Pontocrates arenarius ( Spence Bate, 1858 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5115.4.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6EC597E1-684B-4F42-A3B2-1C389B8E746F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6365420 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5727879F-3750-FFD6-53C7-C6F0FA12FA5A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pontocrates arenarius ( Spence Bate, 1858 ) |
| status |
|
Pontocrates arenarius ( Spence Bate, 1858) View in CoL
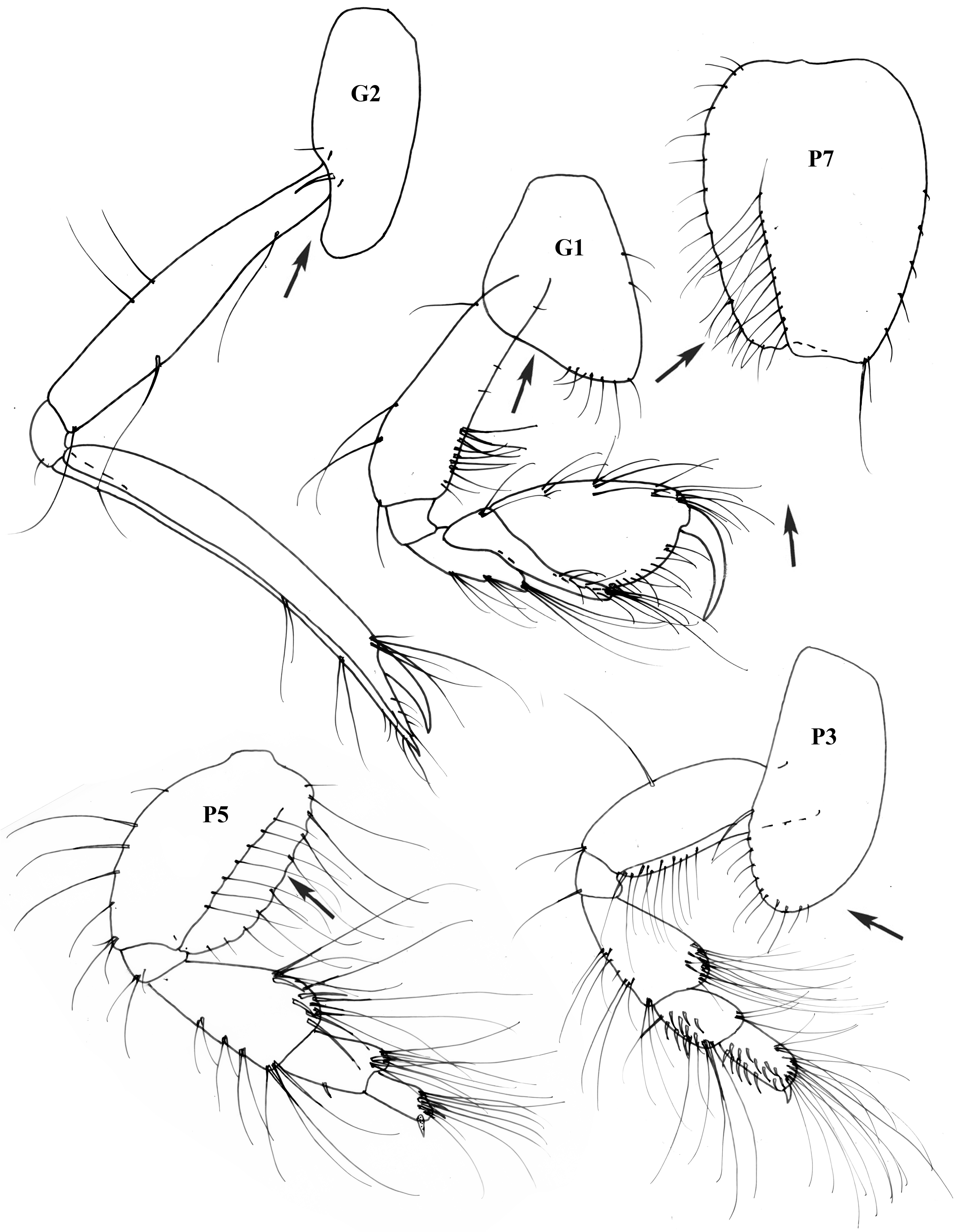
( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Kroyera arenaria Spence Bate, 1858 View in CoL , 15, pl. 2, fig. 1.— Spence Bate & Westwood, 1863, 173, fig. p.173.—Spence Bate, 1862, 106, pl. 17, fig. 4.—? Reibisch, 1905, 182, fig. 6–10 (in part).
Pontocrates arenarius Stebbing, 1906, p. 241 View in CoL .— Stephensen, 1926, 79.— Stephensen, 1928, 215, fig. 43.— Stephensen, 1929, 114, fig. 27.— Oldevig, 1933, 129, fig. 2.— Schellenberg, 1942, 179, fig. 48.— Lincoln, 1979, 342, fig. 160.— Ledoyer, 1993, 604, figs 415 (in part), 416.— Moore & Beare, 1993, 610, figs 1–3.— Zettler & Zettler, 2017, 249, figs 171–17.
Not Pontocrates arenarius Gurjanova, 1951 View in CoL , 524, fig. 342 = P. norvegicus View in CoL .
Pontocrates norvegicus Chevreux & Fage, 1925 View in CoL , 165, figs. 165, 166.— Barnard & Karaman, 1991, 565 (in part).
? Pontocrates norvegicus Elmhirst, 1932 View in CoL . 171.
Not Pontocrates norvegicus Boeck, 1871 View in CoL , 171.
Type material. Holotype ( Kroyera arenaria Spence Bate ), Sunderland, England. ( BMNH 1952.5.7.136-138).
Material studied. 1 male, 12 females; Hartland Point ; 50°43’53.36”N 004°39’07.96”W; intertidal—lower shore; Sand; leg. APEM, 09/09/2013 GoogleMaps . 1 female; Isles of Scilly; 49°53’48.84”N 006°16’20.58”W; 62 m depth; Shelly Coarse Sand; leg. CEFAS, 07/12/2014 GoogleMaps . 1 female; Mounts Bay ; 50°06’38.60”N 005°31’07.16”W; intertidal—lower shore; Fine / Medium Sand; leg. Natural England, 05/03/2014 GoogleMaps . 1 male; The Manacles ; 50°02’24.10”N 005°04’02.44”W; 6.2 m depth; Gravelly Sand; leg. APEM, 15/07/2014 GoogleMaps .
Description (female, Hartland Point, 4.5 mm)
Head Head rostrum short, strongly deflected, triangular in frontal view, eyes confluent dorsally. Antenna 1 short; flagellum longer than peduncle, with 6 articles. Antenna 2 longer than antenna 1.
Pereon. Gnathopod 1 subtriangular, coxa distal margin substraight; basis moderately stout, about 4x as long as broad; merus with short distal extension; propodus subovoid, 1.5 x as long as broad, palm weakly oblique, smooth, distinct from posterior margin, without club-shaped robust setae. Gnathopod 2 coxa posterodistal margin sinuous. anterior margin substraight; basis elongate, slender; carpus small but with elongate spur that extends beyond tip of propodus; propodus very elongate, slender, chelate. Pereopod 3 coxa distal margin convex; basis about 3 x as long as broad; merus anterodistal margin strongly convex; carpus and propodus short, propodus a little longer than carpus, subrectangular, distally truncate; carpus and propodus posterior margins with many stout, robust setae; merus and propodus anterodistal margins clothed in very long slender setae; dactylus small. Pereopod 5 basis posterior margin scalloped; merus anterodistal margin strongly convex and with exceedingly long setae; carpus short, posterior margin irregular, with long setae; propodus subequal in length with carpus, slender, antero-distal margin with long setae; dactylus indistinct. Pereopod 6 propodus shorter than carpus. Pereopod 7 basis subquadrangular, posterior margin substraight.
Pleon. Epimera 1–3 rounded. Uropods 1 slender, rami subequal and shorter than peduncle. Uropod 2 slender, rami subequal and longer than peduncle. Uropod 3 slender, subequal rami longer than peduncle. Telson distally rounded, not incised.
Male (sexually dimorphic characters). Antenna 2 elongate, longer than body, peduncular articles 4 and 5 subequal, flagellum with about 40 articles.
Colour. According to Moore & Beare (1993), P. arenarius is almost transparent, with white speckles. It has bright red eyes, covered by a white reticulation, which are separated by a white strip lacking facets. It has a readily discernible pattern of darkly pigmented patches mid-ventrally on the sternal plates of both sexes, females more so than males, reaching forwards into the head (beneath the mouth-part bundle). The eggs are sky blue.
Habitat and distribution. Found off all British coasts. Intertidal and near-shore shallow sublittoral to a depth of about 30 m in sands and gravelly sands. Elsewhere it is recorded from southwest Norway and northeast Atlantic coasts, but some previous records may be due to confusion with other species. Ledoyer (1993) records this species from the Mediterranean (but see also under P. norvegicus ).
Remarks. Pontocrates arenarius differs from all other Pontocrates species in the sinuous posterior margin of coxa 2 and in the scalloped posterior margin of the pereopod 5 basis. The anterior extension of the gnathopod 1 merus is shared with P. moorei sp. nov. The colour pattern of P. arenarius described above, which survives preservation in spirit quite well, together with differences in egg colour distinguishes P. arenarius from P. moorei sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Pontocrates arenarius ( Spence Bate, 1858 )
| Myers, Alan A. & Ashelby, Christopher W. 2022 |
Pontocrates arenarius
| Stebbing, T. R. R. 1906: 241 |