Daouitherium rebouli
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00272.x |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/557487D0-F770-FF99-FE9A-FC38FE97F99A |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Daouitherium rebouli |
| status |
|
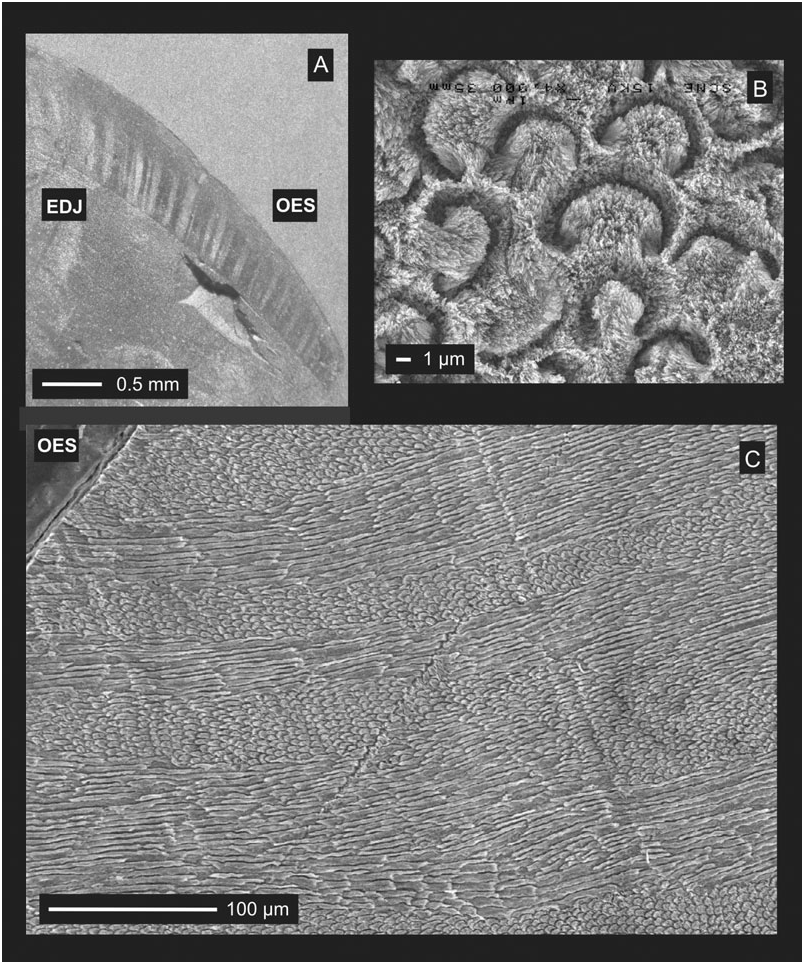
In a vertical section of a m3 tooth, the enamel thickness is around 1500 µm. The Schmelzmuster is entirely constituted by HSB from the EDJ to the OES ( Fig. 3C View Figure 3 ). The HSB run straight outwards and are parallel to each other; they are of variable width, varying in the sample from seven to 20 prisms. Very few bifurcations of HSB occur. In horizontal sections of a fragment removed from a m2 tooth, the prism cross sections present a rounded pattern near the OES. In the inner zone, the prism cross sections vary from a keyhole pattern (the prisms are basally opened and densely packed) to an arc pattern (the prisms are also basally opened, but not densely packed, and they present an important amount of IPM of the enamel) ( Fig. 3B View Figure 3 ); in this zone, the diameter of the prisms is around 5–7 µm. Near the EDJ, the prisms cross sections were not observed. A tangential view of the same specimen shows decussations of low amplitudes; bundles of prisms appear. On an enamel fragment removed from the unique known molar of Daouitherium sp. , the enamel thickness is around 350 µm; the Schmelzmuster is identical to that of D. rebouli .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |