Rhogeessa aenea, Goodwin, 1958
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6397752 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6403574 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4C3D87E8-FF98-6A27-FF8E-9D3C19A1BE5B |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Rhogeessa aenea |
| status |
|
207. View Plate 63: Vespertilionidae
Yucatan Yellow Bat
French: Rhogeessa du Yucatan / German: Yucatan-Gelbfledermaus / Spanish: Rogesa de Yucatan
Taxonomy. Rhogeessa parvula aeneus [sic] G. G. Goodwin, 1958 View in CoL ,
“Chichen Itza, Yucatan,” Mexico.
See R. tumida . Monotypic.
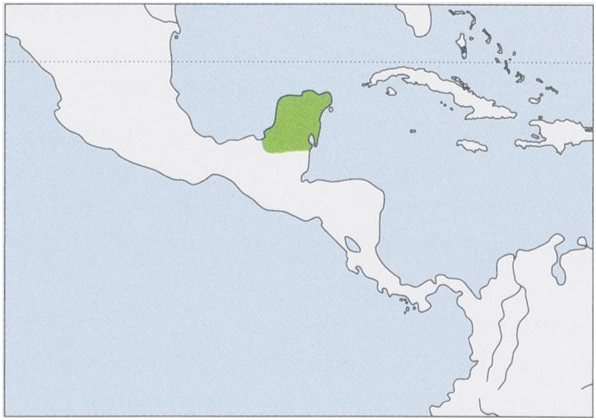
Distribution. Yucatan Peninsula, including SE Mexico, N Guatemala, and N Belize. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body ¢. 37- 43 mm, tail 26-36 mm, ear 11-14 mm, hindfoot 4-6 mm, forearm 25-7-29- 2 mm; weight 3-5 g. Similar to the Northern Little Yellow Bat ( Rhogeessa parvula ), but redder. Dorsal hairs bicolored, with cinnamon-buff bases and prout’s brown tips; venter tawny olive. Ears are short and subacute at tips, and contrast little in coloration with dorsal fur. Wings blackish brown and leathery. Male has prominent glandular area at base of ear, which is related to a strong odor during breeding. Skull is small (greatest skull length of holotype 11- 9 mm), but larger and broader than in the Northern Little Yellow Bat; zygomatic arches widely spread and braincase slightly elevated posteriorly; rostrum relatively long and flattened in interorbital region. Chromosomal complement has 2n = 32 and FN = 58, with a large and submetacentric X-chromosome and a medium-sized submetacentric Y-chromosome.
Habitat. Tropical forests, mainly rainforests, subdeciduous forests, and deciduous forests, at elevations below 50 m.
Food and Feeding. Insectivorous. This speciesis a fast flier, foraging in open areas usually 2-10 m aboveground. It has been observed flying around lights in woodland, near single trees, on forest openings, and over cenotes.
Breeding. Two pregnant females, bearing two embryos each, were collected in May.
Activity patterns. Echolocation search calls are short (2—4 milliseconds) and of high intensity, being repeated every c.13 or c.25 milliseconds. Pulses consist of a steep downsweep, which starts at ¢.65-75 kHz and ends in a short narrowband “tail” at ¢.40- 50 kHz; most of the energy is at 48-59 kHz. When moving from open areas to more restricted spaces, the species switches from 4-millisecond-calls with high intensity and low frequency “tail” (c.48 kHz) to 2-millisecond-calls of lower intensity and higher frequency “tail” (50-53 kHz).
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List (as R. aeneus ). Widespread, and occurs in at least five protected areas in Yucatan Peninsula.
Bibliography. Alvarez-Castafeda & Gonzalez-Ruiz (2018), Audetet al. (1993), Arroyo-Cabrales & Baker (2014a), Baird, Hillis et al. (2008, 2009), Baird, Marchan-Rivadeneira et al. (2012), Birney et al. (1974), Goodwin (1958b), Rydell et al. (2002), Simmons (2005), Solari (2019f).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Rhogeessa aenea
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Rhogeessa parvula aeneus [sic] G. G. Goodwin, 1958
| H. Allen 1866 |