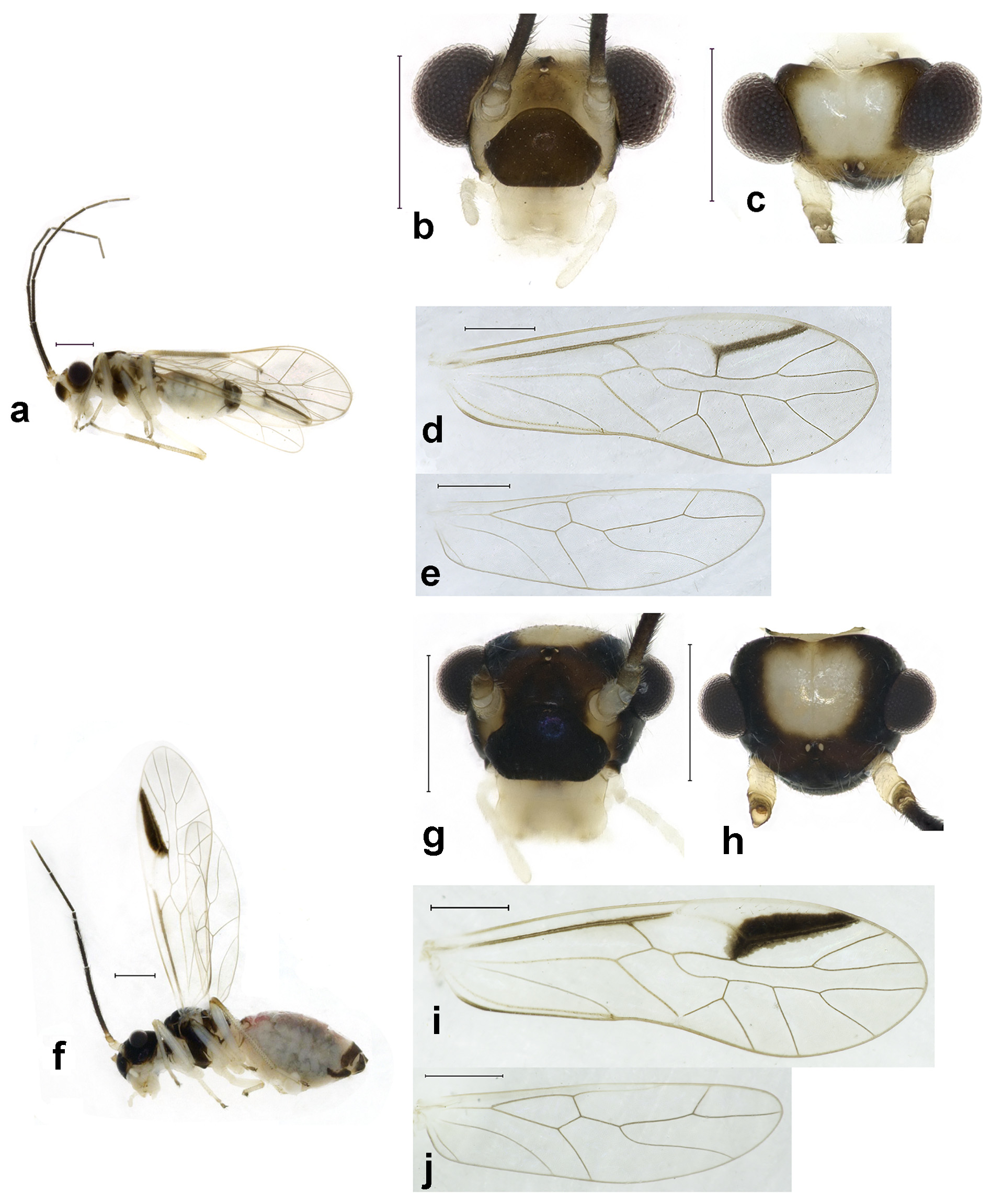
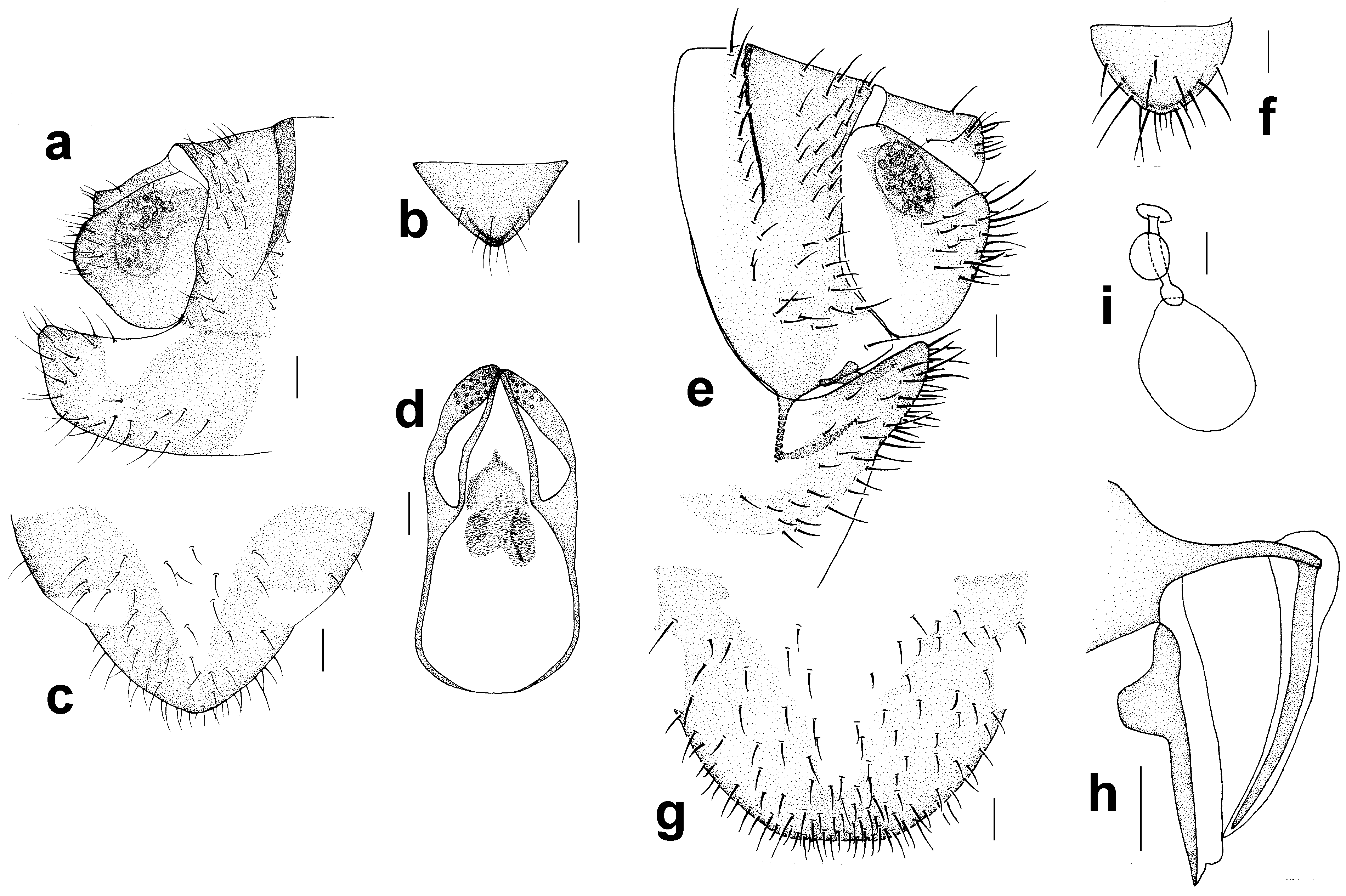
( Figs. 9–10 View FIGURE 9 View FIGURE 10 )
Stenopsocus externus Banks, 1937: 259 View in CoL . Type locality: China ( Taiwan: Taihoku).
Diagnosis. This species is characterized by the antenna with yellowish scape and pedicel, whitish 10–13 segments of antenna, and yellowish pterostigma with narrow brown stripe on the half of posterior margin.
Adult male. Body ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 a) length 2.41 mm, length from postclypeus to wing tip 4.13 mm. IO: 0.38 mm, d: 0.28 mm, IO/d=1.36, f1: 0.71 mm, f2: 0.55 mm, f3: 0.45 mm, FWL: 3.21 mm, FWW: 1.10 mm, HWL: 2.38 mm, HWW: 0.72 mm, t1: 0.35 mm, t2: 0.13 mm.
Colour (in alcohol). Head ( Figs. 9 View FIGURE 9 b, c) dark brown, vertex with a yellowish subtrapezoid area, frontal area yellowish brown, antenna with yellowish scape and pedicel, and 10–13 segmenst whitish. Postclypeus blackish brown, labrum laterally much paler, apex of maxillary palpus pale brown, remaining segments of maxillary palpus whitish.
Thorax brown or dark brown. Leg yellowish; hind leg with yellowish brown tibia. Abdomen whitish. Genital segments dark brown.
Forewings ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 d) transparent. R and R1 dark brown, anterior margin of pterostigma yellowish, other veins brown. Yellowish pterostigma with brown stripe on half of R1. Hindwing ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 e) immaculate.
Genitalia ( Figs. 10 View FIGURE 10 a–d) strongly sclerotized. Epiproct ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 b) subtriangular with a round apex. Paraproct entire sclerotized, with 30 trichobothria. Endophallus ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 d) strongly sclerotized, external parameres robust, with some punctures on broadened apex, not exceeding apex of aedeagal arch; aedeagal arch narrow. Hypandrium ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 c) strongly sclerotized.
Adult female. Body ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 b) length 3.16 mm, length from postclypeus to wing tip 4.48 mm. IO: 0.55 mm, d: 0.20 mm, IO/d=2.75, f1: 0.89 mm, f2: 0.70 mm, f3: 0.58 mm, FWL: 3.21 mm, FWW: 1.04 mm, HWL: 2.38 mm, HWW: 0.65 mm, t1: 0.32 mm, t2: 0.12 mm.
Colour generally similar to male, but slightly darker. Head ( Figs. 9 View FIGURE 9 g, h) with a yellowish area on vertex. Forewing ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 i), R without marking, half of R1 with dark brown marking, and hindwing ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 j) immaculate. Abdomen purplish brown; genital segments blackish brown.
Genitalia ( Figs. 10 View FIGURE 10 e–i) strongly sclerotized. Epiproct ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 f) subtriangle with round apex. Paraproct ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 e) with 19 trichobothria. Gonapophyses ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 h) with external valve reduced, trapezoid, fused with dorsal valve; ventral valve narrowly elongate, with acute apex. Subgenital plate ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 g) with sclerotized area separated into two parts, an obvious sclerotized stripe along margin of subgenital plate to connect two parts.
Specimens examined. CHINA ( TAIWAN), Pingtung, Dahanshan, 1 female, 2.vi.2013, Liang Feiyang; Yilan, Wushibi, 1 female, 8.vi.2013, Luo Xingyu. CHINA, Henan, Xinxian, Liankangshan, Jiulongtan, 1 male, 2 females, 18.vi.2014, Liu Xingyue; Guangxi, Fangcheng, Jinhuacha National Reserve, 1 male, Liu Xingyue; Guangxi, Wuming, Mt. Damingshan, 1 male, 6.vi.2014, Liu Xingyue; Hubei, Yingshan, Taohuachong, 1 male, 1 female, 23.v.2014, Zhang Wei; Shanghai, 1 female, iii.2013, Xu Jin; Guangxi, Nanning, 1 male, 24.v.1984, Yang Ding; Nanning, 1 female, 19.v.1984, Li Fasheng; VIETNAM: Kon Tum, Chu Mom Ray National Park, 1 female, 1.viii.2012, Liang Feiyang.
Distribution. China (Fujian, Gansu, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hebei, He’nan, Hubei, Hu’nan, Sichuan, Shanghai, Taiwan, Zhejiang); Vietnam (Kon Tum).
Remarks. In the original description, Banks (1937) only recorded S. formosanus and S. externus from Taiwan. Subsequently, Li (2002) recorded S. formosanus from Zhejiang and S. externus from several provinces in mainland China, i.e. Fujian, Gansu, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hebei, Hubei, Hunan, Sichuan, Shanghai. Here we record S. externus from Vietnam for the first time.
Based on the concept of Banks (1937), S. formosanus and S. externus can be distinguished based on the antennal colour and forewing marking patterns. S. externus has yellowish pedicel and scape, and it has a brown marking only along half of R1; S. formosanus has dark brown antenna, and it has a brown marking along entire R1. Although, the interspecific genetic divergence between these two species is 0.00%, the genitalia of S. externus differ from those of S. formosanus by the subtriangle male epipcrot and the entire sclerotized paraproct. Thus, we still consider they are different species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Stenopsocus externus Banks
| Liang, Feiyang, Dai, Yuting, Yue, Lu, Li, Fasheng & Liu, Xingyue 2015 |
Stenopsocus externus
| Banks 1937: 259 |