Kerivoula minuta, G. S. Miller, 1898
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6397752 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6581362 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4C3D87E8-FF70-6ACF-FF75-928D1C24B0FB |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Kerivoula minuta |
| status |
|
306. View Plate 67: Vespertilionidae
Least Woolly Bat
French: Petite Kérivoule / German: Zwergwollfledermaus / Spanish: Querivoula pequefo
Taxonomy. Keriwoula minuta G. S. Miller, 1898 ,
“Trong [= Trang Province], Lower Siam [= southern Thailand].”
See K. hardwickii and K. titania . Kerivoula minuta might be related to K. krauensis and K. intermedia (likely due to their identical karyotypes); it is often confused with K. intermedia , and some authors suggest that they are conspecific. Monotypic.
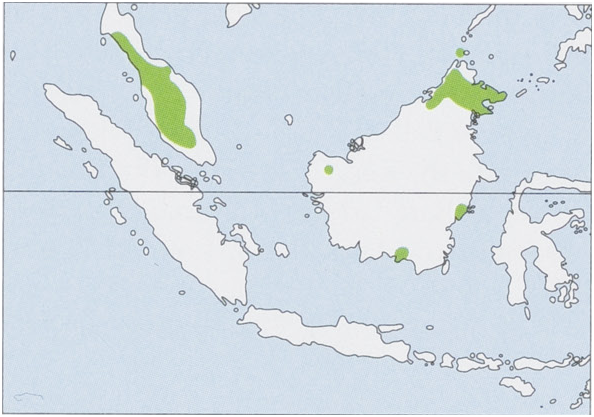
Distribution. Extreme S Thailand, Peninsular Malaysia, and N, SW & SE Borneo (including Balambangan I). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 28- 2-39 mm, tail 27-7-43- 3 mm, ear 7-9-11- 6 mm, hindfoot 4-9-7- 1 mm, forearm 25-3-30- 5 mm; weight 2-5- 3-5 g. Dorsal pelage is orange-brown (hairs with brown bases and light brown tips); venteris slightly paler. Face and lips are hairy, except nostrils. Ears are large and virtually naked, with convex anterior margins, rounded tips, and concavity just below tips on posterior borders; tragus is narrow and tall, with virtually straight anterior margin exceptfor very slight convexity near tip, and has concave posterior margin with small hooked basal lobe. Membranes are light brown, with hairs scattered on posterior margin of uropatagium and no definite fringe; wings are attached at base of outer toes; and calcaris long. Skull is small and bulbous, averaging smaller and more inflated than in the Small Woolly Bat ( K. intermedia ). Upper incisors are bicuspid; I, and I, are tricuspid, and I, is unicuspid; premolars are small and rounded; and talonid of M, is about the same width as trigonid. Chromosomal complement has 2n = 28 and FN = 52,
Habitat. Understories of lowland rainforests and occasionally disturbed areas from sea level up to elevations of ¢. 500 m.
Food and Feeding. No information.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. Least Woolly Bats are slow and fluttery fliers. In southern Thailand, call shapeis steep FM sweep, with start frequencies of 160-1-193-5 kHz (mean 178-4 kHz), end frequencies of 54-97-2 kHz (81-4 kHz), and peak frequencies of 108-2-137-6 kHz (126 kHz). In Peninsular Malaysia, calls had start frequencies of 151-2-185-6 kHz (174 kHz), end frequencies of 66-6-101-6 kHz (85-8 kHz), peak frequencies of 83-2— 134-4 kHz (112-9 kHz), and durations of 0-9-3-3 milliseconds (2-3 milliseconds).
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Near Threatened on The IUCN Red List. The Least Woolly Bat is restricted to primary forests and most common in undisturbed areas, which suggestsit is most threatened by deforestation.
Bibliography. Douangboubpha et al. (2016), Francis (2008a), Hasan & Abdullah (2011), Hill (1965b), Hutson & Kingston (2008d), Khan et al. (2010), Kingston et al. (1999), Kumaran et al. (2006), Kuo Haochih et al. (2017), Lim et al. (2014), Struebig et al. (2012).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Kerivoula minuta
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Keriwoula minuta
| G. S. Miller 1898 |