Chrysosphaerella coronacircumspina Wujek & Kristiansen
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5252/cryptogamie-algologie2020v41a12 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7819061 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4B595A12-FFAB-FFCF-FF39-A82E3F37F994 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Chrysosphaerella coronacircumspina Wujek & Kristiansen |
| status |
|
Chrysosphaerella coronacircumspina Wujek & Kristiansen
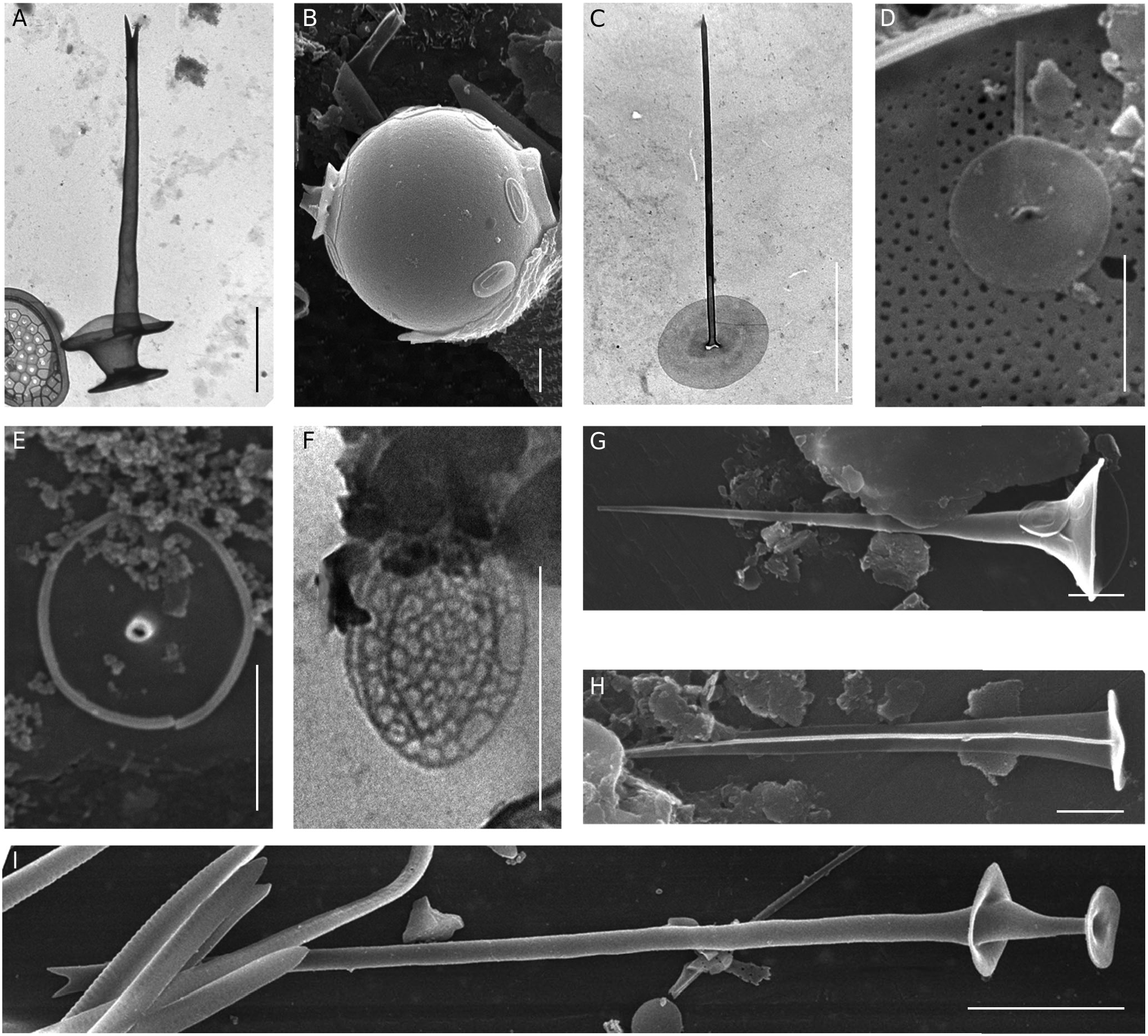
( Fig. 1B View FIG )
Chrysosphaerella solitaria Preisig & D.J.Hibberd, Plant Systematics and Evolution 129: 136 (1978).
DISTRIBUTION. — Widely distributed ( Kristiansen 2000).
REMARKS
This species is easily distinguishable from other Chrysosphaerella species by its spine-scales in which the secondary base-plate is attached directly to the primary base-plate.
We observed C. coronacircumspina during encystment. The stomatocyst was spherical (diameter 11.6 µm) with psilate surface. The collar is cylindrical (diameter 4.19 µm, height 0.8 µm). The pore morphology is unknown.
Preisig & Takahashi (1978) illustrated the stomatocyst of C. solitaria Preisig & E.Takahashi but the pore and collar remained not visible. According to these authors the dimensions of stomatocysts were 13-14.7 µm. Balonov (1980) also observed spherical stomatocysts (diameter 12.3-14.8 µm) but they lacked the collar. Recently, Firsova et al. (2017) revealed that stomatocyst 156 Zeeb & Smol 1993 is produced by C. coronacircumspina .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Chrysosphaerella coronacircumspina Wujek & Kristiansen
| Kapustin, Dmitry A., Gusev, Evgeniy S., Lilitskaya, Galina G. & Kulikovskiy, Maxim S. 2020 |
Chrysosphaerella solitaria Preisig & D.J.Hibberd, Plant Systematics
| Preisig & D. J. Hibberd 1978: 136 |