Myotis indochinensis, Nguyen Truong Son et al., 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6397752 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6581135 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4C3D87E8-FF32-6A8D-FF87-93B91CA9B723 |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Myotis indochinensis |
| status |
|
455. View Plate 73: Vespertilionidae
Indochinese Myotis
Myotis indochinensis View in CoL
French: Murin d'Indochine / German: Laos-Mausohr / Spanish: Ratonero de Indochina
Taxonomy. Myotis indochinensis Nguyen Truong Son a al, 2013 View in CoL ,
“ 16°06°N, 107°19°E, Loa village, Dong Son commune, A Luoi District, Thua Thien-Hue Province, Vietnam, 970 m a.s.l. (above sea level).” GoogleMaps
Subgenus Myotis ; montivagus species group. See M. Jederatus and M. montivagus . Myotis indochinensis appears to be sister to M. federatus (labeled as M. cf. montivagus ) in a clade including M. yanbarensis and M. secundus based on limited genetic data. Populations now attributed to M. indochinensis were previously considered to represent M. montivagus , including those in southwestern China. Monotypic.
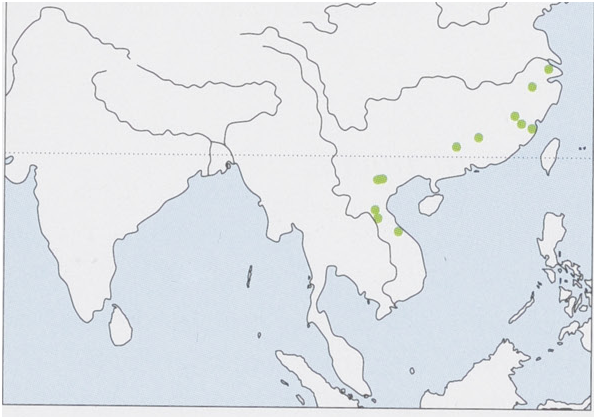
Distribution. SE China (Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Guangdong), N & C Vietnam, and C Laos. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Hindfoot 8:8-10- 6 mm, ear 13-8-16- 1 mm, forearm 43-7-45- 6 mm. Fur is relatively long. Dorsal pelage is dark brown (hairs uniform, some with lighter tips); venteris yellowish brown (hairs dark brown basally and yellowish brown distally). Ears are relatively long and narrow, with convex anterior margins, concave posterior margins with shallow notch, and rounded tips; tragus is ¢50% of ear length and has well-developed posterior basal lobe. Wings attach at base offirst toe; calcaris long, extending halfway to tail. Skull is massive and broad, with short rostrum and flat cranial profile; braincase is shallow; sagittal and lambdoidal crests are well developed; C! is robust and taller than P%, P? and P, are small and intruded from tooth row; C, is about the height of P; lower incisors are four lobed; and lower molars are myotodont.
Habitat. Limestone hills with primary and secondary lowland evergreen forests at elevations of 370-970 m ( Vietnam).
Food and Feeding. No information.
Breeding. A heavily pregnant Indochinese Myotis was caught in mid-June.
Activity patterns. No information.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on The IUCN Red List. The Indochinese Myotis appearsto be widespread but is known from relatively few specimens. Studies on ecology, distribution, and threats are needed to assess its conservation status.
Bibliography. Ruedi, Csorba et al. (2015), Ruedi, Stadelmann et al. (2013), Nguyen Truong Son et al. (2013), Wang Xiaoyun et al. (2017), Yu Jiaming etal. (2015).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |