Mymaridae
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5036.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9047AF72-0A9C-4636-B3A9-1018DA9F686A |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/514B87B5-0139-371C-76E5-FF60E9CA058D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mymaridae |
| status |
|
Key to Afrotropical genera of Mymaridae View in CoL View at ENA . Males
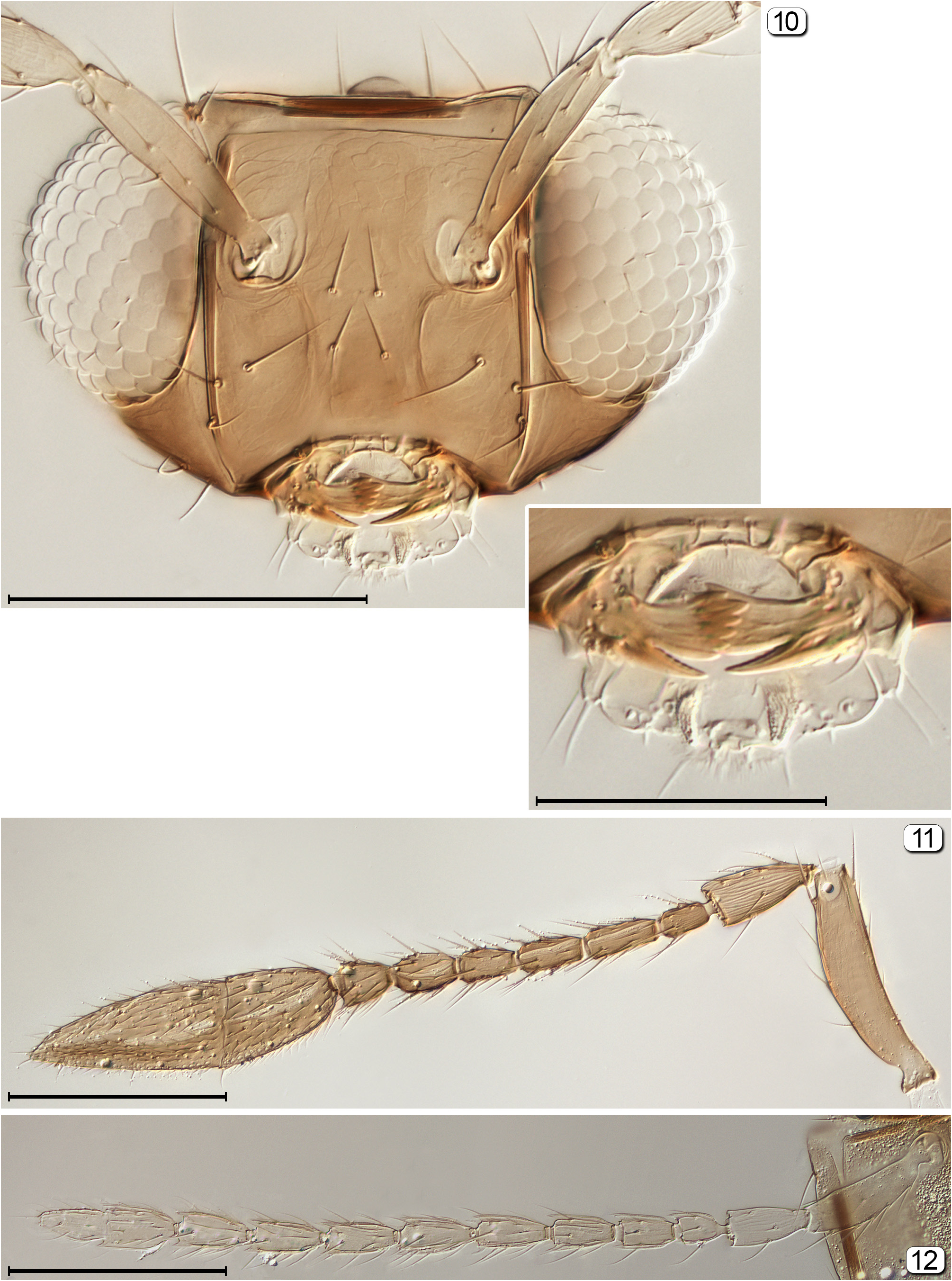
[Antenna without clava, the flagellar segments all about equal in width ( Figs 12 View FIGURES 10–12 , 46 View FIGURES 43–47 , 53 View FIGURES 51–54 , 89 View FIGURES 87–89 , 123 View FIGURES 120–123 , 159 View FIGURES 157–160 , 198, 199 View FIGURES 196–199 , 208 View FIGURES 207–209 )]. In the Afrotropical region, males are unknown for Dorya , Camptoptera ( Eofoersteria) , Litus , Paranaphoidea , Platystethynium and Schizophragma . Except for Platystethynium , whose males are micropterous and otherwise quite modified, they likely resemble females except for the antennae, genitalia and wings. Only Litus and Schizophragma are included in this key.
1(2) Wings short, not extending beyond apex of mesosoma, or absent............................................... 2
- Wings fully developed, extending at least to apex of gaster.................................................... 3
2(1) Wings absent; flagellum 10-segmented; body minute............................................... Dicopus View in CoL , part
- Wings present but short, extending about to base of gaster; flagellum 11-segmented; body larger..................................................................................................... Polynema ( Polynema) , part
3(1) Tarsi 5-segmented.................................................................................... 4
- Tarsi 4-segmented................................................................................... 23
4(3) Fore wing venation (to apex of stigma) at most about 0.4× wing length; marginal vein absent so parastigma joined directly to stigmal vein at the distal macrochaeta; postmarginal vein absent................................................ 5
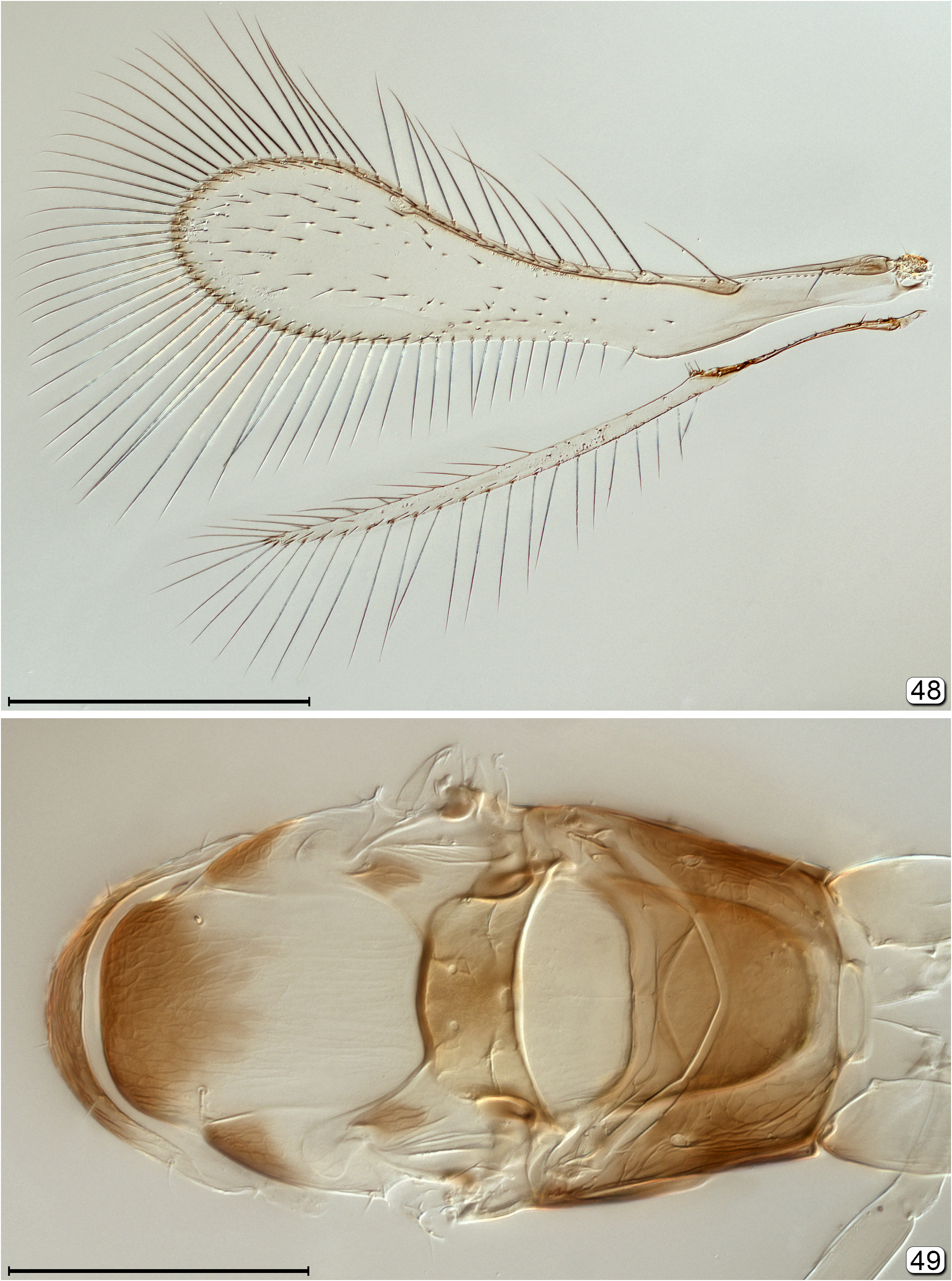
- Fore wing venation (to apex of stigma) at least 0.6× wing length ( Figs 48 View FIGURES 48, 49 , 62 View FIGURES 62, 63 ); marginal vein present and about as long as or longer than parastigma so stigma vein joined to apex of marginal vein distal to distal macrochaeta ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 48, 49 ); postmarginal vein usually present...................................................................................... 21
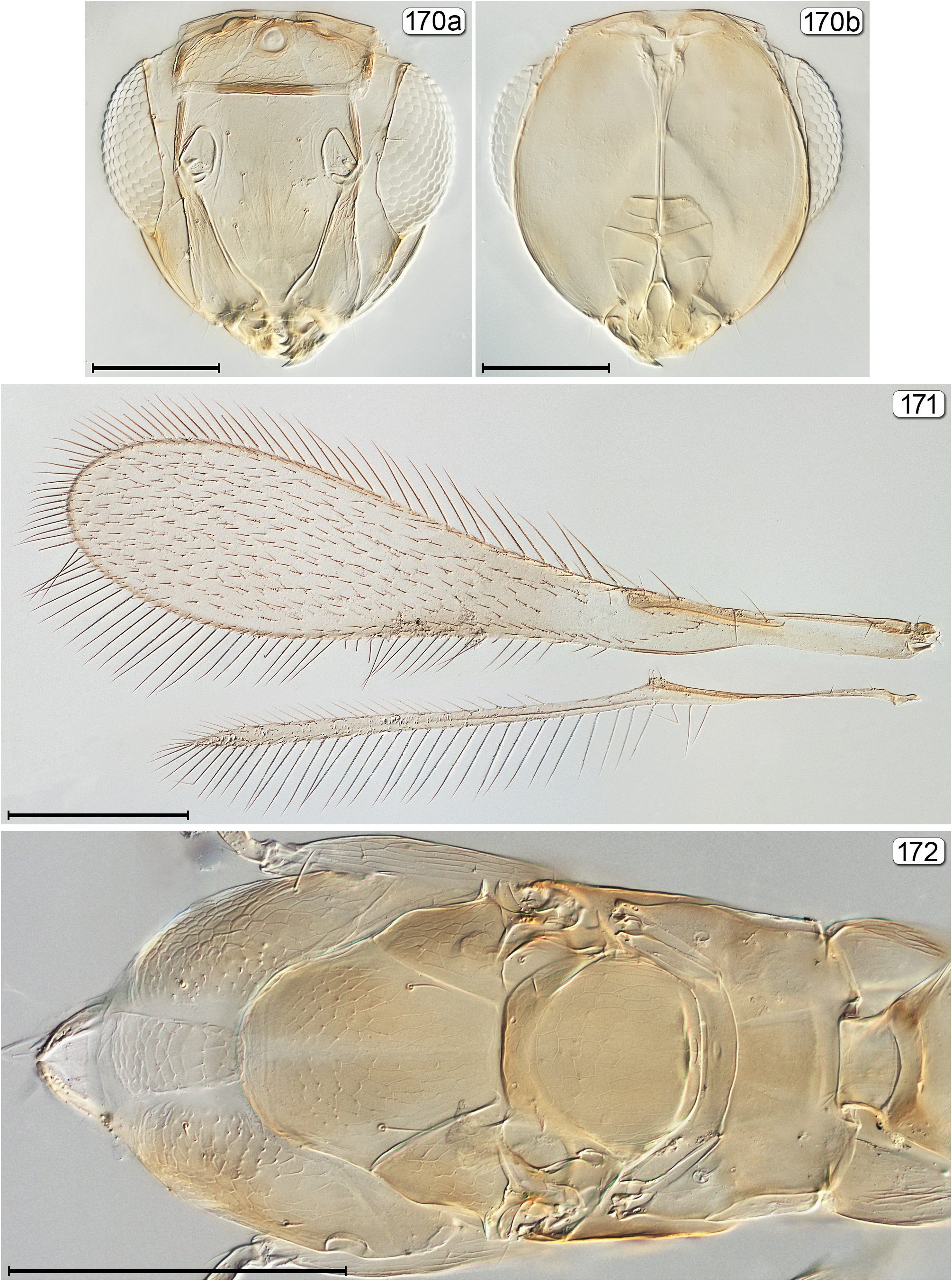
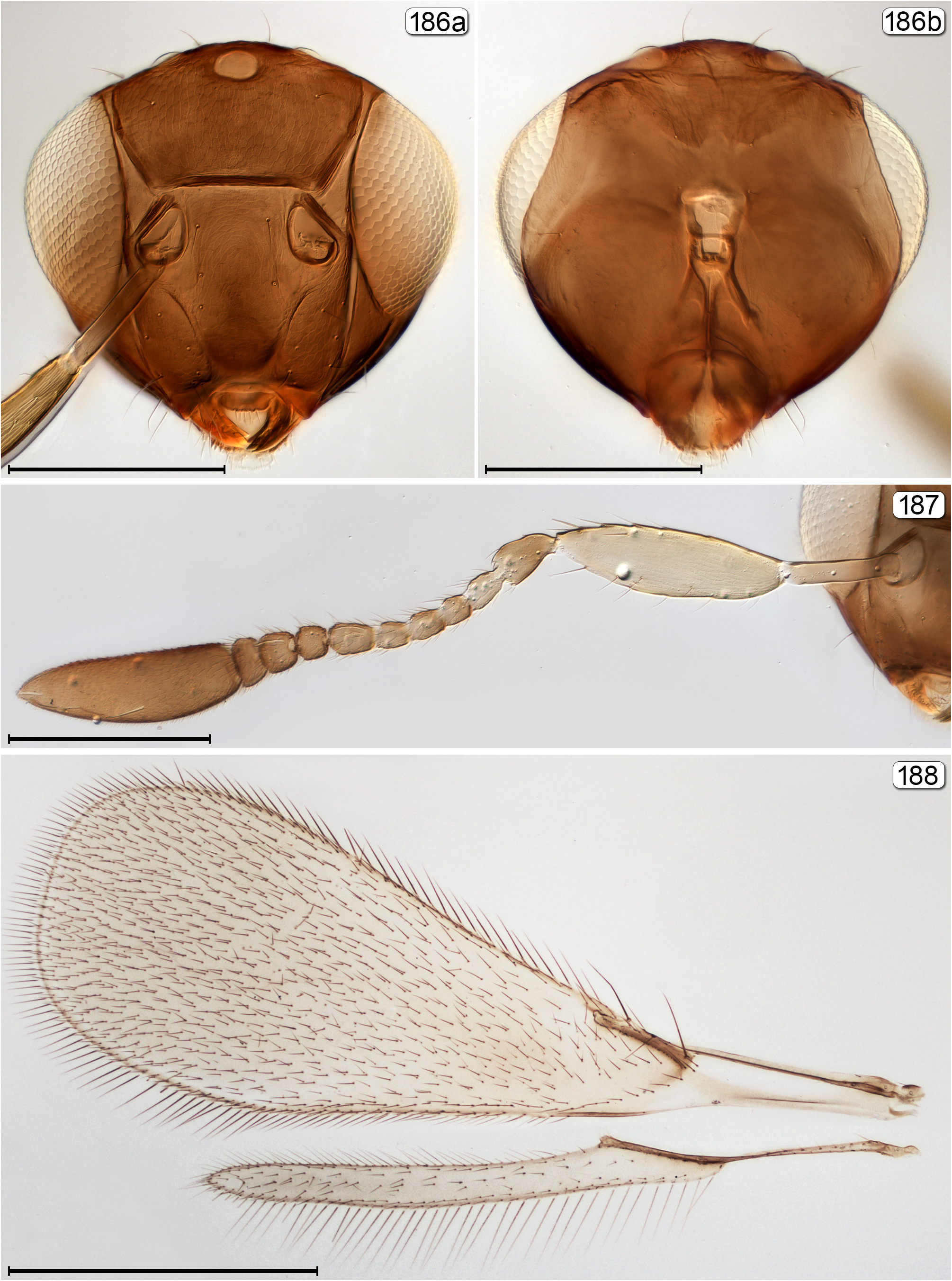
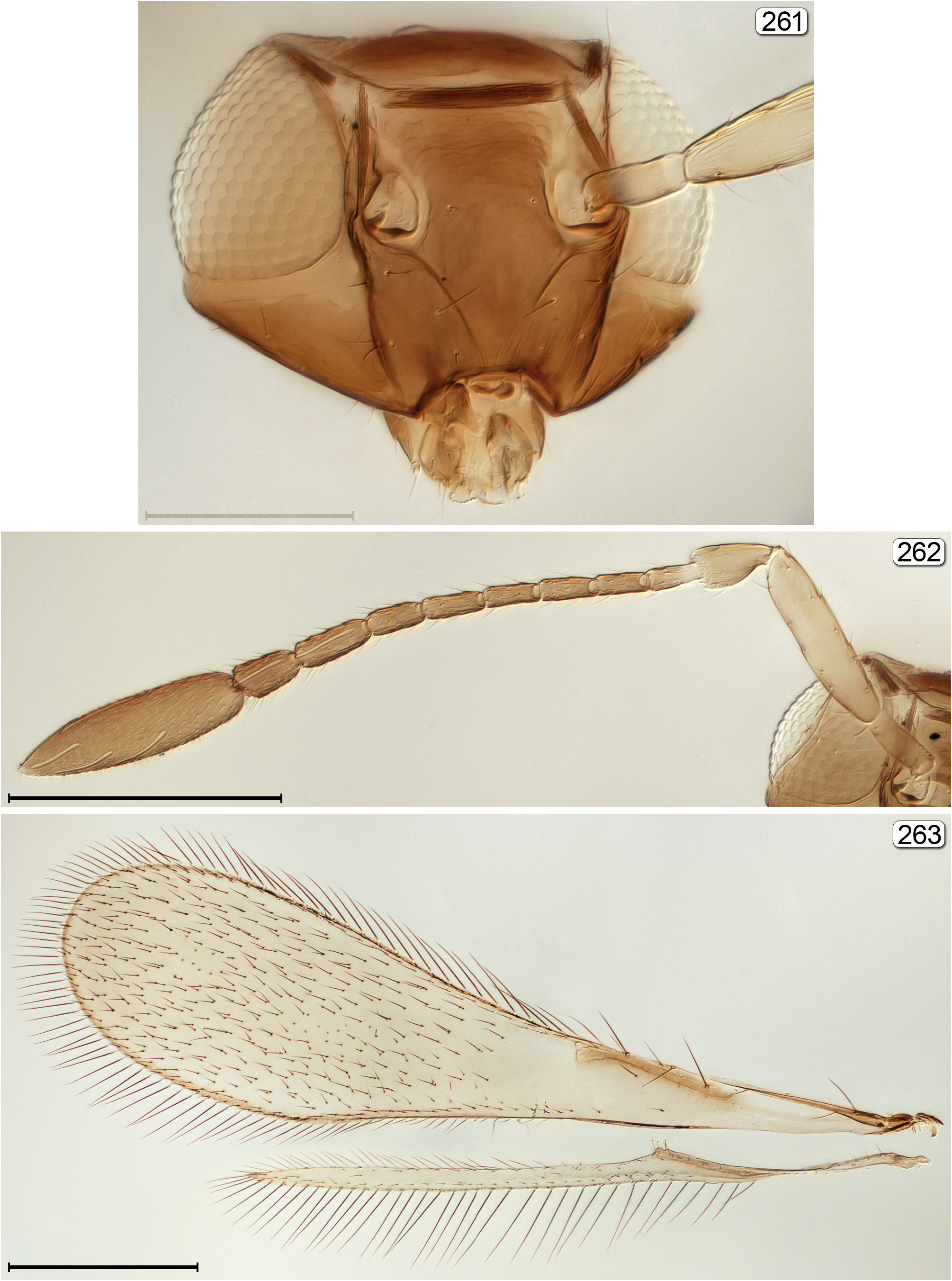
5(4) Fore wing at most 5.0× as long as wide and usually almost completely covered beyond venation with many rows of microtrichia; face often with subantennal grooves extending from torulus to mouth margin ( Figs 103 View FIGURES 102, 103 , 150 View FIGURES 150–152 , 170a View FIGURES 170–172 , 186a View FIGURES 186–188 , 261 View FIGURES 261–263 )..... 6
- Fore wing at least 8.0× as long as wide, rarely completely covered with microtrichia but if so these arranged only in a few rows; face without subantennal grooves....................................................................... 14
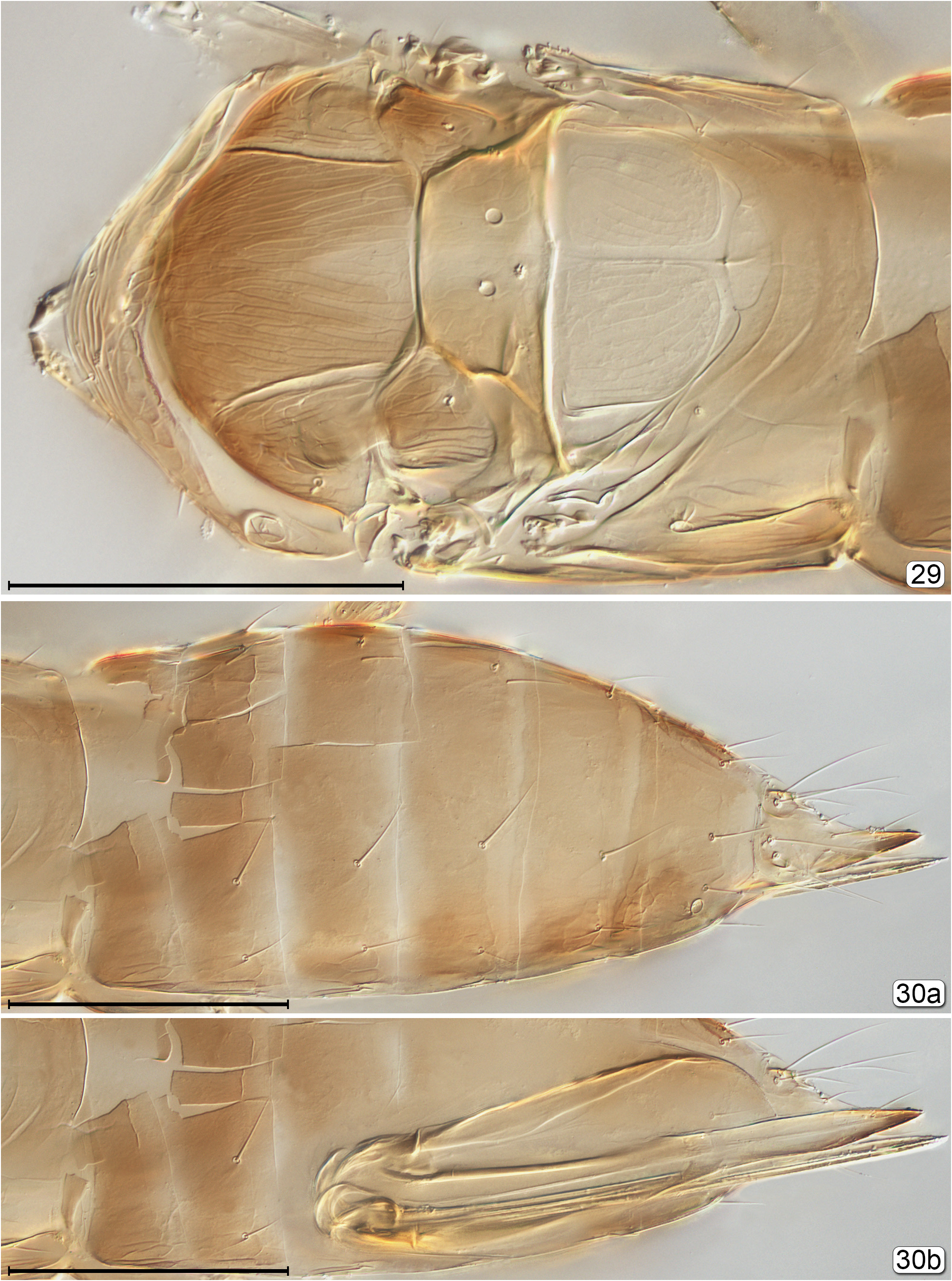
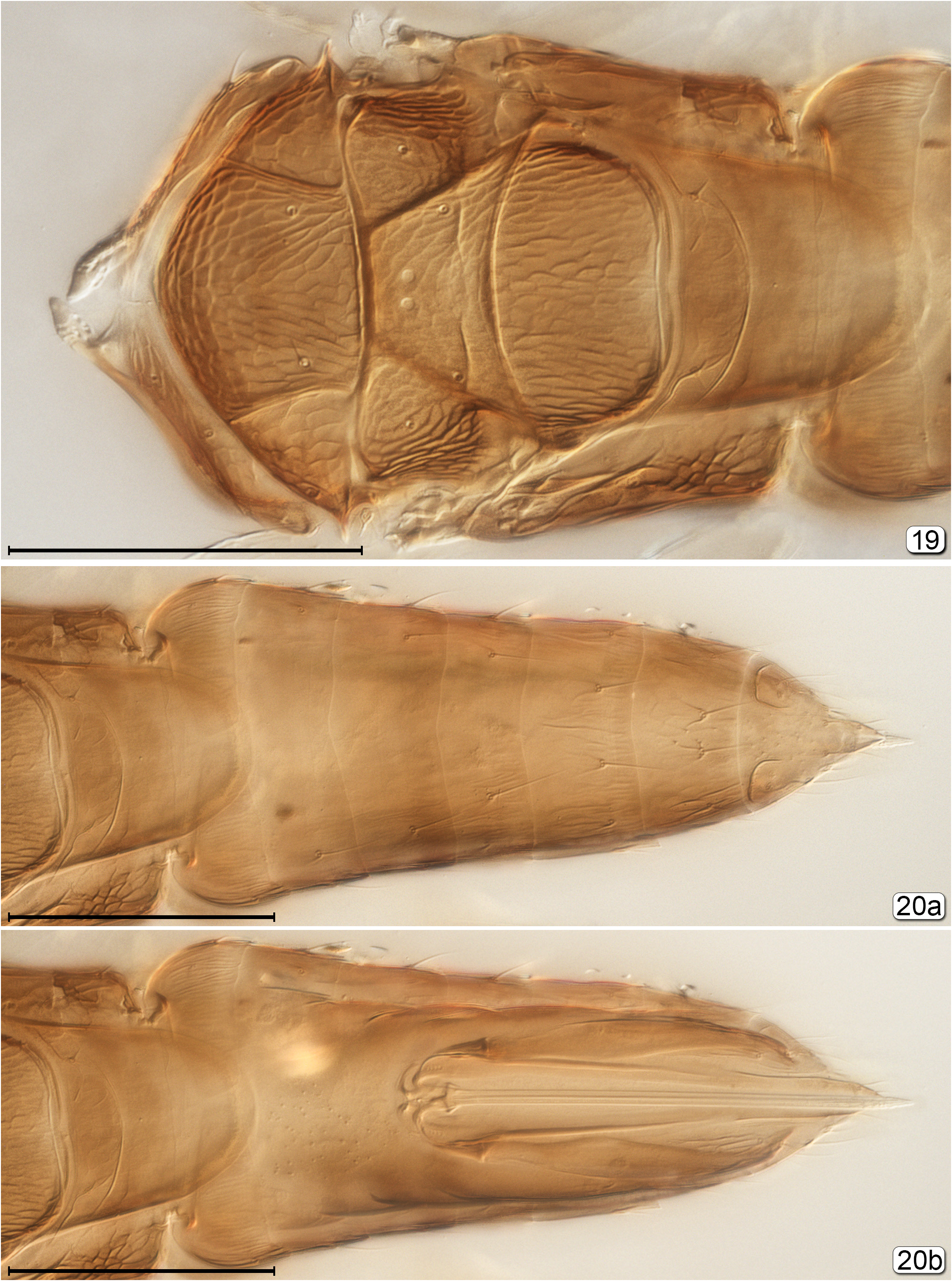
6(5) Propodeum with diamond-like pattern of carinae ( Fig. 207 View FIGURES 207–209 ); metasoma in lateral view with gt 1 distinctly longer than gt 2 ( Fig. 209 View FIGURES 207–209 )........................................................................................ Ooctonus View in CoL
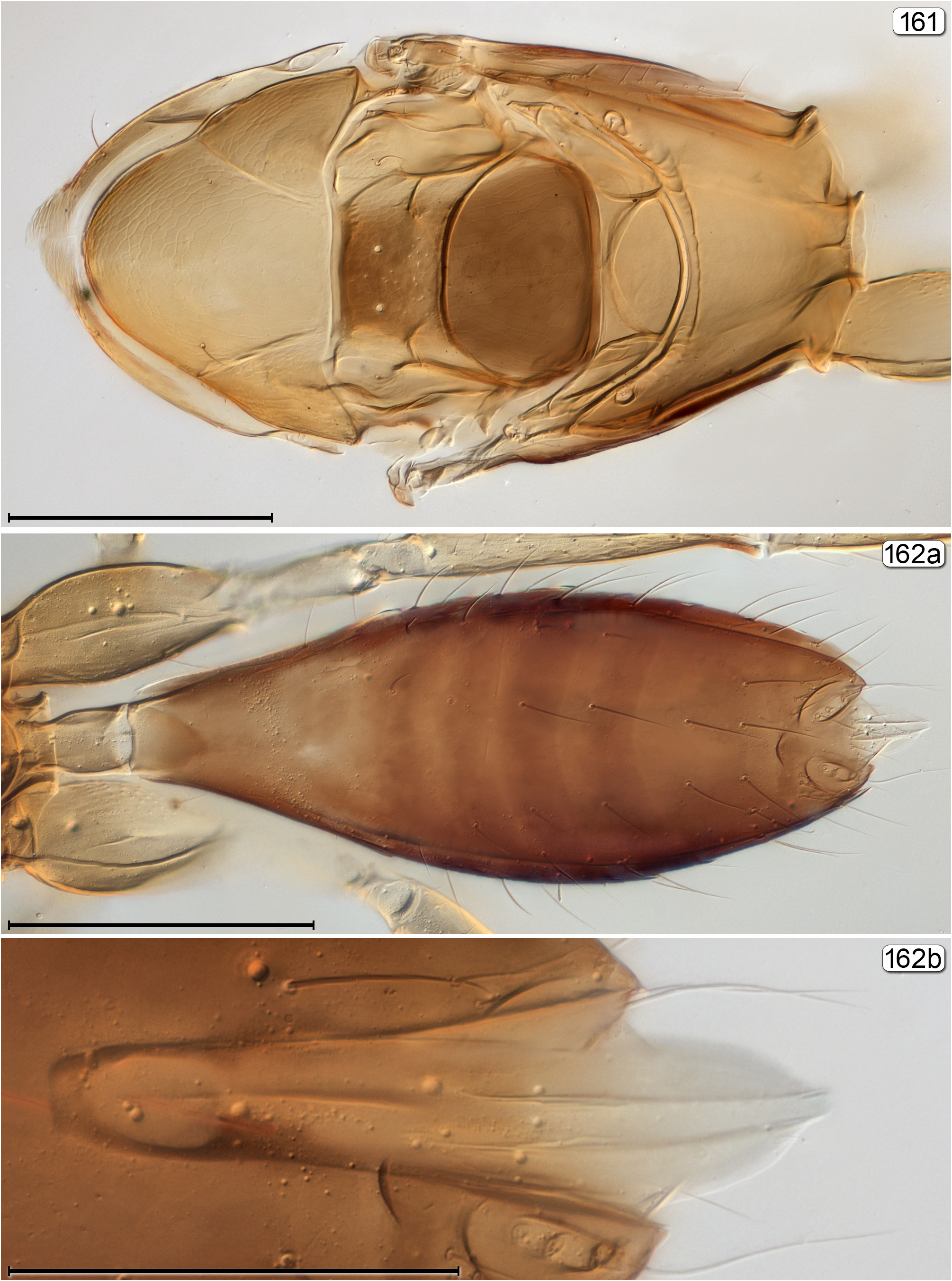
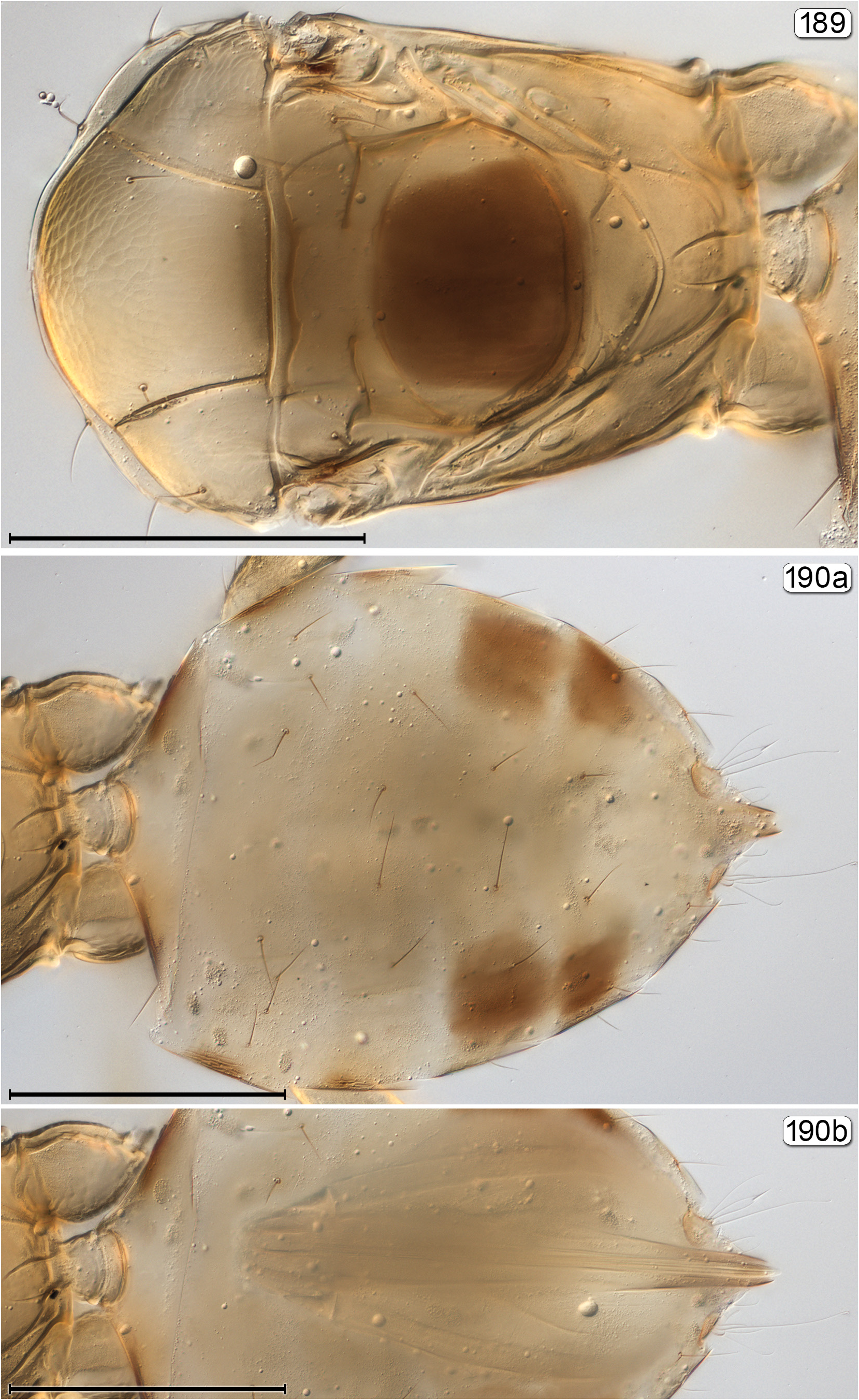
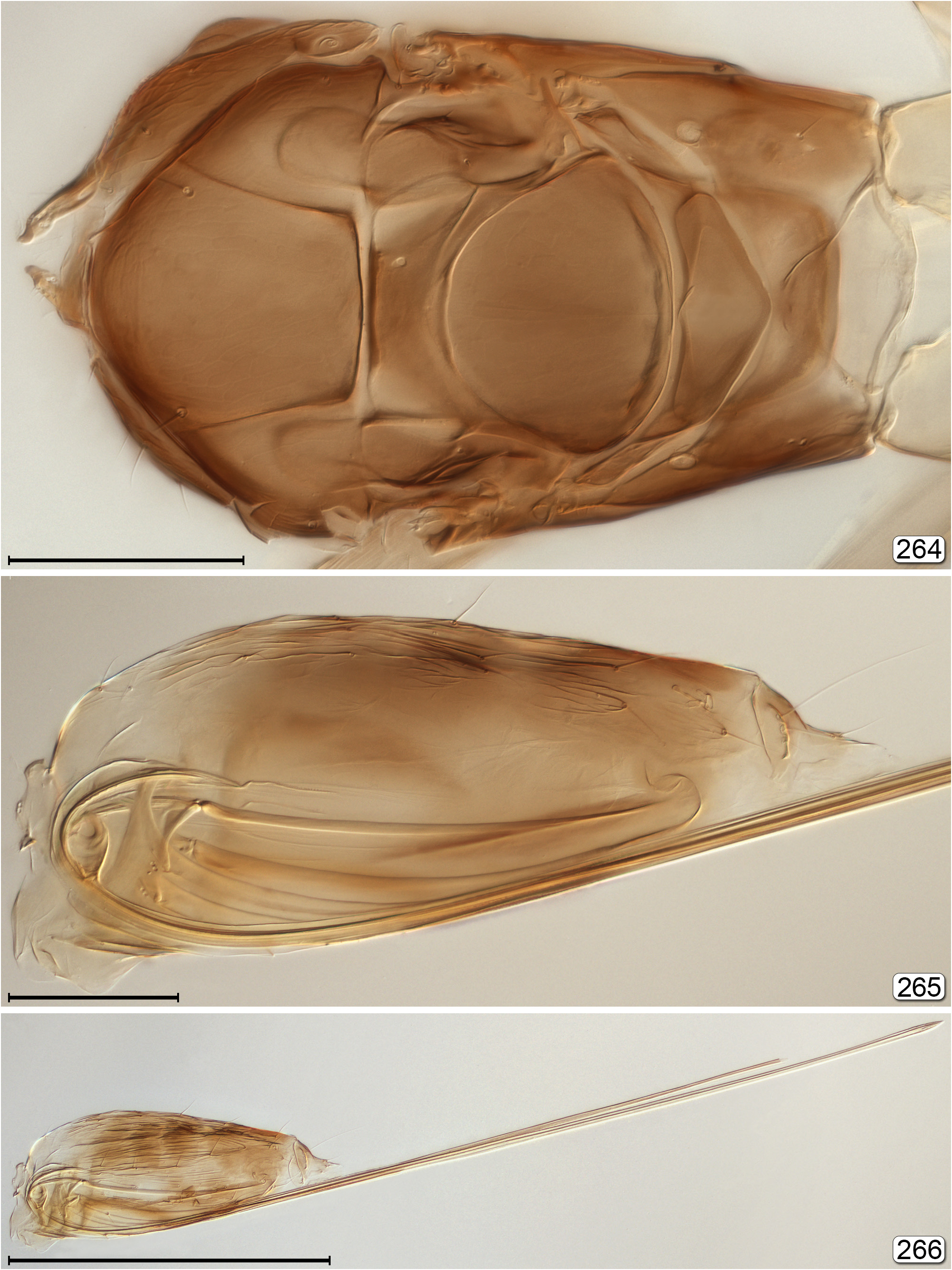
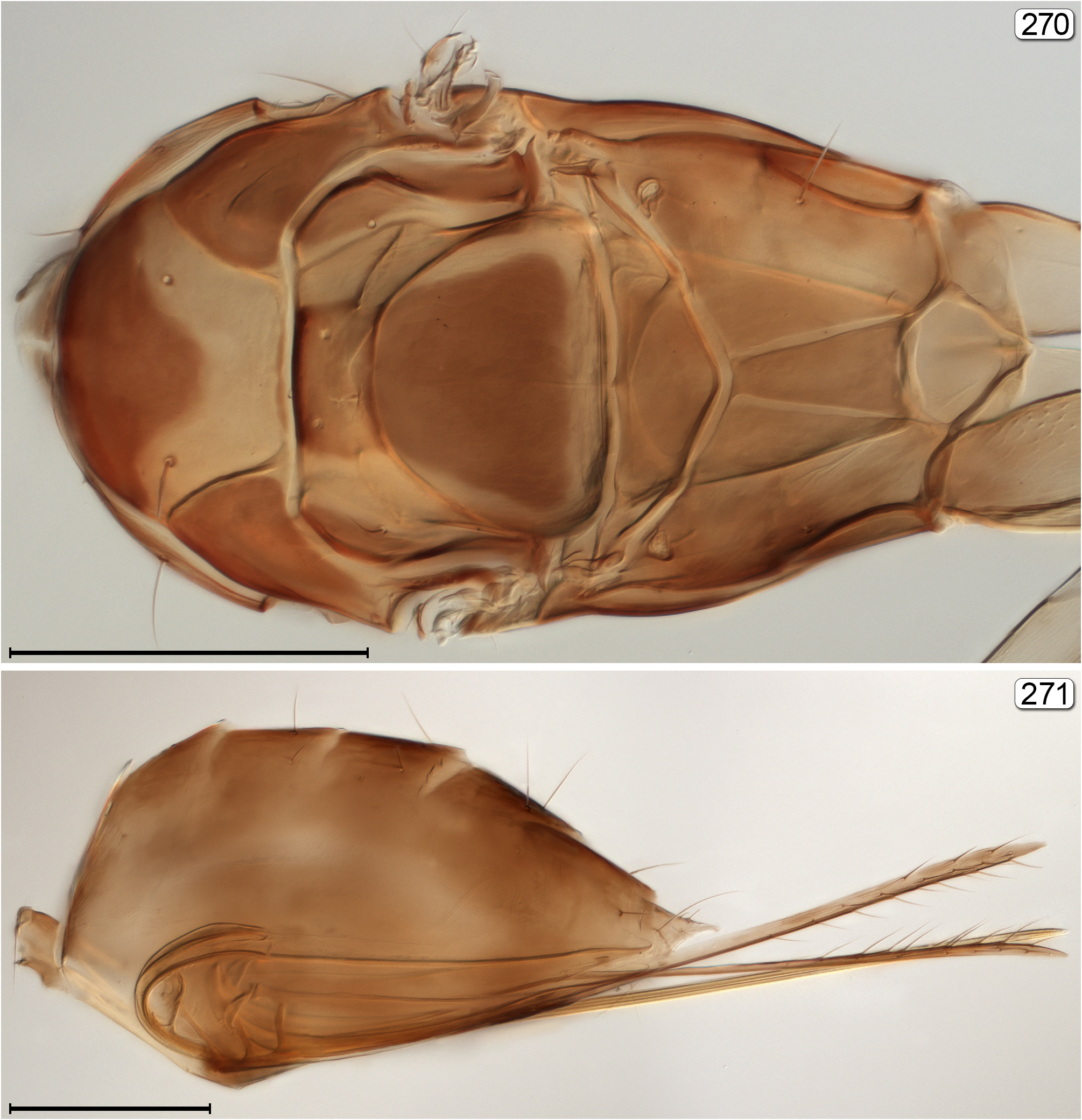
- Propodeum not as above, either with 2 longitudinal, more or less parallel submedian grooves or carinae, these well separated ( Figs 161 View FIGURES 161, 162 , 172 View FIGURES 170–172 , 189 View FIGURES 189, 190 , 264 View FIGURES 264–266 , 270 View FIGURES 270, 271 ) or almost united ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 104–106 ), or carinae absent ( Fig. 153 View FIGURES 153, 154 ) and propodeum almost smooth; metasoma in lateral view with gt 1 only slightly longer than gt 2..................................................... 7
7(6) Head in posterior view with curved, transverse groove extending above foramen from eye to eye, separating occiput from gena......................................................................................... Zeyanus
- Head in posterior view without transverse groove........................................................... 8
8(7) Dorsellum strap-like, with anterior and posterior margins parallel ( Fig. 172 View FIGURES 170–172 ) or almost so ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 104–106 ) and at least 7× as wide as its median length..................................................................................... 9
- Dorsellum rhomboidal, with anterior and posterior margins distinctly diverging and at most about 3× as wide as its median length............................................................................................. 10
9(8) Metasoma with petiole at most 2× as long as wide; pronotum with lateral lobes widely separated by membranous median area ( Fig. 172 View FIGURES 170–172 ); propodeum with submedian lines well separated from each other ( Fig. 172 View FIGURES 170–172 )..................... Lymaenon
- Metasoma with petiole at least 3× as long as wide ( Figs 102 View FIGURES 102, 103 , 106 View FIGURES 104–106 ); pronotum with lateral lobes almost abutting ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 104–106 ); propodeum with submedian lines almost in contact with each other ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 104–106 )........................ Cosmocomopsis
10(8) Face with subantennal grooves almost meeting each other at mouth margin; head relatively wide, and thin in lateral view............................................................................................ Tanyxiphium
- Face with subantennal grooves, when present, wider apart at mouth margin, not meeting; head relatively narrow, and thicker in lateral view........................................................................................ 11
11(10) Face without subantennal grooves ( Fig. 150 View FIGURES 150–152 )................................................ Heptagonatocerus
- Face with subantennal groove extending from each torulus to mouth margin..................................... 12
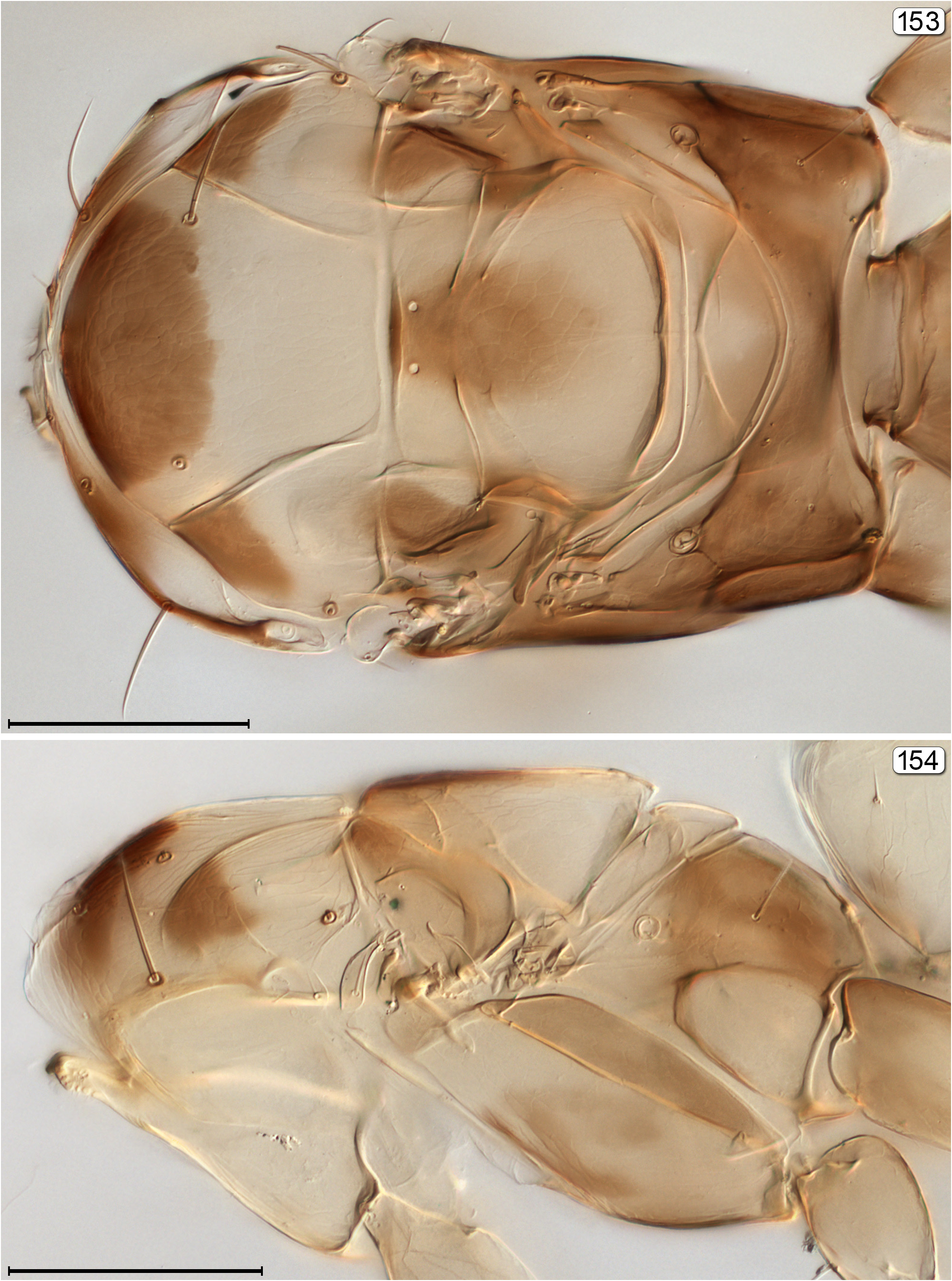
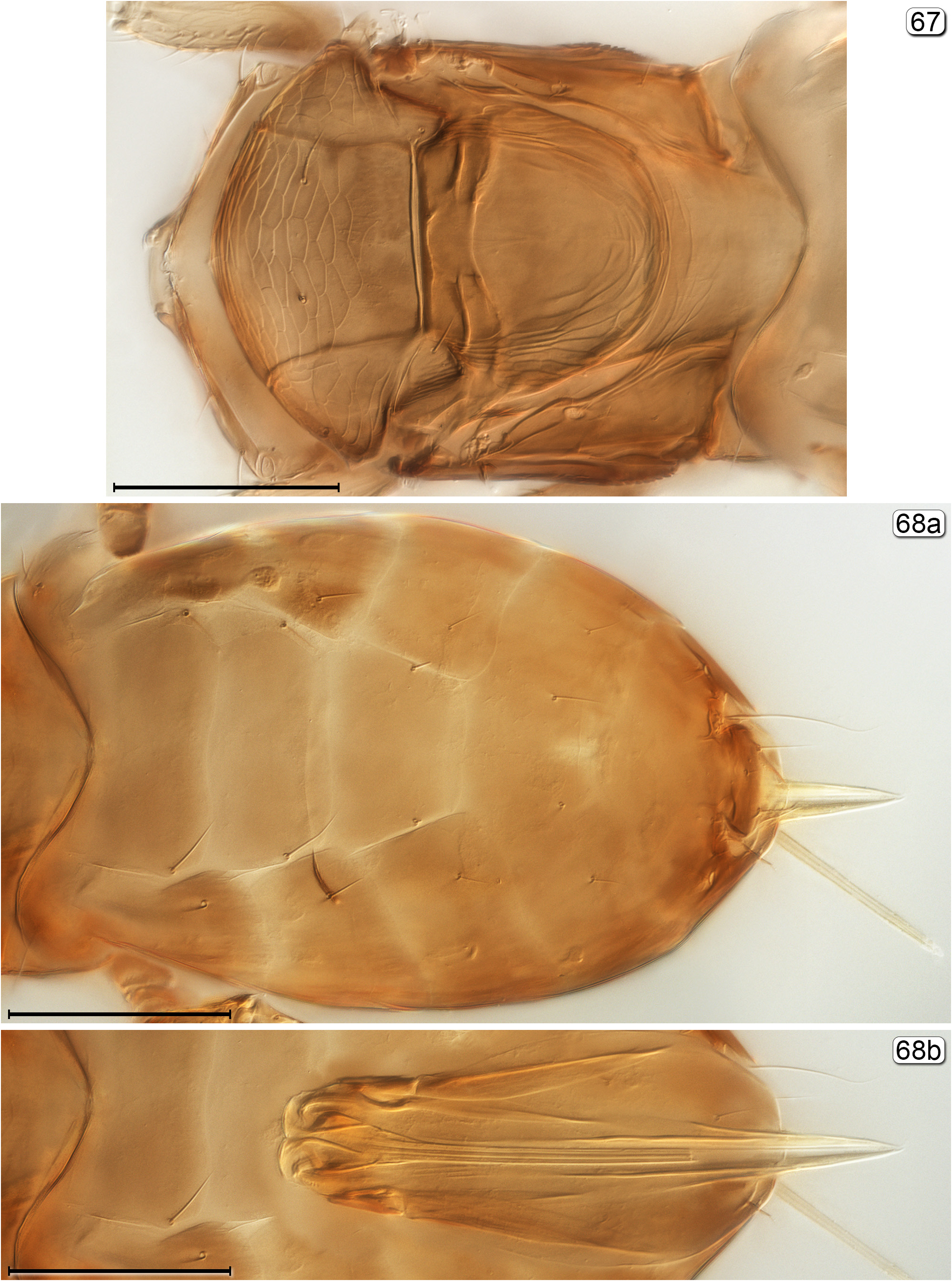
12(11) Propodeum without carinae or at most only with faint longitudinal submedian grooves; fore wing narrower, with apex rounded ( Fig. 153 View FIGURES 153, 154 )................................................................................. Gonatocerus View in CoL
- Propodeum with longitudinal submedian carina extending almost to dorsellum and another carina between each submedian carina and metapleural suture; fore wing wider with apex somewhat truncate ( Fig. 188 View FIGURES 186–188 )................ Octomicromeris
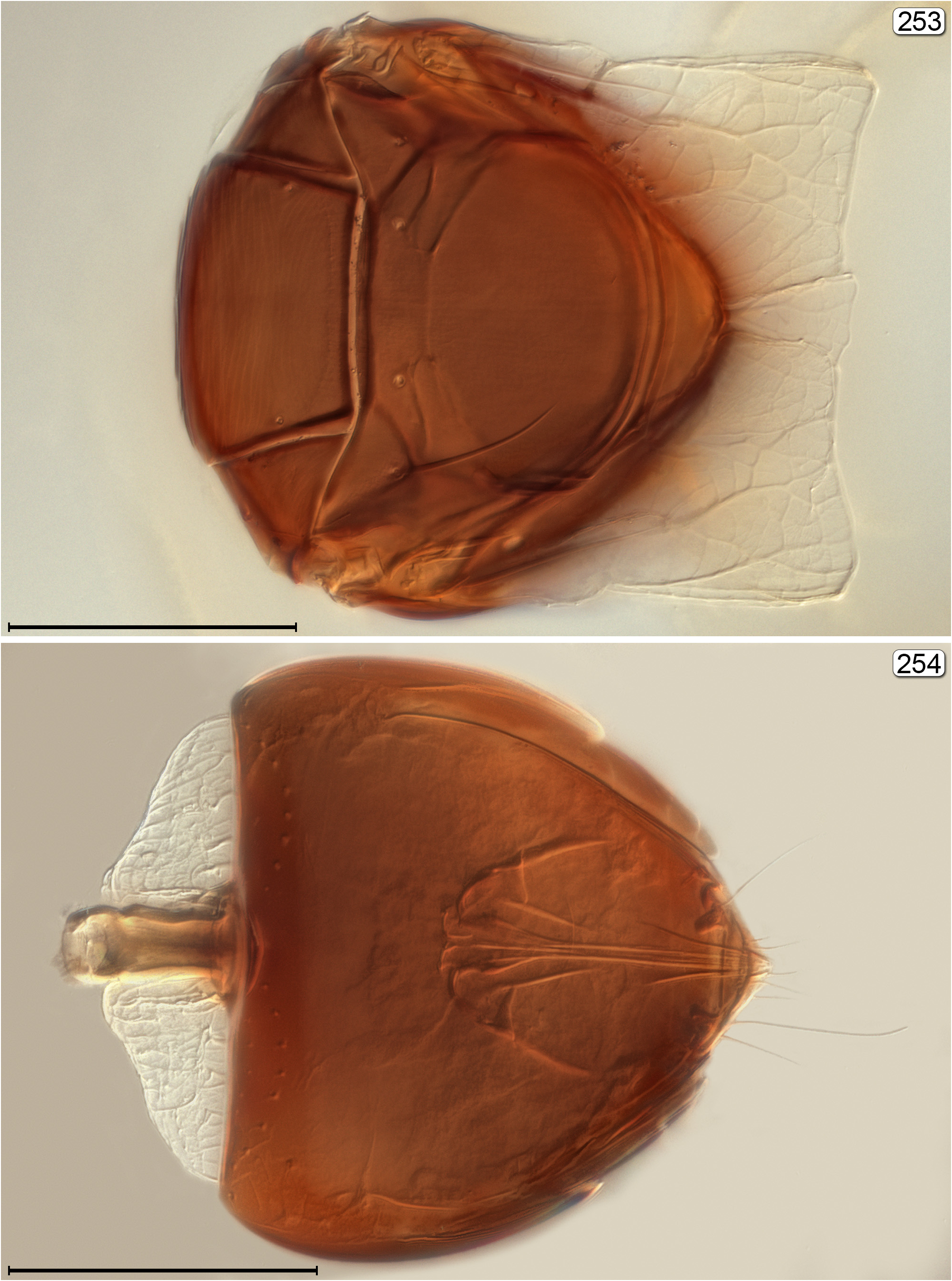
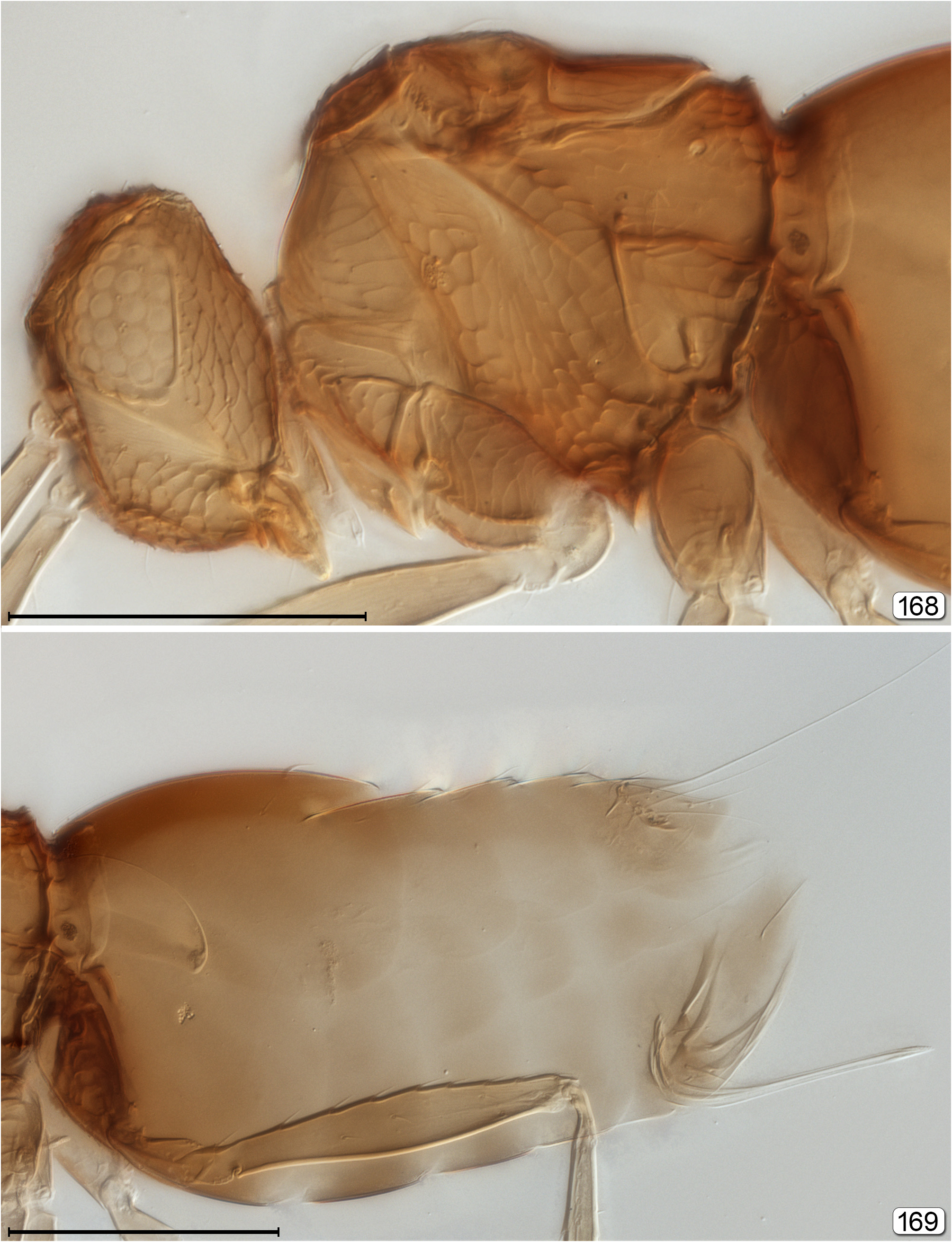
13(5) Metasoma joined to mesosoma by a short, usually distinct and visible, petiole usually much narrower than anterior width of gaster ( Figs 70 View FIGURES 69–71 , 77 View FIGURES 77, 78 , 81 View FIGURES 81, 82 , 254 View FIGURES 253, 254 ) [in Callodicopus View in CoL not much narrower than width of gaster ( Fig. 67 View FIGURES 67, 68 )]..................... 14
- Metasoma joined to mesosoma by an indistinct petiole barely narrower than anterior width of gaster, or apparently so joined [in Litus View in CoL the narrow but distinct petiole is completely hidden by wide base of gt 1].................................... 17
14(13) Propodeum with large translucent reticulated structures submedially and laterally ( Fig. 253 View FIGURES 253, 254 ); petiole ventrally surrounded by translucent reticulated structure ( Fig. 254 View FIGURES 253, 254 ).................................................... Stephanocampta View in CoL
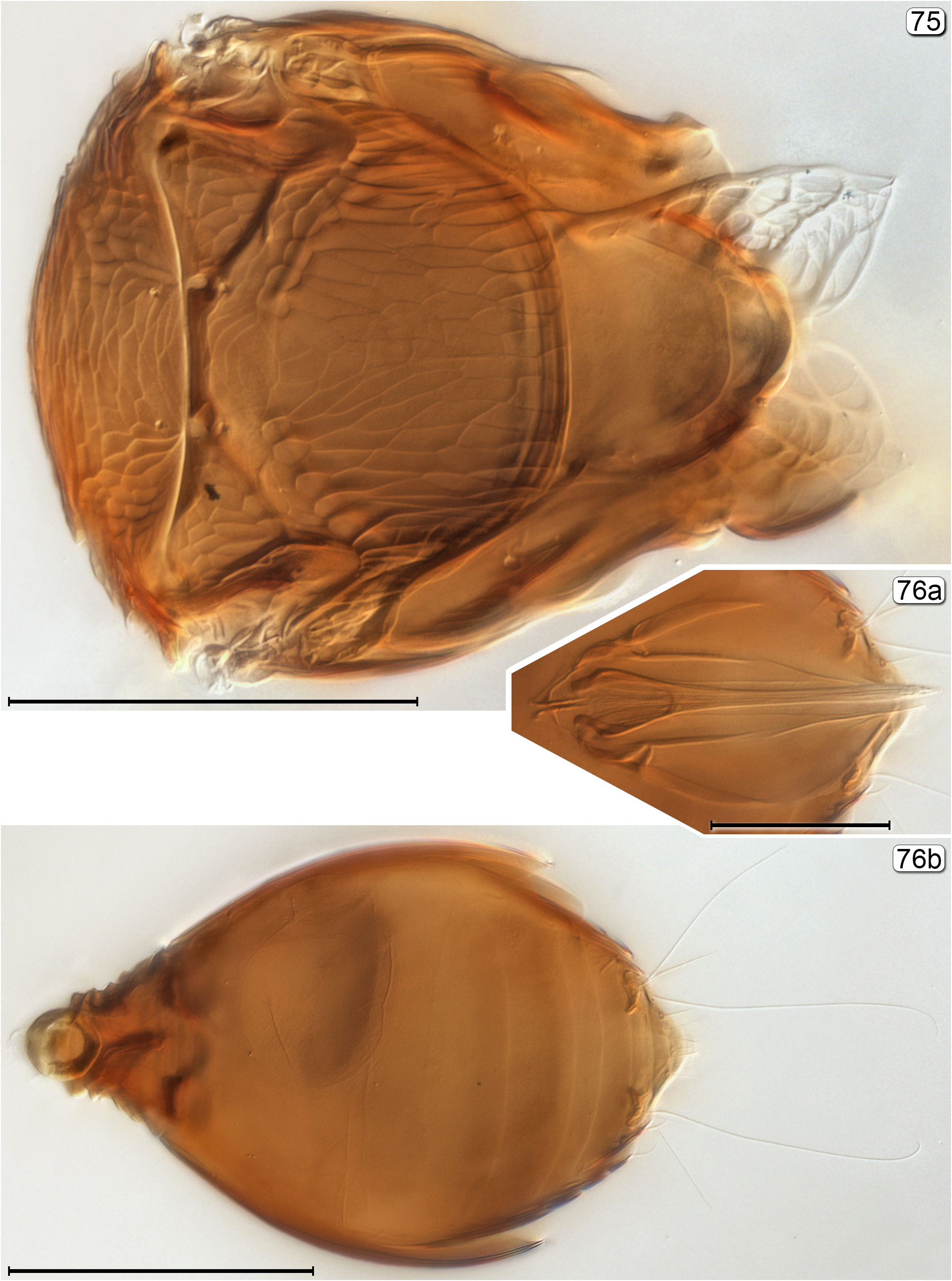
- Propodeum almost always without translucent reticulated structures submedially and laterally, rarely with them submedially ( Fig. 75 View FIGURES 75, 76 ); petiole ventrally not surrounded by translucent reticulated structure.................................... 15
15(14) Fore wing slightly but usually distinctly curved (posterior margin concave) near apex ( Figs 74 View FIGURES 72–74 , 77 View FIGURES 77, 78 ), sometimes almost straight ( Fig. 70 View FIGURES 69–71 ); petiole visible ( Figs 70 View FIGURES 69–71 , 77 View FIGURES 77, 78 ).................................................................... 16
- Fore wing straight (posterior margin straight or almost so) near apex ( Fig. 109 View FIGURES 107–109 ); petiole hidden ( Figs 67 View FIGURES 67, 68 , 83 View FIGURES 83, 84 )........... 17
16(15) Flagellum with 8 segments (excluding the ring segment)............................... Camptoptera ( Camptoptera)
- Flagellum with 7 segments (excluding the ring segment).................................................................................................. Camptoptera ( Camptoptera) [former subgenus C. ( Zemicamptoptera)]
17(15) Frenum and propodeum strongly reticulate ( Fig. 83 View FIGURES 83, 84 )............................................ Camptopteroides View in CoL
- Frenum and propodeum smooth or almost so..................................................... Callodicopus View in CoL
18(13) Head in anterior view distinctly narrowing ventrally; mandibles pointing ventrally and not crossing each other, each with 1 long and 1 short tooth ( Fig. 112 View FIGURES 112–114 ); fore wing extremely narrow beyond venation then widening distinctly to apex ( Fig. 114 View FIGURES 112–114 )............................................................................................... Dicopus View in CoL , part
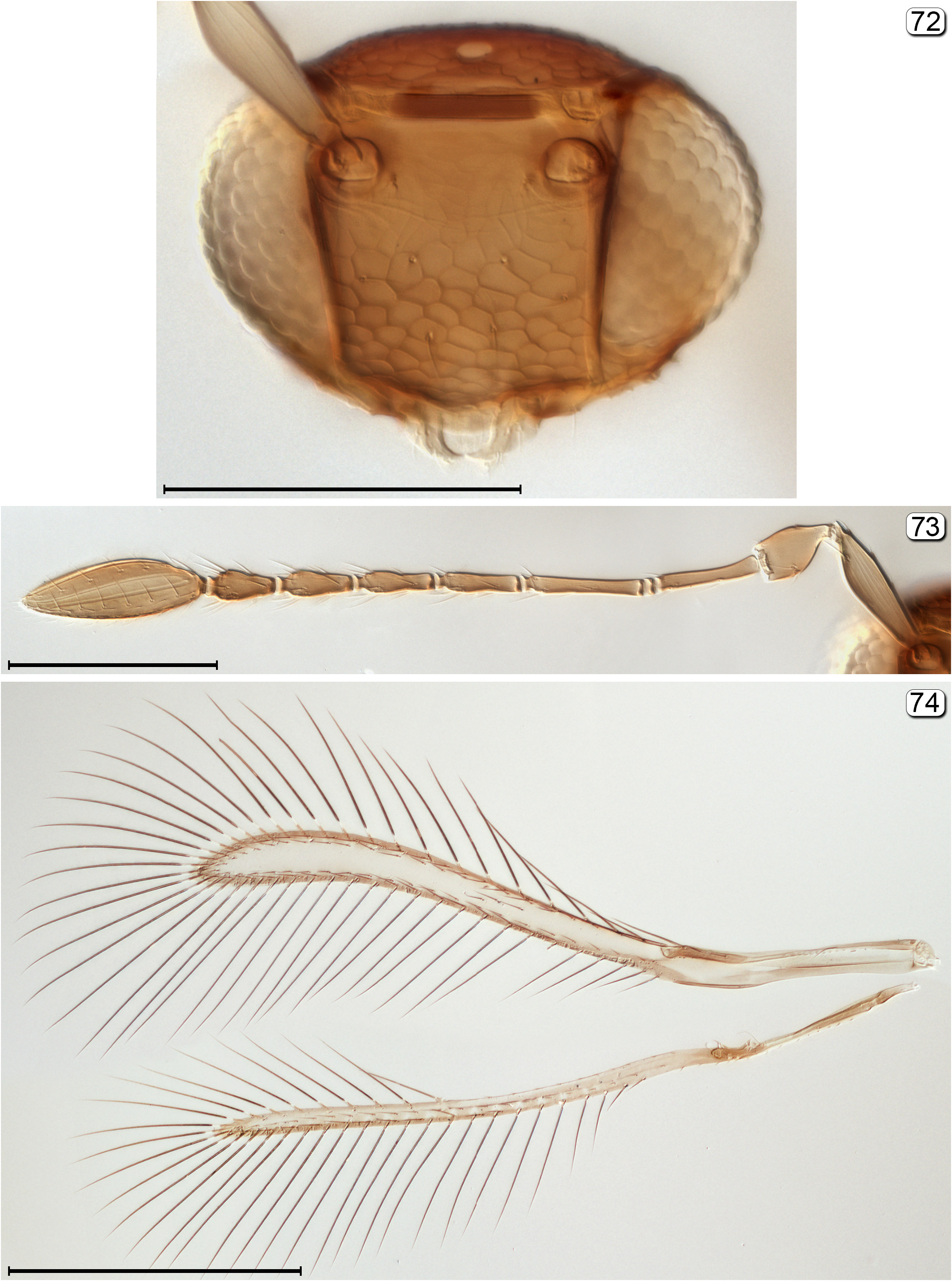
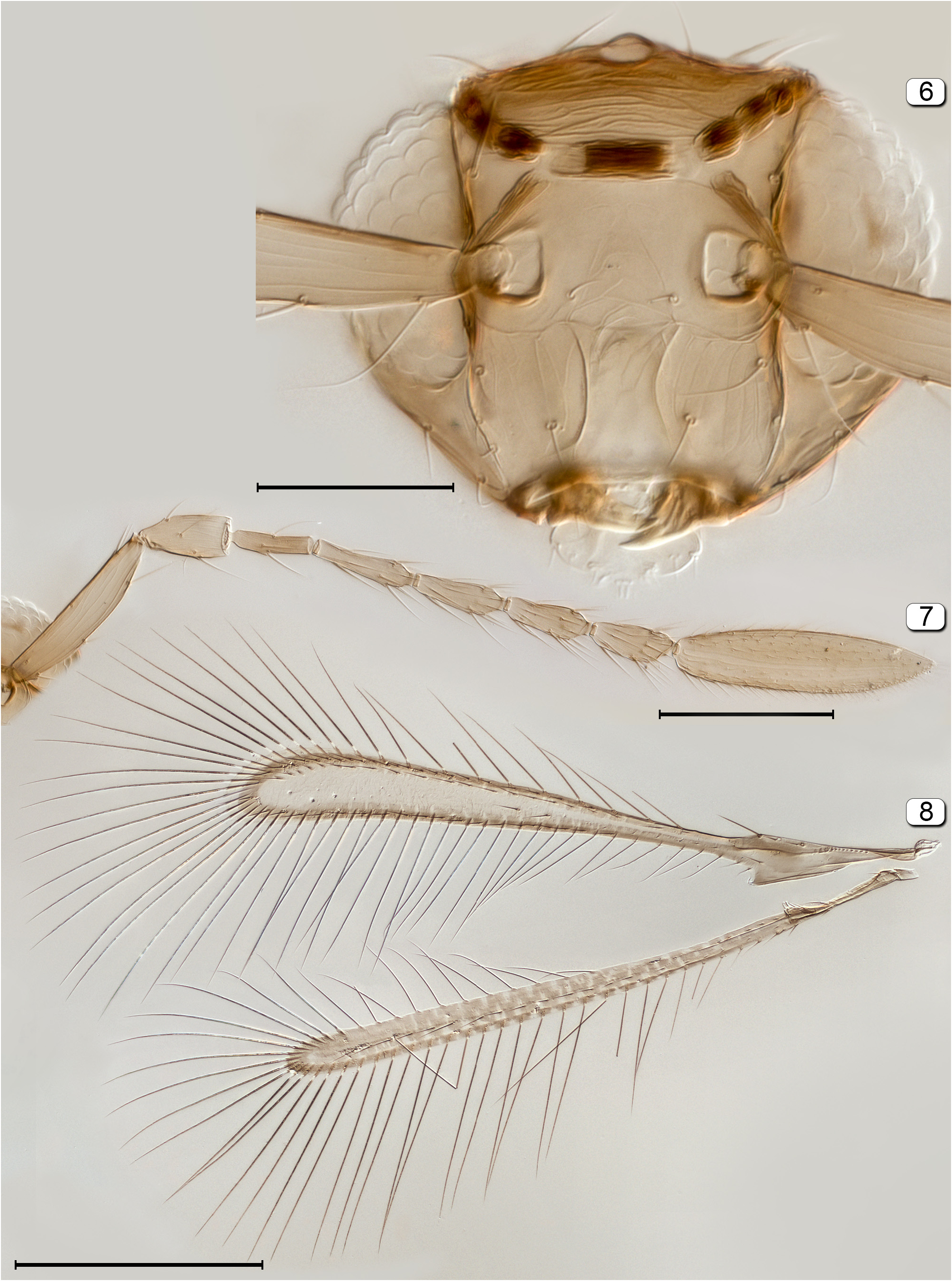
- Head in anterior view not narrowing ventrally so appearing more quadrate; mandibles pointing inwardly and crossing if long enough, each with 2 subequal teeth ( Figs 6 View FIGURES 6–8 , 107 View FIGURES 107–109 ); fore wing wider along its entire length ( Figs 8 View FIGURES 6–8 , 109 View FIGURES 107–109 )................ 19
19(18) Gaster compressed, slightly higher than wide and well sclerotized; gt 1 much longer than each remaining tergum ( Fig. 167a View FIGURES 166, 167 , 169 View FIGURES 168, 169 )........................................................................................... Litus View in CoL
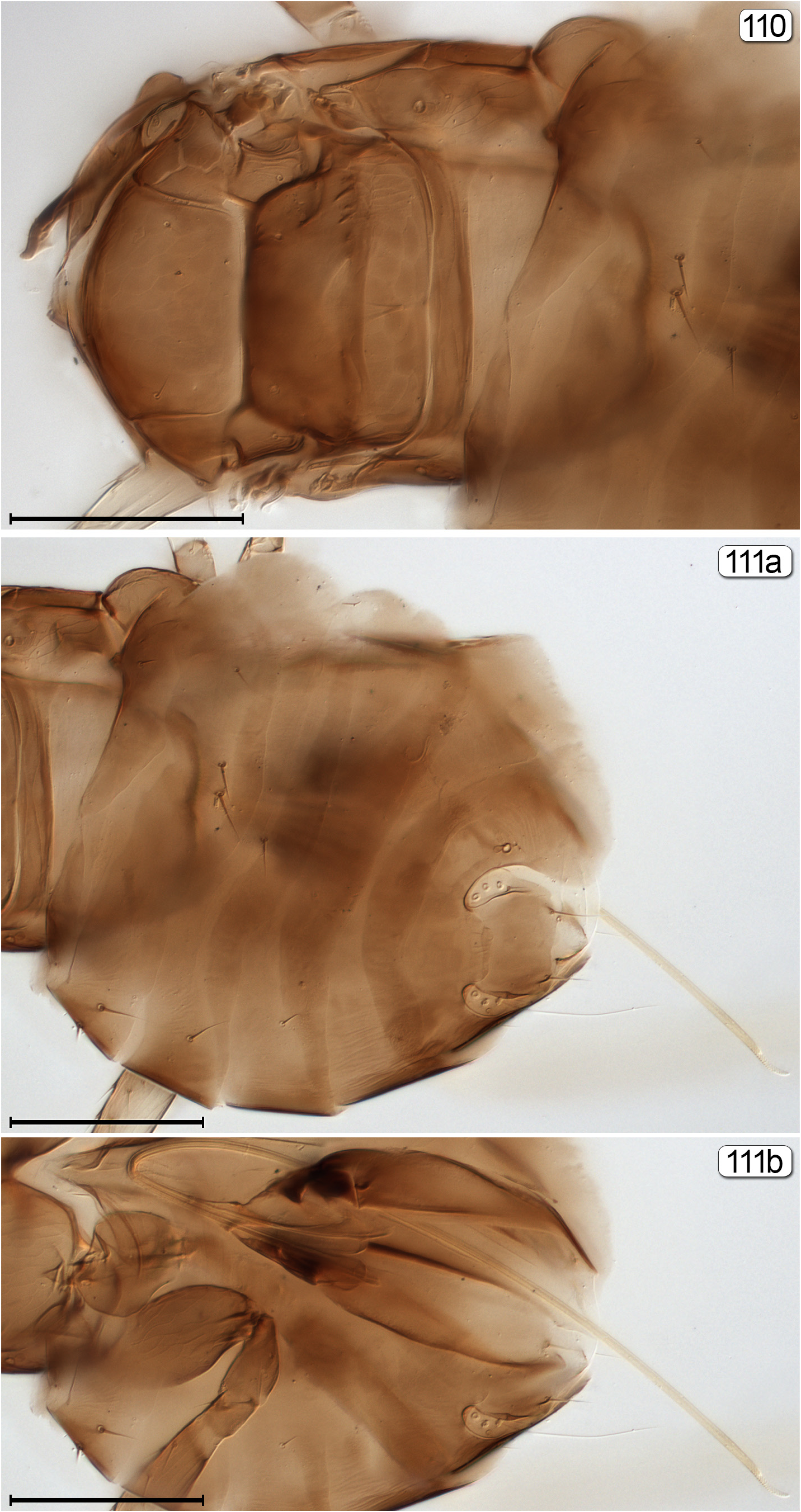
- Gaster slightly depressed, wider than high and weakly sclerotized; gt 1 about same length as each remaining tergum ( Figs 9, 111a View FIGURES 110, 111 )............................................................................................. 20
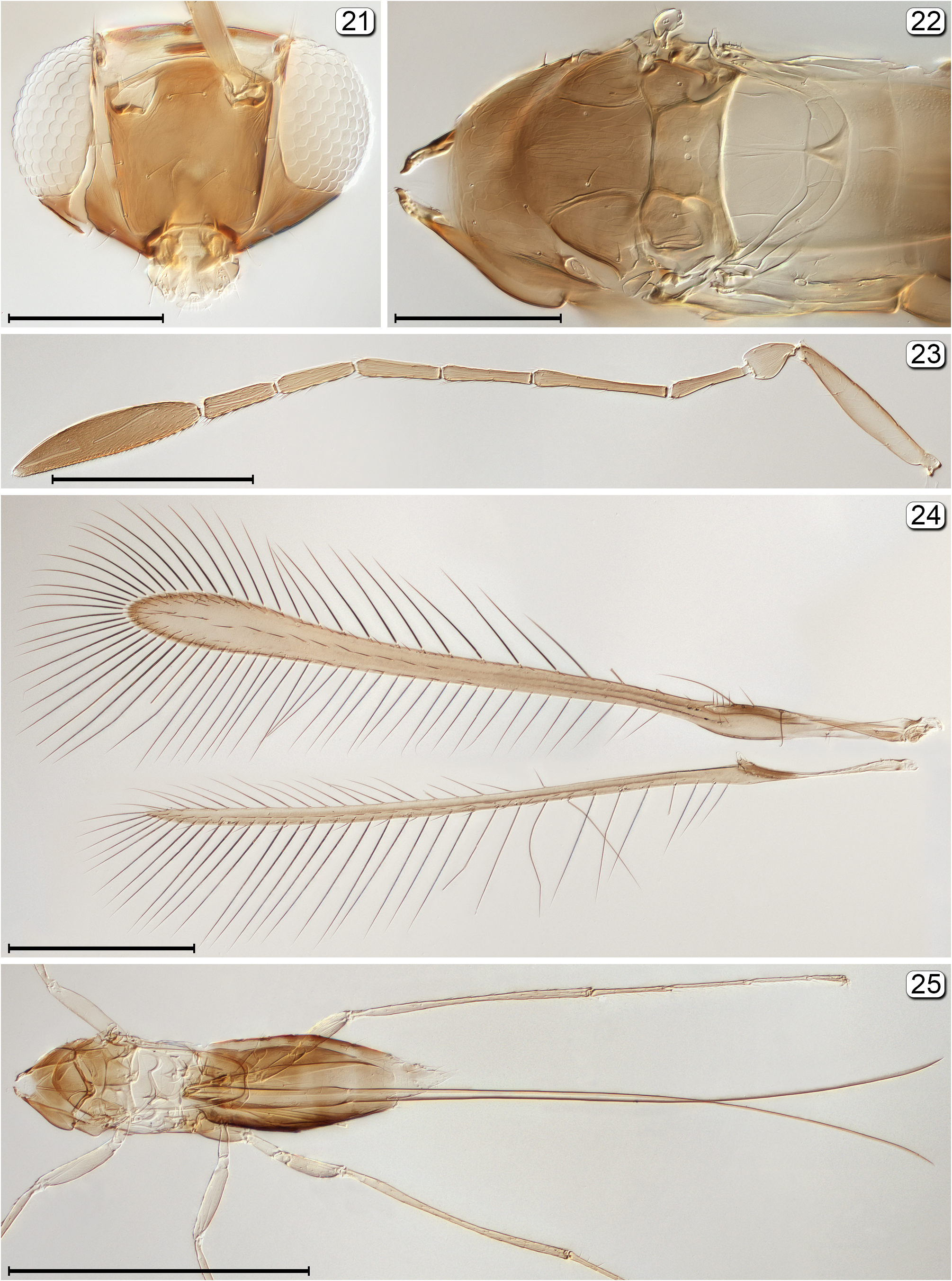
20(19) Fore wing with posterior margin behind venation distinctly notched ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 6–8 )................................ Alaptus View in CoL
- Fore wing with posterior margin behind venation not or barely notched ( Fig. 109 View FIGURES 107–109 )..................... Dicopomorpha View in CoL
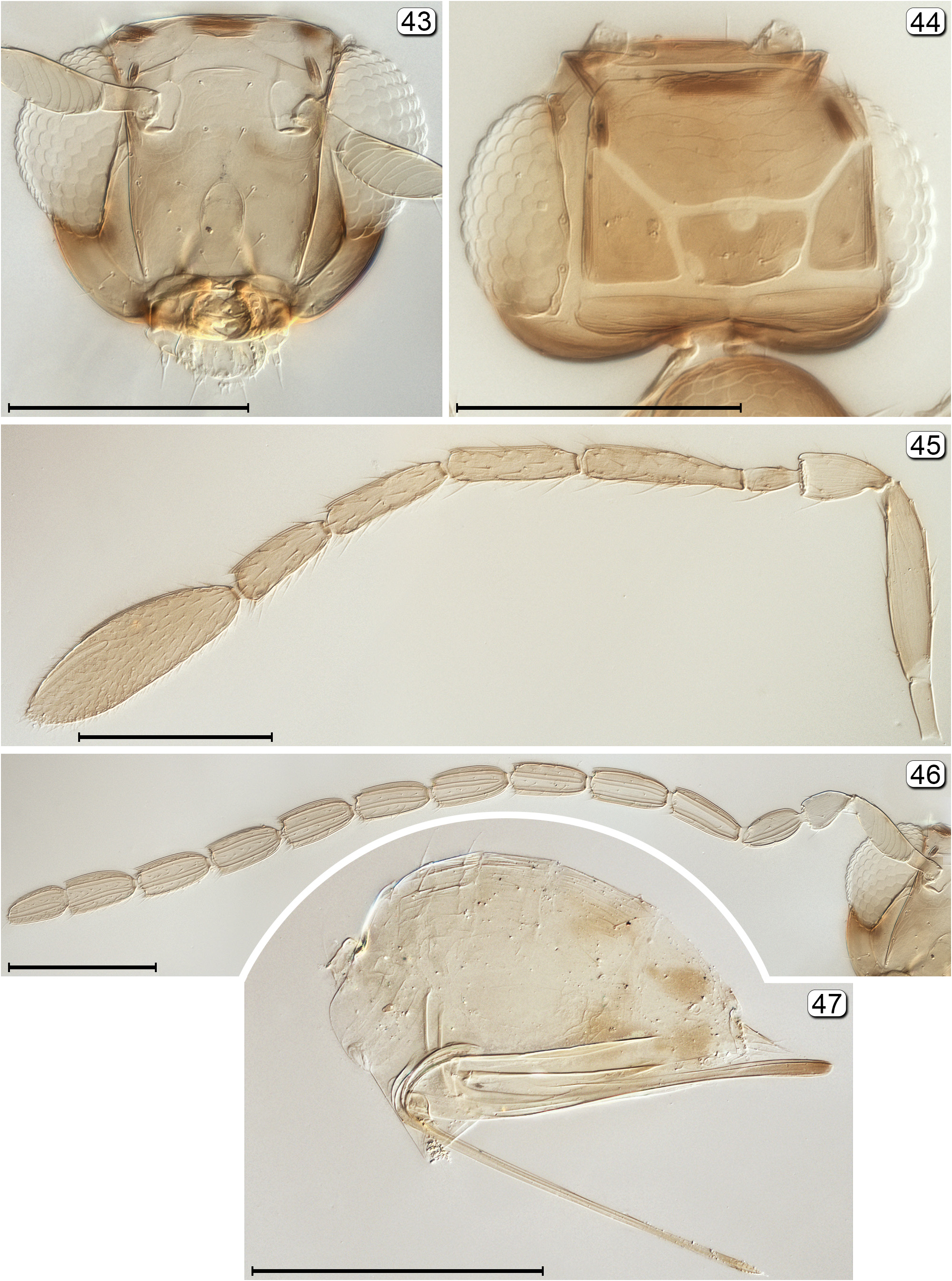
21(4) Head with ocellar triangle surrounded by pale lines, forming a stemmaticum ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 43–47 ); postmarginal vein at most as long as stigmal vein ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 48, 49 )........................................................................... Arescon View in CoL
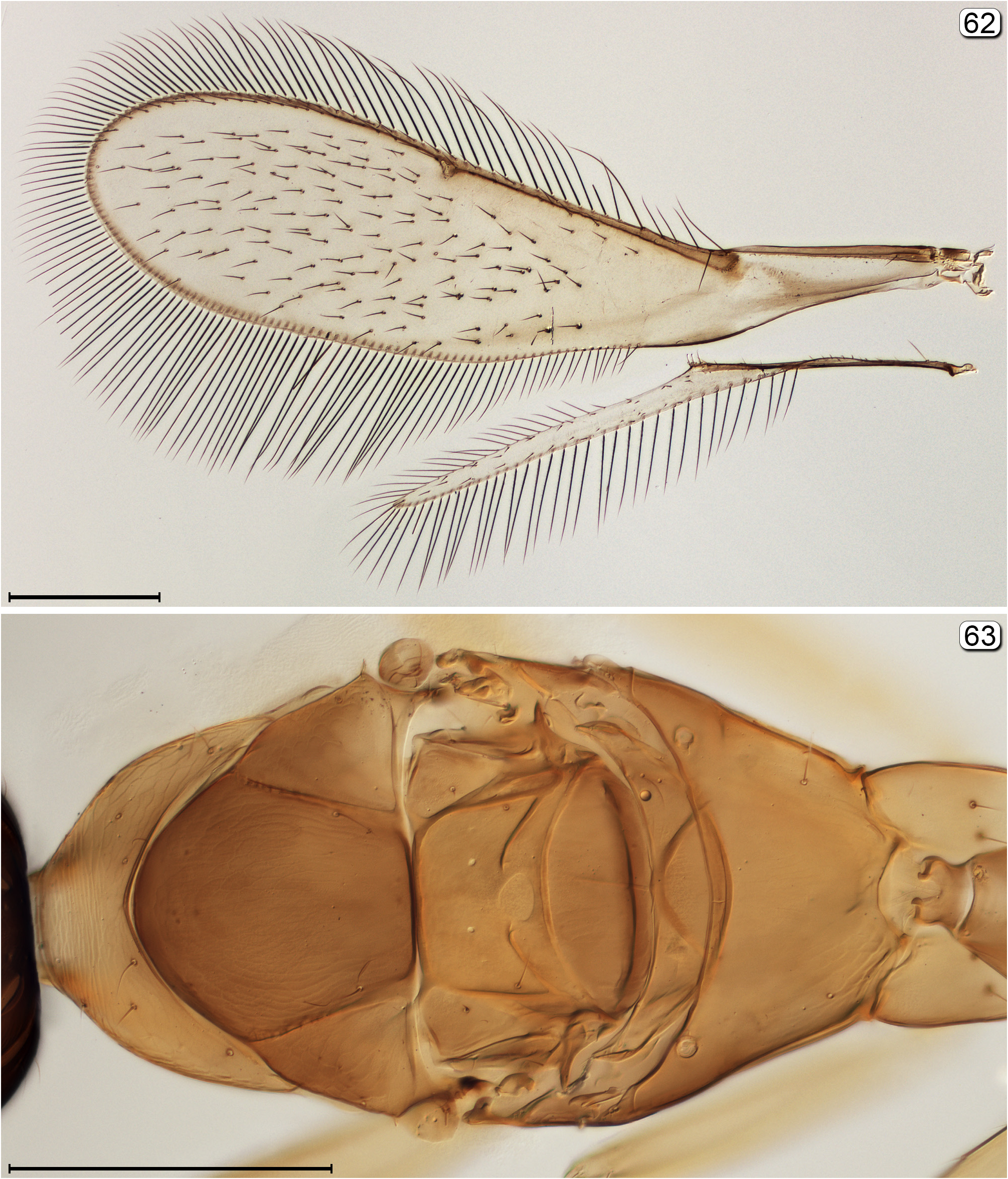
- Head with ocelli not enclosed by stemmaticum; postmarginal vein much longer than stigmal vein ( Fig. 62 View FIGURES 62, 63 )............. 22
22(21) Pronotum in dorsal view extremely short, barely or not visible; mesoscutum without notauli.............. Chrysoctonus View in CoL
- Pronotum in dorsal view about 0.4× length of mesoscutum, clearly visible; mesoscutum with notauli ( Fig. 63 View FIGURES 62, 63 ) Borneomymar View in CoL
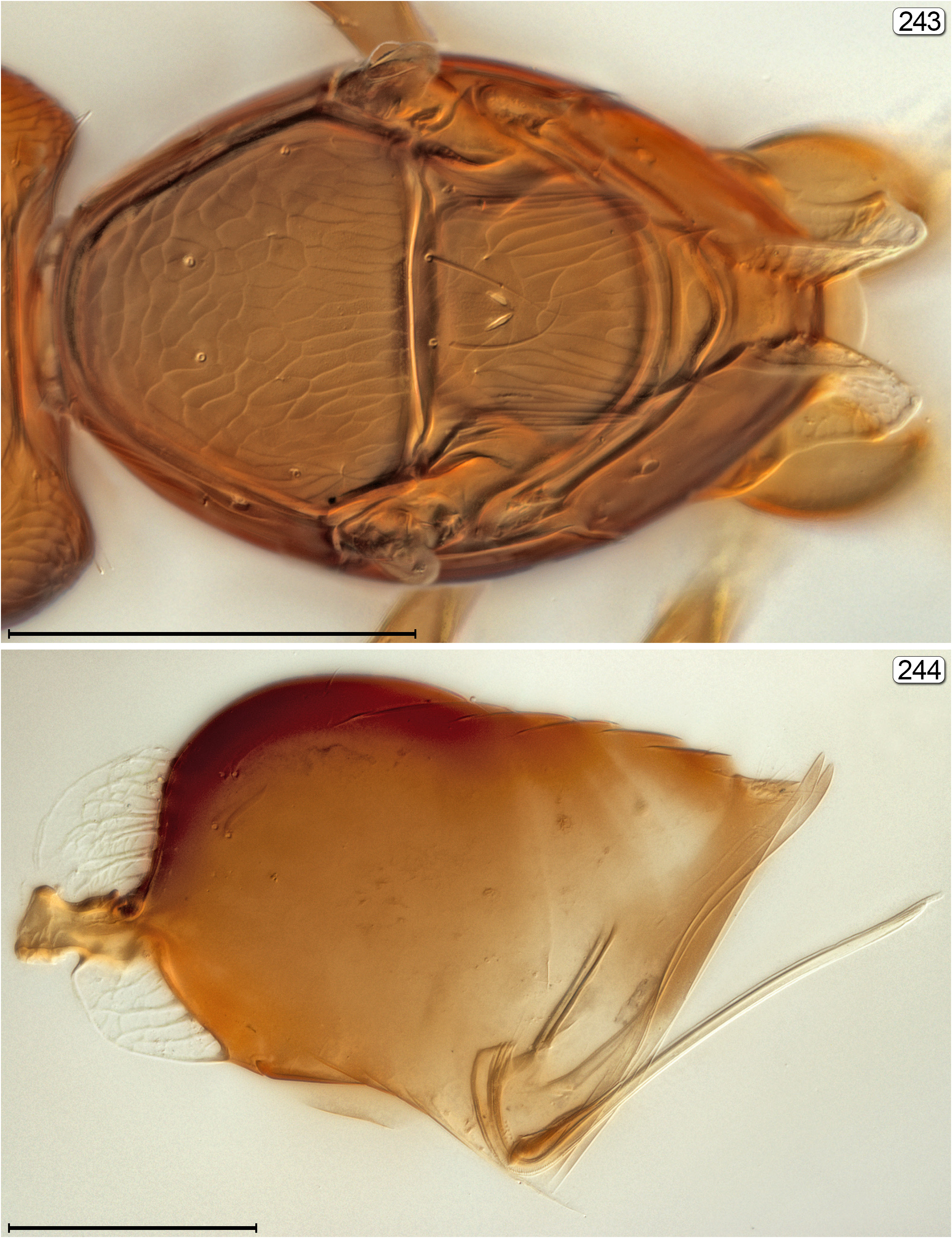
23(3) Propodeum and gt 1 with translucent reticulated structures ( Fig. 243 View FIGURES 243, 244 ).................................... Ptilomymar View in CoL
- Propodeum and gt 1 without translucent reticulated structures................................................. 24
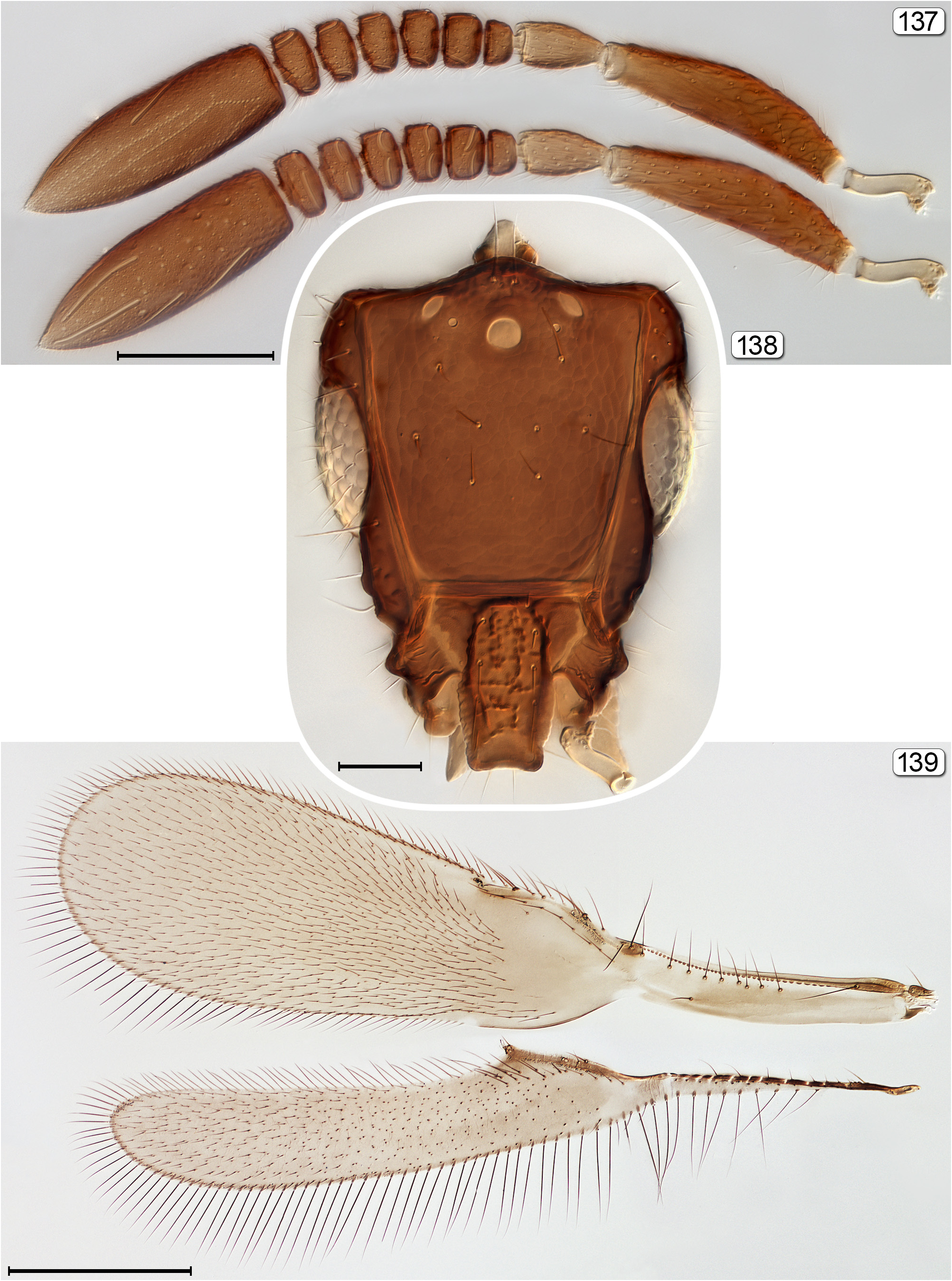
24(23) Mandibles about as long as head height and not capable of crossing medially (mandibular movement is in anterior/posterior direction); head in lateral view triangular; face with a large truncate projection between toruli ( Fig. 138 View FIGURES 137–139 )....... Eubroncus View in CoL
- Mandibles much shorter than head height and crossing medially when closed; head in lateral view quadrate; face without projection between toruli................................................................................ 25
25(24) Petiole in dorsal view shorter than wide, and scarcely visible................................................. 26
- Petiole in dorsal view at least as long as wide but usually much longer, and clearly visible.......................... 34
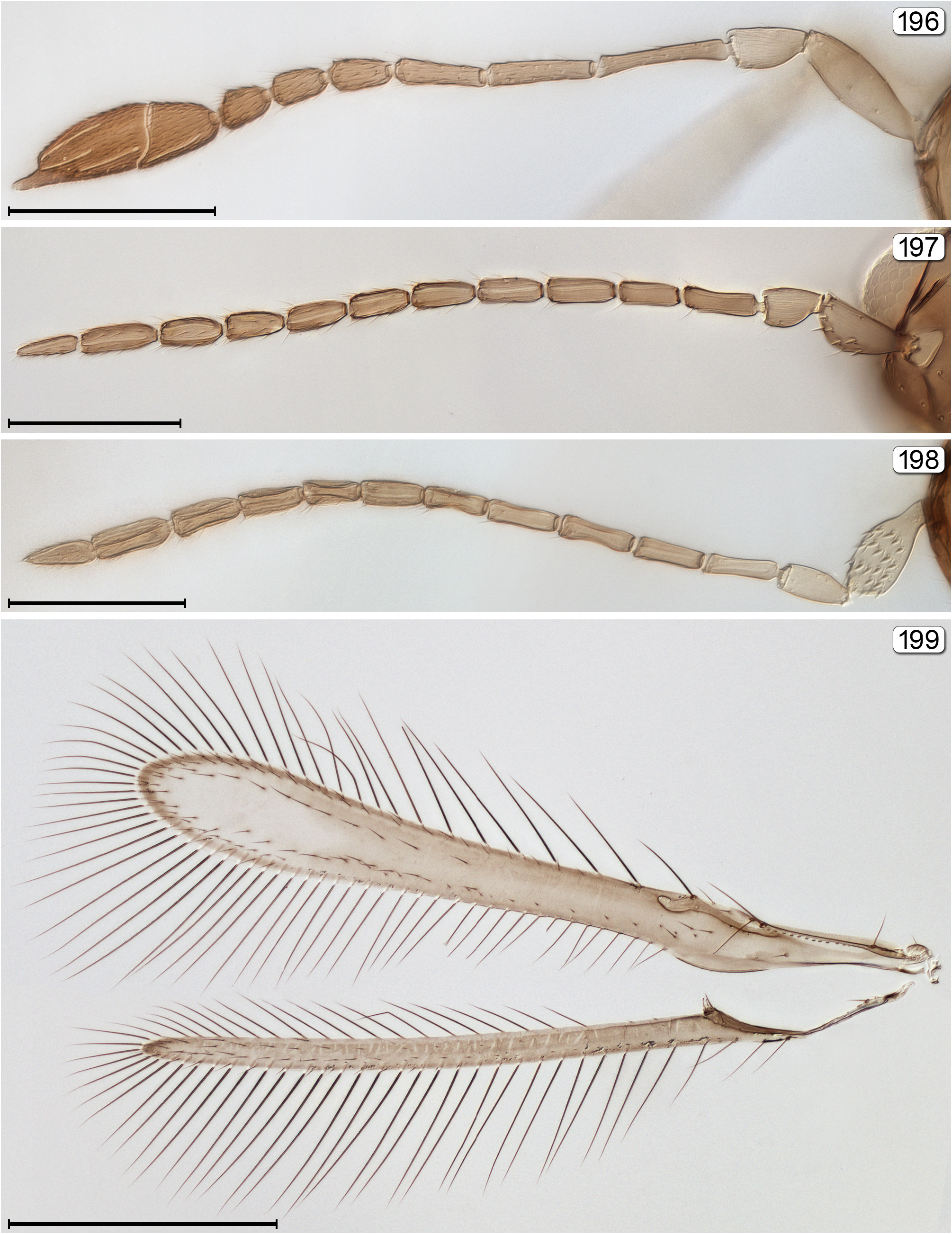
26(25) Scape inner surface almost always with several thickened, peg-like setae ( Fig. 198 View FIGURES 196–199 )......... Omyomymar ( Omyomymar)
- Scape inner surface without setae or, if setae present, these thin, not peg-like..................................... 27
27(26) Frenum completely divided medially by longitudinal groove into paramedial plates ( Figs 29 View FIGURES 29, 30 , 36 View FIGURES 36, 37 )..................... 28
- Frenum entire or not clearly or only partially divided medially by longitudinal groove............................. 29
28(27) Frenum with each paramedial plate wider than long; second phragma with apex truncate or convex ( Figs 22 View FIGURES 21–25 , 29 View FIGURES 29, 30 , 36 View FIGURES 36, 37 )................................................................................................... Anagrus View in CoL
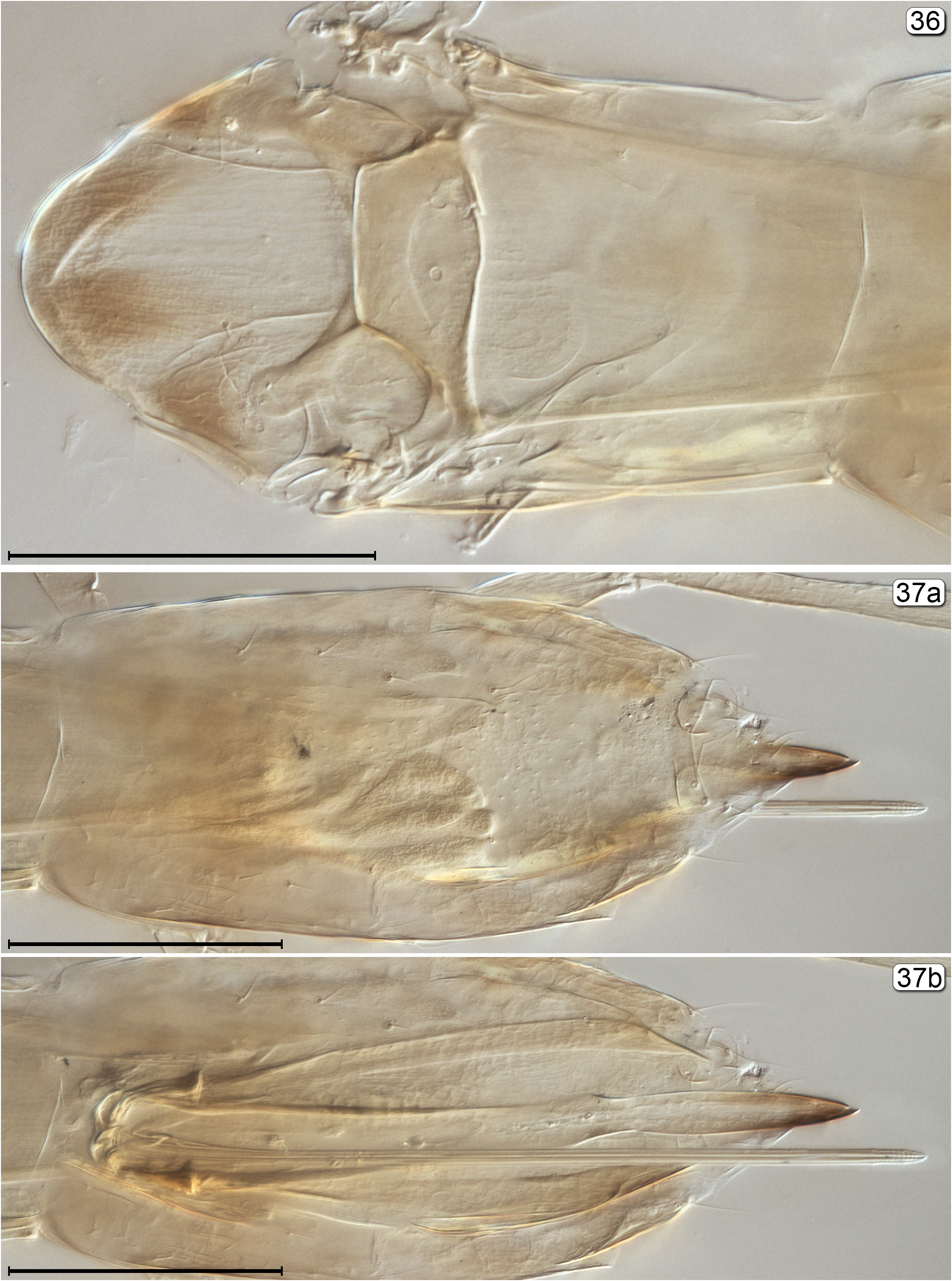
- Frenum with each paramedial plate longer than wide; second phragma with apex notched medially........ Schizophragma View in CoL
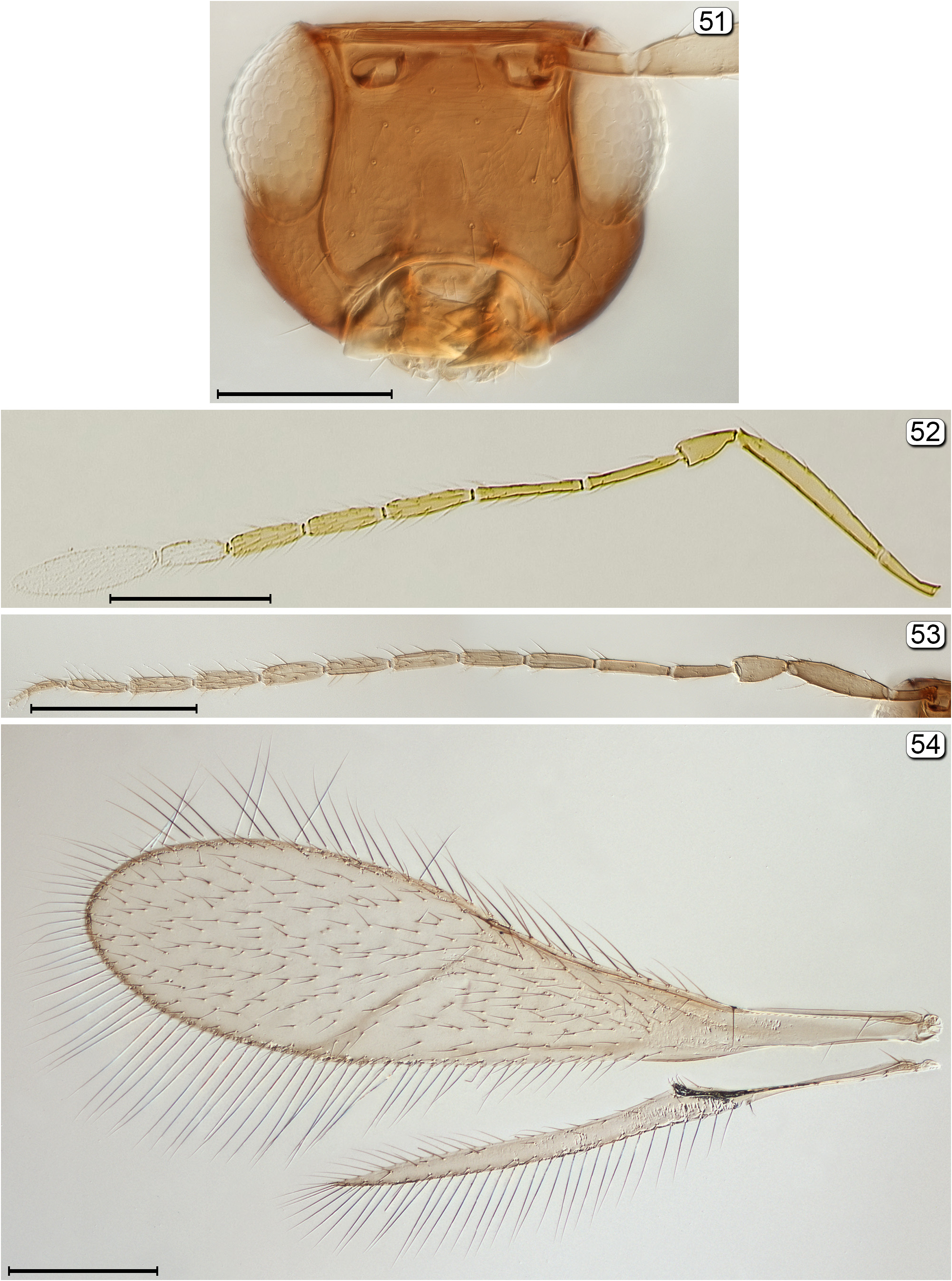
29(27) Fore wing with venation at least 0.5 × wing length and with a distinct line of microtrichia extending from apex of venation obliquely towards posterior margin of wing ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 51–54 )............................................. Australomymar View in CoL
- Fore wing with venation at most 0.4× wing length and without such a line of microtrichia.......................... 30
30(29) Mandible reduced to small stub without teeth ( Fig. 129 View FIGURES 128–130 ); maxillae elongate, together longer than wide; gena in lateral view narrow, almost absent; dorsellum projecting slightly over propodeum ( Fig. 131 View FIGURES 131, 132 ), as best seen in lateral view; genitalia often considerably extruded in dead specimens......................................................... Erythmelus View in CoL
- Mandible not reduced and with teeth; maxillae more quadrate, together as wide as long; gena in lateral view wider; dorsellum not projecting over propodeum; genitalia not or only slightly extruded in dead specimens........................... 31
31(30) Face in lateral view flat or only slightly curved, not bulging anterior to level of eye so head in lateral view more or less rectangular; most flagellomeres longer than wide; propodeum with median groove..................................... 32
- Face in lateral view angular and bulging anterior to level of eye so head in lateral view more or less triangular; all flagellomeres quadrate, as long as wide or only slightly rectangular; propodeum without median groove.......................... 33
32(31) Scutellum without a short seta at lateral margin ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 41, 42 )............................................... Anaphes View in CoL
- Scutellum with a short seta at lateral margin ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 19, 20 )............................................... Allanagrus View in CoL
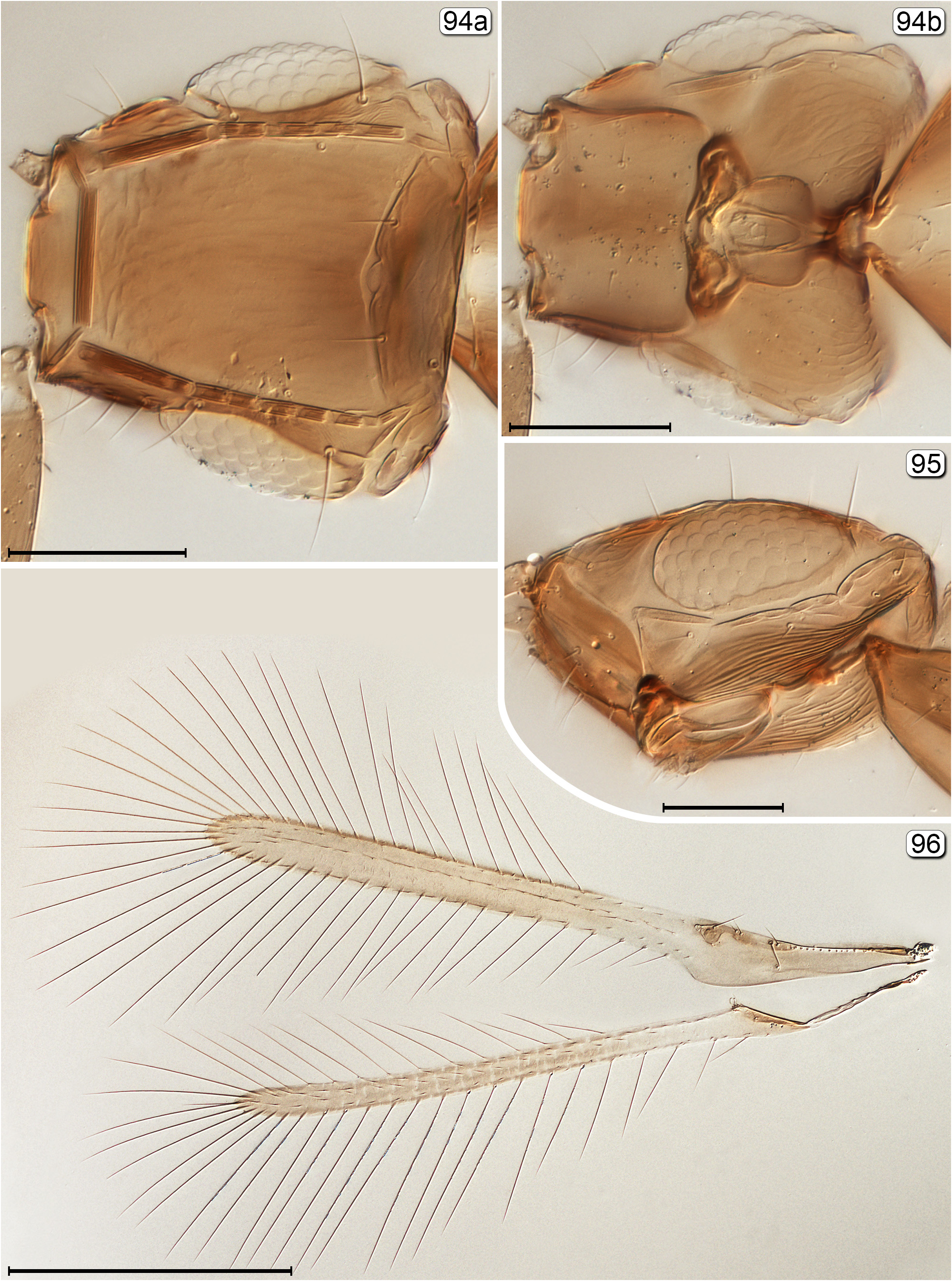
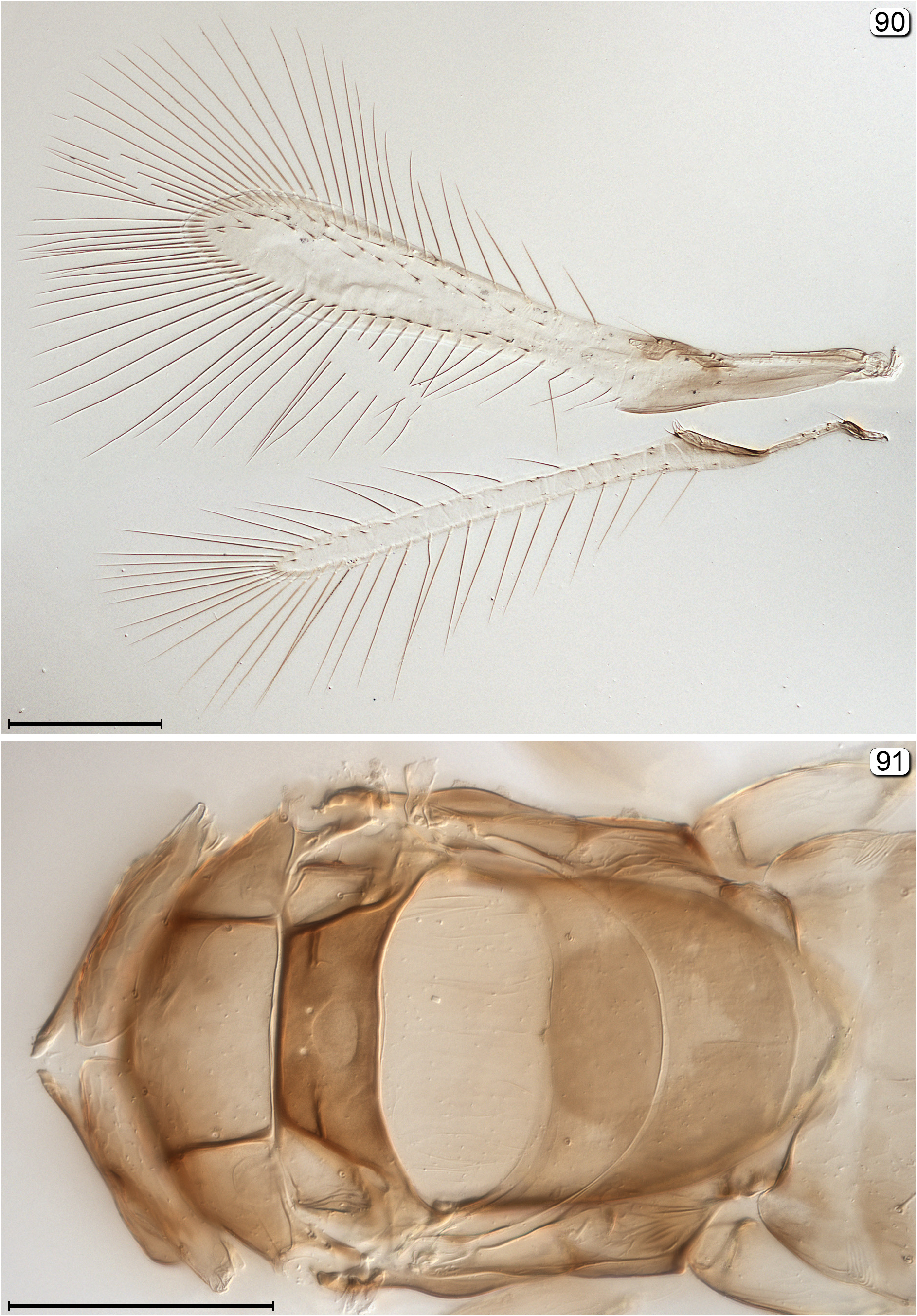
33(31) Fore wing parallel-sided or almost so and without a distinct lobe behind apex of venation ( Fig. 96 View FIGURES 94–96 ); subantennal grooves about same colour as remainder of head................................................................ Cleruchus View in CoL
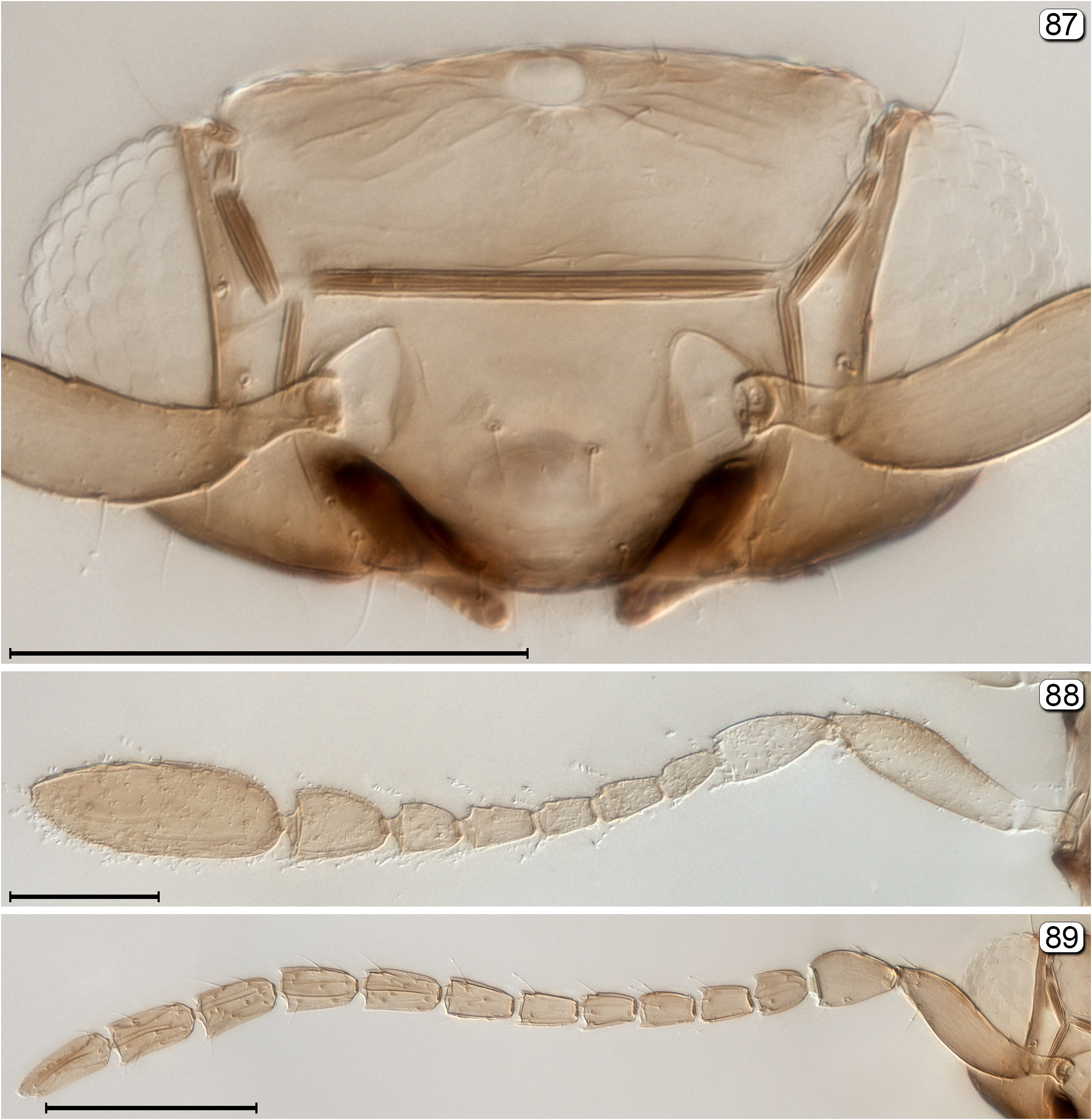
- Fore wing distinctly widening towards apex and with a distinct lobe behind apex of venation ( Fig. 90 View FIGURES 90, 91 ); subantennal grooves black contrasting sharply with light coloured remainder of head ( Fig. 87 View FIGURES 87–89 ).............................. Cleruchoides
34(25) Fore wing extremely narrow and parallel-sided in basal half then widening abruptly and considerably in apical half ( Fig. 177 View FIGURES 175–177 ); hind wing either filamentous, without membrane, or narrow with only about 10 long fringe setae along posterior margin beyond venation and at apex ( Fig. 177 View FIGURES 175–177 ), or reduced to a short stub................................................ Mymar View in CoL
- Fore wing gradually widening from base towards apex; hind wing with wider membrane and fringe setae along both anterior and posterior margins and at apex....................................................................... 35
35(34) Fore wing cigar-like, with anterior and posterior margins strongly inrolled; pronotum slightly longer than length of mesoscutum + scutellum ( Fig. 184 View FIGURES 184, 185 ); mesoscutum about 0.6× as long as scutellum.................................... Mymarilla View in CoL
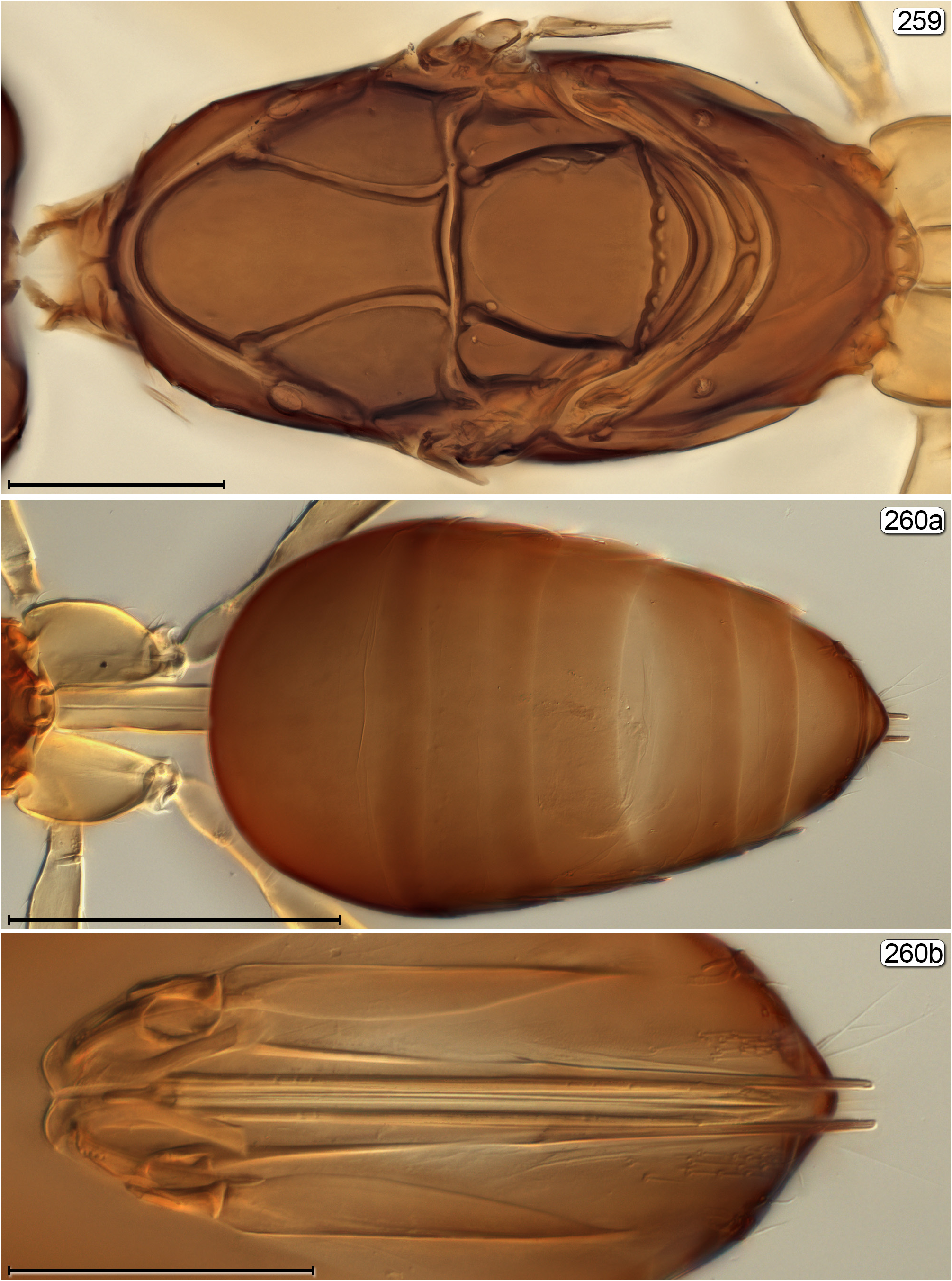
- Fore wing flat, with anterior and posterior margins in same plane; pronotum much shorter than length of mesoscutum + scutellum ( Figs 147 View FIGURES 147–149 , 213, 234, 259); mesoscutum about as long as scutellum ( Figs 147 View FIGURES 147–149 , 213, 234, 259).................... 36
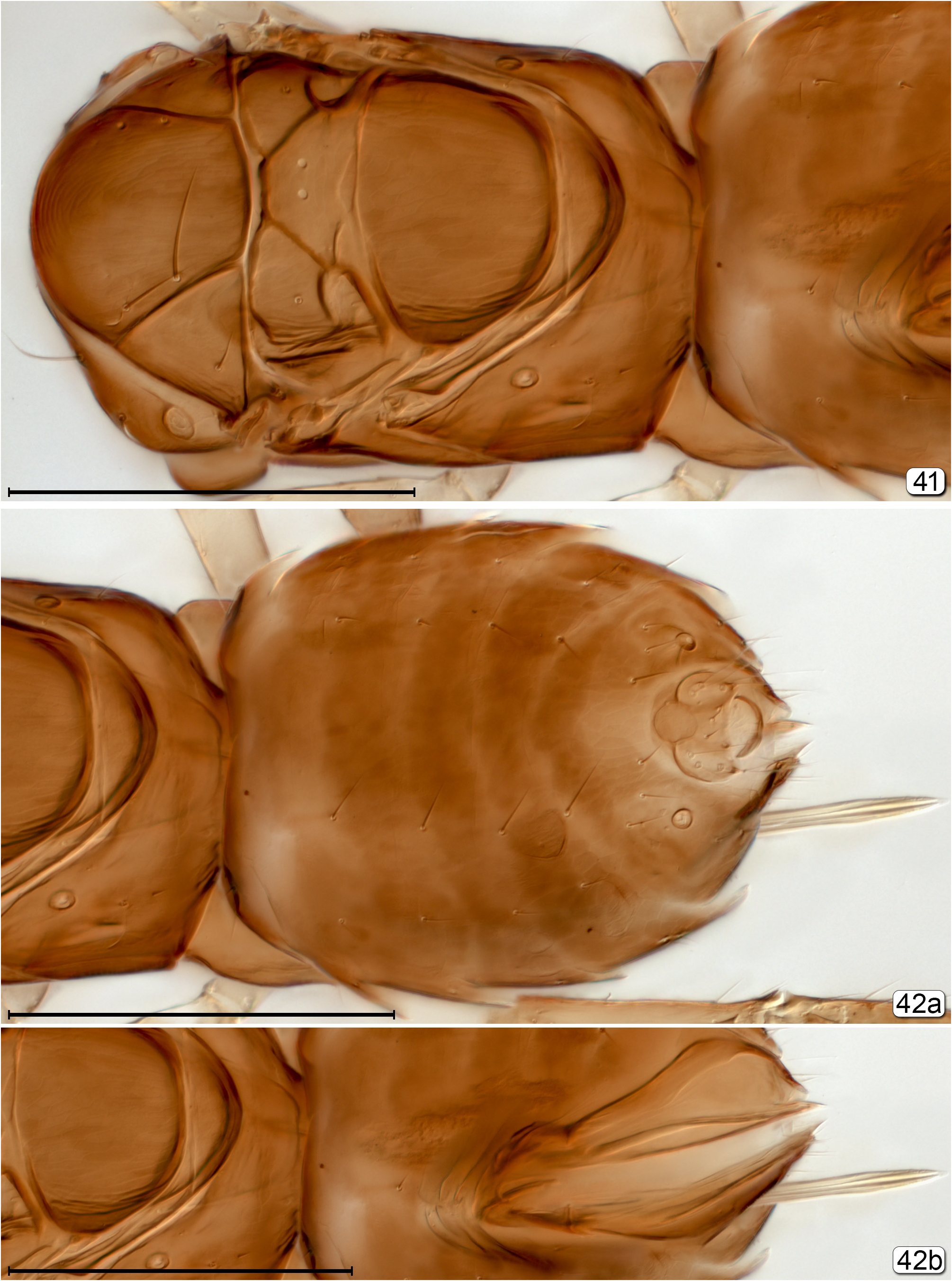
36(35) Mesothoracic spiracle closer to anterior apex of notaulus than to tegula ( Fig. 259 View FIGURES 259, 260 ); mesosoma smooth and shiny.................................................................................................... Stephanodes View in CoL
- Mesothoracic spiracle closer to tegula than to anterior apex of notaulus (Figs 213, 234); mesosoma with at least some faint, usually engraved sculpture, and dull..................................................................... 37
37(35) Propodeum with V-shaped carinae medially ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4, 5 )............................................. Acmopolynema View in CoL
- Propodeum either smooth or with 1 or 2 parallel median/submedian carinae..................................... 38
38(37) Petiole attached to gastral sternum posteriorly.................................................... Ganomymar View in CoL
- Petiole attached to gastral tergum posteriorly.............................................................. 39
39(38) Face with small pit medially next to each torulus.......................................... Polynema ( Doriclytus)
- Face without pit medially next to each torulus............................................................. 40
40(39) Propleura abutting medially anterior to prosternum (Fig. 215)........................................ Palaeoneura View in CoL
- Propleura not abutting medially anterior to prosternum ( Fig. 238 View FIGURES 237, 238 ).............................................. 41
41(40) Fore wing without discal microtrichia only beyond apex of venation ( Fig. 236 View FIGURES 235, 236 ); scape with numerous thick setae on inner surface ( Fig. 235 View FIGURES 235, 236 )................................................................. Polynema ( Dorypolynema)
- Fore wing with discal microtrichia also behind apex of venation; scape smooth or with cross-ridges................................................................................................. Polynema ( Polynema) , part
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |