Bezzia (Bezzia) pulverea (Coquillett, 1901)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4877.3.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5DAFB47B-1A91-45C6-891C-A8D2A4F6BB74 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4562921 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/51478796-2813-FFBD-FF1C-FE20FA59FA2C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bezzia (Bezzia) pulverea |
| status |
|
Key to adults in the Bezzia (Bezzia) pulverea View in CoL complex
(Females of B. leptostyla , n. sp. are unknown)
1 Males .............................................................................................. 2
- Females............................................................................................ 12
2. Apex of gonostylus rounded or blunt, without apical inner or outer prongs ( Figs. 33 View FIGURES 31–36 , 44 View FIGURES 43–48 )............................. 3
- Apex of gonostylus with apical inner and outer prongs ( Figs. 3 View FIGURES 1–6 , 10–14 View FIGURES 7–14 , 25–26 View FIGURES 25–30 , 52 View FIGURES 49–55 , 63 View FIGURES 61–66 , 69–70 View FIGURES 67–71 ) or with only an apical outer prong ( Figs. 20 View FIGURES 20–24 , 38 View FIGURES 37–42 , 59–60 View FIGURES 56–60 )................................................................................... 4
3. Gonocoxite and gonostylus short, apex of gonostylus blunt or slightly rounded ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 31–36 ); aedeagus with moderately long apical section with sharply pointed tip ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 31–36 ); hind tibia brown with narrow pale yellow to light brown basal and broader subapical bands ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 31–36 ); hind tarsomere 1 yellow ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 31–36 ); mid, hind femur with 0–1 ventral spines ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 31–36 )... B. amblystyla View in CoL , n. sp.
- Gonocoxite and gonostylus moderately elongate, apex of gonostylus rounded ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 43–48 ); aedeagus with very slender, greatly elongate apical section with bifid tip ( Fig. 45 View FIGURES 43–48 ); hind tibia dark brown without pale yellow or light brown bands ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 43–48 ); hind tarsomere 1 dark brown ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 43–48 ); mid, hind femora without ventral spines ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 43–48 ).................. B. folkertsi View in CoL , n. sp.
4. Hind tibia brown with moderately broad (0.25 length of tibia) pale yellowish subapical band ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 49–55 ); gonostylus very short without narrow neck-like base, apex broad with long slender pointed outer prong and shorter broader blade-like inner prong ( Fig. 52 View FIGURES 49–55 )............................................................................... B. huberti View in CoL , n. sp.
- Hind tibia brown with or without narrow pale yellowish subapical band; gonostylus moderately long to elongate with narrow neck-like base, apex with inner and outer prongs or only outer prong............................................ 5
5. Hind femur and tibia brown to dark brown without yellowish or light brown bands ( Figs. 8 View FIGURES 7–14 , 16 View FIGURES 15–19 , 28 View FIGURES 25–30 , 37 View FIGURES 37–42 , 56 View FIGURES 56–60 , 62 View FIGURES 61–66 )........... 6
- Hind femur and tibia brown with yellowish or light brown bands on both or only one of these segments( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 21 View FIGURES 20–24 , 67 View FIGURES 67–71 ).... 9
6. Hind tarsomere 1 dark brown ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 37–42 ); gonostylus short, very broad with slender sharply pointed outer prong ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 37–42 )...................................................................................... B. brunneipedia View in CoL , n. sp.
- Hind tarsomere 1 yellowish to light brown ( Figs. 8 View FIGURES 7–14 , 56 View FIGURES 56–60 , 62 View FIGURES 61–66 , 67 View FIGURES 67–71 ); gonostylus elongate with apical inner and outer prongs ( Figs. 3 View FIGURES 1–6 , 10–14 View FIGURES 7–14 , 25–26 View FIGURES 25–30 , 63 View FIGURES 61–66 ), elongate with only a long outer prong ( Figs. 59–60 View FIGURES 56–60 ), or short, broad with apical inner and outer prongs ( Figs. 69–70 View FIGURES 67–71 ), or with only an outer prong ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 20–24 ).......................................................... 7
7. Inner prong of gonostylus longer than outer prong ( Fig. 63 View FIGURES 61–66 ); fore femur with 8–9 ventral spines ( Fig. 62 View FIGURES 61–66 ); antennal flagellum very long, length 1.79–1.83 mm ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES 61–66 )............................................... B. marylandensis View in CoL , n. sp.
- Inner prong of gonostylus much shorter than outer prong ( Figs. 20 View FIGURES 20–24 , 25–26 View FIGURES 25–30 , 60 View FIGURES 56–60 , 69–70 View FIGURES 67–71 ); fore femur with 2–7 (rarely 8) ventral spines; antennal flagellum shorter, length 1.06–1.69 mm ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7–14 )................................................ 8
8. Gonostylus usually slender distally with blunt, folded, flap-like inner prong and very short outer prong ( Figs. 10–11 View FIGURES 7–14 ); aedeagus very broad with relatively short apical section ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 7–14 ); southeastern USA species, Maryland to Florida, west in Texas, Arkansas and Louisiana ............................................................. B. laciniastyla Dow & Turner View in CoL
- Gonostylus broad distally with elongate, curved outer prong with pointed tip and short rounded inner prong ( Figs. 25–26 View FIGURES 25–30 ); aedeagus broad with elongate, triangular relatively narrow apical section ( Fig. 25–26 View FIGURES 25–30 ); wide ranging Nearctic species, Alaska, British Columbia to New Brunswick, south to California, New Mexico, east in Utah, Wyoming, Wisconsin, Nebraska, New York, Connecticut, south to Maryland and Virginia ..................................... B. uncistyla Dow & Turner View in CoL
9. Gonostylus with well-developed inner and outer prongs ( Figs. 3 View FIGURES 1–6 , 69–70 View FIGURES 67–71 )........................................ 10
- Gonostylus with elongate outer prong, and rounded or without an inner prong ( Figs. 20 View FIGURES 20–24 , 59–60 View FIGURES 56–60 )...................... 11
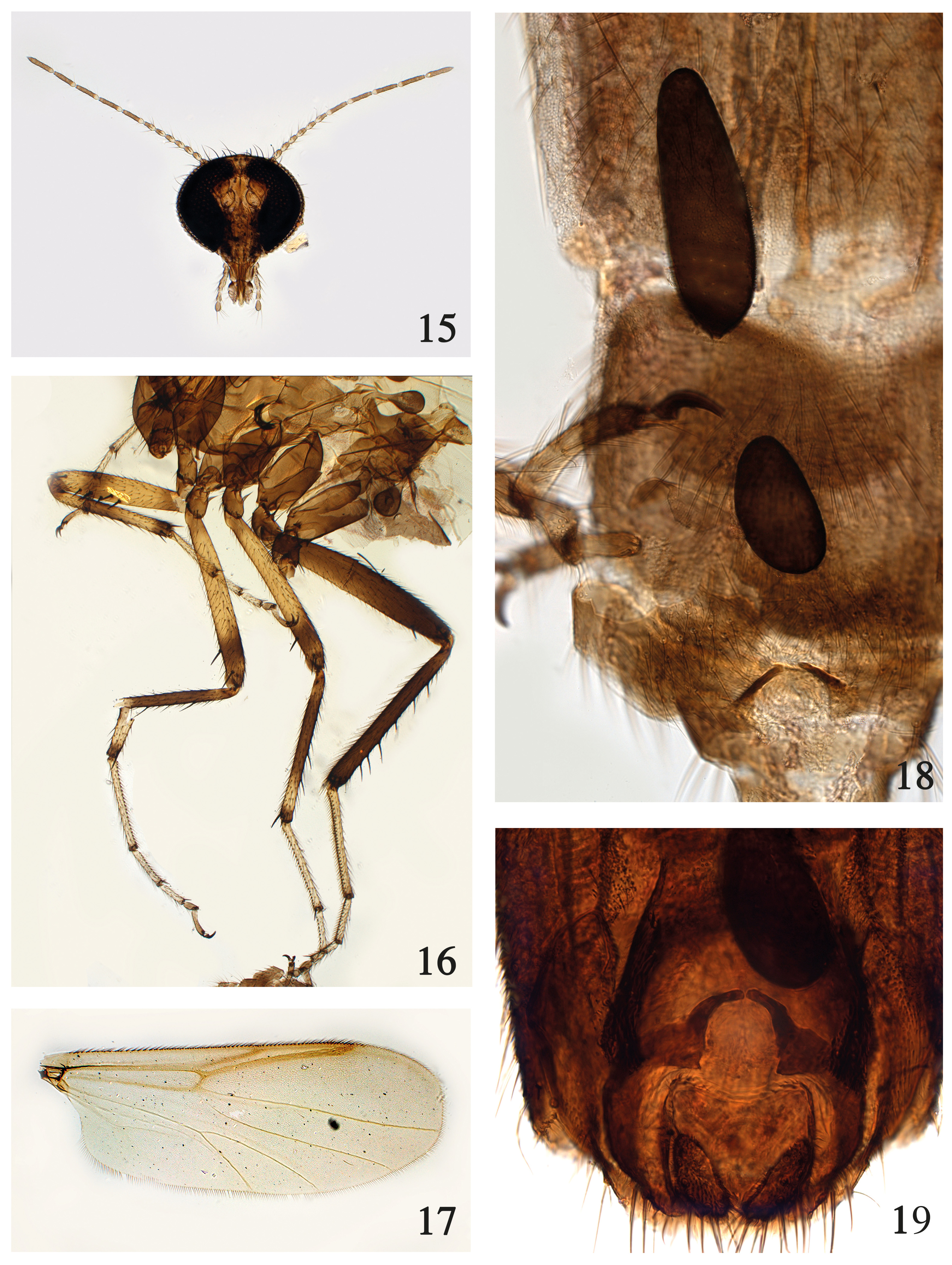
10. Gonostylus moderately long, slender, apex with inner prong longer than outer prong ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ); fore femur yellow without dark bands, with 4–9 ventral spines ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); large species, wing length 1.95–2.35 mm ............... B. pulverea (Coquillett) View in CoL
- Gonostylus very short with very broad claw-like apex, outer prong very long, greatly curved, inner prong shorter, broad, blade-like ( Figs. 69–70 View FIGURES 67–71 ); fore femur yellowish or light brown with brown basal band, with or without poorly developed narrow subapical brown band and 2–4 ventral spines ( Fig. 67 View FIGURES 67–71 ); medium-size species, wing length 1.62–1.81 mm .................................................................................................... B. titanochela View in CoL , n. sp.
11. Fore femur with 4 ventral spines; sternite 9 long with a narrow deep apico-medial excavation that lacks a fringe of setae; gonostylus very short, broad with slender, curved outer prong ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 20–24 ); fore, mid tibiae yellowish brown with darker brown narrow dorsal stripes that extend 4/5 of their total lengths ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 20–24 )................................ B. spicata Dow & Turner View in CoL
- Fore femur with 6–8 ventral spines ( Fig. 56 View FIGURES 56–60 ); sternite 9 moderately long with narrow shallow U-shaped apico-medial excavation that lacks a fringe of setae ( Figs. 59–60 View FIGURES 56–60 ); gonostylus elongate with very long slightly curved outer prong ( Fig. 60 View FIGURES 56–60 ), but lacks an inner prong; fore tibia yellowish to light brown with broad central and narrower apical brown bands, mid tibia brown or medium brown with pale narrow subapical band or with poorly defined basal band and broader well developed pale subapical band ( Fig. 56 View FIGURES 56–60 )......................................................................... B. leptostyla View in CoL , n. sp.
12. Femora, tibiae brown, hind leg darkest with only a poorly developed narrow light brown apical band on forefemur, mid-, hind femur and all tibiae without pale bands ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 43–48 ); mid-, hind femur without ventral spines; spermathecae subequal-size, very small (larger 0.09 mm, smaller 0.08 mm long)................................................ B. folkertsi View in CoL , n. sp.
- Femora, tibiae yellowish to dark brown with yellowish or light brown bands on some or all legs ( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 16 View FIGURES 15–19 , 21 View FIGURES 20–24 , 34 View FIGURES 31–36 , 40 View FIGURES 37–42 , 54 View FIGURES 49–55 , 64 View FIGURES 61–66 ); mid-, hind femur usually with 1 or more ventral spines; spermathecae unequal-size, medium-size to very large (larger 0.13–0.25 mm, smaller 0.08–0.17 mm long) ( Figs. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 18 View FIGURES 15–19 , 23 View FIGURES 20–24 , 30 View FIGURES 25–30 , 36 View FIGURES 31–36 , 42 View FIGURES 37–42 , 55 View FIGURES 49–55 , 66 View FIGURES 61–66 , 71 View FIGURES 67–71 )........................................ 13
13. Hind tibia brown with broad to very broad (0.3–0.7 length of tibia) pale yellow subapical or apical band, without large stout apical spines ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 49–55 ); spermathecae unequal-size with greatly tapered neck regions, the larger very slender ( Fig. 55 View FIGURES 49–55 ); AR 1.42–1.56.............................................................................. B. huberti View in CoL , n. sp.
- Hind tibia brown with ( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 21 View FIGURES 20–24 , 34 View FIGURES 31–36 ) or without narrow, pale yellow subapical band ( Figs. 16 View FIGURES 15–19 , 28 View FIGURES 25–30 , 40 View FIGURES 37–42 , 64 View FIGURES 61–66 ), apex usually with 1 or more large apical spines ( Figs. 1 View FIGURES 1–6 , 22 View FIGURES 20–24 , 65 View FIGURES 61–66 ); spermathecae with or without tapered neck regions, the larger stout or moderately slender; AR 1.00–1.65................................................................................ 14
14. Hind femur and tibia brown to dark brown without yellowish or light brown bands ( Figs. 16 View FIGURES 15–19 , 28 View FIGURES 25–30 , 40 View FIGURES 37–42 ).................. 15
- Hind femur and tibia brown with yellowish or light brown bands on both or only on one of these segments ( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 21 View FIGURES 20–24 , 34 View FIGURES 31–36 )18
15. Hind tarsomere 1 dark brown ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 37–42 ); spermathecae with slightly tapered neck regions ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 37–42 )....................................................................................................... B. brunneipedia View in CoL , n. sp.
- Hind tarsomere 1 yellowish to light brown ( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 16 View FIGURES 15–19 , 21 View FIGURES 20–24 , 28 View FIGURES 25–30 , 34 View FIGURES 31–36 , 64 View FIGURES 61–66 ); spermathecae with broad neck regions, non-tapered or slightly to moderately tapered ( Figs. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 18 View FIGURES 15–19 , 23 View FIGURES 20–24 , 30 View FIGURES 25–30 , 36 View FIGURES 31–36 , 55 View FIGURES 49–55 , 66 View FIGURES 61–66 , 71 View FIGURES 67–71 ).............................................. 16
16. Antennal flagellum moderately long to very long (length 1.22–1.52 mm); AR 1.51–1.65; fore femur with 5–8 ventral spines ( Fig. 64 View FIGURES 61–66 ); spermathecae with broad, non-tapered necks ( Fig. 66 View FIGURES 61–66 )............................. B. marylandensis View in CoL , n. sp.
- Antennal flagellum very short to moderately long (length 0.86–1.28 mm); AR 1.21–1.72; fore femur with 2–8 ventral spines ( Figs. 16 View FIGURES 15–19 , 21 View FIGURES 20–24 , 28 View FIGURES 25–30 ); spermathecae with slightly or moderately tapered necks ( Figs. 23 View FIGURES 20–24 , 36 View FIGURES 31–36 , 71 View FIGURES 67–71 )......................... 17
17. Medium-size to large species (wing length 1.57–2.23 mm; Fig. 17 View FIGURES 15–19 ); AR 1.25–1.72; southeastern USA species, Maryland, Virginia south to Florida, west in Texas, Arkansas and Louisiana .......................... B. laciniastyla Dow & Turner View in CoL
- Large to very large species (wing length 1.97–2.86 mm; Fig. 29 View FIGURES 25–30 ); AR 1.21–1.57; wide ranging Nearctic species, Alaska, British Columbia to New Brunswick, south to California, New Mexico, east to Wisconsin, Nebraska, New York, Connecticut, south to Maryland and Virginia ........................................................... B. uncistyla Dow & Turner View in CoL
18. Hind tibia without large apical spines ( Fig. 34 View FIGURES 31–36 ); antennal flagellum very short to short (length 0.77–1.09 mm); spermathecae with greatly tapered necks ( Figs. 36 View FIGURES 31–36 , 71 View FIGURES 67–71 ).................................................................. 19
- Hind tibia with 3 large apical spines; antennal flagellum short to moderately long (length 1.01–1.35 mm); spermathecae with slightly to non-tapered neck regions ( Figs. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 23 View FIGURES 20–24 )........................................................... 20
19. Smaller species (wing length 1.39–1.76 mm; Fig. 35 View FIGURES 31–36 ); antennal flagellum very short (length 0.77–0.87 mm); palpal segment 3 moderately long (palpal ratio 2.75–4.14)................................................... B. amblystyla View in CoL , n. sp.
- Larger species (wing length 1.74–1.83 mm); antennal flagellum short (length 1.03–1.09 mm); palpal segment 3 very short (palpal ratio 2.50–2.60)................................................................ B. titanochela View in CoL , n. sp.
20. Fore femur with 5–8 ventral spines; fore femur yellow without brown bands, mid-, hind femora yellow with or without narrow brown apical band ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); fore tibia yellow with poorly developed brown apical band, mid tibia brown with broad yellow subapical band ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–6 ); palpal segment 3 moderately stout (palpal ratio 2.82–3.54); spermathecae with non-tapered necks ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 )............................................................................... B. pulverea (Coquillett) View in CoL
- Fore femur with 2–5 ventral spines; fore-, mid femora yellow with basal and subapical brown bands, hind femur brown with broad subapical yellow band ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 20–24 ); fore-, mid tibiae light brown with brown stripes on proximal 4/5 of their dorsal surfaces ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 20–24 ); palpal segment 3 moderately slender (palpal ratio 3.40–4.50); spermathecae with slightly tapered necks ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 20–24 )................................................................................. B. spicata Dow & Turner View in CoL
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Ceratopogoninae |
|
Tribe |
Palpomyiini |
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Bezzia |