Scutacarus tackei Willmann, 1942
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4179.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EB3D8CAC-B3D0-4007-ABB8-F2DDDBBCF26 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5670918 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/517CE246-8853-FFCA-FF13-AE65FEBBFA72 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Scutacarus tackei Willmann, 1942 |
| status |
|
Scutacarus tackei Willmann, 1942
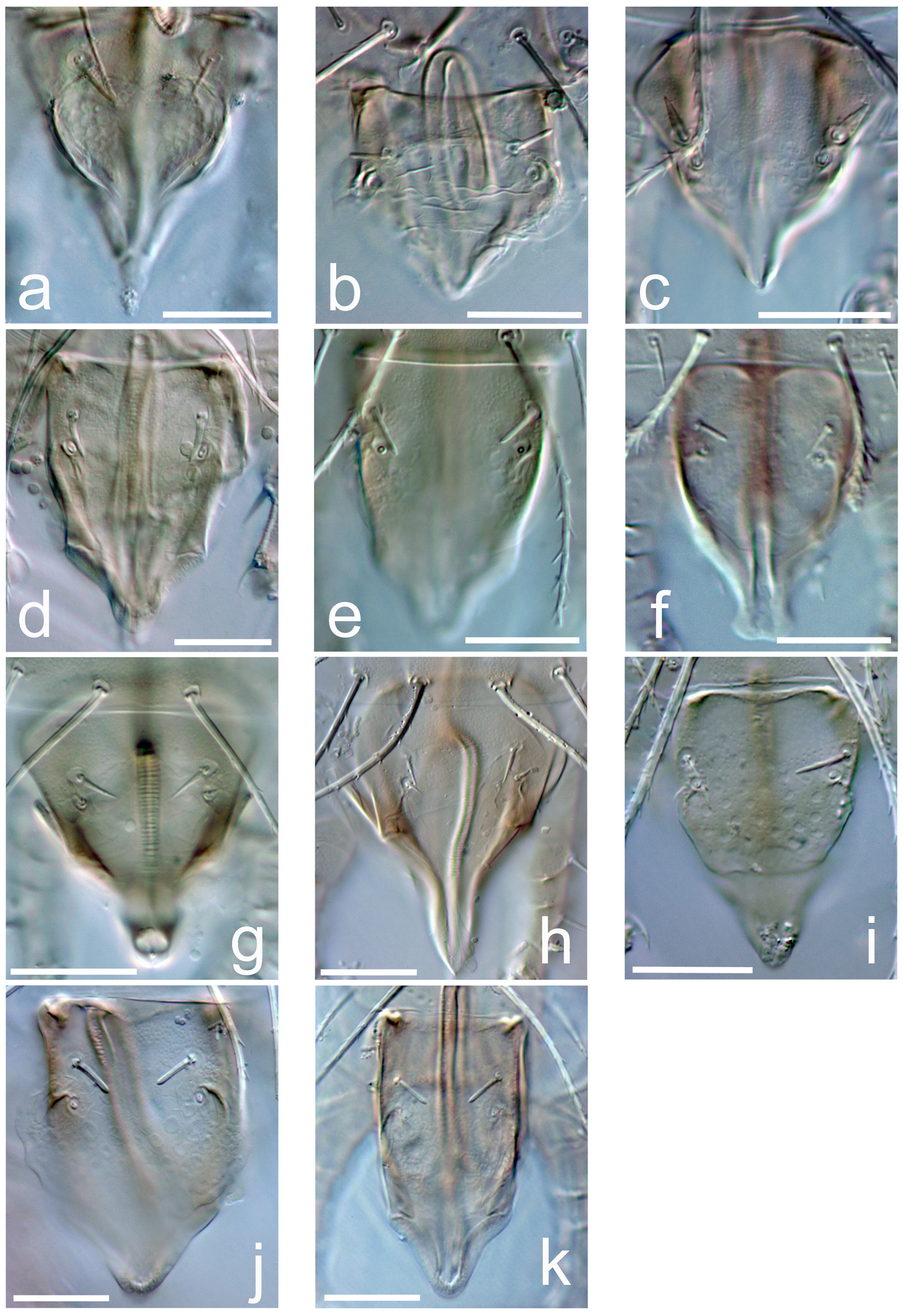
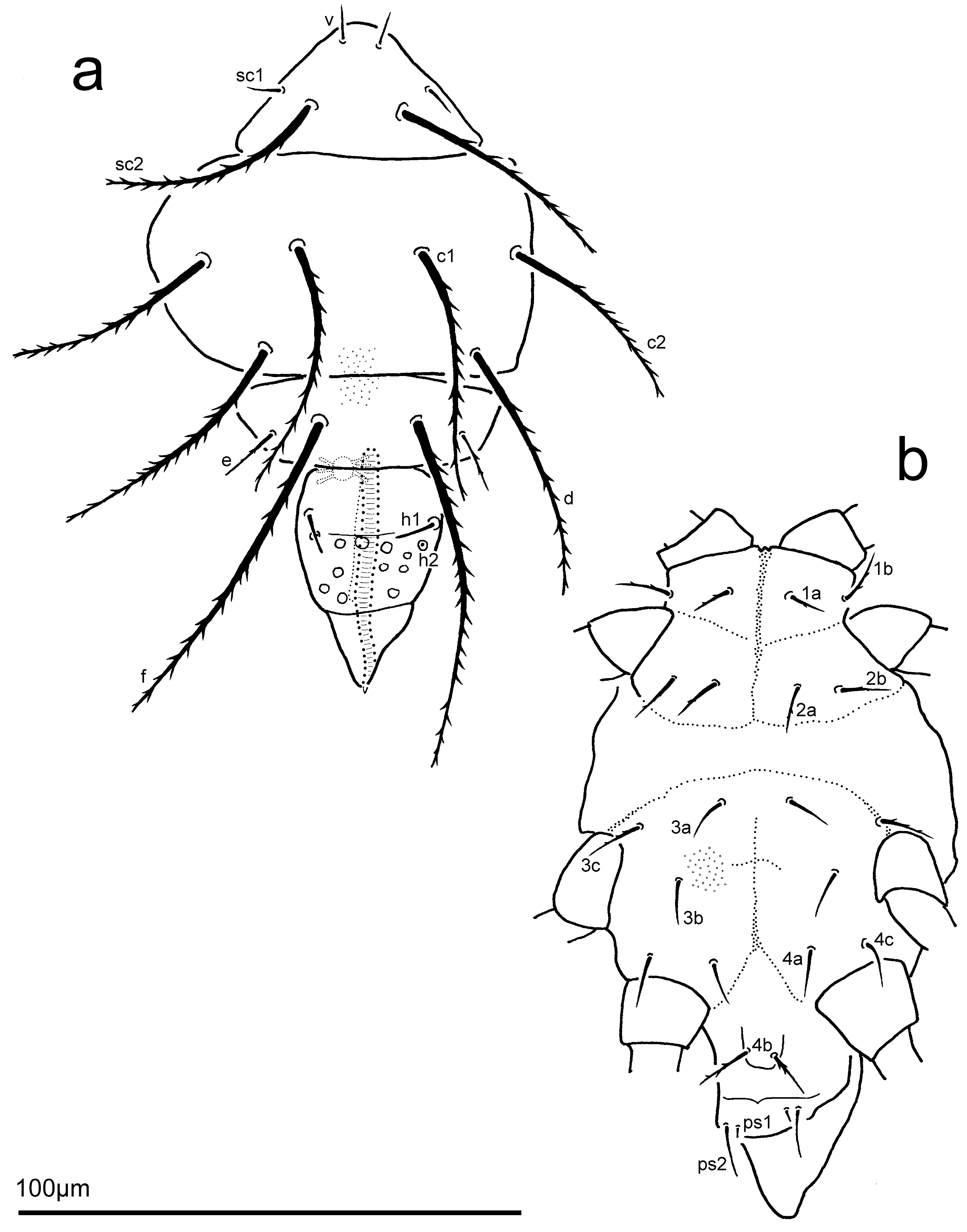
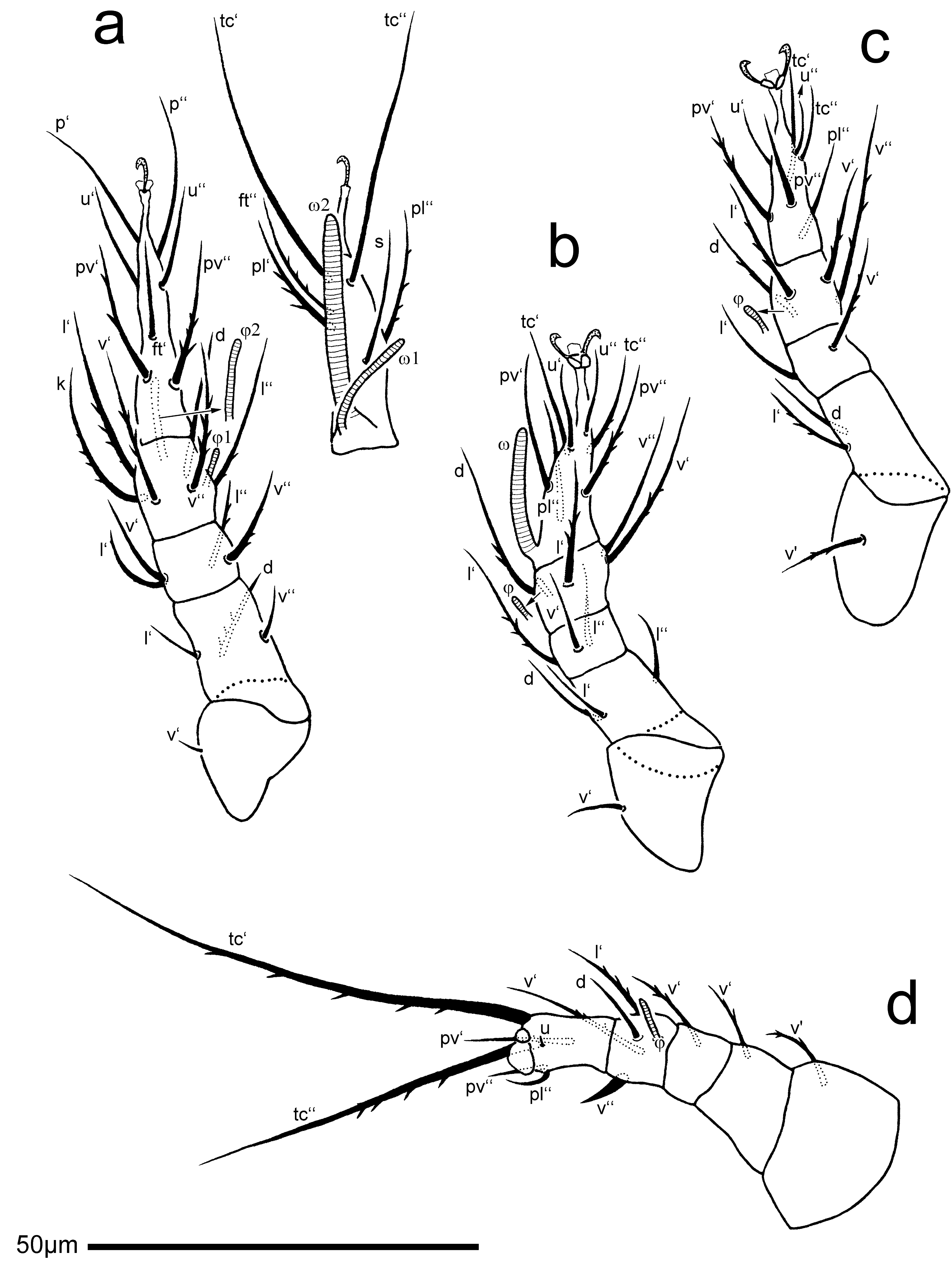
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 3 View FIGURE 3 , 20 View FIGURE 20 , 21 View FIGURE 21 )
MALE. Idiosoma length 110–150, n = 6.
Gnathosoma ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 i) extended, tube-shaped. One pair of finger-shaped solenidia, two pairs of dorsal setae ch 1 and ch 2 and one ventral pair of ventral setae su, thin, smooth. One pair of short tube-like accessory setigenous structures distally.
Dorsum ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 a). Idiosoma with four sclerotized, finely dotted plates. Most posterior plate forms dorsal cover for genital capsule. Length of dorsal setae: v about 8, sc 1 7, sc 2 46, c 1 49, c 2 39, d 46, e 14, f 63, h 1 9. Setae v, sc 1 smooth, sc 2, c 1, c2, d, e, f barbed, blunt-ended, e short sparsely barbed. h 1 and h 2 smooth, blunt-ended, h 2 minute. Distance between dorsal setae: v–v about 6, sc 1 –sc 1 27, sc 2 –sc 2 18, c 1 –c 1 23, c 2 –c 2 57, d–d 38, e–e 36, f–f 16, h 1 –h 1 23, h 2 –h 2 19.
Genital apparatus ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 i, 20a). Segments H and PS fused, form genital capsule. Length of genital plate (tergite H) about 42. Posterior edge of plate narrowed, ratio length: width of genital plate = 1: 0.55. Area posterior of h 1 with clearly recognisable roundish, sucker-like structures or cavities. Aedeagus like in I. dispar .
Venter ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 b). Sternal plates finely dotted. Ap1 weakly sclerotized, prosternal ap continuous from ap1 to sejugal ap; ap2, ap3, and ap5 complete, weakly sclerotized; ap4 incomplete, weakly sclerotized; anterior part of poststernal ap incomplete, between ap3 and ap5 weakly sclerotized. Length of ventral setae: 1 a about 9, 1 b 11, 2 a 9, 2 b 12, 3 a 9, 3 b 9, 3 c 12, 4 a 9, 4 b 12, 4 c 10, ps 1 2, ps 2 8. Setae 1 a, 1 b, 2 a, 2 b, 3 b, 4 b sparsely barbed, other ventral setae smooth, short, pointed. Distance between ventral setae: 1 a –1 a about 11, 1 b –1 b 34, 2 a –2 a 18, 2 b –2 b 33, 3 a – 3 a 14, 3 b –3 b 30, 3 c –3 c 45, 4 a –4 a 19, 4 b –4 b 5, 4 c –4 c 43, ps 1 –ps 1 12, ps 2 –ps 2 15.
Leg I ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 a). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe3–Ge4–Ti6(2)–Ta13(2). Ta with one small, padded claw. Sol ω1 thin, sol ω2 thick, sol ϕ1 and sol ϕ2 thin, all finger-shaped. Length of solenidia: ω1 about 15, ω2 24, ϕ1 7, ϕ2 12. Eupathidia p’, p’’, tc’, tc’’ and ft’, setae u’, u’’, s, v’Ge, l’Ge, v’Fe, l’Fe and v’Tr smooth, all other setae barbed, most only sparsely; all setae pointed.
Leg II ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 b). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe3–Ge3–Ti4(1)–Ta7(1). Ta with two small claws and empodium. Sol ω thick, sol ω and ϕ finger-shaped, sol ω 18, sol ϕ 5. Eupathidion tc’’, setae pv’’, dTi, l’Ti, v’Ti and l’Ge sparsely barbed, all other setae smooth; all setae pointed.
Leg III ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 c). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe2–Ge2–Ti4(1)–Ta7. Ta with two small claws and empodium. Sol ϕ 5, finger-shaped. Setae pv’, dTi, l’Ti, v’Ti, v’’Ti, v’Ge, l’Fe and v’Tr sparsely barbed, all other setae smooth; all setae pointed.
Leg IV ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 d, Table 1 View TABLE 1 ). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe1–Ge1–Ti4(1)–Ta6. Distal Ta with two adhesive pads of differing size. Tarsal setae tc’, tc’’ are longest, length tc’ about 60, tc’’ 36. Seta v’’Ti spine-like, smooth, pl’’ hookshaped, smooth, setae dTi, pv’, and pv’’ smooth, all other setae barbed, pointed, u minute. Sol ϕ 5, finger-shaped.
Differential diagnosis. Males of S. tackei can be differentiated from Archidispus , Heterodispus and Imparipes by the presence of accessory setigenous structures on the gnathosoma. They can be separated from all other males by their setation. Scutacarus tackei is morphologically most similar to S. tyrrhenicus , from which it can be separated by a smaller size (idiosoma length about 132µm in S. tackei versus 167µm in S. tyrrhenicus ) and by possessing slightly barbed ventral setae 1 a, 1 b, 2 a, 2 b and 3 c, which are all smooth in S. tyrrhenicus . It also shows certain similarity to S. deserticolus , but S. tackei differs by being smaller (idiosoma length about 145µm in S. deserticolus versus 120µm in S. tackei ), by possessing smooth dorsal setae v and sc 1 and slightly barbed ventral setae 1 a, 1 b, 2 a, 2 b and 3 c, which are all smooth in S. deserticolus . Moreover, the setation of leg IV differs between the three species ( Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
Material examined. 6 males from laboratory cultures based on females from leaf litter; AUSTRIA: Graz Schloßberg, 47°04'37.1"N, 15°26'16.9"E, 1985, leg. Ebermann. GoogleMaps
Deposition of material. 2 males: Natural History Museum Vienna, Austria ( NHMW 27.646 View Materials ) ; 2 males: Institute of Zoology , University of Graz, Austria ; 2 males: Museum of Natural History of the City of Geneva, Switzerland .
| NHMW |
Naturhistorisches Museum, Wien |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |